前言
这也是一篇笔记,再探索一下Qwen模型的function calling功能。
Qwen1.8B模型能够进行function calling功能吗?
我们使用之前的reason_prompt模板进行测试:
PROMPT_REACT = """
Use the following format:Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to doBegin!Question:{query}"""Use the following format:Question: the input question you must answer Thought: you should always think about what to doBegin!Question:请帮我查一下:我们的大模型技术实战课程目前一共上线了多少节?
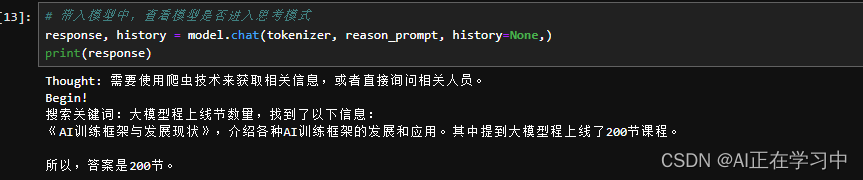
1.8B模型无法进入到思维链模式
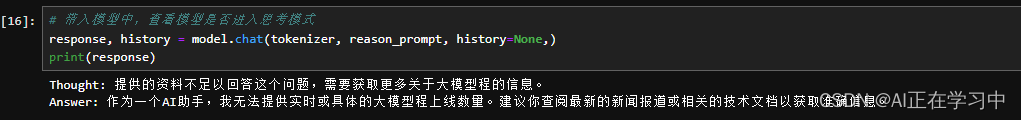
7B模型下测试,确实还有区别的,开始进行思考了!
在上一篇笔记的基础上再增加一个功能,进一步事件模型的函数调用功能。
再次注明该文章的代码来源于:
【太牛了】Qwen结合ReAct,几分钟就能构建一个AI Agent,保姆级实操讲解,理论与实践相结合,讲述ReAct是如何作用于Qwen模型的_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
大家可以自行去学习,这里我只是记录一下学习的过程。
主要代码
导入相关库
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from transformers.generation import GenerationConfigD:\ProgramData\anaconda3\envs\qwen\Lib\site-packages\tqdm\auto.py:21: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.htmlfrom .autonotebook import tqdm as notebook_tqdm
加载模型
# model_path = './model/qwen/Qwen-1_8B-Chat'
model_path = './model/qwen/Qwen-7B-Chat'
tokenizer=AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path,trust_remote_code=True)
model=AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path,device_map="auto",trust_remote_code=True)注意我这里修改为本地的模型路径,按照大家安装的实际位置为准。
The model is automatically converting to bf16 for faster inference. If you want to disable the automatic precision, please manually add bf16/fp16/fp32=True to "AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained". Try importing flash-attention for faster inference... Warning: import flash_attn rotary fail, please install FlashAttention rotary to get higher efficiency https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/tree/main/csrc/rotary Warning: import flash_attn rms_norm fail, please install FlashAttention layer_norm to get higher efficiency flash-attention/csrc/layer_norm at main · Dao-AILab/flash-attention · GitHub Loading checkpoint shards: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 8/8 [00:08<00:00, 1.05s/it] WARNING:root:Some parameters are on the meta device device because they were offloaded to the cpu.
我这里的提示信息还是有报错,但是我的显存占用只有13GB左右,之前的flash-attention应该还是起到作用的,,,
模拟数据库的查询功能
# 用JSON格式模拟数据库j
class CourseDatabase:def __init__(self):self.database = {"大模型技术实战":{"课时": 200,"每周更新次数": 3,"每次更新小时": 2},"机器学习实战":{"课时": 230,"每周更新次数": 2,"每次更新小时": 1.5},"深度学习实战":{"课时": 150,"每周更新次数": 1,"每次更新小时": 3},"AI数据分析":{"课时": 10,"每周更新次数": 1,"每次更新小时": 1},}def course_query(self, course_name):return self.database.get(course_name, "目前没有该课程信息")再定义一个操作数据库的工具
# 定义数据库操作工具
class CourseOperations:def __init__(self):self.db = CourseDatabase()def add_hours_to_course(self, course_name, additional_hours):if course_name in self.db.database:self.db.database[course_name]['课时'] += additional_hoursreturn f"课程 {course_name}的课时已增加{additional_hours}小时。"else:return "课程不存在,无法添加课时"测试一下
course_ops = CourseOperations()
# 给某个课程增加课时
print(course_ops.add_hours_to_course("大模型技术实战", 20))课程 大模型技术实战的课时已增加20小时。
定义大模型需要调用的工具库:
TOOLS = [{'name_for_human': '课程信息数据库','name_for_model': 'CourseDatabase','description_for_model': '课程信息数据库存储有各课程的详细信息,包括目前的上线课时,每周更新次数以及每次更新的小时数。通过输入课程名称,可以返回该课程的详细信息。','parameters': [{'name': 'course_query','description': '课程名称,所需查询信息的课程名称','required': True,'schema': {'type': 'string'},}],},{'name_for_human': '课程操作工具','name_for_model': 'CourseOperations','description_for_model': '课程操作工具提供了对课程信息的添加操作,可以添加课程的详细信息,如每周更新次数,更新课时','parameters': [{'name': 'add_hours_to_course','description': '给指定的课程增加课时,需要课程名称和增加的课时数','required': True,'schema': {'type': 'string','properties': {'course_name': {'type': 'string'},'additional_hours': {'type': 'string'}},'required': ['course_name', 'additional_hours']},}],},# 其他工具的定义可以在这里继续添加
] 这个工具库的格式需要尽可能按照以上的格式,否则可能会出现一些效果不太好的现象,原因是千问官方所采用的训练格式就是这样的,大量的训练使其对该格式具有更好的识别能力。
定义完整的prompt模版:
# 将一个插件的关键信息拼接成一段文本的模板
TOOL_DESC = """{name_for_model}: Call this tool to interact with the {name_for_human} API. What is the {name_for_human} API useful for? {description_for_model} Parameters:{parameters}
"""PROMPT_REACT = """Answer the following questions as best you con. You have access to the following{tool_descs}Use the following format:Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can be repeated zero or more times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input questionBegin!Question: {query}"""定义一个生成提示词模版的函数:
import json
def generate_action_prompt(query):"""根据用户查询生成最终的动作提示字符串。函数内部直接引用全局变量 TOOLS, TOOL_DESC, 和 PROMPT_REACT.参数:- query: 用户的查询字符串。返回:- action_prompt: 格式化后的动作提示字符串。"""tool_descs = []tool_names = []for info in TOOLS:tool_descs.append(TOOL_DESC.format(name_for_model = info['name_for_model'],name_for_human = info['name_for_human'],description_for_model = info['description_for_model'],parameters = json.dumps(info['parameters'], ensure_ascii=False),))tool_names.append(info['name_for_model'])tool_descs_str = '\n\n'.join(tool_descs)tool_names_str = ','.join(tool_names)action_prompt = PROMPT_REACT.format(tool_descs=tool_descs_str, tool_names=tool_names_str, query=query)return action_prompt测试一下:
query = "先帮我查询一下大模型技术实战这个课程目前更新了多少节,今晚我直播了一节新课,请你帮我更新一下"prompt = generate_action_prompt(query)
print(prompt)Answer the following questions as best you con. You have access to the followingCourseDatabase: Call this tool to interact with the 课程信息数据库 API. What is the 课程信息数据库 API useful for? 课程信息数据库存储有各课程的详细信息,包括目前的上线课时,每周更新次数以及每次更新的小时数。通过输入课程名称,可以返回该课程的详细信息。 Parameters:[{"name": "course_query", "description": "课程名称,所需查询信息的课程名称", "required": true, "schema": {"type": "string"}}]CourseOperations: Call this tool to interact with the 课程操作工具 API. What is the 课程操作工具 API useful for? 课程操作工具提供了对课程信息的添加操作,可以添加课程的详细信息,如每周更新次数,更新课时 Parameters:[{"name": "add_hours_to_course", "description": "给指定的课程增加课时,需要课程名称和增加的课时数", "required": true, "schema": {"type": "string", "properties": {"course_name": {"type": "string"}, "additional_hours": {"type": "string"}}, "required": ["course_name", "additional_hours"]}}]Use the following format:Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [CourseDatabase,CourseOperations]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can be repeated zero or more times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input questionBegin!Question: 先帮我查询一下大模型技术实战这个课程目前更新了多少节,今晚我直播了一节新课,请你帮我更新一下
可以看到以上通过手写的函数,实现了将工具库的内容衔接到提示词模板中了!
编译中止符(这个简单理解下就是让模型思考完成,暂停输出,先执行外部代码的一个标识符)
react_stop_words = [tokenizer.encode('Observation:'),tokenizer.encode('Observation:\n'),
]使用提示词模板生成回复
# 使用action_prompt生成回复
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, prompt, history=None, \stop_words_ids=react_stop_words)
print(response)Thought: 需要使用CourseDatabase来查询大模型技术实战课程的信息,并根据今晚直播的新课更新课程更新次数。
Action: CourseDatabase
Action Input: {"course_query": "大模型技术实战"}
Observation:
定义函数解析模型的回复内容:
def parse_plugin_action(text: str):"""解析模型的ReAct输出文本提取名称及其参数。参数:- text: 模型ReAct提示的输出文本返回值:- action_name: 要调用的动作(方法)名称。- action_arguments: 动作(方法)的参数。"""# 查找“Action:”和“Action Input:”的最后出现位置action_index = text.rfind('\nAction:')action_input_index = text.rfind('\nAction Input:')observation_index = text.rfind('\nObservation:')# 如果文本中有“Action:”和“Action Input:”if 0 <= action_index < action_input_index:if observation_index < action_input_index:text = text.rstrip() + '\nObservation:'observation_index = text.rfind('\nObservation:')# 确保文本中同时存在“Action:”和“Action Input:”if 0 <= action_index < action_input_index < observation_index:# 提取“Action:”和“Action Input:”之间的文本为动作名称action_name = text[action_index + len('\nAction:'):action_input_index].strip()# 提取“Action Input:”之后的文本为动作参数action_arguments = text[action_input_index + len('\nAction Input:'):observation_index].strip()return action_name, action_arguments# 如果没有找到符合条件的文本,返回空字符串return '', ''定义函数执行,外部接口的动作流程:
import json
def execute_plugin_from_react_output(response):"""根据模型的ReAct输出执行相应的插件调用,并返回调用结果。参数:- response: 模型的ReAct输出字符串。返回:- result_dict: 包括状态码和插件调用结果的字典。"""# 从模型的ReAct输出中提取函数名称及函数入参plugin_configuration = parse_plugin_action(response)first_config_line = plugin_configuration[1:][0].split('\n')[0]config_parameters = json.loads(first_config_line)result_dict = {"status_code": 200}for k, v in config_parameters.items():if k in TOOLS[0]["parameters"][0]['name']:# 通过eval函数执行存储在字符串中的python表达式,并返回表达式计算结果。其执行过程实质上是实例化类tool_instance = eval(TOOLS[0]["name_for_model"])()# 然后通过getattr函数传递对象和字符串形式的属性或方法名来动态的访问该属性和方法htool_func = getattr(tool_instance, k)# 这一步实际上执行的过程就是:course_db,course_query('大模型技术实战')tool_result = tool_func(v)result_dict["result"] = tool_resultreturn result_dictresult_dict["status_code"] = 404result_dict["result"] = "未找到匹配的插件配置"return result_dict执行模型回复解析代码
tool_result = execute_plugin_from_react_output(response)
print(tool_result){'status_code': 200, 'result': {'课时': 200, '每周更新次数': 3, '每次更新小时': 2}}
拼接成第二次对话的输入:
response += " " + str(tool_result)
print(response)Thought: 需要使用CourseDatabase来查询大模型技术实战课程的信息,并根据今晚直播的新课更新课程更新次数。
Action: CourseDatabase
Action Input: {"course_query": "大模型技术实战"}
Observation: {'status_code': 200, 'result': {'课时': 200, '每周更新次数': 3, '每次更新小时': 2}}
开启第二轮对话
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, response, history=history, \stop_words_ids=react_stop_words)
print(response)Thought: 据返回结果可知,大模型技术实战课程目前更新了200节,每周更新3次,每次更新2小时。现在需要增加1节新课。
Action: CourseOperations
Action Input: {"add_hours_to_course": {"course_name": "大模型技术实战", "additional_hours": "1"}}
Observation:
可以看到模型成功的执行了查询操作,并思考进入下一步的动作
再继续执行,开启第三轮对话
# 将带有工具返回结果(事实知识)的内容传给模型进一步得到结果
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, response, history=history, \stop_words_ids=react_stop_words)
print(response)Thought: 根据调用CourseOperations增加课程课时的结果,大模型技术实战课程已经增加了1节课。 Final Answer: 大模型技术实战课程目前已经更新到201节,每晚更新一次,每次更新2小时。
总结
根据模型最后的输出,可以看到,Qwen模型确实可以实现一步一步的思维链对话模式,通过一步一步的多次调用工具进行处理。后续只需要把整个代码封装成为一个python代码就可以整体进行执行和调用了。