概念
路由模式(Routing)是 RabbitMQ 中的一种消息传递模式,也称为直连模式。它允许生产者将消息发送到一个交换机,并指定一个或多个路由键(routing key),交换机根据路由键将消息路由到与之匹配的队列中。这样消费者只需关注感兴趣的消息,而不需要接收所有的消息。
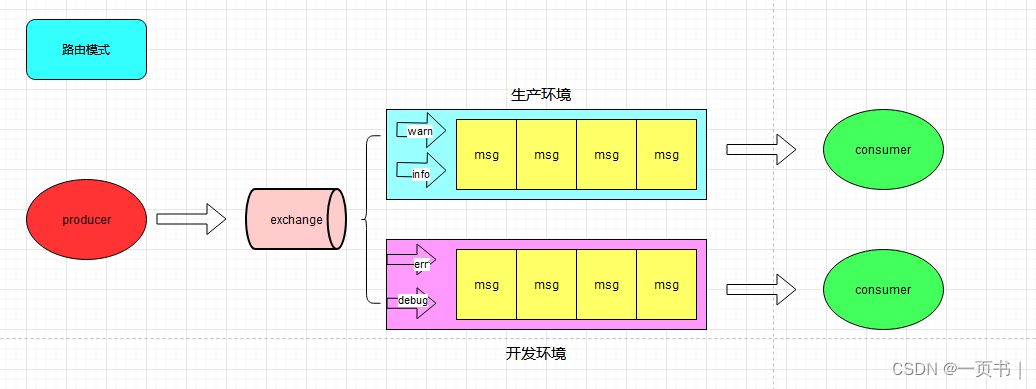
工作流程
-
生产者发送消息: 生产者将消息发送到一个交换机,并指定一个或多个路由键。
-
交换机根据路由键路由消息: 交换机根据消息的路由键将消息发送到与之匹配的队列中。匹配规则可以由交换机的类型和绑定规则决定。
-
消费者监听队列: 消费者可以选择监听特定的队列,或者多个队列,以接收他们感兴趣的消息。
-
消息处理: 消费者从队列中接收消息,并进行相应的处理。只有与队列绑定的交换机根据消息的路由键将消息发送到该队列中。
特点
- 灵活路由:生产者可以根据需要指定不同的路由键来发送消息,交换机根据路由键将消息路由到不同的队列。
- 定向传递:消息只会被发送到与之匹配的队列中,消费者只需关注他们感兴趣的消息,而不需要接收所有的消息。
- 路由规则:可以根据实际需求定义不同的路由规则,例如根据消息的类型、内容、优先级等进行路由。
路由模式适用于需要根据不同的消息属性将消息路由到不同队列的场景,例如消息分类、事件处理、分布式系统等。
Springboot集成
1.创建队列和交换机并绑定
在RoutingConfig文件中配置
package com.model.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** @Author: Haiven* @Time: 2024/4/22 10:09* @Description: TODO*/
@Configuration
public class RoutingConfig {/*** 路由模式交换机* @return exchange*/@Bean(name = "routingExchange")public Exchange getRoutingExchange(){return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("exchange_routing").build();}/*** 路由队列 01* @return queue*/@Bean(name = "routingQueue01")public Queue getRoutingQueue01(){return QueueBuilder.durable("queue_routing_01").build();}/*** 路由队列 02* @return queue*/@Bean(name = "routingQueue02")public Queue getRoutingQueue02(){return QueueBuilder.durable("queue_routing_02").build();}/*** 绑定队列 01* @return binding*/@Beanpublic Binding getRoutingBinding01(){return BindingBuilder.bind(getRoutingQueue01()).to(getRoutingExchange())//路由键 队列1接收debug级别的消息.with("debug").noargs();}/*** 绑定队列 02* @return binding*/@Beanpublic Binding getRoutingBinding02(){return BindingBuilder.bind(getRoutingQueue02()).to(getRoutingExchange())// 路由键 队列2接收info级别的消息.with("info").noargs();}/*** 绑定队列 01* @return binding*/@Beanpublic Binding getRoutingBinding03(){return BindingBuilder.bind(getRoutingQueue01()).to(getRoutingExchange())//路由键 队列1接收debug级别的消息.with("err").noargs();}
}
!!!这里创建的交换机类型为:DirectExchange,如果交换机内容错误,会导致消息错误的分发
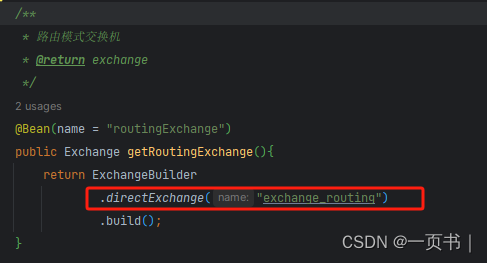
Direct Exchange(直连交换机): 直连交换机将消息的路由键与绑定队列的路由键进行精确匹配,只有当消息的路由键与绑定队列的路由键完全相同时,才会将消息路由到对应的队列。
Fanout Exchange(扇出交换机): 扇出交换机将消息广播到所有与之绑定的队列,无视消息的路由键。这种模式适用于需要将消息广播给多个消费者的场景。
Topic Exchange(主题交换机): 主题交换机根据消息的路由键与绑定队列的路由键进行模糊匹配,支持通配符
*和#。*表示匹配一个单词,#表示匹配零个或多个单词。这种模式适用于需要根据消息的特定属性进行路由的场景。Headers Exchange(头交换机): 头交换机根据消息的头部属性进行匹配,而不是路由键。在绑定队列时,可以指定匹配的头部属性和值,只有当消息的头部属性和值与绑定规则完全匹配时,才会将消息发送到对应的队列。
Default Exchange(默认交换机): 默认交换机是 RabbitMQ 的默认交换机,它将消息的路由键与队列的名称进行匹配,如果消息的路由键与队列的名称完全匹配,则将消息路由到该队列中。默认交换机通常以空字符串表示,不需要显示声明,可以直接使用。
2.创建消费者
RoutingConsumer
package com.model.listener;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** @Author: Haiven* @Time: 2024/4/22 10:08* @Description: TODO*/
@Component
public class RoutingConsumer {@RabbitListener(queues = {"queue_routing_01"})public void routingConsumer01(String msg){System.out.println("消费者 -01- 接收消息:" + msg);}@RabbitListener(queues = {"queue_routing_02"})public void routingConsumer02(String msg){System.out.println("消费者 -02- 接收消息:" + msg);}
}
3.创建生产者并发送消息
package com.model.controller;import com.code.domain.Response;
import com.model.service.RabbitService;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import javax.annotation.Resource;/*** @Author: Haiven* @Time: 2024/4/19 9:46* @Description: TODO*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/producer")
public class ProducerController {@Resourceprivate RabbitService rabbitService;@GetMapping("/simple")public Response<Void> simple(String msg){boolean res = rabbitService.simple(msg);return res ? Response.success() : Response.fail();}@GetMapping("/work")public Response<Void> work(String msg){boolean res = rabbitService.work(msg);return res ? Response.success() : Response.fail();}@GetMapping("/sub")public Response<Void> sub(String msg){boolean res = rabbitService.sub(msg);return res ? Response.success() : Response.fail();}@GetMapping("/routing")public Response<Void> routing(String msg, String type){boolean res = rabbitService.routing(msg, type);return res ? Response.success() : Response.fail();}
}
package com.model.service.impl;import com.model.service.RabbitService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import javax.annotation.Resource;/*** @Author: Haiven* @Time: 2024/4/19 10:51* @Description: TODO*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class RabbitServiceImpl implements RabbitService {@Resourceprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@Value("${rabbitmq.simple.queue}")private String simpleQueue;@Value("${rabbitmq.work.queue}")private String workQueue;@Overridepublic boolean simple(String msg) {try {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(simpleQueue, msg);return true;}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();return false;}}@Overridepublic boolean work(String msg) {try {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(workQueue, msg);return true;}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();return false;}}@Overridepublic boolean sub(String msg) {try {//路由模式就不能直接发送消息到队列了, 而是发送到交换机,由交换机进行广播, routingKey为路由Key 订阅模式给""rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange_sub","", msg);return true;}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();return false;}}@Overridepublic boolean routing(String msg, String type) {System.out.println("理由模式发送消息:msg="+msg+",type="+type+"");try {//路由模式就不能直接发送消息到队列了, 而是发送到交换机,由交换机进行广播, routingKey为路由Key 订阅模式给""rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange_routing",type, msg);return true;}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();return false;}}
}
4.发送消息
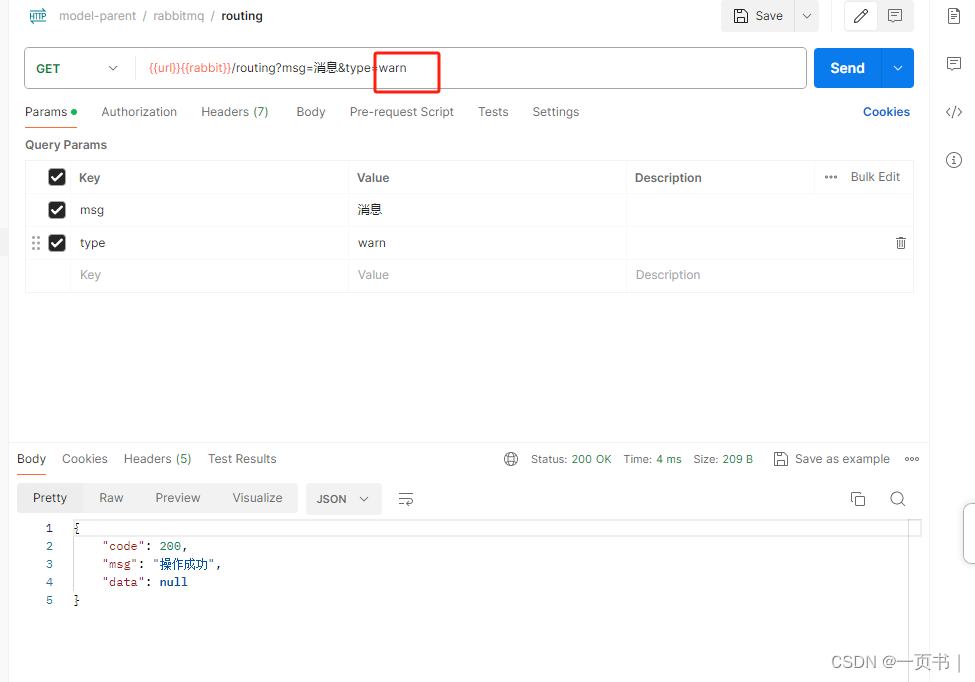
接口调用发送消息, type字段为消息的级别

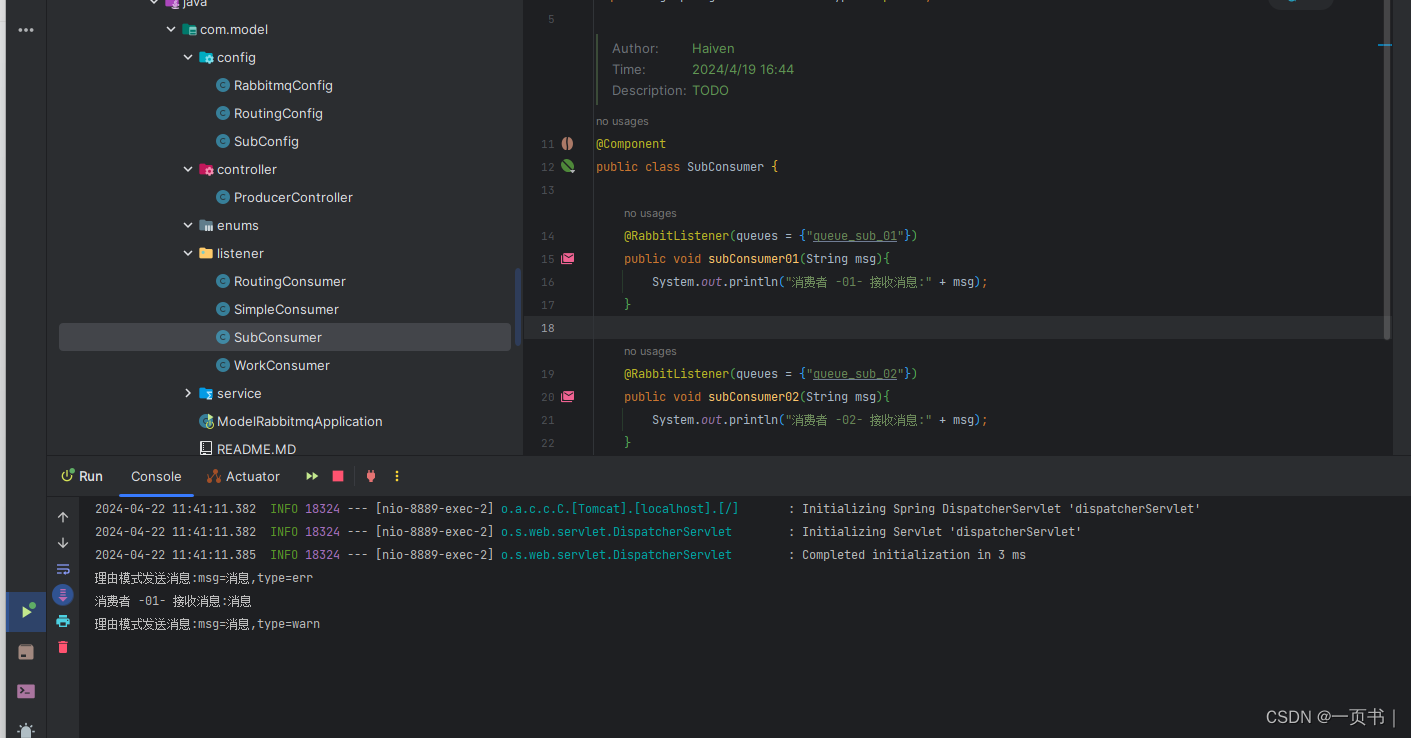
后台接收

debug级别消息只被消费者1消费
info级别的消息只被消费者2消费
5.额外说明
上述消费者1只消费了debug级别,如果还有err级别的消息,只需在将队列1绑定err级别的消息
/*** 绑定队列 01* @return binding*/@Beanpublic Binding getRoutingBinding03(){return BindingBuilder.bind(getRoutingQueue01()).to(getRoutingExchange())//路由键 队列1接收debug级别的消息.with("err").noargs();}发送消息并测试
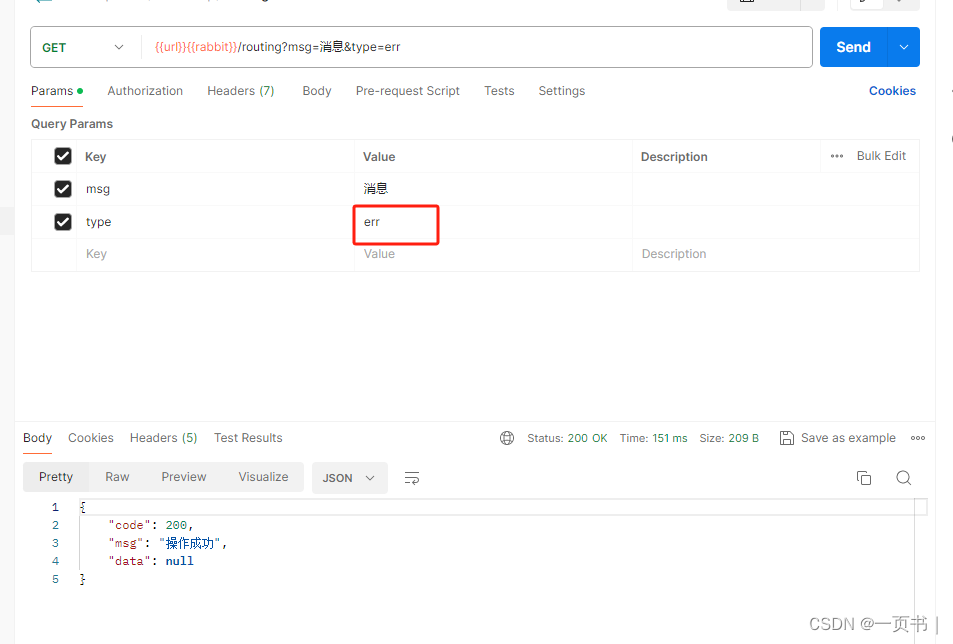
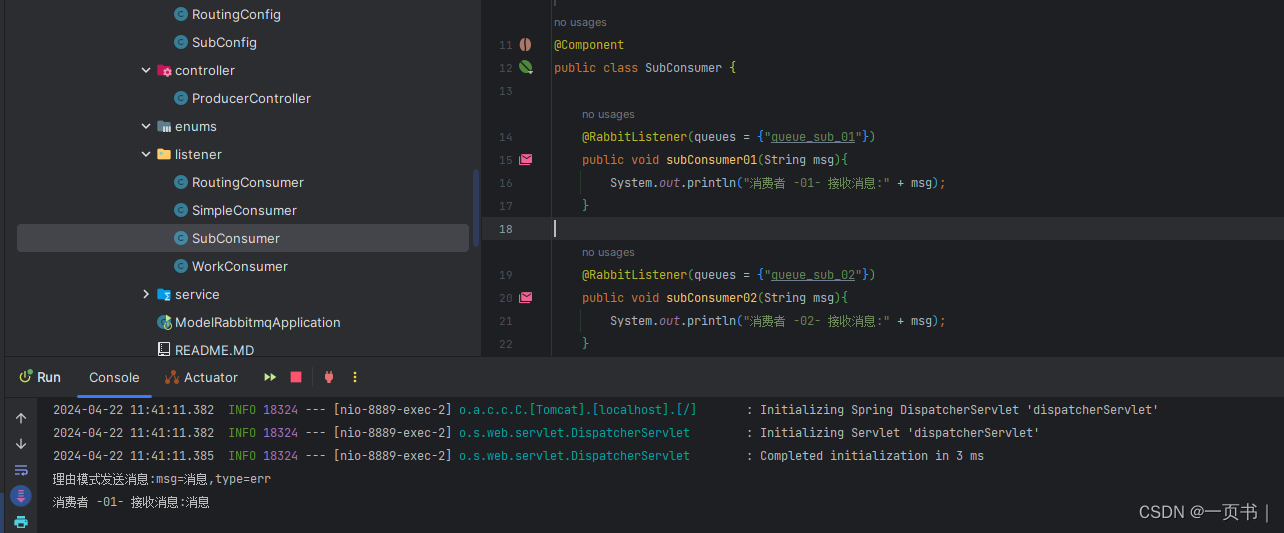
如果某种消息级别(warn)没有被绑定,这该级别的消息会被丢弃