文章目录
- 1. std::initializer_list
- 2. decltype
- 3. 左值引用和右值引用
- 4. 完美转发(模板中的&&万能引用)
- 5. 类的新功能
- 6. 可变参数模板
- 7. lambda表达式
- 8. 包装器
1. std::initializer_list
- 内置类型
int main()
{/* 内置类型 */int x1 = 1;int x2 = { 2 };int x3{ 3 };int y1 = 1;int y2(2);printf("x1:%d, x2:%d, x3:%d, y1:%d, y2:%d\n", x1, x2, x3, y1, y2);//输出结果:x1:1, x2:2, x3:3, y1:1, y2:2return 0;
}

- 自定义类型
struct Student
{int _age;string _name;Student(const int& age, const char* name):_age(age), _name(name){cout << "Student(const int& age, const char* name)" << endl;}};int main()
{Student s1(18, "张三");Student s2{ 20, "李四" };//输出结果://Student(const int& age, const char* name)//Student(const int& age, const char* name)return 0;
}
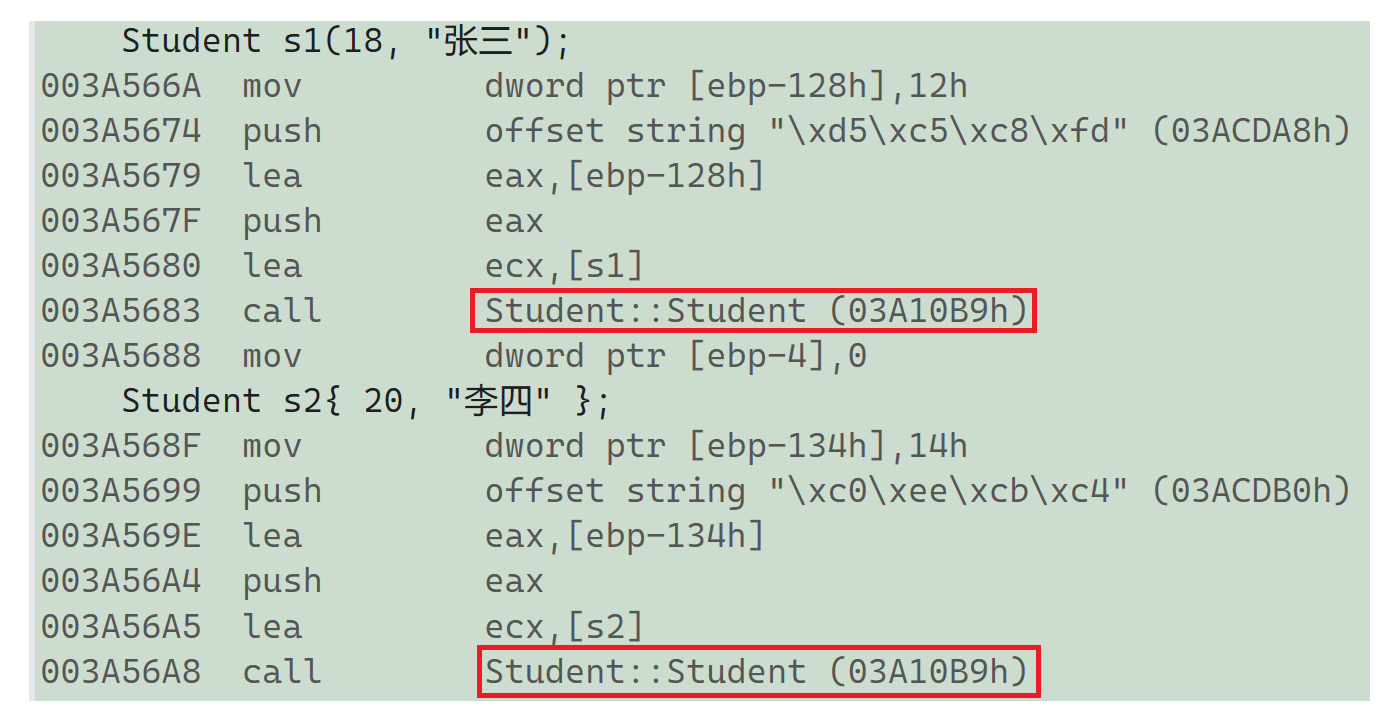
上述例子反汇编可以看出来{}初始化和()初始化一样调用的是构造函数
- 数组和vector{}初始化
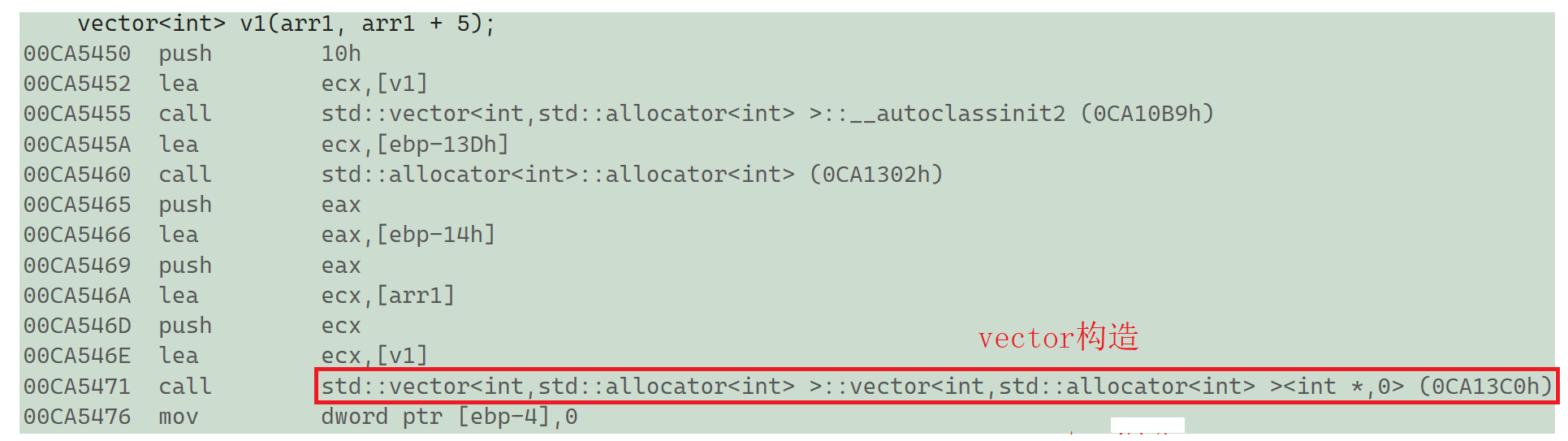
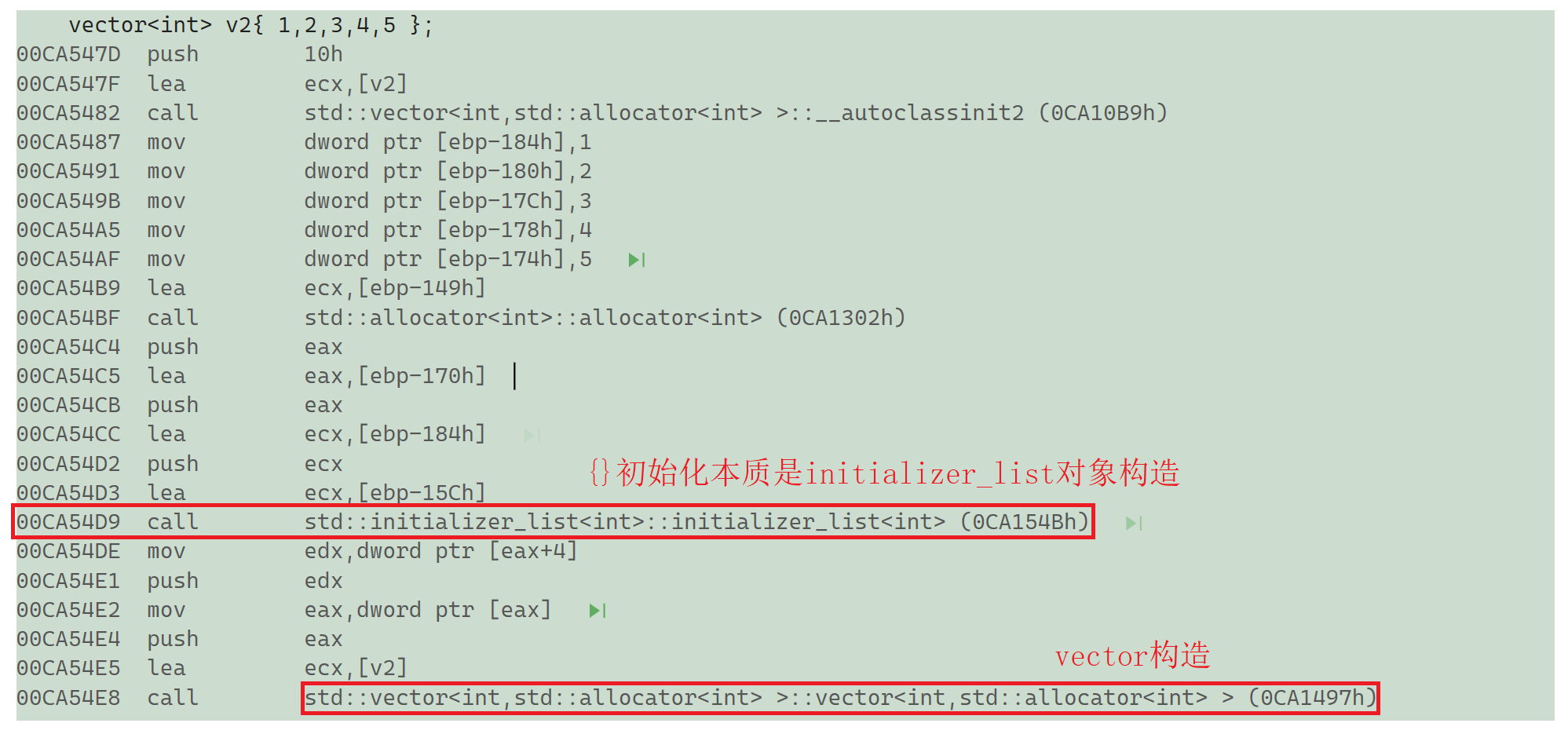
int main()
{int arr1[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };int arr2[]{ 1,2,3,4,5 };vector<int> v1(arr1, arr1 + 5); //简便初始化vector<int> v2{ 1,2,3,4,5 };return 0;
}
- arr1和arr2

- v1
- v2

- list{}初始化和map初始化
int main()
{list<int> l1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };map<string, string> dict = { {"string", "字符串"}, {"sort", "排序"}, {"other", "其他的"} };return 0;
}//同样都会调用initializer_list对象构造
- initializer_list
int main()
{auto f = { 1,2,3,4,5 };cout << typeid(f).name() << endl; //class std::initializer_list<int>initializer_list<int> il = { 1,2,3,4,5 };return 0;
}
2. decltype
关键字decltype将变量的类型声明为表达式指定的类型
struct Object
{string _property = "struct Object";size_t _size = 1;Object(){}
};int main()
{Object ob1;//要求:ob2必须和ob1一个类型decltype(ob1) ob2;cout << typeid(ob2).name() << endl;return 0;
}
3. 左值引用和右值引用
什么是左值?什么是左值引用?什么是右值?什么是右值引用?
左值:数据表达式(变量名或者解引用的指针),可以取地址的值是左值
左值引用:给左值取别名
右值:数据表达式(常量,临时变量,临时对象),不可以取地址的值是右值
右值引用:给右值取别名
struct Object
{static size_t _size;Object(){}
};
size_t Object::_size = 1;
int main()
{// *p,b,c,o都是左值int* p = new int[5];int b = 1;const int c = 1;Object o;cout << o._size << endl;// rp,rb,rc,ro都是左值引用,这里左值引用给左值取别名int*& rp = p;int& rb = b; const int& rc = c;Object& ro = o;int x = 1, y = 2; //左值// 右值1;x + y;// 右值引用int&& rs = x + y; //右值引用给右值取别名 const int& r = x + y; //左值引用给右值取别名//int&& rr = x; //(err)右值引用不能给左值取别名int&& rr = move(x); //右值引用可以给move后的左值取别名return 0;
}
const左值引用可以给右值取别名,那么右值引用有什么作用呢? 看使用场景:
场景一:(作用:参数更匹配)
void test(int& x)
{cout << "void test(int& x)" << endl;
}void test(int&& x)
{cout << "void test(int&& x)" << endl;
}int main()
{int a = 2, b = 4;test(a);test(a + b);return 0;
}
场景二:(移动构造)
移动构造本质是将参数右值的资源窃取过来,占位已有,那么就不用做深拷贝了,所以它叫做移动构造,就是窃取别人的资源来构造自身。
namespace MySTL
{class string{public:string(const char* str = ""): _size(strlen(str)), _capacity(_size){cout << "string(const char* str = "") -- 构造" << endl;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}// 拷贝构造string(const string& s):_str(nullptr){cout << "string(const string& s) -- 拷贝构造" << endl;string tmp(s._str); //构造swap(tmp); //将亡值tmp给到this掌管}string& operator=(const string& s){cout << "string& operator=(string s) -- 拷贝赋值" << endl;string tmp(s); //构造swap(tmp);return *this;}string(string&& s):_str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0){cout << "string(string&& s) -- 移动构造" << endl;swap(s);}string& operator=(string&& s){cout << "string& operator=(string&& s) -- 移动赋值" << endl;swap(s);return *this;}~string(){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}void reserve(size_t n){if (n > _capacity){char* tmp = new char[n + 1];strcpy(tmp, _str);delete[] _str;_str = tmp;_capacity = n;}}void push_back(char ch){if (_size >= _capacity){size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;reserve(newcapacity);}_str[_size] = ch;++_size;_str[_size] = '\0';}string& operator+=(char ch){push_back(ch);return *this;}string operator+(const char ch){string tmp(*this); //拷贝构造tmp += ch;return tmp;}private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity; // 不包含最后做标识的\0};
}int main()
{MySTL::string s("string"); //构造MySTL::string ret1 = s; //拷贝构造MySTL::string ret2 = (s + '?'); //移动构造return 0;
}
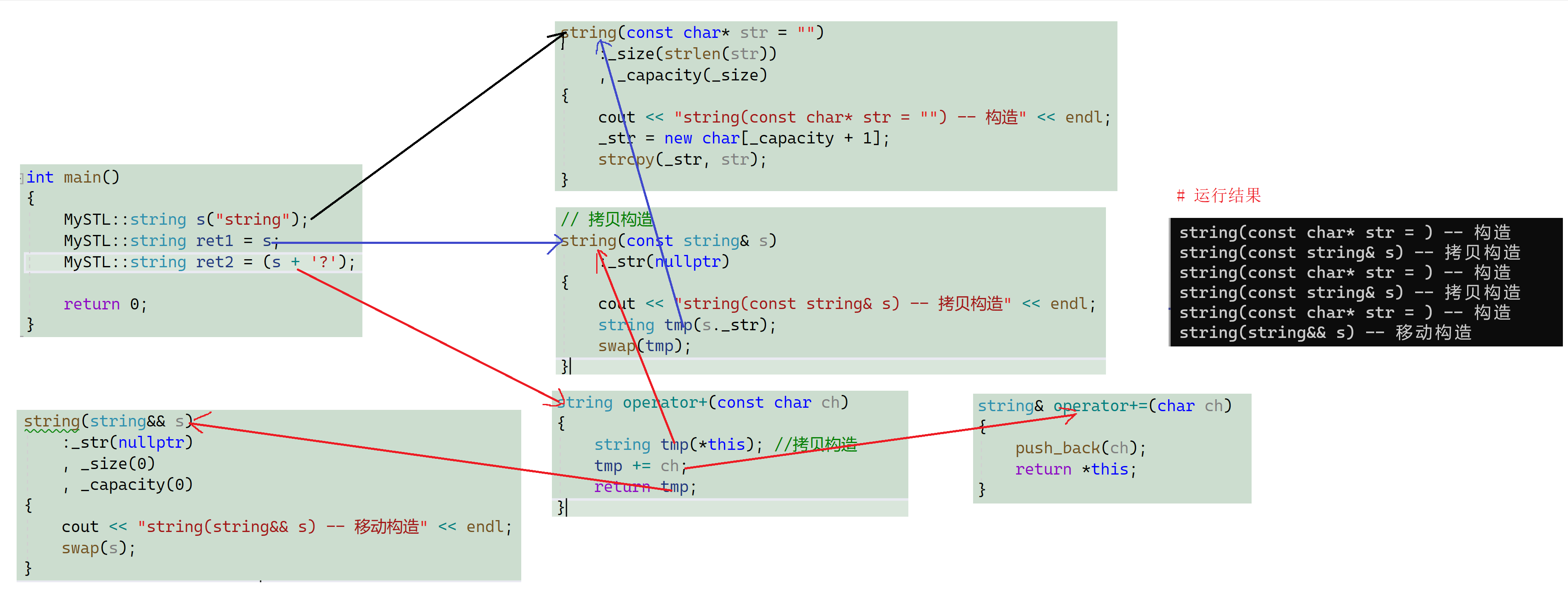

编译器默认临时对象作为函数返回值调用移动构造,ret2和tmp只是发生浅拷贝交换指针,并没有发生深拷贝,而是资源转移,提高了性能。如果这里没有写移动构造,那么会进行拷贝构造发生深拷贝
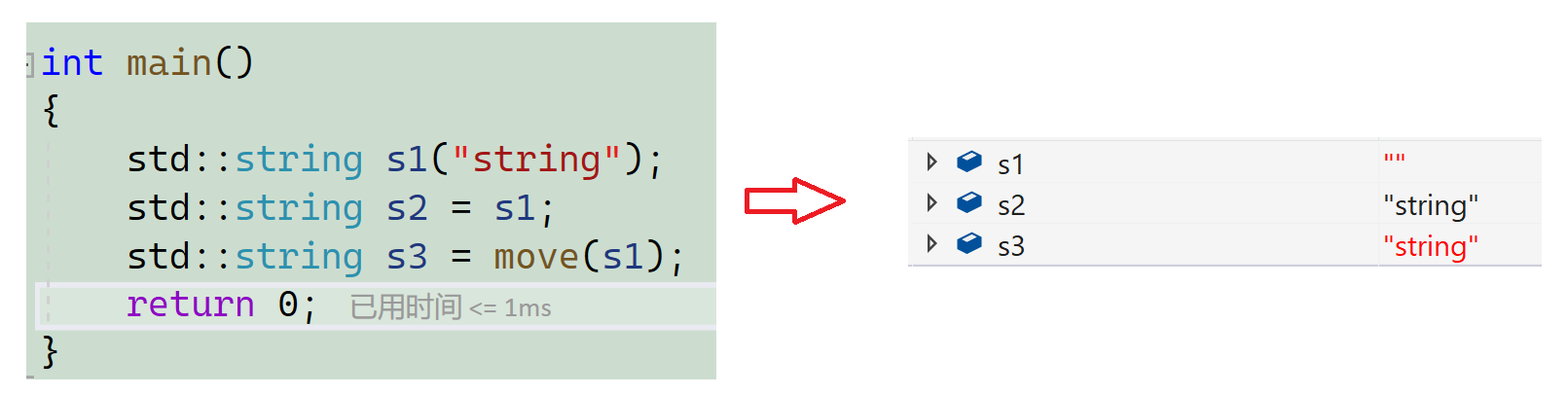
注意:不要轻易move左值(会导致资源转移)
库中使用场景:
namespace MySTL
{class string{public:string(const char* str = ""): _size(strlen(str)), _capacity(_size){cout << "string(const char* str = "") -- 普通构造" << endl;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}// 拷贝构造string(const string& s):_str(nullptr){cout << "string(const string& s) -- 拷贝构造" << endl;string tmp(s._str); //普通构造swap(tmp);}string(string&& s) //移动构造的作用就是浅拷贝将亡值:_str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0){cout << "string(string&& s) -- 移动构造" << endl;swap(s);}~string(){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity; // 不包含最后做标识的\0};
}int main()
{std::list<MySTL::string> list;MySTL::string s1("construct");list.push_back(s1); //调用void push_back(const value_type& val)list.push_back(MySTL::string("move construct")); //调用void push_back (value_type&& val);list.push_back("move construct"); //调用void push_back (value_type&& val);return 0;
}
//输出结果:
//string(const char* str = ) -- 普通构造
//string(const string& s) -- 拷贝构造
//string(const char* str = ) -- 普通构造
//string(const char* str = ) -- 普通构造
//string(string&& s) -- 移动构造
//string(const char* str = ) -- 普通构造
//string(string&& s) -- 移动构造
左值引用和右值引用优点:
都是提高效率,减少数据拷贝。左值引用一般用在函数参数和返回自身对象this,const左值引用会延长传参临时对象的生命周期,右值引用一般用在函数将亡对象返回。
4. 完美转发(模板中的&&万能引用)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;void Fun(int& x) { cout << "左值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(const int& x) { cout << "const 左值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(int&& x) { cout << "右值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(const int&& x) { cout << "const 右值引用" << endl; }
// 模板中的&&不代表右值引用,而是万能引用(引用折叠),其既能接收左值又能接收右值。
// 模板的万能引用只是提供了能够接收同时接收左值引用和右值引用的能力,
// 但是引用类型的唯一作用就是限制了接收的类型,后续使用中都退化成了左值,
// 我们希望能够在传递过程中保持它的左值或者右值的属性, 就需要用我们下面学习的完美转发
template<typename T>
void PerfectForward(T&& t)
{Fun(t);
}
int main()
{PerfectForward(10); int a;PerfectForward(a); //左值PerfectForward(std::move(a)); // 右值const int b = 8;PerfectForward(b); //const 左值PerfectForward(std::move(b)); // const 右值return 0;
}
//输出结果:
//左值引用
//左值引用
//左值引用
//const 左值引用
//const 左值引用
上面这里右值传递依然是左值引用,这是为什么呢?右值引用引用后的属性是左值。怎么来证明?
int main()
{int&& x = 10;cout << &x << endl; //能取地址的皆为左值,右值引用后会把对饮数据存放起来,x就是存放空间的标签,属性变为左值return 0;
}
这里如何解决上述中PerfectForward函数通过模板调用预期对应的函数呢?完美转发方法
函数:
template T&& forward (typename remove_reference::type&& arg) noexcept;
template T&& forward (typename remove_reference::type& arg) noexcept;
作用:如果arg不是左值引用,则返回对arg的右值引用。如果arg是一个左值引用,则该函数返回arg而不修改其类型。
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;void Fun(int& x) { cout << "左值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(const int& x) { cout << "const 左值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(int&& x) { cout << "右值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(const int&& x) { cout << "const 右值引用" << endl; }template<typename T>
void PerfectForward(T&& t)
{Fun(std::forward<T>(t));
}
int main()
{PerfectForward(10); int a;PerfectForward(a); //左值PerfectForward(std::move(a)); // 右值const int b = 8;PerfectForward(b); //const 左值PerfectForward(std::move(b)); // const 右值return 0;
}
//输出结果:
//右值引用
//左值引用
//右值引用
//const 左值引用
//const 右值引用
完美转发使用场景:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS true
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
namespace MySTL
{class string{public:string(const char* str = ""): _size(strlen(str)), _capacity(_size){cout << "string(const char* str = "") -- 普通构造" << endl;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}string(const string& s):_str(nullptr){cout << "string(const string& s) -- 拷贝构造" << endl;string tmp(s._str); swap(tmp);}string(string&& s) :_str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0){cout << "string(string&& s) -- 移动构造" << endl;swap(s);}string& operator=(const string& x){cout << "string& operator=(const string& x) - 拷贝赋值" << endl;string tmp(x);swap(tmp);return *this;}string& operator=(string&& x){cout << "string& operator=(string&& x) - 移动赋值 " << endl;swap(x);return *this;}~string(){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
}namespace MySTL
{template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode* _next = nullptr;ListNode* _prev = nullptr;T _data;};template<class T>class List{typedef ListNode<T> Node;public:List(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}void PushBack(const T& x){Insert(_head, x);}void PushBack(T&& x){//Insert(_head, x); //NO,右值引用引用后属性变为左值->调用void Insert(Node* pos, const T& x)Insert(_head, std::forward<T>(x)); //调用void Insert(Node* pos, T&& x)}void Insert(Node* pos, T&& x){Node* prev = pos->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node;//newnode->_data = x; //No:右值引用引用后属性变为左值(拷贝赋值)->调用void Insert(Node* pos, const T& x)newnode->_data = std::forward<T>(x); // 移动赋值->调用void Insert(Node* pos, T&& x)// prev newnode posprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = pos;pos->_prev = newnode;}void Insert(Node* pos, const T& x){Node* prev = pos->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node;newnode->_data = x; // 拷贝赋值// prev newnode posprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = pos;pos->_prev = newnode;}private:Node* _head;};
}int main()
{MySTL::List<MySTL::string> lt;lt.PushBack("1111");lt.PushBack(MySTL::string("33333"));MySTL::string s("hello world");lt.PushBack(s);return 0;
}
5. 类的新功能
移动构造
如果没有自己实现移动构造函数,且没有实现析构函数 、拷贝构造、拷贝赋值重载中的任意一个。那么编译器会自动生成一个默认移动构造。默认生成的移动构造函数,对于内置类型成员会执行逐成员按字节拷贝,自定义类型成员,则需要看这个成员是否实现移动构造,如果实现了就调用移动构造,没有实现就调用拷贝构造。
移动赋值
如果没有自己实现移动赋值重载函数,且没有实现析构函数 、拷贝构造、拷贝赋值重载中的任意一个,那么编译器会自动生成一个默认移动赋值。默认生成的移动构造函数,对于内置类型成员会执行逐成员按字节拷贝,自定义类型成员,则需要看这个成员是否实现移动赋值,如果实现了就调用移动赋值,没有实现就调用拷贝赋值。(默认移动赋值跟上面移动构造完全类似)
如果你提供了移动构造或者移动赋值,编译器不会自动提供拷贝构造和拷贝赋值。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS true
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
namespace MySTL
{class string{public:string(const char* str = ""): _size(strlen(str)), _capacity(_size){cout << "string(const char* str = "") -- 普通构造" << endl;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}string(const string& s):_str(nullptr){cout << "string(const string& s) -- 拷贝构造" << endl;string tmp(s._str); swap(tmp);}string(string&& s) :_str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0){cout << "string(string&& s) -- 移动构造" << endl;swap(s);}string& operator=(const string& x){cout << "string& operator=(const string& x) - 拷贝赋值" << endl;string tmp(x);swap(tmp);return *this;}string& operator=(string&& x){cout << "string& operator=(string&& x) - 移动赋值 " << endl;swap(x);return *this;}~string(){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
}
class Person
{
public:Person(const char* name = "", int age = 0):_name(name), _age(age){}
private:MySTL::string _name;int _age;
};
int main()
{Person s1("张三", 20);Person s2 = s1; //拷贝赋值Person s3 = std::move(s1); //移动构造Person s4;s4 = std::move(s2); //移动赋值return 0;
}
强制生成默认函数的关键字default
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS true
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace MySTL
{class string{public:string(const char* str = ""): _size(strlen(str)), _capacity(_size){cout << "string(const char* str = "") -- 普通构造" << endl;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}string(const string& s):_str(nullptr){cout << "string(const string& s) -- 拷贝构造" << endl;string tmp(s._str); swap(tmp);}string(string&& s) :_str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0){cout << "string(string&& s) -- 移动构造" << endl;swap(s);}string& operator=(const string& x){cout << "string& operator=(const string& x) - 拷贝赋值" << endl;string tmp(x);swap(tmp);return *this;}string& operator=(string&& x){cout << "string& operator=(string&& x) - 移动赋值 " << endl;swap(x);return *this;}~string(){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
}
class Person
{
public:Person(const char* name = "", int age = 0):_name(name), _age(age){}Person(const Person& p) //自己写了拷贝构造,则编译器不会自动生成移动构造和移动赋值:_name(p._name), _age(p._age){}Person(Person && p) = default; //强制让编译器生成移动构造
private:MySTL::string _name;int _age;
};
int main()
{Person s1;Person s2 = s1;Person s3 = std::move(s1);return 0;
}
禁止生成默认函数的关键字delete
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS true
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace MySTL
{class string{public:string(const char* str = ""): _size(strlen(str)), _capacity(_size){cout << "string(const char* str = "") -- 普通构造" << endl;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}string(const string& s):_str(nullptr){cout << "string(const string& s) -- 拷贝构造" << endl;string tmp(s._str); swap(tmp);}string(string&& s) :_str(nullptr), _size(0), _capacity(0){cout << "string(string&& s) -- 移动构造" << endl;swap(s);}string& operator=(const string& x){cout << "string& operator=(const string& x) - 拷贝赋值" << endl;string tmp(x);swap(tmp);return *this;}string& operator=(string&& x){cout << "string& operator=(string&& x) - 移动赋值 " << endl;swap(x);return *this;}~string(){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
}
class Person
{
public:Person(const char* name = "", int age = 0):_name(name), _age(age){}Person(const Person& p) = delete; //强制不让编译器自动生成拷贝构造(不期望被拷贝)
private:MySTL::string _name;int _age;
};
int main()
{Person s1;Person s2 = s1;Person s3 = std::move(s1);return 0;
}
6. 可变参数模板
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;// Args是一个模板参数包,args是一个函数形参参数包
// 声明一个参数包Args...args,这个参数包中可以包含0到任意个模板参数。
template <class ...Args>
void ShowList(Args... args)
{cout << sizeof...(args) << " "; //打印函数形参参数包个数
}
int main()
{ShowList();ShowList('x', 'y');ShowList('w', 1, 2);ShowList("string", 1, 2, 3);ShowList(3.14, std::vector<int>(5, 1), std::list<int>(5, 2));return 0;
}
如何解析可变参数包?(递归方式展开包)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
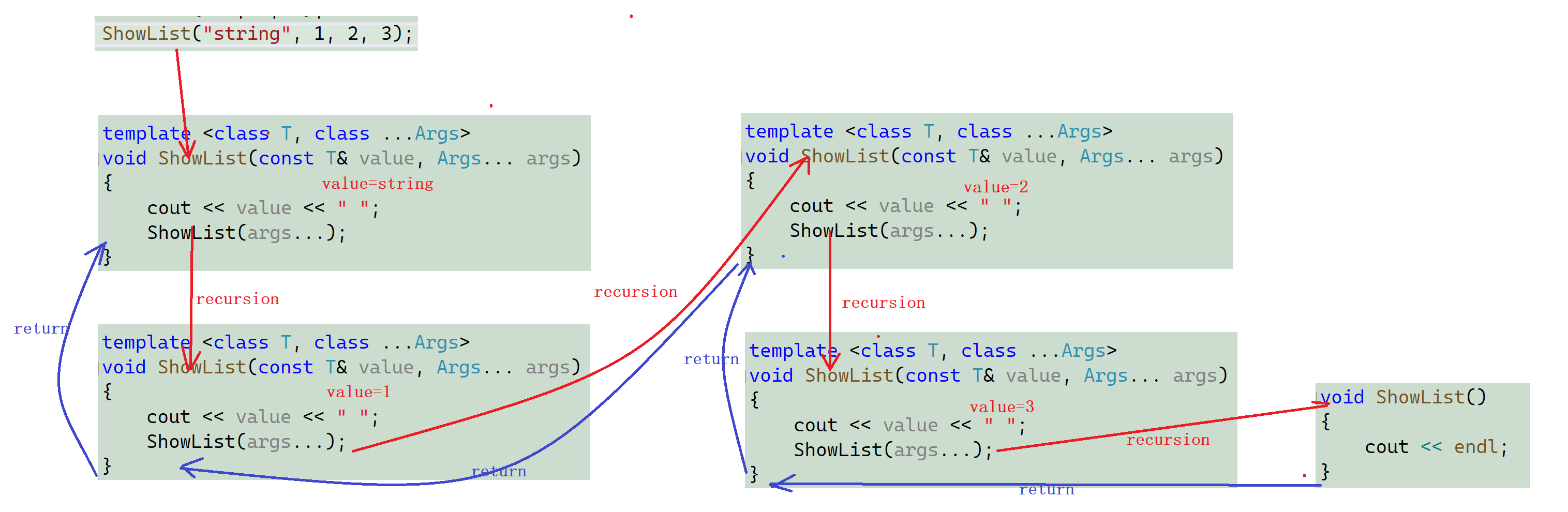
using namespace std;void ShowList()
{cout << endl;
}template <class T, class ...Args>
void ShowList(const T& value, Args... args)
{cout << value << " ";ShowList(args...);
}int main()
{ShowList(); //调用ShowList();ShowList('x', 'y'); //调用ShowList(const T& value, Args... args)ShowList('w', 1, 2);ShowList("string", 1, 2, 3);return 0;
}
画图理解参数包
逗号表达式展开参数包
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template <class T>
void PrintArg(T t)
{cout << t << " ";
}
//展开函数
template <class ...Args>
void ShowList(Args... args)
{//逗号表达式用来初始化arr数组中每个元素为0(先调用PrintArg函数打印参数包数据,然后逗号表达式最后总值为0并赋值给arr数组)int arr[] = { (PrintArg(args), 0)... }; cout << endl;
}
int main()
{ShowList(1);ShowList(1, 'A');ShowList(1, 'A', std::string("sort"));return 0;
}
类似于下面这种形式:
void ShowList(int a, int b, char c, std::string s)
{int arr[] = { PrintArg(a), PrintArg(b), PrintArg(c), PrintArg(s)};cout << endl;
}int main()
{ShowList(1, 2,'A', std::string("string"));return 0;
}
库中list:emplace_back使用场景
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;class Date
{friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Date& date);
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
public:Date(int year, int month, int day):_year(year),_month(month),_day(day){cout << "Date(int year, int month, int day) - 普通构造函数" << endl;}
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Date& date)
{cout << date._year << "/" << date._month << "/" << date._day << endl;return cout;
}int main()
{std::list<Date> list;list.emplace_back(2023, 3, 4); //可变模板推导调用构造函数std::list<Date>::const_iterator it = list.begin();while (it != list.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
7. lambda表达式
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Goods
{string _name;double _price; int _evaluate; // 评价Goods(const char* str, double price, int evaluate):_name(str), _price(price), _evaluate(evaluate){}
};
struct ComparePriceLess
{bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr){return gl._price < gr._price;}
};
struct ComparePriceGreater
{bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr){return gl._price > gr._price;}
};
int main()
{vector<Goods> v = { { "苹果", 2.1, 5 }, { "香蕉", 3, 4 }, { "橙子", 2.2, 3 }, { "菠萝", 1.5, 4 } };std::sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceLess()); //按照价格升序排序std::sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceGreater()); //按照价格降序排序
}
随着C++语法的发展,人们开始觉得上面的写法太复杂了,每次为了实现一个algorithm算法,都要重新去写一个类,如果每次比较的逻辑不一样,还要去实现多个类,特别是相同类的命名,这些都给编程者带来了极大的不便。因此,在C++11语法中出现了Lambda表达式。
lambda表达式语法
书写格式:[capture-list] (parameters) mutable -> return-type { statement}
1.[capture-list] : 捕捉列表,该列表总是出现在lambda函数的开始位置,编译器根据[]来判断接下来的代码是否为lambda函数,捕捉列表能够捕捉上下文中的变量供lambda函数使用。
2.(parameters):参数列表。与普通函数的参数列表一致,如果不需要参数传递,则可以连同()一起省略
3.mutable:默认情况下,lambda函数总是一个const函数,mutable可以取消其常量性。使用该修饰符时,参数列表不可省略(即使参数为空)。
4.->returntype:返回值类型。用追踪返回类型形式声明函数的返回值类型,没有返回值时此部分可省略。返回值类型明确情况下,也可省略,由编译器对返回类型进行推导。
5.{statement}:函数体。在该函数体内,除了可以使用其参数外,还可以使用所有捕获到的变量。
测试用例
int main()
{auto sum = [](int x, int y)->int {return x + y;};cout << [](int x, int y)->int {return x + y; }(1, 2) << endl;cout << sum(1, 2) << endl;return 0;
}
//不使用operator()而是使用lambda表达式
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Goods
{string _name;double _price; int _evaluate; // 评价Goods(const char* str, double price, int evaluate):_name(str), _price(price), _evaluate(evaluate){}
};int main()
{vector<Goods> v = { { "苹果", 2.1, 5 }, { "香蕉", 3, 4 }, { "橙子", 2.2, 3 }, { "菠萝", 1.5, 4 } };auto ComparePriceLess = [](const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2)->bool {return g1._price < g2._price; };sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceLess);sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2)->bool {return g1._price > g2._price; });return 0;
}
捕捉列表的关键
- [var]:表示值传递方式捕捉变量var
- [=]:表示值传递方式捕获所有父作用域中的变量(包括this)
- [&var]:表示引用传递捕捉变量var
- [&]:表示引用传递捕捉所有父作用域中的变量(包括this)
- [this]:表示值传递方式捕捉当前的this指针
- [&, var]、[var, &] : 混合捕捉
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Object
{
public:Object(const string& s):_message(s){}public:Object* get_this(){auto get_this = [this]()->Object* //获取当前类this指针{return this; };return get_this();}const string& get_message() const{return _message;}private:string _message;
};
int main()
{int x1 = 10, y1 = 20;//交换x和y的数据auto swap1 = [](int& rx, int& ry){int tmp = rx;rx = ry;ry = tmp;};swap1(x1, y1);cout << "x1:" << x1 << " y1:" << y1 << endl; //输出:x1:20 y1:10int x2 = 10, y2 = 20;auto swap2 = [x2, y2] () mutable //x2,y2传值捕捉:mutable取消lambda表达式常量性{int tmp = x2;x2 = y2;y2 = tmp;};swap2();cout << "x2:" << x2 << " y2:" << y2 << endl; //输出:x2:10 y2:20int x3 = 10, y3 = 20;//auto swap3 = [&x3, &y3]()auto swap3 = [&]() //x3,y3引用捕捉{int tmp = x3;x3 = y3;y3 = tmp;};swap3();cout << "x3:" << x3 << " y3:" << y3 << endl; //输出:x3:20 y3:10int x4 = 10, y4 = 20;auto swap4 = [&x4, y4]() mutable //混合捕捉{int tmp = x4;x4 = y4;y4 = tmp;};swap4();cout << "x4:" << x4 << " y4:" << y4 << endl; //输出:x4:20 y4:20int x5 = 10, y5 = 20, z5 = 30;auto print = [&, z5]() mutable //除了z5传值捕捉,其他全部采用传引用捕捉{x5 = 100;y5 = 200;z5 = 300;};print();cout << "x5:" << x5 << " y5:" << y5 << " z5:" << z5 << endl;//捕捉对象this指针cout << Object(string("Object")).get_this()->get_message() << endl;return 0;
}
捕捉列表注意事项
- 语法上捕捉列表可由多个捕捉项组成,并以逗号分割
- 捕捉列表不允许变量重复传递,否则就会导致编译错误
- 在块作用域以外的lambda函数捕捉列表必须为空
- lambda表达式之间不能相互赋值
lambda表达式原理
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Rate //利率
{
public:Rate(double rate) : _rate(rate){}double operator()(double money, int year){return money * _rate * year;}
private:double _rate;
};
int main()
{double rate = 0.49;Rate r1(rate);r1(10000, 2);auto r2 = [=](double monty, int year)->double {return monty * rate * year; };r2(10000, 2);return 0;
}
对应的汇编代码:
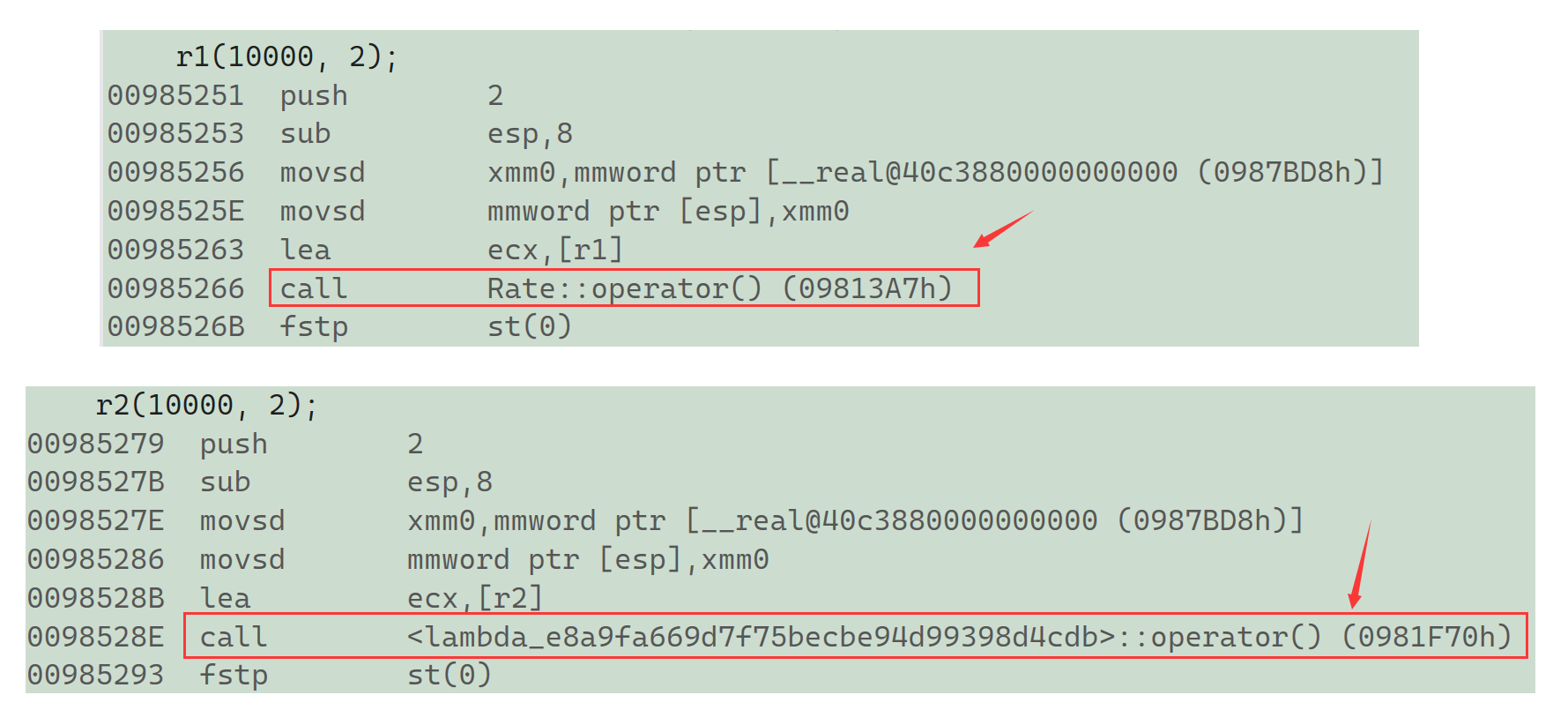
实际在底层编译器对于lambda表达式的处理方式,完全就是按照函数对象的方式处理的,即:如果定义了一个lambda表达式,编译器会自动生成一个类,在该类中重载了operator()。
8. 包装器
template <class Ret, class... Args> class function<Ret(Args...)>;
Ret: 返回值类型, Args:可变参数类型
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <map>
#include <string>int func(int a, int b)
{std::cout << "int func(int a, int b) : ";return a + b;
}class Function
{
public:int operator()(int a, int b){std::cout << "int operator()(int a, int b) : ";return a + b;}
};class Test
{
public:static int add1(int x, int y){std::cout << "static int Test::add1(int x, int y) : ";return x + y;}double add2(double x, double y){std::cout << "double Test::add2(double x, double y) : ";return x + y;}
};int main()
{std::function<int(int, int)> f1 = func;std::function<int(int, int)> f2 = Function();std::function<int(int, int)> f3 = [&](int a, int b) ->int{std::cout << "[&](int a, int b)->int{} : " ;return a + b;};std::function<int(int, int)> f4 = Test::add1;std::function<double(Test, double, double)> f5 = &Test::add2;std::map<std::string, std::function<int(int, int)>> func_map;func_map["lambda"] = [&](int x, int y)->int {std::cout << "func_map: ";return x + y;};std::cout << f1(1, 2) << std::endl;std::cout << f2(10, 20) << std::endl;std::cout << f3(100, 200) << std::endl;std::cout << f4(1000, 2000) << std::endl;std::cout << f5(Test(), 1.1, 2.2) << std::endl;std::cout << func_map["lambda"](5, 8) << std::endl;return 0;
}