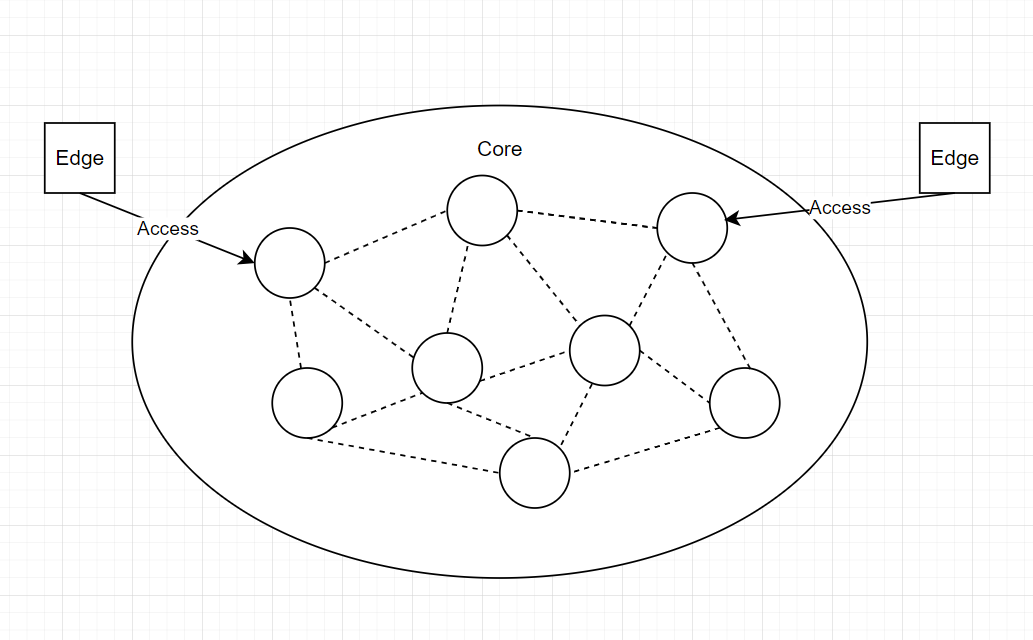
一般而言,互联网被认为由三个部分组成:
Edge Network
- Devices and Endpoints: This part consists of all the devices at the periphery of the network that users directly interact with. It includes personal computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and various Internet of Things (IoT) devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and wearable devices. These devices are the sources and destinations of data in the network.
- Applications and Services: At the edge, there are numerous applications and services that users rely on. This includes web browsers for accessing websites, email clients for sending and receiving messages, video conferencing tools for virtual meetings, and social media platforms for communication and sharing. Online gaming platforms, cloud storage services, and streaming services like Netflix also operate at the edge.
- Function: The edge network's main role is to generate and consume data. It allows users to access and utilize various network resources, such as retrieving information from websites, uploading files to the cloud, or streaming videos. It serves as the interface where users interact with the digital world.
Access Network
- Technologies and Infrastructure: The access network provides the connection between end-user devices and the core network. Common access technologies include Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), which uses existing telephone lines to transmit data; Cable Modem, which utilizes cable TV infrastructure; and Fiber to the Home (FTTH), which offers high-speed data transmission through optical fibers directly to the user's premises. Wireless access technologies like Wi-Fi (WLAN) and cellular networks (such as 4G and 5G) are also part of the access network.
- Connection and Transmission: Its primary function is to enable users to access the broader internet. It receives data from end devices and transmits it to the core network, and vice versa. For example, when a user sends an email from their smartphone, the access network picks up the data and routes it towards the core network for further transmission.
- Service Providers: Internet Service Providers (ISPs) play a crucial role in the access network. They manage and maintain the infrastructure that provides users with network access. Examples of ISPs include Comcast, Verizon, and AT&T in the United States, and China Telecom, China Unicom in China.
Core Network
- Components and Architecture: The core network is the central and most critical part of the internet, often referred to as the "backbone" of the network. It consists of high-performance routers, switches, and high-capacity communication links such as optical fibers. These components are interconnected in a complex architecture to handle large volumes of data traffic.
- Data Routing and Switching: The core network is responsible for routing and switching data packets across different parts of the internet. It uses advanced routing protocols like Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) to determine the most efficient paths for data to travel. It ensures that data from a user in one part of the world can be quickly and accurately delivered to the intended recipient in another part.
- Interconnection and Scalability: It connects different access networks and enables communication between various regions and networks. The core network is designed to be highly scalable to accommodate the ever-increasing amount of data traffic and the growth of the internet. It serves as the foundation that allows the entire internet to function smoothly and efficiently.