1、进程的相关概念
1.1 程序与进程
程序是静态的概念,进程是程序的一次运行活动。
1.2 查看系统中有哪些进程
ps #只显示一小部分进程
ps -aux #会打印当前所有进程
ps -aux|grep init #使用grep筛选出只含有init的进程top #运行显示的进程有点类似windows的任务管理器1.3 进程标识符
每个进程都有一个非负整数表示的唯一ID, 叫做PID,类似身份证 。PID=0:称为交换进程(swapper),作用是进程调度 ,PID=1:init进程,作用是系统初始化。
在编程中可以调用getpid函数获取自身的进程标识符。使用getppid获取父进程的进程标识符。
1.4 父进程、子进程
进程A创建了进程B,那么A叫做父进程,B叫做子进程,父子进程是相对的概念,可以理解为人类中的父子关系。
1.5 C程序存储空间的分配
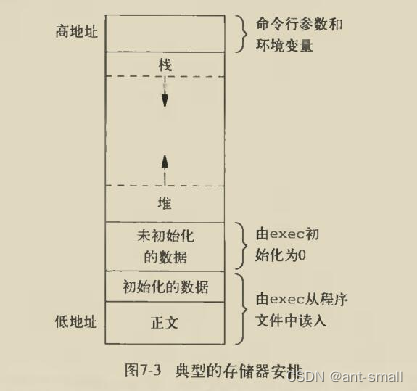
栈,自动变量以及每次函数调用时所需保存的信息都存放在此段中。
堆,通常在堆中进行动态存储分配。
2、进程的创建
//使用fork函数创建一个进程
#include <uinstd.h>
//函数原型pid_t fork(void);
fork();
//fork函数调用成功,返回两次
//返回值为0,代表当前进程是子进程
//返回值非负数,代表当前进程为父进程
//调用失败,返回-1//在使用folk函数创建进程之后的程序,父、子进程都会执行#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{pid_t pid;pid_t pid2;pid = getpid();printf("before fork: pid = %d\n", pid);//创建一个子进程fork();pid2 = getpid();printf("after fork: pid = %d\n", pid2);if(pid == getpid()){printf("this is father process\n");}else{printf("this is child process, child pid is %d\n", getpid());}printf("my pid is %d, current pro id is:%d\n", pid, getpid());return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{pid_t pid;printf("father : id = %d\n", getpid());//创建一个子进程pid = fork();pid2 = getpid();printf("after fork: pid = %d\n", pid2);if(pid > 0){printf("this is father process, pid = %d\n", getpid());}else if(pid == 0){printf("this is child process, child pid is %d\n", getpid());}printf("my pid is %d, current pro id is:%d\n", pid, getpid());return 0;
}使用folk函数创建子进程,子进程会获得父进程数据空间、堆和栈的副本。由于在fork之后经常跟随着exec,所以现在的很多实现并不执行一个父进程数据段、栈和堆的完全复制。作为替代,使用了写时复制(Copy-On-Write, COW)技术。这些区域由父、子进程共享,而且内核将它们的访问权限改变为只读的。如果父、子进程中的任一个试图修改这些区域,则内核只为修改区域的那块内存制作一个副本,通常是虚拟存储器系统中的一“页”。
2.1 使用folk创建一个子进程的一般目的
(1)一个父进程希望复制自己,使父、子进程同时执行不同的代码段。这在网络服务进程中是常见的——父进程等待客户端的服务请求。当这种请求到达时,父进程调用fork,使子进程处理此请求。父进程则继续等待下一个服务请求到达。
(2)一个进程要执行一个不同的程序。这对shell是常见的情况。在这种情况下,子进程从fork返回后立即调用exec。
2.2 vfolk和folk函数
vfolk直接使用父进程存储空间,不拷贝。
vfork保证子进程先运行,当子进程调用exit退出后,父进程才执行。
3、进程退出
进程的正常退出有以下几种:通过main函数调用return;进程调用标准c库的exit()函数进行退出; 进程通过调用_exit()或者_Exit()函数退出,属于系统调用;可以通过进程的最后一个线程返回;可以通过最后一个线程调用pthread_exit。
进程的异常退出:调用abort;当进程收到某些信号时,如ctrl+C;最后一个线程对取消(cancellation)请求做出响应。
3.1 父进程等待子进程退出
3.1.1 为什么要等待子进程退出
我们创建子进程的目的是为了让其完成某个任务,我们要知道这个子进程是否完成任务了。通过等待等待子进程退出,我们就可以知道这个子进程的任务完成状态,并且通过检查wait和waitpid所返回的终止状态的宏来收集子进程的退出状态,如果子进程的退出状态不被收集,那么这个进程就会编程僵尸进程。
//包含头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>//函数原型
//status参数: 是一个整型数指针//非空: 子进程退出状态放在它所指向的地址中。//空: 不关心退出状态pid_t wait(int *status);
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options);
int waitid(idtype_t idtype,id_t id, siginfo_t *infop, int options);//如果其所有子进程都还在运行,则阻塞。
//如果一个子进程已终止,正等待父进程获取其终止状态,则取得该子进程的终止状态立即返回。
//如果它没有任何子进程,则立即出错返回。//区别:wait使调用者阻塞, waitpid有一个选项options,可以使调用者不阻塞,但是不阻塞时,该子进程仍然会变成僵尸进程#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{pid_t pid;int cnt = 0;pid = fork();if(pid > 0){wait(NULL);while(1){printf("cnt = %d\n", cnt);printf("this is father print, pid = %d\n", getpid());sleep(1);}}else if(pid == 0){while(1){printf("this is child print, pid = %d\n", getpid());sleep(1);cnt++;if(cnt == 3){exit(0);}}}return 0;
}3.1.2 孤儿进程
父进程如果不等待子进程退出,在子进程之前就结束了自己的“生命”,此时子进程叫做孤儿进程。Linux避免系统存在过多孤儿进程,init进程收留孤儿进程,变成孤儿进程的新的父进程。
4、exec族函数
4.1.1 exec族函数
exec族函数的作用:当我们用fork函数创建新进程后,经常会在新进程中调用exec函数去执行另外一个程序。当进程调用exec函数时,该进程被完全替换为新程序。因为调用exec函数并不创建新进程,所以前后进程的ID并没有改变。
功能:在调用进程内部执行一个可执行文件。可执行文件既可以是二进制文件,也可以是任何Linux下可执行的脚本文件。
函数族:
exec函数族分别是:execl, execlp, execle, execv, execvp, execvpe
//包含头文件
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;//函数原型
//返回值://exec函数族的函数执行成功后不会返回,调用失败时,会设置errno并返回-1,然后从原程序的调用点接着往下执行。//可以通过perror("why");打印出错误原因
//参数说明://path:可执行文件的路径名字//arg:可执行程序所带的参数,第一个参数为可执行文件名字,没有带路径且arg必须以NULL结束//file:如果参数file中包含/,则就将其视为路径名,否则就按 PATH环境变量,在它所指定的各目录中搜寻可执行文件。原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u014530704/article/details/73848573
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg,..., char * const envp[]);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],char *const envp[]); exec族函数非常难以记忆,函数名中的字符会给我们一些帮助:
l : 使用参数列表
p:使用文件名,并从PATH环境进行寻找可执行文件
v:应先构造一个指向各参数的指针数组,然后将该数组的地址作为这些函数的参数。
e:多了envp[]数组,使用新的环境变量代替调用进程的环境变量
带l的一类exac函数(l表示list),包括execl、execlp、execle,要求将新程序的每个命令行参数都说明为 一个单独的参数。这种参数表以空指针结尾。
//文件execl.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);int main(void)
{printf("before execl\n");if(execl("./bin/echoarg","echoarg","abc",NULL) == -1){printf("execl failed!\n"); }printf("after execl\n");return 0;
}//文件echoarg.c
#include <stdio.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{int i = 0;for(i = 0; i < argc; i++){printf("argv[%d]: %s\n",i,argv[i]); }return 0;
}带p的一类exac函数,包括execlp、execvp、execvpe,如果参数file中包含/,则就将其视为路径名,否则就按 PATH环境变量,在它所指定的各目录中搜寻可执行文件。举个例子,PATH=/bin:/usr/bin
//文件execlp.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int main(void)
{printf("before execlp****\n");if(execlp("ps","ps","-l",NULL) == -1){printf("execlp failed!\n");}printf("after execlp*****\n");return 0;
}带v不带l的一类exac函数,包括execv、execvp、execve,应先构造一个指向各参数的指针数组,然后将该数组的地址作为这些函数的参数。如char *arg[]这种形式,且arg最后一个元素必须是NULL,例如char *arg[] = {“ls”,”-l”,NULL}。
//文件execvp.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);int main(void)
{printf("before execlp****\n");char *argv[] = {"ps","-l",NULL};if(execvp("ps",argv) == -1) {printf("execvp failed!\n"); }printf("after execlp*****\n");return 0;
}带e的一类exac函数,包括execle、execvpe,可以传递一个指向环境字符串指针数组的指针。 参数例如char *env_init[] = {“AA=aa”,”BB=bb”,NULL}; 带e表示该函数取envp[]数组,而不使用当前环境。
//文件execle.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int execle(const char *path, const char *arg,..., char * const envp[]);char *env_init[] = {"AA=aa","BB=bb",NULL};
int main(void)
{printf("before execle****\n");if(execle("./bin/echoenv","echoenv",NULL,env_init) == -1){printf("execle failed!\n");} printf("after execle*****\n");return 0;
}//文件echoenv.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
extern char** environ;
int main(int argc , char *argv[])
{int i;char **ptr;for(ptr = environ;*ptr != 0; ptr++)printf("%s\n",*ptr);return 0;
}4.1.2 exec配合fork使用
实现功能:当父进程检测到输入为1时,创建子进程将配置文件的字段值修改掉。
//文件demo_changeData.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{pid_t pid;int data = 10;while(1){print("please input a data\n");scanf("%d", &data);if(data == 1){pid = fork();//pid=0,代表此时是子进程的一个程序段if(pid == 0){int fdSrc;char *readBuf = NULL;fdSrc = open("config.txt", O_RDWR);int size = lseek(fdSrc, 0, SEEK_END);lseek(fdSrc, 0, SEEK_SET);readBuf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * size + 8);int n_read = read(fdSrc, readBuf, size);char *p =strstr(readBuf, "LENG=");if(p == NULL){printf("not fount");exit(-1);}p = p + strlen("LENG=");*p = '5';lseek(fdSrc, 0, SEEK_SET);int n_write = write(fdSrc, readBuf, strlen(readBuf));close(fdSrc);exit(0);}}}}else{printf("wait, do nothing\n");}return 0;
}//文件demo_exec_fork.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{pid_t pid;int data = 10;while(1){print("please input a data\n");scanf("%d", &data);if(data == 1){pid = fork();//pid=0,代表此时是子进程的一个程序段if(pid == 0){//调用demo_changeData文件执行execl("./demo_changeData", "demo_changeData", "config.txt", NULL);}}}else{printf("wait, do nothing\n");}return 0;
}5、system函数
system函数就是系统封装好的exec和fork结合的函数。
#include <stdlib.h>//函数原型
//返回值://如果 system()调用成功则最后会返回执行shell命令后的返回值;//在调用/bin/sh时失败则返回127;//其他失败原因返回-1;//若参数string为空指针(NULL),则返回非零值。
//注意:在编写具有SUID/SGID权限的程序时请勿使用system(),system()会继承环境变量,通过环境变量可能会造成系统安全的问题。int system(const char *command);//源码
int system(const char * cmdstring)
{pid_t pid;int status;if(cmdstring == NULL){return (1);}if((pid = fork())<0){status = -1;}else if(pid == 0){execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", cmdstring, (char *)0);-exit(127); //子进程正常执行则不会执行此语句}else{while(waitpid(pid, &status, 0) < 0){if(errno != EINTER){status = -1;break;}}}return status;
}6、popen函数
#include <stdio.h>//函数原型
FILE *popen(const char *conmand,const char *type);
int pclose(FILE *stream);
与system函数相比,popen在应用中的好处在于可以获得函数运行的输出结果。
举例,使用popen获取ps指令的运行结果。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(void)
{char ret[1024] = {0};FILE *fp;fp = popen("ps", "r");int n_read = fread(ret, 1, 1024, fp);printf("read ret %d bytes, ret = %s\n", n_read, ret);return 0;
}