2025.1.20——1300
A 1300
You are given a binary string \(s\). A binary string is a string consisting of characters 0 and/or 1.
You can perform the following operation on \(s\) any number of times (even zero):
- choose an integer \(i\) such that \(1 \le i \le |s|\), then erase the character \(s_i\).
You have to make \(s\) alternating, i. e. after you perform the operations, every two adjacent characters in \(s\) should be different.
Your goal is to calculate two values:
- the minimum number of operations required to make \(s\) alternating;
- the number of different shortest sequences of operations that make \(s\) alternating. Two sequences of operations are different if in at least one operation, the chosen integer \(i\) is different in these two sequences.
Input
The first line contains one integer \(t\) (\(1 \le t \le 10^4\)) — the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of one line containing the string \(s\) (\(1 \le |s| \le 2 \cdot 10^5\)). The string \(s\) consists of characters 0 and/or 1 only.
Additional constraint on the input:
- the total length of strings \(s\) over all test cases does not exceed \(2 \cdot 10^5\).
B 1300
You are given two integers \(n\) and \(k\). You are also given an array of integers \(a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n\) of size \(n\). It is known that for all \(1 \leq i \leq n\), \(1 \leq a_i \leq k\).
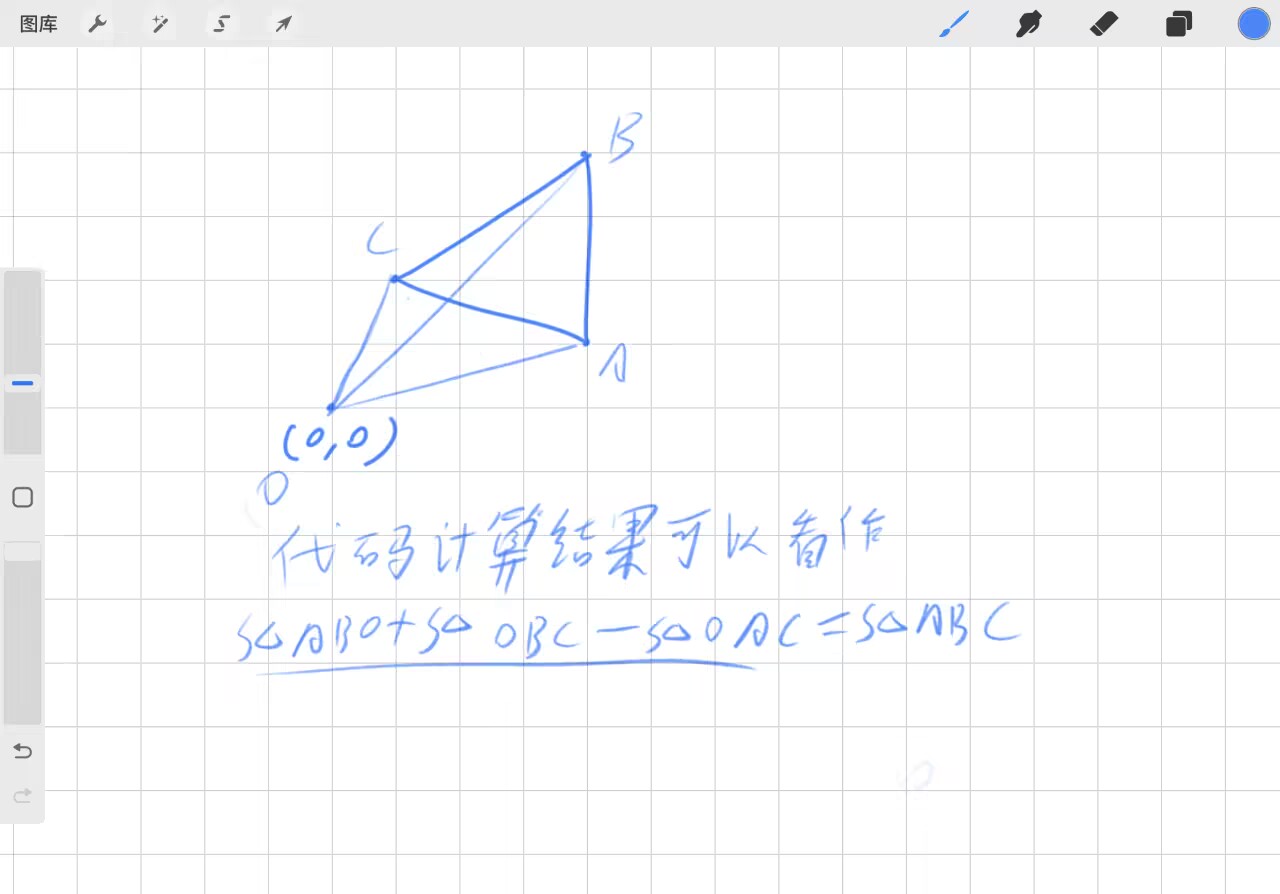
Define a two-dimensional array \(b\) of size \(n \times n\) as follows: \(b_{i, j} = \min(a_i, a_j)\). Represent array \(b\) as a square, where the upper left cell is \(b_{1, 1}\), rows are numbered from top to bottom from \(1\) to \(n\), and columns are numbered from left to right from \(1\) to \(n\). Let the color of a cell be the number written in it (for a cell with coordinates \((i, j)\), this is \(b_{i, j}\)).
For each color from \(1\) to \(k\), find the smallest rectangle in the array \(b\) containing all cells of this color. Output the sum of width and height of this rectangle.
Input
The first line contains a single integer \(t\) (\(1 \leq t \leq 10^4\)) — the number of test cases. Then follows the description of the test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers \(n\) and \(k\) (\(1 \leq n, k \leq 10^5\)) — the size of array \(a\) and the number of colors.
The second line of each test case contains \(n\) integers \(a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n\) (\(1 \leq a_i \leq k\)) — the array \(a\).
It is guaranteed that the sum of the values of \(n\) and \(k\) over all test cases does not exceed \(10^5\).
C 1300
There is an empty matrix \(M\) of size \(n\times m\).
Zhongkao examination is over, and Daniel would like to do some puzzle games. He is going to fill in the matrix \(M\) using permutations of length \(m\). That is, each row of \(M\) must be a permutation of length \(m^\dagger\).
Define the value of the \(i\)-th column in \(M\) as \(v_i=\operatorname{MEX}(M_{1,i},M_{2,i},\ldots,M_{n,i})^\ddagger\). Since Daniel likes diversity, the beauty of \(M\) is \(s=\operatorname{MEX}(v_1,v_2,\cdots,v_m)\).
You have to help Daniel fill in the matrix \(M\) and maximize its beauty.
\(^\dagger\) A permutation of length \(m\) is an array consisting of \(m\) distinct integers from \(0\) to \(m-1\) in arbitrary order. For example, \([1,2,0,4,3]\) is a permutation, but \([0,1,1]\) is not a permutation (\(1\) appears twice in the array), and \([0,1,3]\) is also not a permutation (\(m-1=2\) but there is \(3\) in the array).
\(^\ddagger\) The \(\operatorname{MEX}\) of an array is the smallest non-negative integer that does not belong to the array. For example, \(\operatorname{MEX}(2,2,1)=0\) because \(0\) does not belong to the array, and \(\operatorname{MEX}(0,3,1,2)=4\) because \(0\), \(1\), \(2\) and \(3\) appear in the array, but \(4\) does not.
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer \(t\) (\(1\le t\le 1000\)) — the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
The only line of each test case contains two integers \(n\) and \(m\) (\(1\le n,m\le 2\cdot 10^5\)) — the size of the matrix.
It is guaranteed that the sum of \(n\cdot m\) over all test cases does not exceed \(2\cdot 10^5\).
D 1300
This is an interactive problem!
salyg1n gave Alice a set \(S\) of \(n\) distinct integers \(s_1, s_2, \ldots, s_n\) (\(0 \leq s_i \leq 10^9\)). Alice decided to play a game with this set against Bob. The rules of the game are as follows:
-
Players take turns, with Alice going first.
-
In one move, Alice adds one number \(x\) (\(0 \leq x \leq 10^9\)) to the set \(S\). The set \(S\) must not contain the number \(x\) at the time of the move.
-
In one move, Bob removes one number \(y\) from the set \(S\). The set \(S\) must contain the number \(y\) at the time of the move. Additionally, the number \(y\) must be strictly smaller than the last number added by Alice.
-
The game ends when Bob cannot make a move or after \(2 \cdot n + 1\) moves (in which case Alice's move will be the last one).
-
The result of the game is \(\operatorname{MEX}\dagger(S)\) (\(S\) at the end of the game).
-
Alice aims to maximize the result, while Bob aims to minimize it.
Let \(R\) be the result when both players play optimally. In this problem, you play as Alice against the jury program playing as Bob. Your task is to implement a strategy for Alice such that the result of the game is always at least \(R\).
\(\dagger\) \(\operatorname{MEX}\) of a set of integers \(c_1, c_2, \ldots, c_k\) is defined as the smallest non-negative integer \(x\) which does not occur in the set \(c\). For example, \(\operatorname{MEX}(\{0, 1, 2, 4\})\) \(=\) \(3\).
E 1300
Given two arrays \(a\) and \(b\), both of length \(n\). Elements of both arrays indexed from \(1\) to \(n\). You are constructing a directed graph, where edge from \(u\) to \(v\) (\(u\neq v\)) exists if \(a_u-a_v \ge b_u-b_v\).
A vertex \(V\) is called strong if there exists a path from \(V\) to all other vertices.
A path in a directed graph is a chain of several vertices, connected by edges, such that moving from the vertex \(u\), along the directions of the edges, the vertex \(v\) can be reached.
Your task is to find all strong vertices.
For example, if \(a=[3,1,2,4]\) and \(b=[4,3,2,1]\), the graph will look like this:
 The graph has only one strong vertex with number \(4\)
The graph has only one strong vertex with number \(4\)
Input
The first line contains an integer \(t\) (\(1\le t\le 10^4\)) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains an integer \(n\) (\(2 \le n \le 2\cdot 10^5\)) — the length of \(a\) and \(b\).
The second line of each test case contains \(n\) integers \(a_1,a_2 \dots a_n\) (\(-10^9 \le a_i \le 10^9\)) — the array \(a\).
The third line of each test case contains \(n\) integers \(b_1,b_2 \dots b_n\) (\(-10^9 \le b_i \le 10^9\)) — the array \(b\).
It is guaranteed that the sum of \(n\) for all test cases does not exceed \(2\cdot 10^5\).
------------------------思考------------------------
-
方案数/组合数学+发现结论/优化+MEX构造+交互博弈+guess。
A
- 难点在计算方案数,抽象了半天发现通过模拟可以得出计算方法。
B
- 模拟一下发现结论:本质是对 1~k 找到两侧边界开始大于其的第一个位置。
- 前缀维护最大值,二分可以快速回答。 但是考虑 1~k 单调性询问,发现可以双指针解决。
C
- 构造方式比较好想,再计算即可。
D
- 交互。模拟博弈过程,从答案值域和小数据下界入手。发现结论。
E
- 第一眼从样例猜出了答案。细想证明确实比较巧妙。
------------------------代码------------------------
A
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC, ST) \for (int i = ST; i < VEC.size(); i++) \cout << VEC[i] << ' '; \el;void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}constexpr int mod = 998244353;
void _()
{string s;cin >> s;int n = s.size();s = " " + s;vector<int> len;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int j = i;for (; j <= n && s[j] == s[i]; j++) // j停在的位置为第一个不合法的地方;len.push_back(j - i);i = j - 1;}auto get = [](int len){int ans = 1;for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)ans = ans * i % mod;return ans;};int res = 0, f = 1, t = 0;for (auto len : len)res += len - 1, f = f * len % mod, t += len - 1;f = f * get(t) % mod;cout << res << ' ' << f;el;
}
B
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC, ST) \for (int i = ST; i < VEC.size(); i++) \cout << VEC[i] << ' '; \el;void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n, k;cin >> n >> k;vector<int> a(n + 1);vector<int> color(k + 1);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int x;cin >> x;a[i] = x;color[x] = 1;}int f = 1, g = n;for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++){if (!color[i]){cout << 0 << ' ';continue;}int l = n;for (;; f++)if (a[f] >= i)break;;for (;; g--)if (a[g] >= i)break;;// bug3(i, f, g);cout << (g - f + 1 << 1) << ' ';}el;
}
C
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC, ST) \{ \for (int I = ST; I < VEC.size(); I++) \cout << VEC[I] << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> f(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)f[1][j] = j - 1;for (int i = 2; i <= min(n, m - 1); i++){f[i][1] = f[i - 1][m];for (int j = 2; j <= m; j++)f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1];}for (int i = m; i <= n; i++)for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];auto MEX = [](vector<int> a){sort(a.begin(), a.end());a.erase(unique(a.begin(), a.end()), a.end());for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)if (a[i] - i)return i;return a.back() + 1;};vector<int> t;for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){vector<int> a;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)a.push_back(f[i][j]);t.push_back(MEX(a));}// bugv(t, 0);cout << MEX(t);el;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)bugv(f[i], 1);
}
D
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
// #define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC, ST) \{ \for (int I = ST; I < VEC.size(); I++) \cout << VEC[I] << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n;cin >> n;map<int, bool> has;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int x;cin >> x;has[x] = 1;}auto f = [](int x){cout << x << endl;cin >> x;return x;};if (!has[0]){f(0);return;}int ans = 0;for (;; ans++)if (!has[ans])break;int x = f(ans);while (~x)x = f(x);
}
E
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC, ST) \{ \for (int I = ST; I < VEC.size(); I++) \cout << VEC[I] << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int> f(n);for (int &x : f)cin >> x;int mx = -1e10;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int x;cin >> x;f[i] -= x;mx = max(mx, f[i]);}int cnt = 0;vector<int> res;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)if (f[i] == mx)cnt++, res.push_back(i + 1);cout << cnt;el;bugv(res, 0);
}