系列文章目录
提示:这里可以添加系列文章的所有文章的目录,目录需要自己手动添加
TODO:写完再整理
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 速度规划S曲线
- 机械臂轨迹规划
- 碰撞检查
- 感知导航
- 感知+似然场局部规划(很像DWA但是不依赖地图,完全依赖感知)
- FAR Planner全局路径规划算法
- 车辆在不同场景下的碰撞检测
- 局部路径--多选一的策略
- 自主泊车APA的路径规划
- emplanner
- 使用三方库的步骤之CMakeLists.txt中常用库文件的查找和链接
- Voronoi图的生成与更新
- 室内机器人通过窄区域的局部路径规划方法
- 行为树专栏
- 无人机防御性驾驶-提前感知快速飞行的轨迹规划
- 无人机局部规划Path-Guided Optimization算法
- 无人车高速场景的分层运动规划框架
- 7.【C++】代码实现:数据线性平滑算法
- 非线性优化--路径平滑算法
- 多项式路径平滑
- jps原理
- JPS路径规划实现示例二
- -------------->C/C++编程规范
- -------------->工程经验相关
- 三方库的调用方法
- -------------->产品导航业务方案【从自己做的项目中分离出来】
- -------------->决策逻辑与导航架构相关
- -------------->仿真及开发生态搭建相关
- -------------->感知相关
- -------------->定位相关
- -------------->地图相关
- -------------->决策
- git
- pid轨迹跟踪控制
- lattice算法讲解
- 人工势场地图做规划
- 运动预测(Motion Prediction)
- 双向Dijkstra算法(提升效率)
- A*启发式搜索算法
- 栅格地图生成
- C++11--使用表驱动(Table-Driven)模式消除if-else和switch-case语句
- 三次样条插值(Cubic Spline Interpolation)曲线及Python代码实现
- Hybird A*算法
- Reeds Shepp曲线
- Dubins曲线
- 自动驾驶运动规划(Motion Planning)
- 车辆运动学模型
- 自动驾驶定位算法(十三)-粒子滤波(Particle Filter)
- 直方图滤波定位
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)
- Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
- 卡尔曼滤波
- -------------->路径规划
- 路径跟踪LQR改进
- 路径跟踪MPC
- 三次螺旋曲线生成(局部路径生成)
- 基于优化的离散点平滑算法(平滑性Cost、长度Cost、偏移Cost且带约束条件的非线性优化)Apollo代码
- 无人车导航系统(整体流程、轨迹生成、碰撞检测、路径跟踪)
- 轨迹拼接(Trajectory Stitching)
- 感知中的运动预测(深度神经网络)
- 商业中,自动驾驶是伪命题(除非降级到车路协同),机器人才是正道
- 梯度下降(SGD)原理
- 随机梯度下降原理
- 共轭梯度下降(完整)
- 五点中值梯度下降
- 分段路径优化的策略&非线性优化
- 硬软约束
- 混合A星的后端轨迹优化(可以单独从博客中拿出来)
- APOLLO参考性平滑方法
- 使用梯度下降法
- clothiod曲线进行平滑
- Voronoi路径规划探索
- 分段路径优化的策略
- 使用梯度下降的方式进行路径平滑
- 核心思想
- C++实现(连续点之间转角的平方和)
- -------------->控制
- -------------->优化理论相关
- 滤波器(用不多)
- 一阶低通滤波器
- 巴特沃斯滤波器
- 贝赛尔(Bessel)滤波器
- 切比雪夫滤波器
- 总结
- -------------->相关开发工具
前言
认知有限,望大家多多包涵,有什么问题也希望能够与大家多交流,共同成长!提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容
系列文章目录
提示:这里可以添加系列文章的所有文章的目录,目录需要自己手动添加
TODO:写完再整理
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 速度规划S曲线
- 机械臂轨迹规划
- 碰撞检查
- 感知导航
- 感知+似然场局部规划(很像DWA但是不依赖地图,完全依赖感知)
- FAR Planner全局路径规划算法
- 车辆在不同场景下的碰撞检测
- 局部路径--多选一的策略
- 自主泊车APA的路径规划
- emplanner
- 使用三方库的步骤之CMakeLists.txt中常用库文件的查找和链接
- Voronoi图的生成与更新
- 室内机器人通过窄区域的局部路径规划方法
- 行为树专栏
- 无人机防御性驾驶-提前感知快速飞行的轨迹规划
- 无人机局部规划Path-Guided Optimization算法
- 无人车高速场景的分层运动规划框架
- 7.【C++】代码实现:数据线性平滑算法
- 非线性优化--路径平滑算法
- 多项式路径平滑
- jps原理
- JPS路径规划实现示例二
- -------------->C/C++编程规范
- -------------->工程经验相关
- 三方库的调用方法
- -------------->产品导航业务方案【从自己做的项目中分离出来】
- -------------->决策逻辑与导航架构相关
- -------------->仿真及开发生态搭建相关
- -------------->感知相关
- -------------->定位相关
- -------------->地图相关
- -------------->决策
- git
- pid轨迹跟踪控制
- lattice算法讲解
- 人工势场地图做规划
- 运动预测(Motion Prediction)
- 双向Dijkstra算法(提升效率)
- A*启发式搜索算法
- 栅格地图生成
- C++11--使用表驱动(Table-Driven)模式消除if-else和switch-case语句
- 三次样条插值(Cubic Spline Interpolation)曲线及Python代码实现
- Hybird A*算法
- Reeds Shepp曲线
- Dubins曲线
- 自动驾驶运动规划(Motion Planning)
- 车辆运动学模型
- 自动驾驶定位算法(十三)-粒子滤波(Particle Filter)
- 直方图滤波定位
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)
- Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
- 卡尔曼滤波
- -------------->路径规划
- 路径跟踪LQR改进
- 路径跟踪MPC
- 三次螺旋曲线生成(局部路径生成)
- 基于优化的离散点平滑算法(平滑性Cost、长度Cost、偏移Cost且带约束条件的非线性优化)Apollo代码
- 无人车导航系统(整体流程、轨迹生成、碰撞检测、路径跟踪)
- 轨迹拼接(Trajectory Stitching)
- 感知中的运动预测(深度神经网络)
- 商业中,自动驾驶是伪命题(除非降级到车路协同),机器人才是正道
- 梯度下降(SGD)原理
- 随机梯度下降原理
- 共轭梯度下降(完整)
- 五点中值梯度下降
- 分段路径优化的策略&非线性优化
- 硬软约束
- 混合A星的后端轨迹优化(可以单独从博客中拿出来)
- APOLLO参考性平滑方法
- 使用梯度下降法
- clothiod曲线进行平滑
- Voronoi路径规划探索
- 分段路径优化的策略
- 使用梯度下降的方式进行路径平滑
- 核心思想
- C++实现(连续点之间转角的平方和)
- -------------->控制
- -------------->优化理论相关
- 滤波器(用不多)
- 一阶低通滤波器
- 巴特沃斯滤波器
- 贝赛尔(Bessel)滤波器
- 切比雪夫滤波器
- 总结
- -------------->相关开发工具
前言
认知有限,望大家多多包涵,有什么问题也希望能够与大家多交流,共同成长!本文先对路径跟踪模式–pure_pursuit与原地旋转结合实现做个简单的介绍,具体内容后续再更,其他模块可以参考去我其他文章
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容
速度规划S曲线
https://blog.csdn.net/u010632165/article/details/104951091
机械臂轨迹规划
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/446463459#:~:text=%E6%9C%BA%E6%A2%B0%E8%87%82%E9%92%88%E5%AF%B9%E5%85%B3%E8%8A%82%E7%A9%BA%E9%97%B4%E7%9A%84%E8%A7%84%E5%88%92%E6%96%B9%E5%BC%8F%201%20%E7%A1%AE%E5%AE%9A%E8%BD%A8%E8%BF%B9%E7%9A%84%E8%B5%B7%E7%82%B9%20%28Initial%20Point%29%20-%20%E9%80%94%E5%BE%84%E7%82%B9%20%28Via,%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E5%87%BA%E4%BB%A5%E4%B8%8A%E6%89%80%E6%9C%89%E7%82%B9%E7%9A%84%E5%85%B3%E8%8A%82%E8%A7%92%EF%BC%8C%E5%8D%B3%E5%85%B3%E8%8A%82%E7%A9%BA%E9%97%B4%E4%B8%8B%E7%9A%84%E6%89%80%E6%9C%89%E7%82%B9%E5%85%B3%E4%BA%8E%E6%97%B6%E9%97%B4%E7%9A%84%E4%BD%8D%E7%BD%AE%EF%BC%9B%203%20%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E4%B8%80%E6%9D%A1%E8%BD%A8%E8%BF%B9%E5%B0%86%E5%85%B3%E8%8A%82%E7%A9%BA%E9%97%B4%E6%89%80%E6%9C%89%E7%82%B9%E9%83%BD%E5%B9%B3%E6%BB%91%E7%9A%84%E8%BF%9E%E6%8E%A5%E8%B5%B7%E6%9D%A5%EF%BC%9B%204%20%E5%86%8D%E9%80%9A%E8%BF%87%E6%AD%A3%E5%90%91%E8%BF%90%E5%8A%A8%E5%AD%A6Forword%20Kinematics%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E5%87%BA%E5%9C%A8%E8%BF%99%E7%A7%8D%E6%83%85%E5%86%B5%E4%B8%8B%E6%9C%AB%E7%AB%AF%E5%85%B3%E4%BA%8E%E4%B8%96%E7%95%8C%E5%9D%90%E6%A0%87%E7%9A%84%E6%9B%B2%E7%BA%BF%EF%BC%9B%205%20%E6%A3%80%E6%9F%A5%E4%B8%96%E7%95%8C%E5%9D%90%E6%A0%87%E4%B8%8B%E7%9A%84%E6%9B%B2%E7%BA%BF%E6%98%AF%E5%90%A6%E5%90%88%E7%90%86%E3%80%82
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/445941991
https://blog.csdn.net/Aristotle__/article/details/106729447
碰撞检查
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/93890266
感知导航
感知直接输出局部路径
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/aliPADnpR1Gtfxzer30hoA
感知+似然场局部规划(很像DWA但是不依赖地图,完全依赖感知)
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gmmW0v39tmUDC-3oCJs4HA
FAR Planner全局路径规划算法
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI5MTM1MTQwMw==&mid=2247525152&idx=1&sn=f917e31efcb48be92b9989b82efd7ca6&chksm=ec13dd24db64543291ce9d61a7855e1ccb4b2761c2c420fe3b5403e86795616504dfa744bb4f&mpshare=1&scene=1&srcid=0721EE63j2t5hOefWW4YjycF&sharer_sharetime=1626880766614&sharer_shareid=08197ba589ef0842eb95118b7486efc5&exportkey=AUGS0HcDvDLyCHs8XPM4o6U=&pass_ticket=M/InBNg%2b/KJeIAfn8hW8Xw3lvBpIRa5gJir9Xmor9MCEty/ArltQQhSaAX4S%2bGvK&wx_header=0#rd
车辆在不同场景下的碰撞检测
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/112571436
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/73375021
1、碰撞检测可以用在机器人运动过程中的底层检测,检测到即将发生碰撞就减速甚至停车
2、碰撞检测也可以用在机器人规划过程中,对生成的轨迹做碰撞安全检测,决定是否使用该候选路径
碰撞检测可以基于传感器,也可以基于栅格地图是否被占据,还可以基于几何图形学的位姿判断
局部路径–多选一的策略
根据道路中心线进行采样,构造多项式path,评估每条path的cost,挑选最优轨迹。不同的是评估cost时,百度Lattice仅仅利用了轨迹局部的信息,比如和参考线(道路中心线)的偏移、速度大小、轨迹长短等
自主泊车APA的路径规划
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/95680738
emplanner
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/95100761
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94890742
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94521270
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94044688
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/82142163
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/78349976
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/78330066
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/78158531
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77122649
使用三方库的步骤之CMakeLists.txt中常用库文件的查找和链接
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/73373016
Voronoi图的生成与更新
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/127356467
室内机器人通过窄区域的局部路径规划方法
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/598923900
还有就是割草机的出了图形边界,沿着图形边界进行规划出去
还有就是基于图搜索的全局和局部的路径规划
行为树专栏
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472622265
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472627898
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472630259
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472633529
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472993071
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472996050
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472997963
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/472999056
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/473002787
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/473007194
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/473304887
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/474966739
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/475539706
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/480967725
无人机防御性驾驶-提前感知快速飞行的轨迹规划
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/595303694
无人机局部规划Path-Guided Optimization算法
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/595300559
无人车高速场景的分层运动规划框架
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/595307159
7.【C++】代码实现:数据线性平滑算法
3点线性平滑、5点(1次、2次、3次)线性平滑、7点(1次、2次)线性平滑
https://blog.csdn.net/kingkee/article/details/94389485
https://blog.csdn.net/liyuanbhu/article/details/11119081
https://www.cnblogs.com/T-ARF/p/14882589.html
相关代码实现
void LawnBMap::pathSmoothFivePoint(VectorAgx<PointF>* ori_path, float tolerance, int max_its, float w_origin, float w_smooth, uint8_t n_refine,bool fix) {if (ori_path->size() < 3)return;VectorAgx<PointF> path_float;linearInterpolation(ori_path, &path_float, 0.2f);VectorAgx <int> fix_pid(path_float.size(),0);if (fix) {int j = 0;for (int i = 0; i < path_float.size(); ++i) {if (j >= ori_path->size()) break;if (fabs( path_float[i].x() - ori_path->at(j).x()) < 1e-3f && fabs( path_float[i].y() - ori_path->at(j).y()) < 1e-3f) {fix_pid[i] = 1;j++;}}}PointF tmp_point, tmp_point2;float change_value, tmp_change_value;float v2, v4;int its, x_id, y_id;bool flag = false;VectorAgx<PointF> new_path(&path_float);VectorAgx<PointF> last_path(&path_float);n_refine = n_refine + 1;for (uint8_t n = 0; n < n_refine; ++n) {if (n > 0) {path_float.copyFrom(&last_path);new_path.copyFrom(&path_float);}its = 0;change_value = tolerance + 1;while (change_value >= tolerance) {change_value = 0;tmp_change_value = 0;// 5点for (int i = 2; i < path_float.size() - 3; ++i) {if(fix_pid[i] == 1) continue;v2 = new_path[i].x();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_smooth * (new_path[i+1].x() + new_path[i-1].x() - 2 * new_path[i].x())+ w_smooth * 0.5f * (2 * new_path[i+1].x() - new_path[i+2].x() - new_path[i].x())+ w_smooth * 0.5f * (2 * new_path[i-1].x() - new_path[i-2].x() - new_path[i].x());tmp_point.x() = v2;tmp_change_value = fabs(v2 - v4);v2 = new_path[i].y();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_smooth * (new_path[i+1].y() + new_path[i-1].y() - 2 * new_path[i].y())+ w_smooth * 0.5f * (2 * new_path[i+1].y() - new_path[i+2].y() - new_path[i].y())+ w_smooth * 0.5f * (2 * new_path[i-1].y() - new_path[i-2].y() - new_path[i].y());tmp_point.y() = v2;tmp_change_value += fabs(v2 - v4);convertPointToLocal(&transfor_, tmp_point, &tmp_point2);gridMap()->getXYIndex(tmp_point2.x(), tmp_point2.y(), x_id, y_id);change_value += tmp_change_value;if (gridMap()->insideBoundary(x_id, y_id)) {if (!gridMap()->isObstacle(x_id, y_id)) {new_path[i] = tmp_point;}}}last_path.copyFrom(&new_path);flag = true;if (++its >= max_its) break;}}if (flag) {ori_path->resize(last_path.size());ori_path->clear();for (int i = 0; i < last_path.size(); ++i)ori_path->push_back(last_path[i]);}
};void LawnBMap::pathSmoothThreePoint(VectorAgx<PointF>* ori_path, float tolerance, int max_its, float w_origin, float w_smooth, uint8_t n_refine) {if (ori_path->size() < 3)return;VectorAgx<PointF> path_float;linearInterpolation(ori_path, &path_float, 0.2);VectorAgx <int> fix_pid(path_float.size(),0);PointF tmp_point, tmp_point2;float change_value, tmp_change_value;float v2, v4;int its, x_id, y_id;bool flag = false;VectorAgx<PointF> new_path(&path_float);VectorAgx<PointF> last_path(&path_float);n_refine = n_refine + 1;for (uint8_t n = 0; n < n_refine; ++n) {if (n > 0) {path_float.copyFrom(&last_path);new_path.copyFrom(&path_float);}its = 0;change_value = tolerance + 1;while (change_value >= tolerance) {change_value = 0;tmp_change_value = 0;// 3点for (int i = 1; i < path_float.size() - 1; ++i) {v2 = new_path[i].x();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_origin * (path_float[i].x() - v2) + w_smooth * (new_path[i+1].x() + new_path[i-1].x() - v2- v2);tmp_point.x() = v2;tmp_change_value = fabs(v2 - v4);v2 = new_path[i].y();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_origin * (path_float[i].y() - v2) + w_smooth * (new_path[i+1].y() + new_path[i-1].y() - v2 - v2);tmp_point.y() = v2;tmp_change_value += fabs(v2 - v4);convertPointToLocal(&transfor_, tmp_point, &tmp_point2);gridMap()->getXYIndex(tmp_point2.x(), tmp_point2.y(), x_id, y_id);change_value += tmp_change_value;if (gridMap()->insideBoundary(x_id, y_id)) {if (!gridMap()->isObstacle(x_id, y_id))new_path[i] = tmp_point;}}last_path.copyFrom(&new_path);flag = true;if (++its >= max_its) break;}}if (flag) {ori_path->resize(last_path.size());ori_path->clear();for (int i = 0; i < last_path.size(); ++i)ori_path->push_back(last_path[i]);}
};
.
.
非线性优化–路径平滑算法
https://www.jianshu.com/p/cc7ba7f18c15
多项式路径平滑
void pathSmoothFivePoint(const Costmap* const map, uint8_t compare_cost_value,std::vector<PointF>* const ori_path, float tolerance,unsigned int max_its, float w_origin, float w_smooth,uint8_t n_refine, bool fix) {if (ori_path->size() < 3) return;std::vector<PointF> path_float;// 先对平滑路径进行线性插值linearInterpolationPath(ori_path, &path_float, 0.2f, false);std::vector<int> fix_pid(path_float.size(), 0);if (fix) {std::size_t j = 0;for (std::size_t i = 0; i < path_float.size(); ++i) {if (j >= ori_path->size()) break;if (fabs(path_float[i].x() - ori_path->at(j).x()) < 1e-3f &&fabs(path_float[i].y() - ori_path->at(j).y()) < 1e-3f) {fix_pid[i] = 1;j++;}}}PointD tmp_point, tmp_point2;double change_value, tmp_change_value;double v2, v4;unsigned int its, x_id, y_id;bool flag = false;std::vector<PointF> new_path = path_float;std::vector<PointF> last_path = path_float;n_refine = n_refine + 1;for (uint8_t n = 0; n < n_refine; ++n) {if (n > 0) {path_float = last_path;new_path = path_float;}its = 0;change_value = tolerance + 1;while (change_value >= tolerance) { // 拟合的总误差change_value = 0;tmp_change_value = 0;// 5点共轭梯度for (std::size_t i = 2; i + 3 < path_float.size(); ++i) {// 拟合公式if (fix_pid[i] == 1) continue;v2 = new_path[i].x();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 +w_smooth * (new_path[i + 1].x() + new_path[i - 1].x() -2 * new_path[i].x()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i + 1].x() - new_path[i + 2].x() -new_path[i].x()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i - 1].x() - new_path[i - 2].x() -new_path[i].x());tmp_point.x() = v2;tmp_change_value = fabs(v2 - v4);v2 = new_path[i].y();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 +w_smooth * (new_path[i + 1].y() + new_path[i - 1].y() -2 * new_path[i].y()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i + 1].y() - new_path[i + 2].y() -new_path[i].y()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i - 1].y() - new_path[i - 2].y() -new_path[i].y());tmp_point.y() = v2;tmp_change_value += fabs(v2 - v4);map->worldToMap(tmp_point.x(), tmp_point.y(), x_id, y_id);change_value += tmp_change_value;if (compare_cost_value > map->getCost(x_id, y_id)) {new_path[i] = tmp_point;}}last_path = new_path;flag = true;if (++its >= max_its) break; // 拟合的迭代次数}}if (flag) {ori_path->resize(last_path.size());ori_path->clear();for (std::size_t i = 0; i < last_path.size(); ++i)ori_path->push_back(last_path[i]);}
};void pathSmoothThreePoint(const Costmap* const map, uint8_t compare_cost_value,std::vector<PointF>* const ori_path, float tolerance,unsigned int max_its, float w_origin, float w_smooth,uint8_t n_refine) {if (ori_path->size() < 3) return;std::vector<PointF> path_float;linearInterpolationPath(ori_path, &path_float, 0.2, false);std::vector<int> fix_pid(path_float.size(), 0);PointD tmp_point, tmp_point2;double change_value, tmp_change_value;double v2, v4;unsigned int its, x_id, y_id;bool flag = false;std::vector<PointF> new_path = path_float;std::vector<PointF> last_path = path_float;n_refine = n_refine + 1;for (uint8_t n = 0; n < n_refine; ++n) {if (n > 0) {path_float = last_path;new_path = path_float;}its = 0;change_value = tolerance + 1;while (change_value >= tolerance) {change_value = 0;tmp_change_value = 0;// 3点共轭梯度for (std::size_t i = 1; i + 1 < path_float.size(); ++i) {// xv2 = new_path[i].x();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_origin * (path_float[i].x() - v2) +w_smooth *(new_path[i + 1].x() + new_path[i - 1].x() - v2 - v2);tmp_point.x() = v2;tmp_change_value = fabs(v2 - v4);// yv2 = new_path[i].y();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_origin * (path_float[i].y() - v2) +w_smooth *(new_path[i + 1].y() + new_path[i - 1].y() - v2 - v2);tmp_point.y() = v2;tmp_change_value += fabs(v2 - v4);map->worldToMap(tmp_point.x(), tmp_point.y(), x_id, y_id);change_value += tmp_change_value;if (compare_cost_value > map->getCost(x_id, y_id)) {new_path[i] = tmp_point;}}last_path = new_path;flag = true;if (++its >= max_its) break;}}if (flag) {ori_path->resize(last_path.size());ori_path->clear();for (std::size_t i = 0; i < last_path.size(); ++i)ori_path->push_back(last_path[i]);}
};jps原理
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/595298960
JPS路径规划实现示例二
//H#ifndef JPS_PLAN_H_
#define JPS_PLAN_H_
#include "bmap.h"
#include "dubins_curves.h"
#include "global_plan.h"
#include "global_plan_base.h"
#include "static_layer.h"class BJpsPlan : public GlobalPlanBase {public:BJpsPlan() {lawn_map_ = nullptr;costmap_ = nullptr;param_data_ = nullptr;max_search_dis_ = 1.0;init_ = use_dubins_ = debug_ = false;print_ = true;w_diagonal_edge_ = 7;w_straight_edge_ = 5;min_dis_boundary_id_ = -1;max_x_ = 0;max_y_ = 0;min_x_ = 0;min_y_ = 0;compare_cost_value_ = INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE;};~BJpsPlan(){};ErrorCode init(LawnBMap* lawn_map, const ParameterData* const param_data);virtual ErrorCode plan(std::vector<PoseF>* const path_result,const Pose* const start_pos,const Pose* const goal_pos, bool use_smooth = true);ErrorCode doPlan(std::vector<PoseF>* const path_result,const Pose* const start_pos, const Pose* const goal_pos,bool use_smooth);void setMaxSearchDis(float max_search_dis) {max_search_dis_ =fabs(max_search_dis) > 0 ? fabs(max_search_dis) : max_search_dis_;};void setIfUseDubins(bool use_dubins) { use_dubins_ = use_dubins; };void openPrint() { print_ = true; }void closePrint() { print_ = false; }// 以上函数供外界调用private:bool findFreeGridPoint(const PointD& input_global_point,PointD& result_Point, float tolerance_distance);void newNode(NodePart* const node_part, uint64_t cost_g, uint64_t cost_h,Node* const new_node);void getNeighbors(NodePartList* const node_list, Node* const cur_node,std::vector<Node>* const jump_points);bool searchJumpPoint(NodePartList* const node_list, PointI cur_pos,PointI next_direction, Node* const result);PointI searchBit(PointI cur_pose, PointI next_direction);// 需要满足next_direction 不能为对角线运行PointI bitSearchStraightJumpFast(PointI cur_pose, PointI next_direction);bool checkGoal(PointI pose);int getCost(NodePart* const node1, NodePart* const node2);bool getValue(int x, int y) {return (costmap_->getCost(x, y) >= compare_cost_value_);}void checkOutPath(NodePartList* const node_list, int index_x, int index_y,std::vector<PointI>* const path);private:LawnBMap* lawn_map_;Costmap* costmap_;const ParameterData* param_data_;PointInt8 neighbors8_[8];PointI goal_;float max_search_dis_;int min_dis_boundary_id_;int max_x_;int max_y_;int min_x_;int min_y_;int w_diagonal_edge_;int w_straight_edge_;uint8_t compare_cost_value_;bool use_dubins_;bool debug_;bool init_;bool print_;
};#endif // BGLOBAL_PLAN_H_//CPP
#include "jps.h"#include <time.h>ErrorCode BJpsPlan::init(LawnBMap* lawn_map,const ParameterData* const param_data) {init_ = 0;// 输入地图和规划参数if (!lawn_map || !param_data) {MCU_LOG("JPS init ErrorPointerObject");return ErrorPointerObject;}if (!lawn_map->isMapReady()) {return ErrorMapNotReady;}lawn_map_ = lawn_map;param_data_ = param_data;costmap_ = lawn_map_->getGlobalMap()->getCostmap();min_x_ = param_data_->offset_grid_ * 0.5f;min_y_ = min_x_;max_x_ = costmap_->getSizeInCellsX() - min_x_;max_y_ = costmap_->getSizeInCellsY() - min_y_;debug_ = 0;print_ = true;w_diagonal_edge_ = 7;w_straight_edge_ = 5;min_dis_boundary_id_ = -1;neighbors8_[0] = PointInt8(-1, -1);neighbors8_[1] = PointInt8(-1, 0);neighbors8_[2] = PointInt8(-1, 1);neighbors8_[3] = PointInt8(0, -1);neighbors8_[4] = PointInt8(0, 1);neighbors8_[5] = PointInt8(1, -1);neighbors8_[6] = PointInt8(1, 0);neighbors8_[7] = PointInt8(1, 1);init_ = 1;return SuccessNoError;
};bool BJpsPlan::findFreeGridPoint(const PointD& input_global_point,PointD& result_Point,float tolerance_distance) {PointD local_point;PointI start_id;int max_search_grid = ceil(tolerance_distance / costmap_->getResolution());convertPointToLocal(&lawn_map_->transform_, input_global_point,&local_point);costmap_->worldToMapNoBounds(local_point.x(), local_point.y(), start_id.x(),start_id.y());if (costmap_->getCost(start_id.x(), start_id.y()) >= LETHAL_OBSTACLE) {int x_ind = start_id.x();int y_ind = start_id.y();double wx = 0, wy = 0;bool flag = false;for (int n = 1; n < max_search_grid + 1; ++n) {for (int i = -n; i < n + 1; ++i) {for (int j = -n; j < n + 1; ++j) {if (abs(i) == n || abs(j) == n) {if (costmap_->getCost(x_ind + i, y_ind + j) <LETHAL_OBSTACLE) {flag = 1;costmap_->mapToWorld(x_ind + i, y_ind + j, wx, wy);convertPointToGlobal(&lawn_map_->transform_,PointD(wx, wy), &result_Point);break;}}}if (flag) break;}if (flag) break;}if (!flag) return false;}return true;
}
ErrorCode BJpsPlan::plan(std::vector<PoseF>* const path_result,const Pose* const start_pos,const Pose* const goal_pos, bool use_smooth) {// 多档进行路径搜索// 参数50是两个格子30cm,参数100是1个格子15cm,30cm开外可能搜出来不是可执行的最优路径了ErrorCode error = SuccessNoError;compare_cost_value_ = 50;MCU_LOG("first compare_cost_value_ = %d\n", compare_cost_value_);error = doPlan(path_result, start_pos, goal_pos, use_smooth);if (ErrorJpsPlanFailed == error) {compare_cost_value_ = 100;MCU_LOG("second compare_cost_value_ = %d\n", compare_cost_value_);error = doPlan(path_result, start_pos, goal_pos, use_smooth);if (ErrorJpsPlanFailed == error) {compare_cost_value_ = INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE;MCU_LOG("third compare_cost_value_ = %d\n", compare_cost_value_);error = doPlan(path_result, start_pos, goal_pos, use_smooth);}}return error;
}ErrorCode BJpsPlan::doPlan(std::vector<PoseF>* const path_result,const Pose* const start_pos,const Pose* const goal_pos, bool use_smooth) {// jps搜索的实现if (!lawn_map_->isMapReady()) return ErrorMapNotReady;if (!init_) return ErrorNoInitJpsPlan;costmap_ = lawn_map_->getGlobalMap()->getCostmap();PathResult path_;std::vector<PointI> debug_path_id;std::vector<Node> neighbors;NodePartList node_list;Node cur_node;Pose start_copy = *start_pos, goal_copy = *goal_pos;if (print_) {MCU_LOG("JPS input: start_pos %f %f, goal_pos %f %f\n",start_copy.point_.x(), start_copy.point_.y(),goal_copy.point_.x(), goal_copy.point_.y());}Pose start, goal;PointI start_id;double pos_x, pos_y;if (fabs(start_copy.point_.x() - goal_copy.point_.x()) < 0.01f &&fabs(start_copy.point_.y() - goal_copy.point_.y()) < 0.01f) {path_result->clear();path_result->push_back(start_copy);path_result->push_back(goal_copy);if (print_) {MCU_LOG("JPS output ~= input: %f %f, %f %f\n",path_result->at(0).point_.x(), path_result->at(0).point_.y(),path_result->back().point_.x(), path_result->back().point_.y());}return SuccessNoError;}if (findFreeGridPoint(start_copy.point_, start_copy.point_,max_search_dis_)) {convertPointToLocal(&lawn_map_->transform_, start_copy.point_,&start.point_);unsigned int mx = 0, my = 0;costmap_->worldToMap(start.point_.x(), start.point_.y(), mx, my);start_id = PointI(mx, my);} elsereturn ErrorJpsStartPosition;if (findFreeGridPoint(goal_copy.point_, goal_copy.point_,max_search_dis_)) {convertPointToLocal(&lawn_map_->transform_, goal_copy.point_,&goal.point_);unsigned int mx = 0, my = 0;costmap_->worldToMap(goal.point_.x(), goal.point_.y(), mx, my);goal_ = PointI(mx, my);} elsereturn ErrorJpsGoalPosition;if (isLineFree(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, start_id.x(), start_id.y(),goal_.x(), goal_.y(), false, false)) {std::vector<PointF> plan_path;plan_path.resize(2);plan_path.data()[0] = (*start_pos).point_;plan_path.data()[1] = (*goal_pos).point_;transformPointPathToPosePath(plan_path, *path_result);path_result->at(path_result->size() - 1).yaw_ = goal_copy.yaw_;if (print_) {MCU_LOG("JPS output LineFree: %f %f, %f %f\n",path_result->at(0).point_.x(), path_result->at(0).point_.y(),path_result->back().point_.x(), path_result->back().point_.y());}return SuccessNoError;}NodePart node_part;Node new_node;node_part.point.x() = start_id.x();node_part.point.y() = start_id.y();node_list.ptrAt(&node_part);newNode(node_list.ptrBack(), 0,w_straight_edge_ *blockDistance(start_id.x(), start_id.y(), goal_.x(), goal_.y()),&new_node);node_list.ptrBack()->parent = node_list.ptrBack();Heap::PriorityQueue queue = Heap::createPriorityQueue(20);if (!queue) {Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);return ErrorMalloc;}if (Heap::insert(queue, &new_node) != SuccessNoError) {Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);return ErrorMalloc;}costmap_->setCost(goal_.x(), goal_.y(), LETHAL_OBSTACLE);while (queue->current_size > 0) {Heap::remove(queue, &cur_node);if (debug_) {debug_path_id.emplace_back(cur_node.node_part->point.x(),cur_node.node_part->point.y());MCU_LOG("i = %ld, %d , % d \n", debug_path_id.size(),cur_node.node_part->point.x(),cur_node.node_part->point.y());}if (checkGoal(PointI(cur_node.node_part->point.x(),cur_node.node_part->point.y()))) {costmap_->setCost(goal_.x(), goal_.y(), FREE_SPACE);std::vector<PointI> path_id;bool use_more_smooth = true;if (use_smooth && use_more_smooth) {std::vector<PointI> path_id_tmp;std::vector<PointI> path_id1, path_id2;float len1, len2;checkOutPath(&node_list, cur_node.node_part->point.x(),cur_node.node_part->point.y(), &path_id_tmp);linearInterpolationIntPath(&path_id_tmp, &path_id,param_data_->add_grid_);path_id_tmp = path_id;floydSmooth(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, &path_id_tmp,&path_id1, false, true);path_id_tmp = path_id;std::reverse(path_id_tmp.begin(), path_id_tmp.end());floydSmooth(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, &path_id_tmp,&path_id2, false, true);len1 = calPathLength(path_id1);len2 = calPathLength(path_id2);if (len1 <= len2) {path_id_tmp = path_id1;} else {path_id_tmp = path_id2;std::reverse(path_id_tmp.begin(), path_id_tmp.end());}floydSmooth(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, &path_id_tmp,&path_id, true, false);} else {checkOutPath(&node_list, cur_node.node_part->point.x(),cur_node.node_part->point.y(), &path_id);}std::vector<PointF> plan_path;for (int64_t i = (int64_t)path_id.size() - 1; i > -1; --i) {costmap_->mapToWorld(path_id.at(i).x(), path_id.at(i).y(),pos_x, pos_y);plan_path.emplace_back(pos_x, pos_y);}if (use_smooth) {pathSmoothFivePoint(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, &plan_path,0.00001, 100, 0.7, 0.003, 0,false); // 0.00001, 600, 0.7, 0.003, 2}convertPointsToGlobal(&lawn_map_->transform_, plan_path.data(),plan_path.size());plan_path.back() = goal_copy.point_;removeCollinearPoints(&plan_path);transformPointPathToPosePath(plan_path, *path_result);path_result->at(path_result->size() - 1).yaw_ = goal_copy.yaw_;path_result->at(0).point_ = (*start_pos).point_;path_result->at(path_result->size() - 1).point_ =(*goal_pos).point_;Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);if (print_) {MCU_LOG("JPS output: %f %f, %f %f\n",path_result->at(0).point_.x(),path_result->at(0).point_.y(),path_result->back().point_.x(),path_result->back().point_.y());}return SuccessNoError;}getNeighbors(&node_list, &cur_node, &neighbors);for (unsigned int i = 0; i < neighbors.size(); ++i) {uint64_t cost_g =cur_node.node_part->cost_g +getCost(cur_node.node_part, neighbors.at(i).node_part);uint64_t cost_h =w_straight_edge_ *blockDistance(neighbors.at(i).node_part->point.x(),neighbors.at(i).node_part->point.y(), goal_.x(),goal_.y());if (neighbors.at(i).node_part->state == 0) {newNode(neighbors.at(i).node_part, cost_g, cost_h, &new_node);new_node.node_part->parent = cur_node.node_part;if (Heap::insert(queue, &new_node) != SuccessNoError) {Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);return ErrorMalloc;}} else if (neighbors.at(i).node_part->state == 1 &&cost_g < neighbors.at(i).node_part->cost_g) {neighbors.at(i).node_part->cost_g = cost_g;queue->nodes[neighbors.at(i).node_part->heap_id].cost_f =cost_g + cost_h;if (Heap::insertOrRearrange(queue, neighbors.at(i).node_part->heap_id) !=SuccessNoError) {Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);return ErrorMalloc;}} else if (cost_g < neighbors.at(i).node_part->cost_g) {newNode(neighbors.at(i).node_part, cost_g, cost_h, &new_node);new_node.node_part->parent = cur_node.node_part;if (Heap::insert(queue, &new_node) != SuccessNoError) {Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);return ErrorMalloc;}}}}if (debug_) {costmap_->setCost(goal_.x(), goal_.y(), FREE_SPACE);std::vector<PointF> plan_path;plan_path.clear();for (std::size_t i = 0; i < debug_path_id.size(); ++i) {costmap_->mapToWorld(debug_path_id.at(i).x(),debug_path_id.at(i).y(), pos_x, pos_y);plan_path.emplace_back(pos_x, pos_y);}convertPointsToGlobal(&lawn_map_->transform_, plan_path.data(),plan_path.size());transformPointPathToPosePath(plan_path, *path_result);path_result->at(path_result->size() - 1).yaw_ = goal_copy.yaw_;Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);return SuccessNoError;}Heap::deletePriorityQueue(queue);MCU_LOG("ErrorJpsPlanFailed\n");return ErrorJpsPlanFailed;
};void BJpsPlan::getNeighbors(NodePartList* const node_list, Node* const cur_node,std::vector<Node>* const jump_points) {jump_points->clear();Node jump_point;PointI cur_pose(cur_node->node_part->point.x(),cur_node->node_part->point.y());if (cur_node->node_part->parent == cur_node->node_part) {for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose,PointI(neighbors8_[i].x(), neighbors8_[i].y()),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);}} else {int dx = cur_pose.x() - cur_node->node_part->parent->point.x();int dy = cur_pose.y() - cur_node->node_part->parent->point.y();dx = dx > 0 ? 1 : (dx < 0 ? -1 : 0);dy = dy > 0 ? 1 : (dy < 0 ? -1 : 0);if (dx != 0 && dy != 0) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(dx, 0),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(0, dy),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(dx, dy),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);if (getValue(cur_pose.x() - dx, cur_pose.y())) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(-dx, dy),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);}if (getValue(cur_pose.x(), cur_pose.y() - dy)) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(dx, -dy),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);}} else {if (dx != 0) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(dx, 0),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);if (getValue(cur_pose.x(), cur_pose.y() - 1)) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(dx, -1),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);}if (getValue(cur_pose.x(), cur_pose.y() + 1)) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(dx, 1),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);}} else {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(0, dy),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);if (getValue(cur_pose.x() + 1, cur_pose.y())) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(1, dy),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);}if (getValue(cur_pose.x() - 1, cur_pose.y())) {if (searchJumpPoint(node_list, cur_pose, PointI(-1, dy),&jump_point))jump_points->push_back(jump_point);}}}}
}bool BJpsPlan::searchJumpPoint(NodePartList* const node_list, PointI cur_pos,PointI next_direction, Node* const result) {PointI res;res = searchBit(cur_pos, next_direction);if (res.x() != -1) {NodePart node_part;node_part.point = res;result->node_part = node_list->ptrAt(&node_part);return true;}return false;
}PointI BJpsPlan::searchBit(PointI cur_pose, PointI next_direction) {PointI to_pose(cur_pose.x() + next_direction.x(),cur_pose.y() + next_direction.y());while (1) {if (fabs(to_pose.x() - goal_.x()) < 2 &&fabs(to_pose.y() - goal_.y()) < 2)return goal_;if (getValue(to_pose.x(), to_pose.y())) return PointI(-1, -1);if (next_direction.x() != 0 && next_direction.y() != 0) {if ((!getValue(to_pose.x() - next_direction.x(),to_pose.y() + next_direction.y()) &&getValue(to_pose.x() - next_direction.x(), to_pose.y())) ||(!getValue(to_pose.x() + next_direction.x(),to_pose.y() - next_direction.y()) &&getValue(to_pose.x(), to_pose.y() - next_direction.y())))return to_pose;} else {PointI res = bitSearchStraightJumpFast(cur_pose, next_direction);if (res.x() != -1) {if (res.x() == goal_.x() && res.y() == goal_.y()) {if (isLineFree(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, to_pose.x(),to_pose.y(), goal_.x(), goal_.y(), true,true))return goal_;}return res;} elsereturn PointI(-1, -1);}if (next_direction.x() != 0 && next_direction.y() != 0) {PointI res2 = bitSearchStraightJumpFast(to_pose, PointI(next_direction.x(), 0));if (res2.x() != -1) {if (res2.x() == goal_.x() && res2.y() == goal_.y()) {if (isLineFree(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, to_pose.x(),to_pose.y(), goal_.x(), goal_.y(), false,false))return goal_;}return to_pose;}res2 = bitSearchStraightJumpFast(to_pose,PointI(0, next_direction.y()));if (res2.x() != -1) {if (res2.x() == goal_.x() && res2.y() == goal_.y()) {if (isLineFree(costmap_, compare_cost_value_, to_pose.x(),to_pose.y(), goal_.x(), goal_.y(), false,false))return goal_;}return to_pose;}}if (!getValue(to_pose.x() + next_direction.x(), to_pose.y()) ||!getValue(to_pose.x(), to_pose.y() + next_direction.y())) {to_pose.x() = to_pose.x() + next_direction.x();to_pose.y() = to_pose.y() + next_direction.y();} elsereturn PointI(-1, -1);}
}PointI BJpsPlan::bitSearchStraightJumpFast(PointI cur_pose,PointI next_direction) {int dx = next_direction.x();int dy = next_direction.y();PointI to_pose(cur_pose.x() + dx, cur_pose.y() + dy);if (fabs(to_pose.x() - goal_.x()) < 2 && fabs(to_pose.y() - goal_.y()) < 2)return goal_;if (getValue(to_pose.x(), to_pose.y())) return PointI(-1, -1);uint32_t bit_map_current, bit_map_up, bit_map_down, bit_map_left,bit_map_right;uint32_t tmp;int current_id, jump_id;while (true) {bit_map_current = bit_map_up = bit_map_down = bit_map_left =bit_map_right = 0;if (dx == 1) {for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {if (to_pose.x() + i >= min_x_ && to_pose.x() + i <= max_x_) {bit_map_up = bit_map_up << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() + i, to_pose.y() + 1);bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() + i, to_pose.y());bit_map_down = bit_map_down << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() + i, to_pose.y() - 1);} else {bit_map_up = bit_map_up << 1 | 1;bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 | 1;bit_map_down = bit_map_down << 1 | 1;}}int current_id_tmp = __builtin_clz(bit_map_current);if (to_pose.y() == goal_.y() &&(goal_.x() - to_pose.x() == current_id_tmp))return goal_;tmp = ((bit_map_up >> 1) & (~bit_map_up)) |((bit_map_down >> 1) & (~bit_map_down));if (bit_map_current == 0 && tmp == 0) {to_pose.x() += 31;} else if (tmp == 0) {return PointI(-1, -1);} else if (bit_map_current == 0) {to_pose.x() += __builtin_clz(tmp) - 1;return to_pose;} else {current_id = current_id_tmp;jump_id = __builtin_clz(tmp);if (current_id > jump_id) {to_pose.x() += jump_id - 1;return to_pose;} else {return PointI(-1, -1);}}} else if (dx == -1) {for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {if (to_pose.x() - i >= min_x_ && to_pose.x() - i <= max_x_) {bit_map_up = bit_map_up << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() - i, to_pose.y() + 1);bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() - i, to_pose.y());bit_map_down = bit_map_down << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() - i, to_pose.y() - 1);} else {bit_map_up = bit_map_up << 1 | 1;bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 | 1;bit_map_down = bit_map_down << 1 | 1;}}int current_id_tmp = __builtin_clz(bit_map_current);if (to_pose.y() == goal_.y() &&(to_pose.x() - goal_.x() == current_id_tmp))return goal_;tmp = ((bit_map_up >> 1) & (~bit_map_up)) |((bit_map_down >> 1) & (~bit_map_down));if (bit_map_current == 0 && tmp == 0) {to_pose.x() -= 31;} else if (tmp == 0) {return PointI(-1, -1);} else if (bit_map_current == 0) {to_pose.x() += 1 - __builtin_clz(tmp);return to_pose;} else {current_id = current_id_tmp;jump_id = __builtin_clz(tmp);if (current_id > jump_id) {to_pose.x() += 1 - jump_id;return to_pose;} else {return PointI(-1, -1);}}} else if (dy == 1) {for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {if (to_pose.y() + i >= min_y_ && to_pose.y() + i <= max_y_) {bit_map_left = bit_map_left << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() - 1, to_pose.y() + i);bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x(), to_pose.y() + i);bit_map_right = bit_map_right << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() + 1, to_pose.y() + i);} else {bit_map_left = bit_map_left << 1 | 1;bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 | 1;bit_map_right = bit_map_right << 1 | 1;}}int current_id_tmp = __builtin_clz(bit_map_current);if (to_pose.x() == goal_.x() &&(goal_.y() - to_pose.y() == current_id_tmp))return goal_;tmp = ((bit_map_left >> 1) & (~bit_map_left)) |((bit_map_right >> 1) & (~bit_map_right));if (bit_map_current == 0 && tmp == 0) {to_pose.y() += 31;} else if (bit_map_current == 0) {to_pose.y() += __builtin_clz(tmp) - 1;return to_pose;} else if (tmp == 0) {if (to_pose.y() <= goal_.y() && to_pose.x() == goal_.x() &&to_pose.y() + current_id_tmp >= goal_.y())return goal_;return PointI(-1, -1);} else {current_id = current_id_tmp;jump_id = __builtin_clz(tmp);if (current_id >= jump_id) {to_pose.y() += jump_id - 1;return to_pose;} else {if (to_pose.y() <= goal_.y() && to_pose.x() == goal_.x() &&to_pose.y() + current_id_tmp >= goal_.y())return goal_;return PointI(-1, -1);}}} else if (dy == -1) {for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {if (to_pose.y() - i >= min_y_ && to_pose.y() - i <= max_y_) {bit_map_left = bit_map_left << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() - 1, to_pose.y() - i);bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x(), to_pose.y() - i);bit_map_right = bit_map_right << 1 |getValue(to_pose.x() + 1, to_pose.y() - i);} else {bit_map_left = bit_map_left << 1 | 1;bit_map_current = bit_map_current << 1 | 1;bit_map_right = bit_map_right << 1 | 1;}}int current_id_tmp = __builtin_clz(bit_map_current);if (to_pose.x() == goal_.x() &&(to_pose.y() - goal_.y() == current_id_tmp))return goal_;tmp = ((bit_map_left >> 1) & (~bit_map_left)) |((bit_map_right >> 1) & (~bit_map_right));if (bit_map_current == 0 && tmp == 0)to_pose.y() -= 31;else if (bit_map_current == 0) {to_pose.y() += 1 - __builtin_clz(tmp);return to_pose;} else if (tmp == 0) {if (to_pose.y() >= goal_.y() && to_pose.x() == goal_.x() &&to_pose.y() - current_id_tmp <= goal_.y())return goal_;return PointI(-1, -1);} else {current_id = current_id_tmp;jump_id = __builtin_clz(tmp);if (current_id >= jump_id) {to_pose.y() += 1 - jump_id;return to_pose;} else {if (to_pose.y() >= goal_.y() && to_pose.x() == goal_.x() &&to_pose.y() - current_id_tmp <= goal_.y())return goal_;return PointI(-1, -1);}}}}
}void BJpsPlan::newNode(NodePart* const node_part, uint64_t cost_g,uint64_t cost_h, Node* const new_node) {new_node->node_part = node_part;new_node->cost_f = cost_g + cost_h;node_part->cost_g = cost_g;node_part->state = 1;
}bool BJpsPlan::checkGoal(PointI pose) {if (fabs(pose.x() - goal_.x()) < 2 && fabs(pose.y() - goal_.y()) < 2)return true;return false;
}int BJpsPlan::getCost(NodePart* const node1, NodePart* const node2) {int dx, dy, dmin, dmax;dx = abs(node1->point.x() - node2->point.x());dy = abs(node1->point.y() - node2->point.y());if (dx > dy) {dmin = dy;dmax = dx;} else {dmin = dx;dmax = dy;}return (dmin * w_diagonal_edge_ + (dmax - dmin) * w_straight_edge_);
}void BJpsPlan::checkOutPath(NodePartList* const node_list, int index_x,int index_y, std::vector<PointI>* const path) {path->clear();NodePart node_part;NodePart* node_part_ptr;PointI point(index_x, index_y);node_part.point = point;path->push_back(goal_);if (index_x != goal_.x() || index_y != goal_.y()) path->push_back(point);node_part_ptr = node_list->ptrAt(&node_part)->parent;point = node_part_ptr->point;while (node_part_ptr != node_part_ptr->parent) {path->push_back(point);node_part_ptr = node_list->ptrAt(node_part_ptr->parent);point = node_part_ptr->point;}path->push_back(point);
}其他数据结构struct NodePart {NodePart() {cost_g = 0;heap_id = state = 0;parent = nullptr;}NodePart(const NodePart& other) = delete;NodePart* parent;PointI point;double cost_g;int64_t heap_id;uint8_t state;
};struct Node {Node() : node_part(nullptr), cost_f(0) {}NodePart* node_part;double cost_f;
};class NodePartList {public:NodePartList();NodePartList(const NodePartList& other) = delete;NodePartList& operator=(const NodePartList& other) = delete;~NodePartList();// void printData();void freeVec();NodePart** data() { return data_; };uint64_t size() { return count_; };int8_t pointCompare(PointI* p1, PointI* p2);NodePart* ptrBack() { return data_[count_ - 1]; };NodePart* ptrAt(NodePart* node_part);private:uint64_t capacity_;uint64_t count_;NodePart** data_;
};namespace Heap {PriorityQueue createPriorityQueue(uint32_t capacity) {PriorityQueue queue = nullptr;try {queue = new Heap();queue->capacity_ = capacity;queue->current_size = 0;try {queue->nodes = new Node[capacity]();} catch (std::bad_alloc&) {MCU_LOG("bad_alloc\n");queue->capacity_ = 0;delete queue;queue = nullptr;}} catch (std::bad_alloc&) {MCU_LOG("bad_alloc\n");return nullptr;}return queue;
};void deletePriorityQueue(PriorityQueue& queue) {if (queue) {if (queue->nodes) {delete [] queue->nodes;queue->nodes = nullptr;}delete queue;queue = nullptr;}
};bool isFull(PriorityQueue queue) {return queue->capacity_ == queue->current_size;
};bool isEmpty(PriorityQueue queue) { return 0 == queue->current_size; };ErrorCode resizePriorityQueue(PriorityQueue queue, uint32_t capacity) {if (queue->capacity_ == 0) {queue->capacity_ = 20;queue->current_size = 0;try {queue->nodes = new Node[queue->capacity_]();} catch (std::bad_alloc&) {MCU_LOG("bad_alloc\n");queue->capacity_ = 0;return ErrorMalloc;}} else {try {int capacity_tmp = 1 + (queue->capacity_ << 1);Node* new_ptr = new Node[capacity_tmp];if(queue->current_size > 0) {memcpy(new_ptr, queue->nodes, sizeof(Node) * queue->current_size);}delete []queue->nodes;queue->nodes = new_ptr;queue->capacity_ = capacity_tmp;} catch (std::bad_alloc&) {MCU_LOG("bad_alloc\n");return ErrorRealloc;}}return SuccessNoError;
};ErrorCode insert(PriorityQueue queue, Node* new_node) {if (isFull(queue)) {if (resizePriorityQueue(queue) != SuccessNoError) return ErrorMalloc;}int64_t index, parent;for (index = queue->current_size; index > 0;) {parent = floor((index - 1) * 0.5);if (new_node->cost_f < queue->nodes[parent].cost_f) {queue->nodes[index] = queue->nodes[parent];queue->nodes[index].node_part->heap_id = index;index = parent;} elsebreak;}queue->current_size++;queue->nodes[index] = *new_node;queue->nodes[index].node_part->heap_id = index;return SuccessNoError;
};ErrorCode insertOrRearrange(PriorityQueue queue, int64_t from_heap_id,Node* new_node) {if (isFull(queue)) {if (resizePriorityQueue(queue) != SuccessNoError) return ErrorMalloc;}int64_t index, parent;if (from_heap_id == -1 && new_node != nullptr) {from_heap_id = queue->current_size;queue->current_size++;} else if (from_heap_id >= 0 && (uint32_t)from_heap_id < queue->current_size) {new_node = &queue->nodes[from_heap_id];} else// return false;return SuccessNoError;for (index = from_heap_id; index > 0;) {parent = floor((index - 1) * 0.5);if (new_node->cost_f < queue->nodes[parent].cost_f) {queue->nodes[index] = queue->nodes[parent];queue->nodes[index].node_part->heap_id = index;index = parent;} elsebreak;}queue->nodes[index] = *new_node;queue->nodes[index].node_part->heap_id = index;return SuccessNoError;
};bool remove(PriorityQueue queue, Node* min_cost_node) {if (!isEmpty(queue)) {int64_t index = 0, left_child, right_child, small_index;Node* compare_element;*min_cost_node = queue->nodes[0];queue->nodes[0].node_part->state = 2;compare_element = &queue->nodes[queue->current_size - 1];queue->current_size--;for (index = 0; index < floor(queue->current_size * 0.5);) {left_child = (index << 1) + 1;right_child = left_child + 1;if (queue->nodes[left_child].cost_f <queue->nodes[right_child].cost_f)small_index = left_child;elsesmall_index = right_child;if (compare_element->cost_f > queue->nodes[small_index].cost_f) {queue->nodes[index] = queue->nodes[small_index];queue->nodes[index].node_part->heap_id = index;index = small_index;} elsebreak;}queue->nodes[index] = *compare_element;queue->nodes[index].node_part->heap_id = index;return true;}return false;
};
} // namespace Heap-------------->C/C++编程规范
-------------->工程经验相关
三方库的调用方法
在C++工程中使用Boost库涉及几个关键步骤,以下是一个概述流程:
-
下载并安装Boost库(三方库):
- 访问Boost(三方库)官网或者其他镜像站点,下载最新版本的Boost库(三方库)源码。
- 解压下载的(三方库)源码文件。
- 根据操作系统和编译环境,使用合适的方法编译Boost库,把三方库源码安装在开发环境中(注意:并非在运行环境中)(例如,在Linux上通常使用
./bootstrap.sh、./b2等命令)。
-
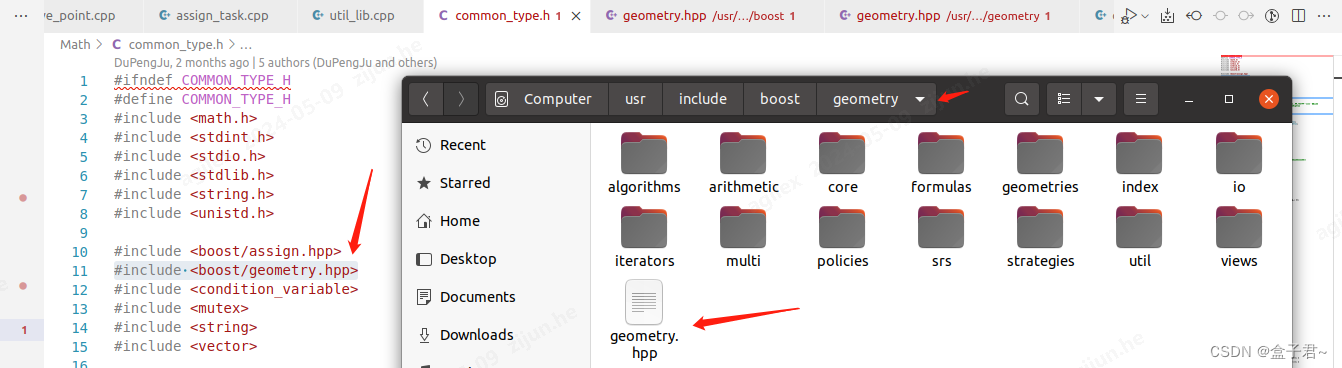
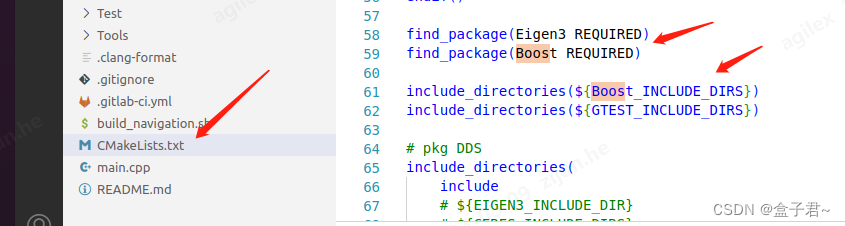
配置开发环境:
- 确保您的编译器设置正确,以便能够找到Boost(三方库)头文件和库文件(cpp工程一般是通过配置cmakelist文件)。
- 对于IDE用户,可能需要在项目设置中添加对Boost(三方库)头文件路径的定义,以及链接器选项中的Boost库路径。
-
包含Boost(三方库)头文件:
- 在您的C++源文件(项目工程)中,使用
#include指令引入所需的Boost头文件。例如,如果您想使用Boost的asio库,您需要包含<boost/asio.hpp>。
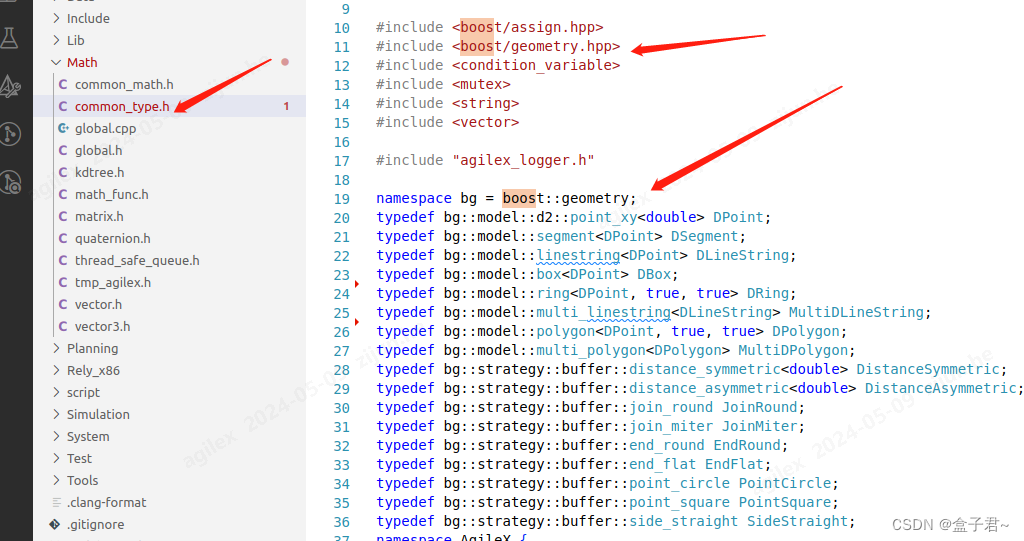
- 在您的C++源文件(项目工程)中,使用
-
编写代码:
- 通过三方库的官方使用教程及API的使用方法,使用Boost库(三方库)提供的功能编写代码。由于Boost是头文件库,您不需要链接到任何特定的Boost对象文件,只需在代码中直接使用其功能即可。
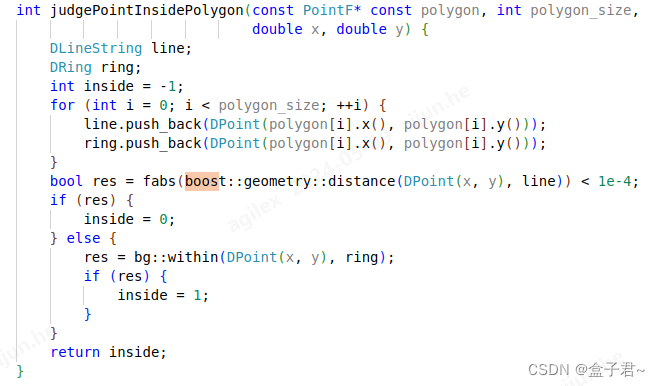
-
链接Boost库(三方库):
- 在编译您的工程时,确保链接器能够找到Boost库文件。这通常需要在编译命令中加入
-lboost_system等参数,具体取决于您使用的Boost组件。
- 在编译您的工程时,确保链接器能够找到Boost库文件。这通常需要在编译命令中加入
-
构建与测试:
- 构建您的工程,并进行充分的测试,以确保Boost库被正确地集成和使用。
-
部署:
- 当部署应用程序时,确保目标系统上安装了相应版本的Boost库,或者将所需的Boost库文件随应用程序一起分发。
-
版本管理:
- 由于Boost库经常更新,因此建议在项目文档中记录所使用的Boost版本,以便将来维护和升级。
请注意,上述步骤可能会根据具体的操作系统、编译器和IDE有所不同。此外,Boost库的某些部分可能需要额外的依赖项,因此在编译和链接时需要注意这些依赖关系。
参考链接
在Linux下引入C++ Boost库:下载、编译、安装、使用详细教程
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41868108/article/details/105778471
https://blog.csdn.net/Aliven888/article/details/111153535
https://www.cnblogs.com/mingzhang/p/11349808.html
-------------->产品导航业务方案【从自己做的项目中分离出来】
-------------->决策逻辑与导航架构相关
.
-------------->仿真及开发生态搭建相关
-------------->感知相关
-------------->定位相关
-------------->地图相关
-------------->决策
git
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989710
pid轨迹跟踪控制
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989706
lattice算法讲解
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989617
人工势场地图做规划
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989592
运动预测(Motion Prediction)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989576
双向Dijkstra算法(提升效率)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989507
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989509
A*启发式搜索算法
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989495
栅格地图生成
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989505
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989500
C++11–使用表驱动(Table-Driven)模式消除if-else和switch-case语句
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989496
三次样条插值(Cubic Spline Interpolation)曲线及Python代码实现
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989491
Hybird A*算法
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989481
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989483
Reeds Shepp曲线
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989478
Dubins曲线
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989471
自动驾驶运动规划(Motion Planning)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989463
车辆运动学模型
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989461
自动驾驶定位算法(十三)-粒子滤波(Particle Filter)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989445
直方图滤波定位
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989436
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989440
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989439
卡尔曼滤波
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989394
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989400
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989403
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989428
-------------->路径规划
路径跟踪LQR改进
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2357587
路径跟踪MPC
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989738
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989736
三次螺旋曲线生成(局部路径生成)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2333012
三次多项式曲线+后端优化
基于优化的离散点平滑算法(平滑性Cost、长度Cost、偏移Cost且带约束条件的非线性优化)Apollo代码
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2190924
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI1NjkxOTMyNQ==&mid=2247492799&idx=1&sn=869a9dfcde89d2f04054bbf0da13aa2d&scene=21&poc_token=HFXvPWaja8Fu6V95swe0MwX1lDJK71HFOb2zKrIS
无人车导航系统(整体流程、轨迹生成、碰撞检测、路径跟踪)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2090235
轨迹拼接(Trajectory Stitching)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2028649
感知中的运动预测(深度神经网络)
自动驾驶运动预测-VectorNet论文复现
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989731
商业中,自动驾驶是伪命题(除非降级到车路协同),机器人才是正道
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989714
梯度下降(SGD)原理
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/152566066
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/EXumVg7EPcl0ZeRVeUk82g
随机梯度下降原理
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/680858421
共轭梯度下降(完整)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/b6c1206e4035
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29796781/article/details/80113026
五点中值梯度下降
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43879302/article/details/116092810
代码从工程里面拿
void pathSmoothFivePoint(const Costmap* const map, uint8_t compare_cost_value,std::vector<PointF>* const ori_path, float tolerance,unsigned int max_its, float w_origin, float w_smooth,uint8_t n_refine, bool fix) {if (ori_path->size() < 3) return;std::vector<PointF> path_float;linearInterpolationPath(ori_path, &path_float, 0.2f, false);std::vector<int> fix_pid(path_float.size(), 0);if (fix) {std::size_t j = 0;for (std::size_t i = 0; i < path_float.size(); ++i) {if (j >= ori_path->size()) break;if (fabs(path_float[i].x() - ori_path->at(j).x()) < 1e-3f &&fabs(path_float[i].y() - ori_path->at(j).y()) < 1e-3f) {fix_pid[i] = 1;j++;}}}PointD tmp_point, tmp_point2;double change_value, tmp_change_value;double v2, v4;unsigned int its, x_id, y_id;bool flag = false;std::vector<PointF> new_path = path_float;std::vector<PointF> last_path = path_float;n_refine = n_refine + 1;for (uint8_t n = 0; n < n_refine; ++n) {if (n > 0) {path_float = last_path;new_path = path_float;}its = 0;change_value = tolerance + 1;while (change_value >= tolerance) {change_value = 0;tmp_change_value = 0;// 5点for (std::size_t i = 2; i + 3 < path_float.size(); ++i) {if (fix_pid[i] == 1) continue;v2 = new_path[i].x();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 +w_smooth * (new_path[i + 1].x() + new_path[i - 1].x() -2 * new_path[i].x()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i + 1].x() - new_path[i + 2].x() -new_path[i].x()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i - 1].x() - new_path[i - 2].x() -new_path[i].x());tmp_point.x() = v2;tmp_change_value = fabs(v2 - v4);v2 = new_path[i].y();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 +w_smooth * (new_path[i + 1].y() + new_path[i - 1].y() -2 * new_path[i].y()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i + 1].y() - new_path[i + 2].y() -new_path[i].y()) +w_smooth * 0.5f *(2 * new_path[i - 1].y() - new_path[i - 2].y() -new_path[i].y());tmp_point.y() = v2;tmp_change_value += fabs(v2 - v4);map->worldToMap(tmp_point.x(), tmp_point.y(), x_id, y_id);change_value += tmp_change_value;if (compare_cost_value > map->getCost(x_id, y_id)) {new_path[i] = tmp_point;}}last_path = new_path;flag = true;if (++its >= max_its) break;}}if (flag) {ori_path->resize(last_path.size());ori_path->clear();for (std::size_t i = 0; i < last_path.size(); ++i)ori_path->push_back(last_path[i]);}
};void pathSmoothThreePoint(const Costmap* const map, uint8_t compare_cost_value,std::vector<PointF>* const ori_path, float tolerance,unsigned int max_its, float w_origin, float w_smooth,uint8_t n_refine) {if (ori_path->size() < 3) return;std::vector<PointF> path_float;linearInterpolationPath(ori_path, &path_float, 0.2, false);std::vector<int> fix_pid(path_float.size(), 0);PointD tmp_point, tmp_point2;double change_value, tmp_change_value;double v2, v4;unsigned int its, x_id, y_id;bool flag = false;std::vector<PointF> new_path = path_float;std::vector<PointF> last_path = path_float;n_refine = n_refine + 1;for (uint8_t n = 0; n < n_refine; ++n) {if (n > 0) {path_float = last_path;new_path = path_float;}its = 0;change_value = tolerance + 1;while (change_value >= tolerance) {change_value = 0;tmp_change_value = 0;// 3点for (std::size_t i = 1; i + 1 < path_float.size(); ++i) {v2 = new_path[i].x();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_origin * (path_float[i].x() - v2) +w_smooth *(new_path[i + 1].x() + new_path[i - 1].x() - v2 - v2);tmp_point.x() = v2;tmp_change_value = fabs(v2 - v4);v2 = new_path[i].y();v4 = v2;v2 = v2 + w_origin * (path_float[i].y() - v2) +w_smooth *(new_path[i + 1].y() + new_path[i - 1].y() - v2 - v2);tmp_point.y() = v2;tmp_change_value += fabs(v2 - v4);map->worldToMap(tmp_point.x(), tmp_point.y(), x_id, y_id);change_value += tmp_change_value;if (compare_cost_value > map->getCost(x_id, y_id)) {new_path[i] = tmp_point;}}last_path = new_path;flag = true;if (++its >= max_its) break;}}if (flag) {ori_path->resize(last_path.size());ori_path->clear();for (std::size_t i = 0; i < last_path.size(); ++i)ori_path->push_back(last_path[i]);}
};分段路径优化的策略&非线性优化
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/60728960
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43879302/article/details/116092810
硬软约束
基于硬约束的方法是在八叉树地图生成飞行走廊,然后使用二次约束二次规划(QCQP)生成完全约束在走廊内的轨迹
https://blog.csdn.net/Travis_X/article/details/115617112
混合A星的后端轨迹优化(可以单独从博客中拿出来)
https://www.guyuehome.com/45716
Hybrid A*平滑
优化目标包括障碍物、曲率、顺滑、voronoi势场项等。代码并没有使用论文中共轭梯度下降法,而是使用了普通的梯度下降法。
参考链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/113697820
代码:
https://github.com/karlkurzer/path_planner【源代码】
https://github.com/linxigjs/path_smoother【加curvature项、voronoi成本、平滑项重写】
APOLLO参考性平滑方法
参考线平滑,高精地图给出的道路中心线的平滑性往往都不能满足规划模块的需求,因此规划中是不能拿来直接用的,需要对其进行平滑操作。共有三种参考性平滑算法:
1)QpSpline Smoother:分段5次多项式拟合+二次规划
参考链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/345175084
2)SpiralReferenceLine Smoother:多项式螺旋线优化
参考链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/347373426
3)DiscretePoints Smoother:默认配置,离散点平滑
参考链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/371585754
使用梯度下降法
移动和插入顶点使得离障碍物更远、离障碍物近的地方路径点更密集;使用基于cost的short-cutting方法删除不必要的路径点。
参考资料:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/113697820
代码:https://github.com/eric-heiden/grips
clothiod曲线进行平滑
clothiod的曲率半径和长度成线性关系。可以考虑有限长度的clothoid应用到机器人领域
Voronoi路径规划探索
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1989513
分段路径优化的策略

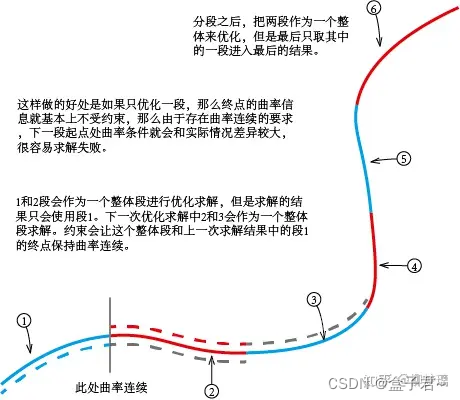
使用梯度下降的方式进行路径平滑
核心思想
在数学和优化中,梯度下降算法用于找到函数的局部最小值。如果我们将这个概念应用到路径的平滑上,我们可以假设路径是由一系列点定义的,并且我们想要找到一个平滑的路径,这个路径可能是由某种代价函数(或目标函数)所定义的,该函数衡量了路径的“粗糙度”或“不平滑度”。
为了平滑一个路径,我们可以使用梯度下降来最小化一个定义了路径不平滑程度的目标函数。这个目标函数可能会涉及到路径上的点的曲率、速度变化或其他度量,这些度量了路径的不连续性或“颠簸”。
以下是一个简单的例子,说明如何使用梯度下降来平滑一个路径:
-
定义路径: 假设我们有一系列的2D坐标点,这些点定义了一个路径。
-
定义目标函数: 我们定义一个目标函数,它衡量了路径的不平滑度。例如,我们可以计算每两个连续点之间的转角,并将这些转角的平方和作为目标函数。
-
计算梯度: 我们计算目标函数相对于路径上每个点的梯度。在这个例子中,梯度将指示如何移动每个点以减少转角。
-
更新路径: 使用梯度下降规则,我们更新路径上的每个点,使得路径变得更加平滑。
-
重复: 我们重复这个过程多次,直到达到某个停止准则,比如梯度的大小变得非常小,或者达到了预设的迭代次数。
下面是一个简化的数学表示,说明如何使用梯度下降来平滑路径:
假设路径由点 P 1 , P 2 , . . . , P n P_1, P_2, ..., P_n P1,P2,...,Pn 定义,目标函数 F F F 是路径上连续点之间转角的平方和:
F ( P ) = ∑ i = 1 n − 1 ( θ i + 1 − θ i ) 2 F(\mathbf{P}) = \sum_{i=1}^{n-1} (\theta_{i+1} - \theta_i)^2 F(P)=i=1∑n−1(θi+1−θi)2
其中 θ i \theta_i θi 是点 P i P_i Pi 和 P i + 1 P_{i+1} Pi+1 之间线段与x轴的夹角。
梯度下降更新规则为:
P i : = P i − α a b l a F ( P ) ∣ P = P i P_i := P_i - \alpha abla F(\mathbf{P}) |_{P=P_i} Pi:=Pi−αablaF(P)∣P=Pi
其中 α \alpha α 是学习率,$
abla F(\mathbf{P})$ 是目标函数相对于点 P i P_i Pi 的梯度。
这个过程会迭代进行,直到路径足够平滑。在实际应用中,目标函数和梯度的计算可能会更加复杂,需要考虑路径的具体特性和平滑度的要求。
C++实现(连续点之间转角的平方和)
以下是一个简单的C++实现,用于平滑路径。这个例子使用了梯度下降算法来最小化路径上连续点之间转角的平方和。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>struct Point {double x, y;
};// 计算两点之间的距离
double distance(const Point& p1, const Point& p2) {return std::sqrt((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y));
}// 计算两点之间的转角(弧度)
double angle(const Point& p1, const Point& p2) {return std::atan2(p2.y - p1.y, p2.x - p1.x);
}// 计算目标函数的值(路径上连续点之间转角的平方和)
double objective_function(const std::vector<Point>& path) {double sum = 0;for (size_t i = 1; i < path.size(); ++i) {double theta = angle(path[i-1], path[i]);sum += theta * theta;}return sum;
}// 计算目标函数相对于路径上每个点的梯度
std::vector<Point> gradient(const std::vector<Point>& path) {std::vector<Point> grad(path.size());for (size_t i = 1; i < path.size() - 1; ++i) {double theta_prev = angle(path[i-1], path[i]);double theta_next = angle(path[i], path[i+1]);double dtheta = theta_next - theta_prev;grad[i].x = -2 * dtheta * (path[i].x - path[i-1].x);grad[i].y = -2 * dtheta * (path[i].y - path[i-1].y);}return grad;
}// 使用梯度下降算法平滑路径
void smooth_path(std::vector<Point>& path, double learning_rate, int iterations) {for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; ++iter) {std::vector<Point> grad = gradient(path);for (size_t i = 1; i < path.size() - 1; ++i) {path[i].x -= learning_rate * grad[i].x;path[i].y -= learning_rate * grad[i].y;}}
}int main() {// 初始化路径(示例)std::vector<Point> path = {{0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 0}, {3, 1}, {4, 0}};// 平滑路径smooth_path(path, 0.1, 100);// 输出平滑后的路径for (const auto& point : path) {std::cout << "(" << point.x << ", " << point.y << ")" << std::endl;}return 0;
}在这个例子中,我们首先定义了一个Point结构体来表示2D坐标点。然后,我们定义了两个辅助函数:distance用于计算两点之间的距离,angle用于计算两点之间的转角。接下来,我们定义了目标函数objective_function和梯度函数gradient。最后,我们实现了smooth_path函数,该函数使用梯度下降算法来平滑路径。在main函数中,我们初始化了一个示例路径,并调用smooth_path函数进行平滑。最后,我们输出平滑后的路径。
.
-------------->控制
.
-------------->优化理论相关
滤波器(用不多)
巴特沃斯滤波器、切比雪夫滤波器、贝塞尔滤波器均包括模拟滤波器和数字滤波器两种形式。
一阶低通滤波器
一阶低通滤波器主要用于允许低频信号通过,同时减少或阻止高频信号的传递。
一阶低通滤波器的工作原理是基于一个简单的算法公式Y(n) = αX(n) + (1 - α)Y(n - 1),其中α是滤波系数,X(n)是当前采样值,Y(n - 1)是上一次滤波的输出值,Y(n)是当前滤波输出值。该公式表明当前的输出值是当前输入值和前一次输出值的加权平均。
在实际应用中,截止频率的选择非常关键,因为它决定了哪些频率的信号能够通过滤波器。截止频率过低可能导致有用信号被削减,而截止频率过高则可能无法充分滤除噪声。因此,选择适当的截止频率对于确保滤波效果至关重要。
总的来说,一阶低通滤波器因其简单性和有效性在各种信号处理场合中得到了广泛应用。
以下是一个简单的C++代码实现,用于计算一阶低通滤波器的输出值:
一阶低通滤波器的C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>// 计算一阶低通滤波器的输出值
double lowPassFilter(double alpha, double xn, double yn_minus_1) {double yn = alpha * xn + (1 - alpha) * yn_minus_1;return yn;
}int main() {double alpha, xn, yn_minus_1;std::cout << "请输入滤波系数alpha、当前采样值xn和上一次滤波的输出值yn_minus_1:" << std::endl;std::cin >> alpha >> xn >> yn_minus_1;double result = lowPassFilter(alpha, xn, yn_minus_1);std::cout << "一阶低通滤波器的输出值为:" << result << std::endl;return 0;
}
这个程序首先定义了一个名为lowPassFilter的函数,该函数接受三个参数:滤波系数alpha、当前采样值xn和上一次滤波的输出值yn_minus_1。然后,它使用上述公式计算一阶低通滤波器的输出值。最后,在main函数中,程序提示用户输入滤波系数、当前采样值和上一次滤波的输出值,并调用lowPassFilter函数来计算结果。最后,程序输出一阶低通滤波器的输出值。
巴特沃斯滤波器
巴特沃斯滤波器通带最平坦,阻带下降慢。
巴特沃斯滤波器的原理基于所谓的“最大平坦”特性,即在通带内提供尽可能平坦的频率响应,而在阻带内则逐步衰减到零。
以下是关于巴特沃斯滤波器的详细介绍:
- 基本概念:巴特沃斯滤波器的设计旨在没有纹波的情况下提供一个尽可能平坦的通带响应。这种滤波器不会在通带和阻带之间出现剧烈的变化。
- 数学公式:巴特沃斯低通滤波器的传递函数通常表示为(D(u,v) = frac{1}{1 + [(u - u_0)/f]^{2N}}),其中(D(u,v))是频域中点( (u,v) )到中心点的距离,(N)是滤波器的阶数,(f)是截止频率。
- 振幅与阶数的关系:巴特沃斯滤波器的振幅随着角频率的增加而逐步减少,趋向负无穷大。每增加一阶,滤波器的衰减率就会增加6分贝。
总的来说,巴特沃斯滤波器以其在通带内的平坦响应和阻带内逐渐下降至零的特性,在信号处理中有着广泛的应用。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/580306412
https://blog.csdn.net/wanrenqi/article/details/124717517
https://blog.csdn.net/dieju8330/article/details/103003778
https://blog.csdn.net/zhaitianbao/article/details/116518632
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/580458091
巴特沃斯滤波器C++代码实现
以下是一个简单的C++代码实现,用于计算巴特沃斯滤波器的传递函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>// 计算阶数为n的巴特沃斯滤波器的传递函数
double butterworth(int n, double f) {double sum = 0.0;for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {sum += pow(-1, k - 1) * pow(f, 2 * k - 1) / (2 * k - 1);}return 1 / (1 + 2 * sum);
}int main() {int n;double f;std::cout << "请输入阶数n和截止频率f:" << std::endl;std::cin >> n >> f;double result = butterworth(n, f);std::cout << "巴特沃斯滤波器的传递函数为:" << result << std::endl;return 0;
}
这个程序首先定义了一个名为butterworth的函数,该函数接受两个参数:阶数n和截止频率f。然后,它使用一个循环来计算巴特沃斯滤波器的传递函数。最后,在main函数中,程序提示用户输入阶数和截止频率,并调用butterworth函数来计算结果。最后,程序输出巴特沃斯滤波器的传递函数。
class bwf {public:bwf(double cutOff) {cut_off_ = cutOff * 2 * M_PI;T_sample_ = kActionRunningPeriod;a_ = T_sample_ * cut_off_ / (T_sample_ * cut_off_ + 2);b_ = (T_sample_ * cut_off_ - 2) / (T_sample_ * cut_off_ + 2);prev_u_ = 0;prev_y_ = 0;}double filterUpdate(double &v) {double vk = a_ * (v + prev_u_) - b_ * (prev_y_);prev_u_ = v;prev_y_ = vk;return vk;}void reset() {prev_u_ = 0;prev_y_ = 0;}void setState(double last_input, double last_output) {prev_u_ = last_input;prev_y_ = last_output;}double cut_off_;double T_sample_;double a_;double b_;double prev_u_;double prev_y_;
};bwf speed_up_filter(0.3);
bwf speed_down_filter(1.0);void smoothVelocityCmd(double &velocity_cmd, double &angular_cmd) {double filtered_velocity = 0.0;double current_velocity = 0.0, current_angular = 0.0;double unfiltered_vel_cmd = velocity_cmd;getRobotVW(current_velocity, current_angular);if (unfiltered_vel_cmd * current_velocity >= 0 &&fabs(unfiltered_vel_cmd) > fabs(current_velocity)) {filtered_velocity = speed_up_filter.filterUpdate(unfiltered_vel_cmd);speed_down_filter.setState(unfiltered_vel_cmd, filtered_velocity);} else {filtered_velocity = speed_down_filter.filterUpdate(unfiltered_vel_cmd);speed_up_filter.setState(unfiltered_vel_cmd, filtered_velocity);}velocity_cmd = filtered_velocity;if (fabs(unfiltered_vel_cmd) > 1e-3) {angular_cmd *= rangeLimited(fabs(filtered_velocity / unfiltered_vel_cmd), 0.0, 1.0);}unfiltered_velocity_cmd_ = unfiltered_vel_cmd;filtered_velocity_cmd_ = filtered_velocity;
}void resetVelocityCmdFilter() {speed_down_filter.reset();speed_up_filter.reset();unfiltered_velocity_cmd_ = 0;filtered_velocity_cmd_ = 0;
}贝赛尔(Bessel)滤波器
贝赛尔(Bessel)滤波器是具有最大平坦的群延迟(线性相位响应)的线性过滤器。贝赛尔滤波器常用在音频天桥系统中。模拟贝赛尔滤波器描绘为几乎横跨整个通频带的恒定的群延迟,因而在通频带上保持了被过滤的信号波形。贝塞尔(Bessel)滤波器具有最平坦的幅度和相位响应。带通(通常为用户关注区域)的相位响应近乎呈线性。Bessel滤波器可用于减少所有IIR滤波器固有的非线性相位失真。
贝赛尔(Bessel)滤波器C++代码实现
以下是一个简单的C++代码实现,用于计算贝塞尔滤波器的传递函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>// 计算阶数为n的贝塞尔滤波器的传递函数
double bessel(int n, double f) {double sum = 0.0;for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {sum += pow(-1, k - 1) * pow(f, 2 * k - 1) / (2 * k);}return sum;
}int main() {int n;double f;std::cout << "请输入阶数n和截止频率f:" << std::endl;std::cin >> n >> f;double result = bessel(n, f);std::cout << "贝塞尔滤波器的传递函数为:" << result << std::endl;return 0;
}
这个程序首先定义了一个名为bessel的函数,该函数接受两个参数:阶数n和截止频率f。然后,它使用一个循环来计算贝塞尔滤波器的传递函数。最后,在main函数中,程序提示用户输入阶数和截止频率,并调用bessel函数来计算结果。最后,程序输出贝塞尔滤波器的传递函数。
切比雪夫滤波器
切比雪夫滤波器通带等纹波,阻带下降较快。
切比雪夫滤波器是在通带或阻带上频率响应幅度等波纹波动的滤波器,振幅特性在通带内是等波纹。在阻带内是单调的称为切比雪夫I型滤波器;振幅特性在通带内是单调的,在阻带内是等波纹的称为切比雪夫II型滤波器。采用何种形式的切比雪夫滤波器取决于实际用途。
切比雪夫滤波器C++代码实现
以下是一个简单的C++代码实现,用于计算切比雪夫滤波器的传递函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>// 计算阶数为n的切比雪夫滤波器的传递函数
double chebyshev(int n, double f) {double sum = 0.0;for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {sum += pow(-1, k - 1) * pow(f, 2 * k - 1) / (2 * k - 1);}return 1 / (1 + 2 * sum);
}int main() {int n;double f;std::cout << "请输入阶数n和截止频率f:" << std::endl;std::cin >> n >> f;double result = chebyshev(n, f);std::cout << "切比雪夫滤波器的传递函数为:" << result << std::endl;return 0;
}
这个程序首先定义了一个名为chebyshev的函数,该函数接受两个参数:阶数n和截止频率f。然后,它使用一个循环来计算切比雪夫滤波器的传递函数。最后,在main函数中,程序提示用户输入阶数和截止频率,并调用chebyshev函数来计算结果。最后,程序输出切比雪夫滤波器的传递函数。
总结
【这个非常有用,记录抄袭到博客中】
https://blog.csdn.net/Ijerome/article/details/129203287
【巴特沃斯滤波器】(这三种都不常用)
一阶巴特沃斯滤波器,二阶巴特沃斯滤波器,高阶巴特沃斯滤波器就是一个低通滤波器
(巴特沃斯滤波器的设计步骤)
https://blog.csdn.net/dieju8330/article/details/103003778
https://blog.csdn.net/wanrenqi/article/details/124717517
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/580458091
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_50624597/article/details/124611767