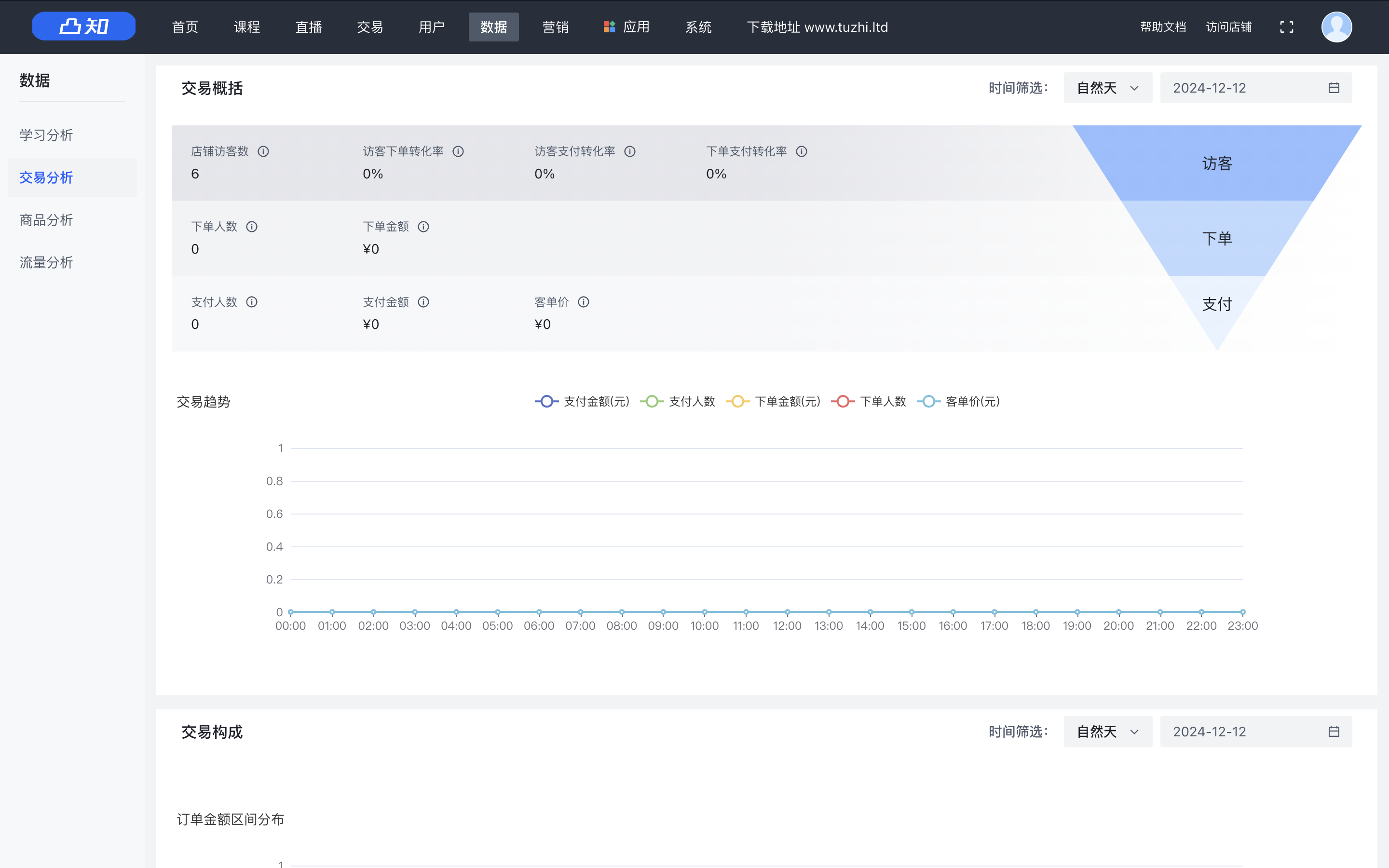
Sum of Max Matching:简单贪心,但我场上没切,唐完了。
思路
显然,对于最大边权最小问题,首先想到最小瓶颈路的 trick:按边的大小排序,对原图进行加边。
同时可以发现,这个匹配有个很好的性质:某个点要么在 \(A\) 中,要么在 \(b\) 中,要么都不在。
我们把 \(A\) 中的点称作红点,把 \(B\) 中的点称作蓝点,显然一个点不可能既是红点也是蓝点。
那么我们考虑加边的合并操作,当两个连通块合并成一个连通块时,这两个连通块内部本质是缩成了一个点的,因此里面的蓝点和红点拿哪个来匹配本质上是一样的,同时因为边权从小到大枚举,一个连通块内只可能有同色点。
接下来就很好做了,合并的时候取两个连通块异色点的最大值,然后根据贪心,我们尽可能地多匹配就好了。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define lc (p<<1)
#define rc ((p<<1)|1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
int n,m,k,tot[200005][2],f[200005];
ll ans=0,noww;
struct edge{int u,v,w;
}e[200005];
bool cmp(edge a,edge b)
{return a.w<b.w;
}
void init()
{for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)f[i]=i,tot[i][0]=tot[i][1]=0;
}
int findf(int x)
{if(f[x]!=x)f[x]=findf(f[x]);return f[x];
}
void combine(int x,int y)
{int fx=findf(x),fy=findf(y);if(fx!=fy){if(tot[fx][0]>0){ll ad=min(tot[fx][0],tot[fy][1]);tot[fx][0]-=ad;tot[fy][1]-=ad;ans=ans+ad*noww;}else{ll ad=min(tot[fx][1],tot[fy][0]);tot[fx][1]-=ad;tot[fy][0]-=ad;ans=ans+ad*noww; }f[fx]=fy;tot[fy][0]+=tot[fx][0];tot[fy][1]+=tot[fx][1];}
}
int main()
{//freopen("sample.in","r",stdin);//freopen("sample.out","w",stdout);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cin>>n>>m>>k;init();for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){cin>>e[i].u>>e[i].v>>e[i].w;}for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){int x;cin>>x;tot[x][0]++;}for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){int x;cin>>x;tot[x][1]++;} sort(e+1,e+m+1,cmp);for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){noww=e[i].w;combine(e[i].u,e[i].v);}cout<<ans;return 0;
}