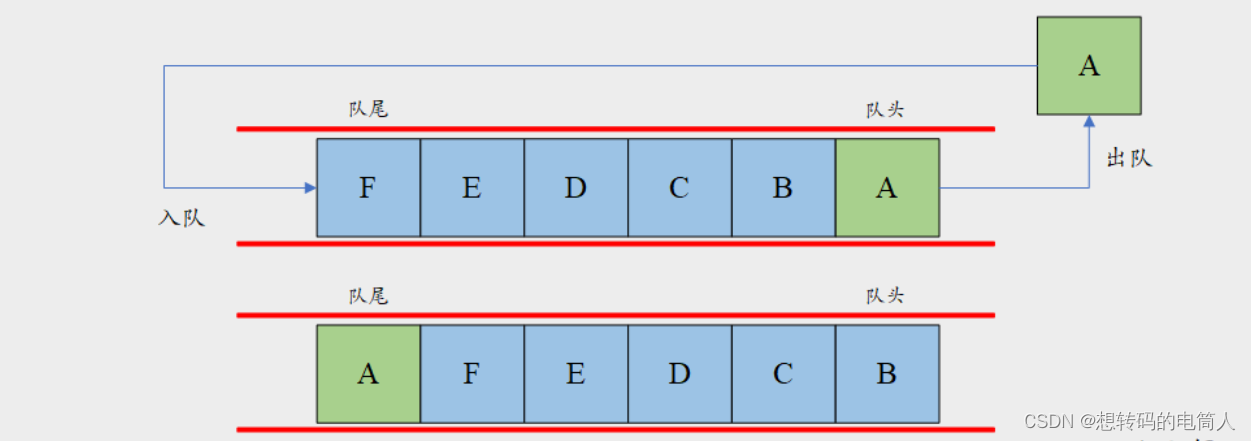
队列
基本概念
队列的定义
队列(Queue):队列是一种常见的数据结构,遵循先进先出(First-In-First-Out, FIFO)的原则。在队列中,元素按照进入队列的顺序排列。队列是一个线性的数据结构,并且这个数据结构只允许在一端进行插入,另一端进行删除,禁止直接访问除这两端以外的一切数据。

队首(Front):最先进入队列的元素,可以被访问或移除
队尾(Rear):最后进入队列的元素,不允许进行访问和删除的另一端。
空队列:不含任何元素的队列。
队列的特点
队列是一种先进先出(First in First out,FIFO)的数据类型。每次元素的入队都只能添加到队列尾部,出队时从队列头部开始出。
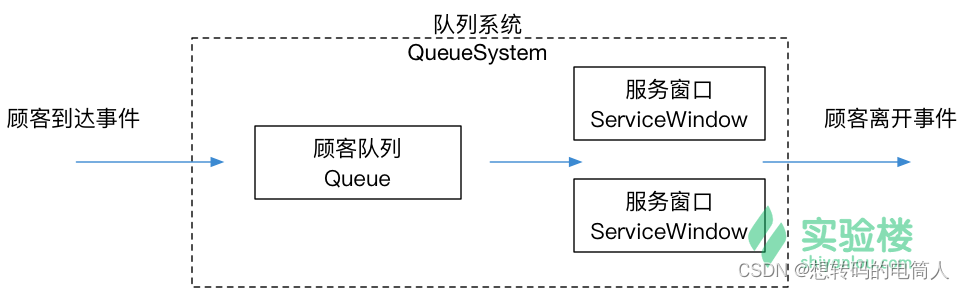
队列的常见基本操作
-
入队(Enqueue):将新元素添加到队列的末尾(队尾)。
-
出队(Dequeue):移除队列中的第一个元素(队首)。
-
获取队首元素(Front):获取队列中的第一个元素,但不将其从队列中移除。
-
获取队列大小(Size):获取队列中当前元素的数量。
-
检查队列是否为空(IsEmpty):检查队列中是否有元素。
优先级队列
上文已经提到了队列先进先出的特点,而优先级队列不满足先进先出的条件,更像是数据类型中的“堆”。
入队(Enqueue):优先级队列入队时会根据优先级来考虑哪个元素先入队,优先级可以通过元素的大小等进行定义。比如定义元素越大优先级越高,则元素大的先入队。
出队(Dequeue):优先级队列每次出队的元素是队列中优先级最高的那个元素,而不是队首的元素。比如定义元素越大优先级越高,那么每次出队,都是将当前队列中最大的那个元素出队。
队列通常用于模拟排队的场景,如任务调度、消息传递等。在计算机科学中,队列也是广泛应用的一种数据结构,在算法设计和实现中发挥着重要作用。所以下面让我们动手实现一个优先级队列,用来模拟银行排队问题
队列的应用
银行排队问题
题目描述
假设银行有 K 个柜台,所有顾客按到达时间排队,当有柜台空闲,队伍最前面的顾客前往空闲柜台处理事务,求顾客的平均排队时间(排队时间=到空闲柜台开始处理事务时间-到达时间)。
提示
用优先级队列实现,并且以到达时间和服务时间作为数组输入
输入
第一行输入柜台个数≥1——int 型;
第二行输入顾客个数≥1——int 型;
第三行输入每位顾客的到达时间≥0——int 型数组,默认升序。
第四行输入每位顾客的服务时间≥0——int 型数组;
输出
第一行输出顾客的平均排队时间——int 型,向下取整。
样例输入
1
10
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
样例输出
40
解题思路
该问题要求模拟银行顾客排队的过程,通过输入柜台数、顾客数、每位顾客的到达时间和服务时间,模拟了顾客在银行排队办理业务的过程,计算顾客的平均排队时间。解题思路如下:
-
创建优先级队列:使用优先级队列来模拟顾客的排队情况。队列中的元素按到达时间排序,即到达时间越早的顾客排在队列前面。这样,在柜台空闲时,就可以直接从队列头部取出顾客进行服务。
-
初始化:读取输入的柜台个数、顾客个数、到达时间数组和服务时间数组。将顾客的到达时间和对应的服务时间插入到优先级队列中。
-
模拟排队过程:开始模拟银行排队的过程,直到所有顾客都被服务完毕为止。在每个时间点,检查是否有柜台空闲,如果有,则从队列中取出最早到达的顾客进行服务,计算其排队时间并累加到总的排队时间中。
-
计算平均排队时间:将总的排队时间除以顾客总数,即可得到平均排队时间,向下取整并输出结果
代码实现
结点类(node)
首先是队列的结点设计,可以设计出两个结构体,一个结构体 Node 表示结点,其中包含有 data 域和 next 指针,如下图:

其中 data 表示数据,其可以是简单的类型,也可以是复杂的结构体,故采用泛型编程template<typename eT>。next 指针表示,下一个的指针,其指向下一个结点,通过 next 指针将各个结点链接。结点类还有构造函数,在创建结点时可以进行初始化,
template<typename eT>
class node {
public:eT data;node* next;node(const eT& data_, node<eT>* next_ = NULL){data = data_;next = next_;}node() : next(NULL) {}~node() {}
};自定义队列(linkQueue)
自定义队列linkQueue采用泛型编程,其中 eT 是模板参数,代表队列中元素的类型。
front 和 tail 分别是指向队列前端和尾端的指针,用于操作队列中的元素。

构造函数和析构函数
构造函数用于初始化队列,将 front 和 tail 初始化为 NULL,表示队列为空。
析构函数用于释放队列中所有节点的内存。它通过循环遍历队列中的所有节点,逐个删除节点,并更新 front 指针,直到队列为空。
成员函数 isEmpty
isEmpty函数用于检查队列是否为空,如果front指针为空,则队列为空,返回true,否则返回false
成员函数 enQueue
enQueue 函数用于向队列尾部添加一个新元素。如果队列为空(即 tail 为空),则创建一个新节点,将 front 和 tail 都指向该节点。如果队列非空,则在 tail 指向的节点后面添加一个新节点,并更新 tail 指针。
成员函数 deQueue
deQueue 函数用于从队列头部移除一个元素,并返回其值。
首先保存队列头部节点的指针 tmp,并保存头部节点的值到 value 中。
然后更新 front 指针,指向原头部节点的下一个节点。如果队列只有一个节点(即移除后为空),则将 tail 也置为空。
最后释放原头部节点的内存,并返回其值。
template<typename eT>
class linkQueue{
public:node<eT>* front, * tail;
public:linkQueue() { front = tail = NULL; }~linkQueue() {node<eT>* tmp;while (front != NULL) {tmp = front;front = front->next;delete tmp;}}bool isEmpty() { return front == NULL; }void enQueue(const eT& x) {if (tail == NULL)front = tail = new node<eT>(x);else {tail->next = new node<eT>(x);tail = tail->next;}}eT deQueue() {node<eT>* tmp = front;eT value = front->data;front = front->next;if (front == NULL) tail = NULL;delete tmp;return value;}
};优先级队列(priorityQueue)
与自定义队列(linkQueue)相同,采用泛型编程,其中 eT 是模板参数,代表队列中元素的类型。front 和 tail 分别是指向队列前端和尾端的指针,用于操作队列中的元素。
同样地,优先级队列(priorityQueue)与自定义队列(linkQueue)的初始化,判断非空,出队操作基本相同,主要不同点在于入队操作。
成员函数 enQueue
enQueue 函数用于向队列尾部添加一个新元素。如果队列为空(即 tail 为空),则创建一个新节点,将 front 和 tail 都指向该节点。如果队列非空,则寻找较大元素的前继结点进行插入操作,以保持队列的有序性。
template <typename eT>
class priorityQueue {
public:node<eT>* front, * tail;priorityQueue() { front = tail = NULL; }~priorityQueue() {node<eT>* tmp;while (front != NULL) {tmp = front;front = front->next;delete tmp;}}bool isEmpty() { return front == NULL; }eT deQueue() {node<eT>* tmp = front;eT value = front->data;front = front->next;if (front == NULL) tail = NULL;delete tmp;return value;}void enQueue(const eT& x) {if (tail == NULL)front = tail = new node<eT>(x);else {node<eT>* p;if (x < front->data){p = new node<eT>(x, front); front = p;}else {p = front;while (p->next != NULL && p->next->data < x) p = p->next;if (p->next == NULL){tail->next = new node<eT>(x);tail = tail->next;}else p->next = new node<eT>(x, p->next);}}}
};模拟银行排队系统(simulator)
成员变量
1.noOfServer:表示银行柜台的数量。
2.customNum:表示顾客的数量。
3.arrivalTimeList:存储每位顾客到达银行的时间。
4.serviceTimeList:存储每位顾客所需的服务时间。
内部结构体 eventT
1.用于描述事件,包括事件发生时间 time 和事件类型 type(0 表示到达,1 表示离开)。
2.重载了小于操作符,以便将事件按照发生时间进行排序。
class simulator {int noOfServer;int customNum;int* arrivalTimeList;int* serviceTimeList;struct eventT{int time; //事件发生时间int type; //事件类型。0 为到达,1 为离开bool operator<(const eventT& e) const { return time < e.time; }};
};构造函数和析构函数
构造函数从标准输入中读取柜台数、顾客数以及每位顾客的到达时间和服务时间,然后分配内存给 arrivalTimeList 和 serviceTimeList,分别用这两个数组储存每位顾客的到达时间和服务时间
析构函数释放动态分配的内存,防止内存泄漏
public:simulator() {//std::cout << "请输入柜台数:";std::cin >> noOfServer;//std::cout << "请输入模拟的顾客数:";std::cin >> customNum;arrivalTimeList = new int[customNum];serviceTimeList = new int[customNum];for (int i = 0; i < customNum; i++) {std::cin >> arrivalTimeList[i];}for (int i = 0; i < customNum; i++) {std::cin >> serviceTimeList[i];}}~simulator() {delete arrivalTimeList;delete serviceTimeList;}成员函数avgWaitTime
该函数用来模拟顾客排队,到达和离开的过程,并且计算出平均等待时间。在该函数中我们需要用自定义队列(linkQueue)来存储等待的顾客事件和顾客的服务时间,并且用优先级队列(priorityQueue)存储顾客到达和离开的事件。
1.定义变量并进行初始化
变量表示的内容已注释
int serverBusy = 0; // 记录当前服务中的柜台数量
int serviceTime = 0; // 记录当前服务所需时间
int currentTime = 0; // 记录当前时间
int totalWaitTime = 0; // 记录总的等待时间
linkQueue<eventT> waitQueue; // 等待队列,存储等待的顾客事件
priorityQueue<eventT> customerQueue; // 顾客队列,存储到达和离开的顾客事件
linkQueue<int> serviceTimeQueue; // 服务时间队列,存储顾客的服务时间
eventT currentEvent; // 当前事件
2.生成初始事件队列
for (int i = 0; i < customNum; ++i) {currentEvent.type = 0;currentTime = arrivalTimeList[i]; // 每个顾客的到达时刻currentEvent.time = currentTime;customerQueue.enQueue(currentEvent); // 将顾客到达事件加入到顾客队列中serviceTimeQueue.enQueue(serviceTimeList[i]); // 将顾客的服务时间加入到服务时间队列中
}
3.模拟顾客到达和离开的过程
(1)用while循环不断取出顾客队列,直到顾客队列为空,即所有顾客都已经离开银行。从顾客队列中取出事件,并将其赋值给 currentEvent,将当前时间更新为当前事件的发生时间,即顾客到达或离开的时间。
(2)根据事件类型进行处理
a.顾客到达
如果有空闲的柜台,则顾客直接前往柜台处理业务,将当前事件的结束时间继续存入顾客队列,即顾客离开;如果所有柜台都忙碌,则顾客加入等待队列。
b.顾客离开
如果等待队列不为空,则从等待队列中取出顾客,并计算顾客等待的时间;如果等待队列为空,则只需更新柜台的繁忙状态。
while (!customerQueue.isEmpty()) {currentEvent = customerQueue.deQueue(); // 取出顾客队列中的事件currentTime = currentEvent.time; // 更新当前时间switch (currentEvent.type) {case 0: // 顾客到达事件if (serverBusy < noOfServer) { // 如果有空闲的柜台serverBusy++;currentEvent.time = currentTime + serviceTimeQueue.deQueue(); // 计算顾客服务结束时间currentEvent.type = 1; // 设置事件类型为离开customerQueue.enQueue(currentEvent); // 将离开事件加入到顾客队列中} else { // 如果所有柜台都忙碌waitQueue.enQueue(currentEvent); // 将顾客加入等待队列}break;case 1: // 顾客离开事件if (!waitQueue.isEmpty()) { // 如果等待队列不为空serverBusy--;currentEvent = waitQueue.deQueue(); // 取出等待队列中的顾客事件totalWaitTime += currentTime - currentEvent.time; // 计算等待时间currentEvent.time = currentTime + serviceTimeQueue.deQueue(); // 计算顾客服务结束时间currentEvent.type = 1; // 设置事件类型为离开customerQueue.enQueue(currentEvent); // 将离开事件加入到顾客队列中} else {serverBusy--;}break;default:break;}
}
4.返回平均等待时间
return totalWaitTime / customNum; // 返回平均等待时间
完整代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
template<typename eT>
class node {
public:eT data;node* next;node(const eT& data_, node<eT>* next_ = NULL){data = data_;next = next_;}node() : next(NULL) {}~node() {}
};
template<typename eT>
class linkQueue{
public:node<eT>* front, * tail;
public:linkQueue() { front = tail = NULL; }~linkQueue() {node<eT>* tmp;while (front != NULL) {tmp = front;front = front->next;delete tmp;}}bool isEmpty() { return front == NULL; }void enQueue(const eT& x) {if (tail == NULL)front = tail = new node<eT>(x);else {tail->next = new node<eT>(x);tail = tail->next;}}eT deQueue() {node<eT>* tmp = front;eT value = front->data;front = front->next;if (front == NULL) tail = NULL;delete tmp;return value;}
};
template <typename eT>
class priorityQueue {
public:node<eT>* front, * tail;priorityQueue() { front = tail = NULL; }~priorityQueue() {node<eT>* tmp;while (front != NULL) {tmp = front;front = front->next;delete tmp;}}bool isEmpty() { return front == NULL; }eT deQueue() {node<eT>* tmp = front;eT value = front->data;front = front->next;if (front == NULL) tail = NULL;delete tmp;return value;}void enQueue(const eT& x) {if (tail == NULL)front = tail = new node<eT>(x);else {node<eT>* p;if (x < front->data){p = new node<eT>(x, front); front = p;}else {p = front;while (p->next != NULL && p->next->data < x) p = p->next;if (p->next == NULL){tail->next = new node<eT>(x);tail = tail->next;}else p->next = new node<eT>(x, p->next);}}}
};
class simulator {int noOfServer;int customNum;int* arrivalTimeList;int* serviceTimeList;struct eventT{int time; //事件发生时间int type; //事件类型。0 为到达,1 为离开bool operator<(const eventT& e) const { return time < e.time; }};public:simulator() {//std::cout << "请输入柜台数:";std::cin >> noOfServer;//std::cout << "请输入模拟的顾客数:";std::cin >> customNum;arrivalTimeList = new int[customNum];serviceTimeList = new int[customNum];for (int i = 0; i < customNum; i++) {std::cin >> arrivalTimeList[i];}for (int i = 0; i < customNum; i++) {std::cin >> serviceTimeList[i];}}~simulator() {delete arrivalTimeList;delete serviceTimeList;}int avgWaitTime() {int serverBusy = 0;int serviceTime = 0;int currentTime = 0;int totalWaitTime = 0;linkQueue<eventT> waitQueue;priorityQueue<eventT> customerQueue;linkQueue<int> serviceTimeQueue;eventT currentEvent;//生成初始的事件队列int i;for (i = 0; i < customNum; ++i){currentEvent.type = 0;currentTime = arrivalTimeList[i];//每个顾客的到达时刻currentEvent.time = currentTime;customerQueue.enQueue(currentEvent);serviceTimeQueue.enQueue(serviceTimeList[i]);//每个顾客的服务时间}while (!customerQueue.isEmpty()){currentEvent = customerQueue.deQueue();currentTime = currentEvent.time;switch (currentEvent.type){case 0: if (serverBusy < noOfServer){serverBusy++;currentEvent.time = currentTime + serviceTimeQueue.deQueue();currentEvent.type = 1;customerQueue.enQueue(currentEvent);}else {waitQueue.enQueue(currentEvent);}break;case 1:{if (waitQueue.isEmpty() == 0){serverBusy--;currentEvent = waitQueue.deQueue();totalWaitTime = totalWaitTime + currentTime - currentEvent.time;currentEvent.time = currentTime + serviceTimeQueue.deQueue();currentEvent.type = 1;customerQueue.enQueue(currentEvent);}else serverBusy--;break;}default:break;}}return totalWaitTime / customNum;}};int main(){simulator sim;cout << sim.avgWaitTime() <<endl;return 0;}附录
分类专栏
链接:
手把手教数据结构与算法
本专栏上一节
链接:
手把手教数据结构与算法:栈的应用(平衡符号和简单计算器)-CSDN博客