网络编程
软件结构
- C/S结构:QQ、迅雷、百度网盘
- 程序员:开发客户端和服务端程序
- 用户:需要下载升级更新客户端
- 对网络带宽要求相对较低
- 数据安全性相对较高
- B/S结构:IE、谷歌、火狐
- 程序员:只需要开发服务端程序
- 用户:用户无需下载客户端
- 对网络带宽要求相对较高,不适合游戏软件
- 数据安全性相对较高
网络通信协议
通信协议指计算机相互沟通时发送数据的规则。这些规则规定了发送数据的格式、传递的速度、传输的步骤。
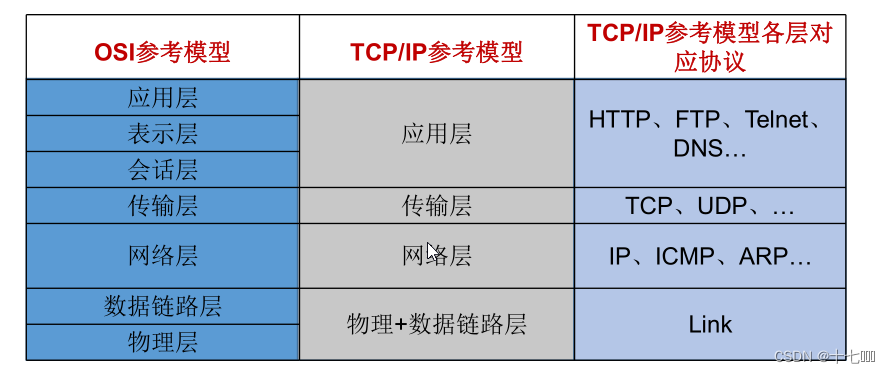
- TCP/IP协议(实际模型)
- 应用层:HTTP
- 传输层: TCP/UDP
- 网络层: IP、ICMP、ARP
- 物理+数据链路层:Link
TCP和UDP的区别
TCP和UDP是传输层的协议,其中TCP是面向连接的协议,UDP是不面向连接的协议。
- UDP 不用建立连接即可发送
- 比如发短信
- 传输的数据量有限
- 数据不可靠
- TCP 建立连接后才能发送
- 比如打电话
- 理论上数据量无限制
- 效率相对较低
- 数据可靠
网络编程三要素
- 协议
- IP地址:电脑的编号,唯一标识。
- ipv4和ipv6
- 常用命令:
- ipconfig / all
- ping 网址
- 因特网和局域网
- 子网掩码:划分网络地址和主机地址
- DHCP服务器:自动分配IP地址
- DNS服务器:域名解析服务器
- 端口:计算机进程的唯一标识
- Tomcat 8080
- MySQL 3306
- Oracle 1521
IP + 端口 = 网络中运行进程的唯一标识
TCP协议模拟实现
这里是使用TCP协议来实现一个从客户端发送数据到服务器端的代码。
客户端:
public class TcpClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建客户端Socket对象Socket socket = new Socket("192.168.16.76",12306);//插座//通过socket获取输出流OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//创建文件对象File file = new File("test/server.txt");String filename = file.getName();//创建数据流上传文件名DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);dos.writeUTF(filename);//创建高效流读取文件数据BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));//循环读写数据byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len;while((len = bis.read(bytes))!=-1){bos.write(bytes,0,len);}bos.close();bis.close();os.close();socket.close();}
}
服务器端
接收线程类:
public class TcpServerThread extends Thread{private Socket socket;public TcpServerThread(Socket socket) {this.socket = socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {//3.获取输入流InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test/server.txt"));//获取客户端的IP地址InetAddress inetAddress = socket.getInetAddress();String hostAddress = inetAddress.getHostAddress();System.out.println("文件上传服务器启动");//System.out.println(hostAddress+"客户端正在上传文件");byte[] bys = new byte[1024];int len;while((len = bis.read(bys))!=-1){bos.write(bys,0,len);}System.out.println("文件上传成功");bos.close();bis.close();is.close();//serverSocket.close();} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
文件接收类:
public class UploadServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(12380);System.out.println("文件上传服务器启动");while(true){Socket clientSocket = ss.accept();new TcpServerThread(clientSocket).start();}}
}
UDP模拟实现
发送端:
public class UDP_send {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();byte[] bytes = "hello, udp".getBytes();int len = bytes.length;InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getByName("10.10.0.28");//192.168.16.76//创建数据包DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, len, ip, 10086);ds.send(dp);ds.close();}
}
接收端:
public class UDP_receive {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086);//创建一个空的包裹byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length);//接收数据到包裹ds.receive(dp);//解析包裹byte[] data = dp.getData();int length = dp.getLength();String s = new String(data, 0, length);System.out.println("s = " + s);InetAddress address = dp.getAddress();System.out.println("address = " + address);String hostAddress = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();System.out.println("hostAddress = " + hostAddress);}
}