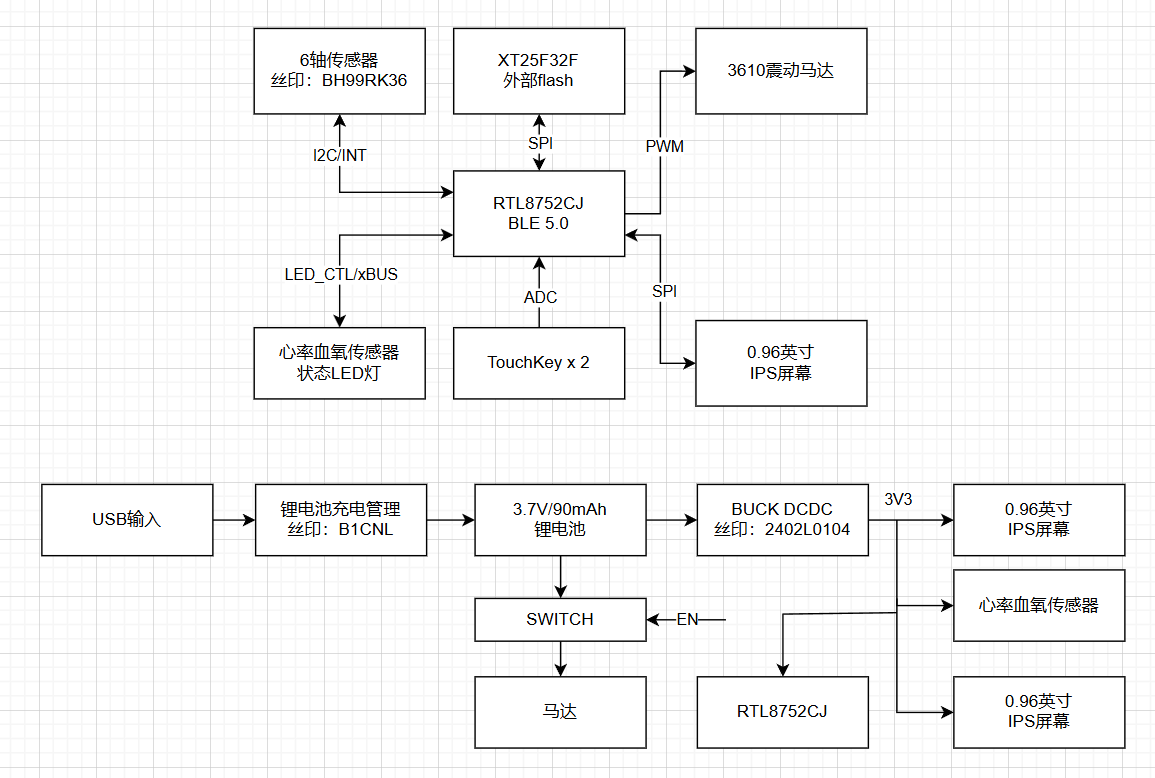
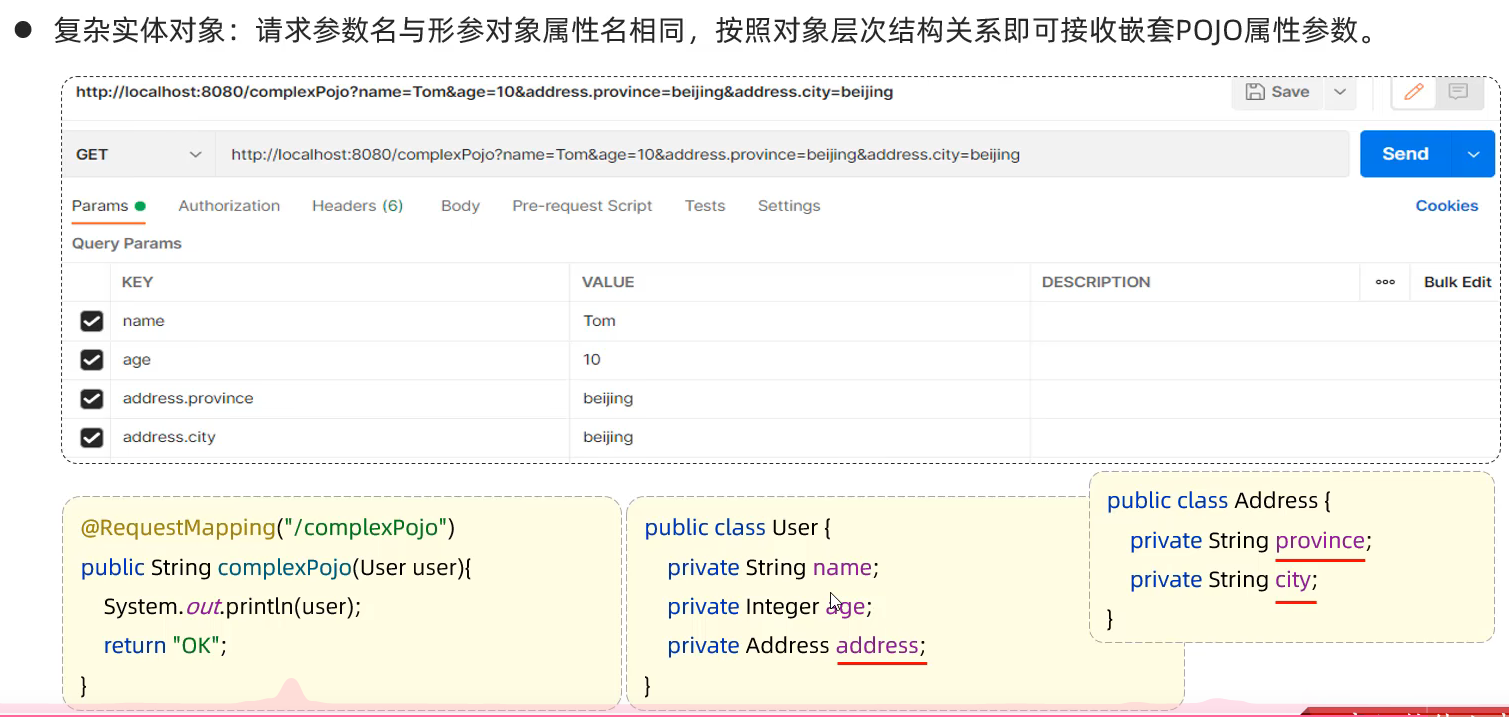
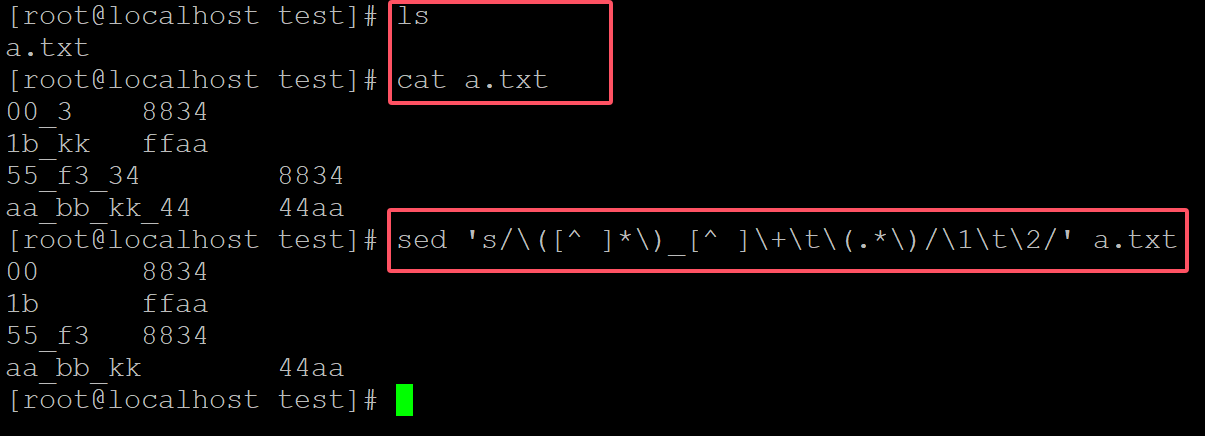
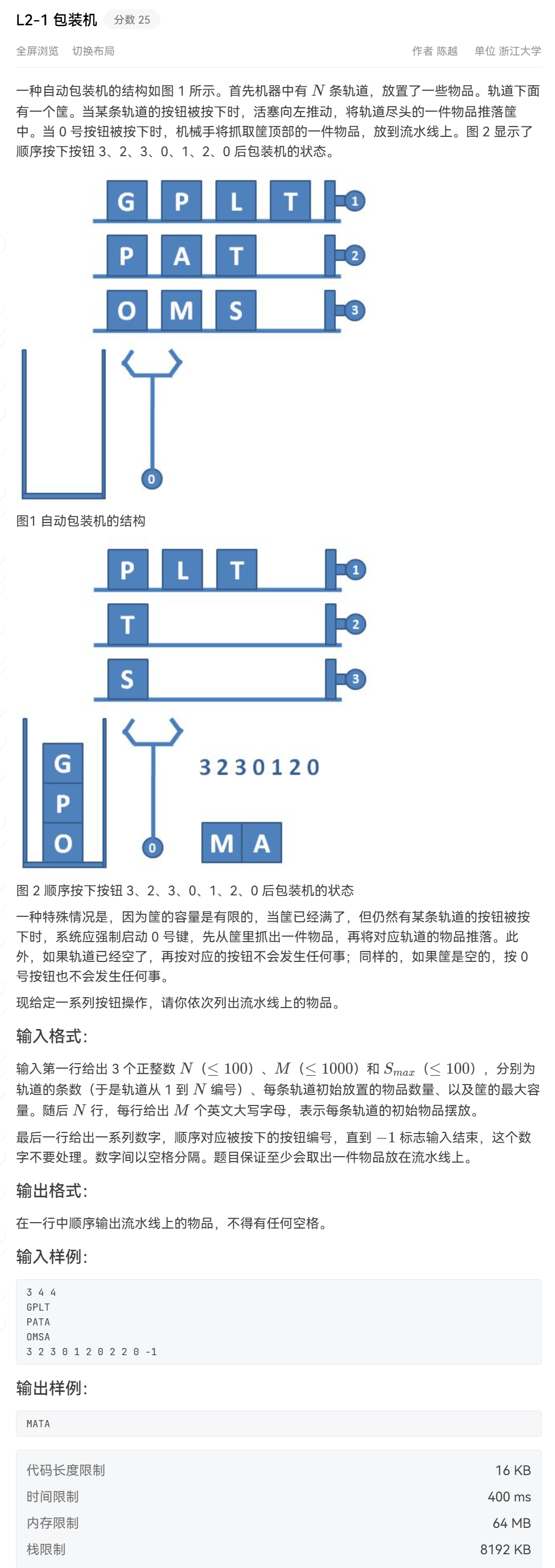
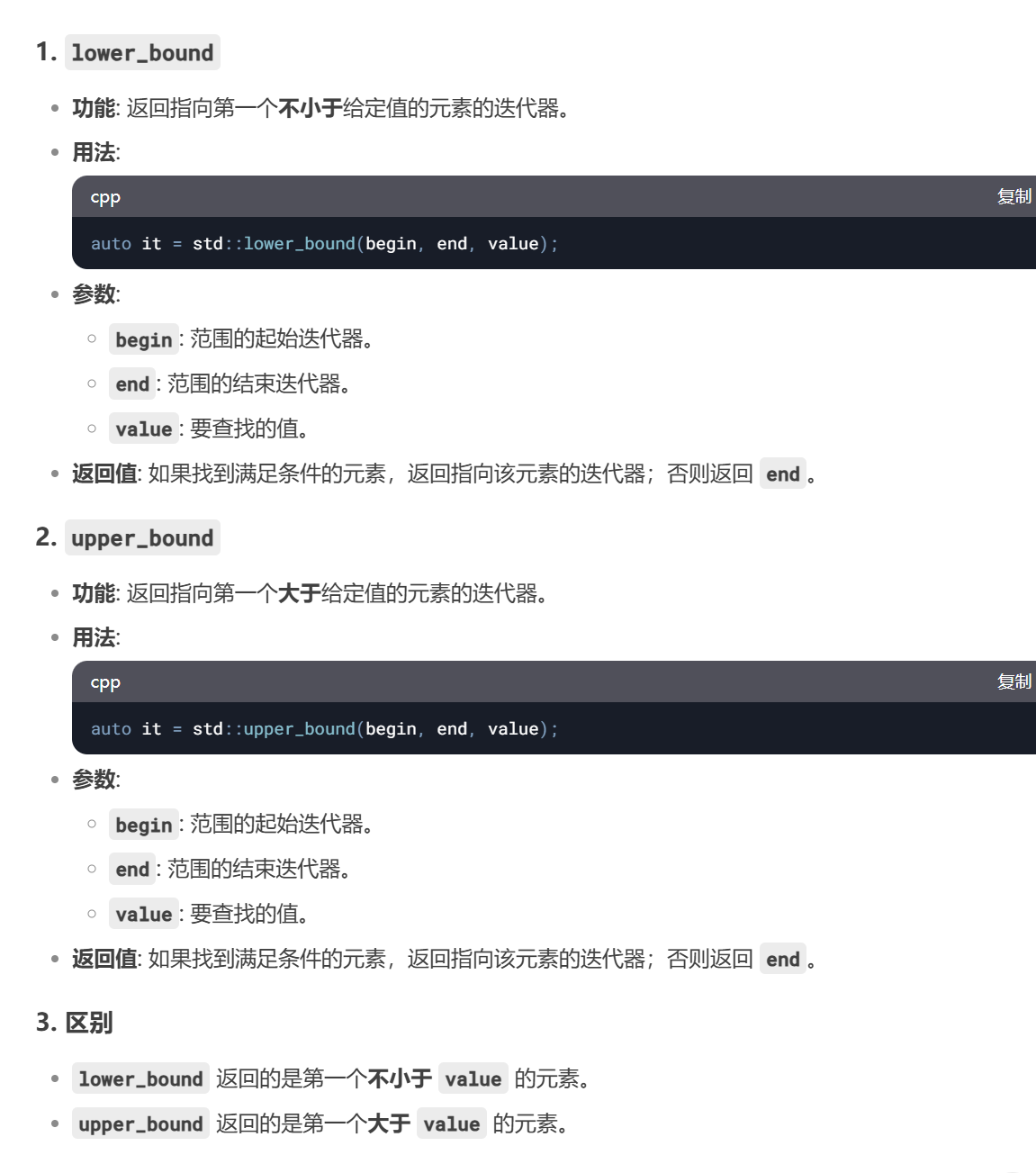
Nginx 是开源、高性能、高可靠的 Web 和反向代理服务器,而且支持热部署,几乎可以做到 7 * 24 小时不间断运行,即使运行几个月也不需要重新启动,还能在不间断服务的情况下对软件版本进行热更新。性能是 Nginx 最重要的考量,其占用内存少、并发能力强、能支持高达 5w 个并发连接数,最重要的是, Nginx 是免费的并可以商业化,配置使用也比较简单。
Nginx特点:
- 高并发、高性能;
- 模块化架构使得它的扩展性非常好;
- 异步非阻塞的事件驱动模型这点和 Node.js 相似;
- 相对于其它服务器来说它可以连续几个月甚至更长而不需要重启服务器使得它具有高可靠性;
- 热部署、平滑升级;
- 完全开源,生态繁荣;
一、配置(nginx.conf)
nginx.conf 配置文件的语法规则:
- 配置文件由
指令与指令块构成; - 每条指令以
;分号结尾,指令与参数间以空格符号分隔; - 指令块以
{}大括号将多条指令组织在一起; include语句允许组合多个配置文件以提升可维护性;- 通过
#符号添加注释,提高可读性; - 通过
$符号使用变量; - 部分指令的参数支持正则表达式,例如常用的 location 指令.
Nginx 的典型配置示例:

-
main 全局配置,对全局生效;
-
events 配置影响 Nginx 服务器与用户的网络连接;
-
http 配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置;
-
server 配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个 http 块中可以有多个 server 块;
-
location 用于配置匹配的 uri ;
-
upstream 配置后端服务器具体地址,负载均衡配置不可或缺的部分;
#1. main段配置信息 user nginx; #运行用户,默认即是nginx,可以不进行设置 worker_processes auto; #Nginx 进程数,一般设置为和 CPU 核数一样 error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; #Nginx 的错误日志存放目录 pid /var/run/nginx.pid; #Nginx 服务启动时的 pid 存放位置#2. events段配置信息 events {use epoll; #使用epoll的I/O模型(缺省会自动选择一个最适合你操作系统的)worker_connections 1024; #每个进程允许最大并发数 }#3. http段配置信息 #配置使用最频繁的部分,代理、缓存、日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置都在这里设置 http { #设置日志模式log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; #Nginx访问日志存放位置sendfile on; #开启高效传输模式tcp_nopush on; #减少网络报文段的数量tcp_nodelay on;keepalive_timeout 65; #保持连接的时间,也叫超时时间,单位秒types_hash_max_size 2048;include /etc/nginx/mime.types; #文件扩展名与类型映射表default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型#4. server段配置信息server {listen 80; #配置监听的端口server_name localhost; #配置的域名#5. location段配置信息location / {root /usr/share/nginx/html; #网站根目录index index.html index.htm; #默认首页文件deny 172.168.22.11; #禁止访问的ip地址,可以为allallow 172.168.33.44; #允许访问的ip地址,可以为all}error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; #默认50x对应的访问页面error_page 400 404 error.html; #同上}#加载子配置项include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; }
1.1 内置变量
nginx 常用的内置全局变量,你可以在配置中随意使用,点此查看效果:内置变量实例演示
| 变量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| $args | 请求中的参数,例: baidu.com/?a=1&b=1 中的a和b |
| $content_length | HTTP 请求信息里的"Content-Length" |
| $content_type | HTTP 请求信息里的"Content-Type" |
| $document_root | nginx 虚拟主机配置文件中的 root 参数对应的值 |
| $document_uri | 当前请求中不包含指令的 URI |
| $host | 主机头,也就是域名 |
| $http_user_agent | 客户端的详细信息,也就是浏览器的标识 |
| $http_cookie | 客户端的 cookie 信息 |
| $limit_rate | 如果 nginx服务器使用limit_rate 配置了显示网络速率,则会显示,如果没有设置,则显示0 |
| $remote_addr | 客户端的公网ip |
| $remote_user | 如果 nginx有配置认证,该变量代表客户端认证的用户名 |
| $request_body_file | 做反向代理时发给后端服务器的本地资源的名称 |
| $request_method | 请求资源的方式,GET /PUT /DELETE等 |
| $request_filename | 当前请求的资源文件的路径名称 |
| $request_uri | 请求的链接,包括$document_uri 和$args |
| $scheme | 请求的协议,如ftp, http, https |
| $server_addr | 服务器IP地址 |
| $server_name | 服务器的主机名 |
| $server_port | 服务器的端口号 |
1.2 全局配置
1.2.1 配置文件 main 段核心参数
#1. user: 指定运行 Nginx 的 woker 子进程的属主和属组,其中组可以不指定。
#语法:user USERNAME [GROUP]
user nginx lion; #用户是nginx; 组是lion#2. pid: 指定运行 Nginx master 主进程的 pid 文件存放路径。
pid /opt/nginx/logs/nginx.pid; #master主进程的的pid存放在nginx.pid的文件#3. worker_rlimit_nofile_number: 指定worker子进程可以打开的最大文件句柄数。
worker_rlimit_nofile 20480; #可以理解成每个worker子进程的最大连接数量。#4. worker_rlimit_core: 指定 worker 子进程异常终止后的 core 文件,用于记录分析问题。
worker_rlimit_core 50M; #存放大小限制
working_directory /opt/nginx/tmp; #存放目录#5. worker_processes_number:指定 Nginx 启动的 worker 子进程数量。
worker_processes 4; #指定具体子进程数量
worker_processes auto; #与当前cpu物理核心数一致#6. worker_cpu_affinity:将每个 worker 子进程与我们的 cpu 物理核心绑定。
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000; #4个物理核心,4个worker子进程#7. worker_priority: 指定 worker 子进程的 nice 值,以调整运行 Nginx 的优先级,通常设定为负值,以优先调用 Nginx 。
worker_priority -10; #120-10=110,110就是最终的优先级
#Linux 默认进程的优先级值是120,值越小越优先; nice 值范围为 -20 到 +19 。#备注:应用的默认优先级值是120加上 nice 值等于它最终的值,这个值越小,优先级越高。#8. worker_shutdown_timeout: 指定 worker 子进程优雅退出时的超时时间。
worker_shutdown_timeout 5s;#9. timer_resolution: worker 子进程内部使用的计时器精度,调整时间间隔越大,系统调用越少,有利于性能提升;反之,系统调用越多,性能下降。
timer_resolution 100ms;
#在 Linux 系统中,用户需要获取计时器时需要向操作系统内核发送请求,有请求就必然会有开销,因此这个间隔越大开销就越小。#10. daemon: 指定 Nginx 的运行方式,前台还是后台,前台用于调试,后台用于生产。
daemon off; #默认是on,后台运行模式
worker_cpu_affinity:将每个 worker 子进程与特定 CPU 物理核心绑定,优势在于,避免同一个 worker 子进程在不同的 CPU 核心上切换,缓存失效,降低性能。但其并不能真正的避免进程切换。

1.2.2 配置文件 events 段核心参数
#1. use:Nginx 使用何种事件驱动模型。
use method; #不推荐配置它,让nginx自己选择
#method 可选值为:select、poll、kqueue、epoll、/dev/poll、eventport#2. worker_connections:worker 子进程能够处理的最大并发连接数。
worker_connections 1024; #每个子进程的最大连接数为1024#3. accept_mutex:是否打开负载均衡互斥锁。
accept_mutex on; #默认是off关闭的,这里推荐打开
1.3 核心配置
| 配置 | 位置 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| worker_processes 8 | 开始 | 工作进程, 通常等于CPU数最或者2倍于CPU |
| include filename | 任意 | 用于引入其他文件 |
| worker_connections | events | 最大连接数 |
| keepalive_timeout | http | 连接超时时间,默认为75s |
| gzip on | http | 开启 gzip 压缩 |
| client_header_buffer_size | http | 设定请求缓冲 |
| client_max_body_size | http | 上传文件的大小限制,默认 1m |
| keepalive_requests | server | 单连接请求上限次数 |
| listen 80 | server | 监听 80 端口 |
| server_name | server | 监听地址 |
| error_page | server | 定义错误提示界面 |
| set | server | 定义变量 |
| proxy_pass | location | 代理转发 |
| rewrite | location | 重定向 |
| return | location | 停止处理请求 |
1.3.1 server_name
指定虚拟主机域名
#语法:server_name <name_1> [<name_2> ...]
server_name www.nginx.com;
域名匹配的四种写法:
-
精确匹配:
server_name www.nginx.com -
左侧通配:
server_name *.nginx.com -
右侧统配:
server_name www.nginx.* -
正则匹配:
server_name ~^www.nginx.*$匹配优先级:精确匹配 > 左侧通配符匹配 > 右侧通配符匹配 > 正则表达式匹配
点此查看:server_name实例演示
1.3.2 location
#配置 URL路径
location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }
匹配规则(点此查看:location实例演示):
-
=精确匹配; -
~正则匹配,区分大小写; -
~*正则匹配,不区分大小写; -
^~匹配到即停止搜索;匹配优先级:
=>^~>~>~*>无符号
location 的末尾斜线 /
#当访问 www.nginx-test.com/test 时,location 中的是否有末尾反斜线,结果如下:
location /test/ { ... }
#末尾带 / 时,Nginx 只会找 test/index.html 文件。location /test { ... }
#末尾不带 / 时,Nginx 会先找 test/index.html 文件,没有再找 test 文件。
##即:先找是否有 test 目录,有则找 test 目录下的 index.html ;没有则会找是否有 test 文件。
1.3.3 root 与 alias
root 与 alias 都可以指定静态资源目录位置,两者选其一即可
寻找资源时:root 会将定义路径与URI叠加,alias 则只取定义路径
当用户访问 http://www.test.com/image/1.png 时,实际在服务器找的路径是 /opt/nginx/static/image/1.png
-
root:指定静态资源目录位置,可以写在 http、server、location 等配置中。
#语法:root path location /image {root /opt/nginx/static; } -
alias:指定静态资源目录位置,只能写在 location 中,且资源路径以
/结尾。#语法:root path/ location /image {alias /opt/nginx/static/image/; }
1.3.4 proxy_pass
用于配置代理服务器,如:正向代理,反向代理(点击即可查看演示)
#上下文:location、if、limit_except#语法:proxy_pass URL;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081/proxy
URL 参数原则:
- URL 必须以 http 或 https 开头;
- URL 中可以携带变量;
- URL 中是否带 URI ,会直接影响发往上游请求的 URL ;
在配置代理时,proxy_pass 有末尾 带和 不带 / 两种用法,它们的区别可大了:proxy_pass实例演示
1.3.5 upstream
用于定义上游服务器(指的就是后台提供的应用服务器)的相关信息。

#上下文:http##语法
#upstream name {
# server address [parameters] #定义上游服务器地址。
#}##配置示例
upstream back_end_server {#上游服务器 权重 最大连接数 判定失败的超时时间 连接失败数server 127.0.0.1:8081 weight=3 max_conns=1000 fail_timeout=10s max_fails=2;keepalive 32;keepalive_requests 50;keepalive_timeout 30s;
}
在 upstream 内可使用的指令:
zone#定义共享内存,用于跨 worker 子进程;keepalive <connections>#对上游服务启用长连接,限制每个 worker 子进程与上游服务器空闲长连接的最大数量。keepalive_requests <number>#一个长连接最多请求 HTTP 的个数(默认100);:单个长连接可以处理的最多 HTTP 请求个数。keepalive_timeout <time>#空闲情形下,一个长连接的超时时长;空闲长连接的最长保持时间(默认60s)。hash#哈希负载均衡算法;ip_hash#依据 IP 进行哈希计算的负载均衡算法;least_conn#最少连接数负载均衡算法;least_time#最短响应时间负载均衡算法;random#随机负载均衡算法,random 还支持两种可选的负载均衡模式如下:random two:从后端服务器列表中,随机选择两个服务器,然后根据配置的权重(weight)选择其中一个。random two least_conn:从后端服务器列表中,随机选择两个服务器,然后选择其中连接数较少的服务器。(结合了随机性和最少连接数的优点)
server <address> [parameters]#定义上游服务器地址,parameters 可选值:weight=<number>#权重值,默认为1;max_conns=<number>#上游服务器的最大并发连接数;fail_timeout=<time>#服务器不可用的判定时间;max_fails=<numer>#服务器不可用的检查次数;backup#备份服务器,仅当其他服务器都不可用时才会启用;down#标记服务器长期不可用,离线维护;
点此查看:负载均衡演示
1.3.6 return
停止处理请求,直接返回响应码或重定向到其他 URL ;执行 return 指令后, location 中后续指令将不会被执行。
#语法:
#return code [text];
#return code URL;
#return URL;#例如:
location / {return 404; #直接返回状态码
}location / {return 404 "pages not found"; #返回状态码 + 一段文本
}location / {return 302 /bbs; #返回状态码 + 重定向地址
}location / {return https://www.baidu.com; #返回重定向地址
}
1.3.7 rewrite
根据指定正则表达式匹配规则,重写 URL 。
#上下文(标签):server、location、if#语法:rewrite <正则表达式> <要替换的内容> [flag];
rewirte /images/(.*\.jpg)$ /pic/$1; #变量$1 是前面括号(.*\.jpg)的反向引用
flag 可选值的含义:
last重写后的 URL 发起新请求,再次进入 server 段,重试 location 的中的匹配;break直接使用重写后的 URL ,不再匹配其它 location 中语句;redirect返回 302 临时重定向;permanent返回 301 永久重定向;
点此查看:rewrite实例演示
1.3.8 if
#上下文:server、location#语法:if (condition) { ... }
if ($http_user_agent ~ Chrome) {rewrite /(.*) /browser/$1 break;
}#实例:当访问 localhost:8080/images/ 时,会进入 if 判断里面,并执行 rewrite 命令。
server {listen 8080;server_name localhost;root html;location / {if ( $uri = "/images/" ) {rewrite (.*) /pics/ break;}}
}
condition 判断条件:
$variable#仅为变量时,值为空或以0开头,字符串都会被当做 false 处理;=!=#相等或不等;~#正则匹配;~*#正则匹配,不区分大小写;-f#检测 文件 存在;-d#检测 目录 存在;-e#检测 文件、目录、符号链接 等存在;-x#检测文件可以执行;!#取反,非;如! ~非正则匹配;或! -f文件不存在
1.3.9 autoindex
用户请求以 / 结尾时,列出目录结构,可以用于快速搭建静态资源下载网站。

autoindex-nginx.conf 配置信息:
#当访问 fe.lion.com/download/ 时,会把服务器 /opt/source/download/ 路径下的文件展示出来
server {listen 80;server_name fe.lion-test.club;location /download/ {root /opt/source;autoindex on; #打开 autoindex,可选参数有 on | offautoindex_exact_size on; #修改为off(默认on),以bytes(KB、MB、GB)显示出⽂件的确切⼤⼩autoindex_format html; #以html的方式进行格式化,可选参数有 html | json | xmlautoindex_localtime off; #显示的⽂件时间为⽂件的服务器时间(默认off)。显示的⽂件时间为GMT时间}
}
1.4 HTTPS
在学习如何配置 HTTPS 之前,我们先来简单回顾下 HTTPS 的工作流程是怎么样的?它是如何进行加密保证安全的?
1.4.1 HTTPS 工作流程
- 客户端(浏览器)访问 https://www.baidu.com 百度网站;
- 百度服务器返回 HTTPS 使用的 CA 证书;
- 浏览器验证 CA 证书是否为合法证书;
- 验证通过,证书合法,生成一串随机数并使用公钥(证书中提供的)进行加密;
- 发送公钥加密后的随机数给百度服务器;
- 百度服务器拿到密文,通过私钥进行解密,获取到随机数(公钥加密,私钥解密,反之也可以);
- 百度服务器把要发送给浏览器的内容,使用随机数进行加密后传输给浏览器;
- 此时浏览器可以使用随机数进行解密,获取到服务器的真实传输内容;
这就是 HTTPS 的基本运作原理,使用对称加密和非对称机密配合使用,保证传输内容的安全性。
有兴趣的可点此查看:什么是 SSL、TLS 和 HTTPS?
1.4.2 配置证书
下载证书的压缩文件,里面有个 Nginx 文件夹,把 xxx.crt 和 xxx.key 文件拷贝到服务器目录,再进行如下配置:
server {listen 443 ssl http2 default_server; #SSL 访问端口号为 443server_name lion.club; #填写绑定证书的域名(我这里是随便写的)ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/https/lion.club_bundle.crt; #证书地址ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/https/lion.club.key; #私钥地址ssl_session_timeout 10m;ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; #支持ssl协议版本,默认为后三个,主流版本是[TLSv1.2]location / {root /usr/share/nginx/html;index index.html index.htm;}
}
注意:
- ssl_certificate证书的后缀不固定,目前知道的有有:.cer、.pem、.crt ;
- ssl_certificate_key的文件的后缀是固定的为.key
1.5 CORS 跨域配置
CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing,跨源资源共享)是一种浏览器机制,允许网页从不同的域(源)请求资源。它通过使用额外的 HTTP 头来告诉浏览器,允许某个源(协议 + 域名 + 端口)访问资源,即使这些资源来自不同的源。
1.5.1 跨域的定义
同源策略限制了从同一个源加载的文档或脚本如何与来自另一个源的资源进行交互。
这是一个用于隔离潜在恶意文件的重要安全机制。通常不允许不同源间的读操作。
1.5.2 同源的定义
如果两个页面的协议,域名和端口都相同,则两个页面具有相同的源。
与 URL http://store.company.com/dir/page.html 的源进行对比的示例:
- http://store.company.com/dir2/other.html 同源
- https://store.company.com/secure.html 不同源:协议不同
- http://store.company.com:81/dir/etc.html 不同源:端口不同
- http://news.company.com/dir/other.html 不同源:主机不同
不同源会有如下限制:
- Web 数据层面:同源策略限制了不同源的站点读取当前站点的 Cookie 、 IndexDB 、 LocalStorage 等数据。
- DOM 层面:同源策略限制了来自不同源的 JavaScript 脚本对当前 DOM 对象读和写的操作。
- 网络层面:同源策略限制了通过 XMLHttpRequest 等方式将站点的数据发送给不同源的站点。
1.5.3 Nginx 跨域方案
例如:
- 前端服务的域名为: fe.server.com
- 后端服务的域名为: dev.server.com
现在我在 fe.server.com 对 dev.server.com 发起请求一定会出现跨域。
- 启动一个 Nginx 服务器,将 server_name 设置为 fe.server.com
- 设置相应的 location 以拦截前端需要跨域的请求
- 最后将请求代理回 dev.server.com
如下面的配置:
server {listen 80;server_name fe.server.com;location / {proxy_pass http://dev.server.com;}
}
这样可以完美绕过浏览器的同源策略:
- fe.server.com 访问 Nginx 的 fe.server.com 属于同源访问,
- 而 Nginx 对服务端转发的请求不会触发浏览器的同源策略。
1.6 配置开启 gzip 压缩
GZIP 是规定的三种标准 HTTP 压缩格式之一。目前绝大多数的网站都在使用 GZIP 传输 HTML、CSS、JavaScript 等资源文件。
对于文本文件, GZiP 的效果非常明显,开启后传输所需流量大约会降至 1/4~1/3 。
启用 gzip 同时需要客户端和服务端的支持,然而并不是每个浏览器都支持 gzip 的。
可以通过请求头中的 Accept-Encoding 来标识对压缩的支持,如图:

如果客户端支持 gzip 的解析,那么只要服务端能够返回 gzip 的文件就可以启用 gzip 了,
可以通过 Nginx 的配置来让服务端支持 gzip 。下面的 respone 中 content-encoding:gzip ,指服务端开启了 gzip 的压缩方式。

#是否开启gzip
gzip on; #默认 off#采用 gzip 压缩的 MIME 文件类型,其中 text/html 被系统强制启用;
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;#---- 以上两个参数开启就可以支持Gzip压缩了 ----##该模块启用后,Nginx 首先检查是否存在请求静态文件的 gz 结尾的文件,如果有则直接返回该 .gz 文件内容;
gzip_static on; #默认 off#nginx做为反向代理时启用,用于设置"启用或禁用"从代理服务器上收到相应内容 gzip 压缩;
gzip_proxied any; #默认 off#用于在响应消息头中添加 Vary:Accept-Encoding,使代理服务器根据请求头中的 Accept-Encoding 识别是否启用 gzip 压缩;
gzip_vary on;#gzip 压缩比,压缩级别是 1-9,级别越高压缩率越大,压缩时间越长;1 压缩级别最低,9 最高,建议 4-6;
gzip_comp_level 6;#获取多少内存,用于缓存压缩结果
gzip_buffers 16 8k; #16 8k 表示以 8k*16 为单位获得#允许压缩的页面最小字节数,页面字节数从header头中的 Content-Length 中进行获取。
#建议设置成大于 1k 的字节数,小于 1k 可能会越压越大;(默认值是 0,不管页面多大都压缩)
gzip_min_length 1k;#启用 gzip 所需的 HTTP 最低版本;
gzip_http_version 1.1; #默认 1.1
1.7 Nginx 配置黑/白名单
Nginx 利用 deny 和 allow 指令来实现黑 /白名单的配置,利用黑白名单进行安全配置。
#上下文:http、server、location#语法
allow address | CIDR | all; #允许访问
deny address | CIDR | all; #禁止访问
参数说明:
- address:具体的ip地址。
- CIDR:ip加掩码形式地址。
- all:所有ip地址。
例子:
-
黑名单: 配置禁止的ip访问,允许其他所有的地址访问。
deny 192.168.1.234 deny 192.168.1.235 deny 192.168.1.236allow all;在这个配置下,234、235和236的ip访问不了服务器,会显示403 Forbidden,而其他ip都可以访问。
-
白名单: 配置允许的ip访问,禁止其他所有的地址访问。
allow 192.168.1.234 allow 192.168.1.235 allow 192.168.1.236deny all;在这个配置下,234、235和236的ip可以访问服务器,而其他所有ip都不允许访问,显示403 Forbidden。
-
配置禁止访问文件或文件夹
location ^~ /project/deny.txt { #明确请求是对其起作用的;alias /webroot/proj/; #解析到 /webroot/proj 目录deny all; #屏蔽任何来源
}
也可以把 deny all 改换成 return 404,这样将返回 404 而不是 403 Forbidden,更有“欺骗性”。
1.8 缓存配置
缓存可以非常有效的提升性能,因此不论是客户端(浏览器),还是代理服务器( Nginx ),乃至上游服务器都多少会涉及到缓存。可见缓存在每个环节都是非常重要的。
存储一些之前被访问过、而且可能将要被再次访问的资源,使用户可以直接从代理服务器获得,从而减少上游服务器的压力,加快整个访问速度。
下面让我们来学习 Nginx 中如何设置缓存策略。
1.8.1 缓存文件设置
#上下文:http#### proxy_cache_path
#设置缓存文件的存放路径。
proxy_cache_path path [level=levels] ... #默认值:proxy_cache off;
参数含义:
- path #缓存文件的存放路径;
- level #path的目录层级;
- keys_zone #设置共享内存;
- inactive #在指定时间内没有被访问,缓存会被清理,默认10分钟;
1.8.2 缓存条件设置
#上下文:http、server、location#### proxy_no_cache
#定义相应保存到缓存的条件,如果字符串参数的至少一个值不为空且不等于 “0”,则将不保存该响应到缓存。
#语法:proxy_no_cache string;
proxy_no_cache $http_pragma $http_authorization;#### proxy_cache_bypass
#定义条件,在该条件下将不会从缓存中获取响应。
#语法:proxy_cache_bypass string;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_pragma $http_authorization;
1.4.3 缓存参数配置
#上下文:http、server、location#### proxy_cache
#缓存开关
proxy_cache zone | off ; # zone 是共享内存的名称(默认值:off;)#### proxy_cache_valid
#配置什么状态码可以被缓存,以及缓存时长。
#语法:proxy_cache_valid [code...] time;
proxy_cache_valid 200 304 2m; #说明对于状态为200和304的缓存文件的缓存时间是2分钟#### proxy_cache_key
#设置缓存文件的 key
proxy_cache_key #默认值 $scheme$proxy_host$request_uri;
upstream_cache_status 变量,设置在响应头信息中,在调试中非常有用,它存储了缓存是否命中的信息,如下:
MISS: #未命中缓存HIT:: #命中缓存EXPIRED: #缓存过期STALE: #命中了陈旧缓存REVALIDDATED: #Nginx验证陈旧缓存依然有效UPDATING: #内容陈旧,但正在更新BYPASS: #响应从原始服务器获取
1.4.4 缓存配置实例
上游服务器:121.42.11.34 ,配置如下:
server {listen 1010;root /usr/share/nginx/html/1010;location / {index index.html;}
}server {listen 1020;root /usr/share/nginx/html/1020;location / {index index.html;}
}
代理服务器:121.5.180.193 ,配置如下:
# 缓存文件设置
proxy_cache_path /etc/nginx/cache_temp levels=2:2 keys_zone=cache_zone:30m max_size=2g inactive=60m use_temp_path=off;upstream cache_server {server 121.42.11.34:1010;server 121.42.11.34:1020;
}server {listen 80;server_name cache.lion.club;location / {proxy_cache cache_zone; #设置缓存内存,上面配置中已经定义好的proxy_cache_valid 200 5m; #缓存状态为200的请求,缓存时长为5分钟proxy_cache_key $request_uri; #缓存文件的key为请求的URIadd_header Nginx-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status #把缓存状态设置为头部信息,响应给客户端proxy_pass http://cache_server; #代理转发}
}
缓存就是这样配置,我们可以在 /etc/nginx/cache_temp 路径下找到相应的缓存文件。
对于一些实时性要求非常高的页面或数据来说,就不应该去设置缓存,下面来看看如何配置不缓存的内容。
添加过滤条件,过滤请求不缓存:
# 缓存文件设置
proxy_cache_path /etc/nginx/cache_temp levels=2:2 keys_zone=cache_zone:30m max_size=2g inactive=60m use_temp_path=off;upstream cache_server {server 121.42.11.34:1010;server 121.42.11.34:1020;
}server {listen 80;server_name cache.lion.club;# URI 中后缀为 .txt 或 .text 的设置变量值为 "no cache"if ($request_uri ~ \.(txt|text)$) {set $cache_name "no cache"}location / {proxy_no_cache $cache_name; #判断该变量是否有值,如果有值则不进行缓存,如果没有值则进行缓存proxy_cache cache_zone; #设置缓存内存proxy_cache_valid 200 5m; #缓存状态为200的请求,缓存时长为5分钟proxy_cache_key $request_uri; #缓存文件的key为请求的URIadd_header Nginx-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status #把缓存状态设置为头部信息,响应给客户端proxy_pass http://cache_server; #代理转发}
}
二、栗子
rewrite实例演示
server{listen 80;server_name fe.lion.club; #要在本地hosts文件进行配置root html;location /search {rewrite ^/(.*) https://www.baidu.com redirect; #返回 302 并临时重定向到百度}location /images {rewrite /images/(.*) /pics/$1;}location /pics {rewrite /pics/(.*) /photos/$1;}location /photos {}
}
按照这个配置我们来分析:
- 当访问 fe.lion.club/search 时,自动重定向到 https://www.baidu.com
- 当访问 fe.lion.club/images/1.jpg 时:
- 找到 /images 的 location ,然后重写 URL 为 fe.lion.club/pics/1.jpg
- 找到 /pics 的 location ,继续重写 URL 为 fe.lion.club/photos/1.jpg
- 找到 /photos 的 location 后,去 html/photos 目录下寻找 1.jpg 静态资源。
负载均衡演示
配置负载均衡主要是要使用 upstream 指令。
我们把 121.42.11.34 服务器作为上游服务器,做如下配置:
server {listen 8020;location / {return 200 'return 8020 \n';}
}server {listen 8030;location / {return 200 'return 8030 \n';}
}server {listen 8040;location / {return 200 'return 8040 \n';}
}
把 121.5.180.193 服务器作为代理服务器,做如下配置:
#1. 配置本地 hosts
sudo tee -a /etc/hosts <<-EOF
121.5.180.193 balance.lion.club
EOF#2. 代理配置
#/etc/nginx/conf.d/demo-nginx.conf
tee /etc/nginx/conf.d/demo-nginx.conf <<-EOF
upstream demo_server {server 121.42.11.34:8020;server 121.42.11.34:8030;server 121.42.11.34:8040;
}server {listen 80;server_name balance.lion.club;location /balance/ {proxy_pass http://demo_server;}
}
配置完成后重启 Nginx 服务器。并且在需要访问的客户端配置好 ip 和域名的映射关系。
在客户端机器执行 curl http://balance.lion.club/balance/ 命令:

如图所示:负载均衡的配置已经生效了,通过简单的"轮询策略"进行上游服务器分发,每次给我们分发的上游服务器都不一样。
接下来,我们再来了解下 Nginx 的其它分发策略:hash、ip_hash 和 least_conn最少连接数算法。
hash、ip_hash 和 least_conn
#### hash 算法
#通过指定关键字作为 hash-key ,基于 hash 算法映射到特定的上游服务器中。
#关键字可以包含有变量、字符串。
upstream demo_server {#表示使用 request_uri变量作为 hash的 key值,只要访问的 URI 保持不变,就会一直分发给同一台服务器。hash $request_uri;server 121.42.11.34:8020;server 121.42.11.34:8030;server 121.42.11.34:8040;
}#### ip_hash 算法(可以有效解决后台服务器 session 保持的问题)
#根据客户端的请求 ip进行判断,只要 ip地址不变,就永远分配到同一台主机。
upstream demo_server {ip_hash;server 121.42.11.34:8020;server 121.42.11.34:8030;server 121.42.11.34:8040;
}#### least_conn最少连接数算法
#各个 worker子进程通过读取共享内存的数据,获取后端服务器的信息来挑选一台,当前已建立“连接数最少”的服务器进行分配请求。
upstream demo_server {zone test 10M; #zone可以设置共享内存空间的名字和大小least_conn;server 121.42.11.34:8020;server 121.42.11.34:8030;server 121.42.11.34:8040;
}server {listen 80;server_name balance.lion.club;location /balance/ {proxy_pass http://demo_server;}
}
配置本地 hosts
sudo tee -a /etc/hosts <<-EOF
121.5.180.193 balance.lion.club
EOF
proxy_pass实例演示
用户请求URL:/bbs/abc/test.html
-
不带 / 的用法:
#不带 / 意味着 Nginx 不会修改用户 URL ,而是直接透传给上游的应用服务器; location /bbs/ {proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; }分析:与 alias 相似
- 请求到达 Nginx 的 URL:/bbs/abc/test.html
- 请求到达上游应用服务器的 URL:/bbs/abc/test.html
- alias值=url: alias /$PATH/bbs/abc/
-
带 / 的用法:
#带 / 意味着 Nginx 会修改用户 URL ,修改方法是将 location 的参数从用户 URL 中删除; location /bbs/ {proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/; }分析:与 root 相似,没有拼接上 location
- 请求到达 Nginx 的 URL: /bbs/abc/test.html
- 请求到达上游应用服务器的URL: /abc/test.html
- root值=url-location:root /$PATH/abc/
正向代理
如果把局域网外的Internet想象成一个巨大的资源库,则局域网中的客户端要访问Internet,则需要通过代理服务器来访问,这种代理服务就称为正向代理。
Nginx正向代理涉及到的指令较少,只是对用户的访问进行一个转发,不做其他处理。配置如下:
server { resolver 192.168.1.1; #指定DNS服务器IP地址 listen 8080;location / {#设定代理服务器的协议和地址proxy_pass http://$http_host$request_uri;}
}
其中:
- resolver 必须的,表示DNS服务器;
- listen 指定监听端口号(不指定默认监听 80 端口);
- location 表示匹配用户访问的资源,并作进一步转交和处理,可用正则表达式匹配;
- proxy_pass 表示需要代理的地址;
- $http_host 表示用户访问资源的主机部分;
- $request_uri 表示用户访问资源的URI部分。
如:http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.6.3.tar.gz,则 $http_host=nginx.org,$request_uri=/download/nginx-1.6.3.tar.gz
反向代理
为了演示更加接近实际,准备了两台云服务器,分别是:121.42.11.34 与 121.5.180.193
我们把 121.42.11.34 服务器作为上游服务器,做如下配置:
#1. 页面 index.html
tee /usr/share/nginx/html/proxy/index.html <<-EOF
<h1> 121.42.11.34 proxy html </h1>
EOF#2. 代理配置
#/etc/nginx/conf.d/proxy-nginx.conf
tee /etc/nginx/conf.d/proxy-nginx.conf <<-EOF
server{listen 8080;server_name localhost;location /proxy/ {root /usr/share/nginx/html/proxy;index index.html;}
}
EOF#3. 配置完成后重新加载配置文件
nginx -s reload
把 121.5.180.193 服务器作为代理服务器,做如下配置:
#1. 配置本地 hosts
sudo tee -a /etc/hosts <<-EOF
121.5.180.193 proxy.lion.club
EOF#2. 代理配置
#/etc/nginx/conf.d/proxy-nginx.conf
tee /etc/nginx/conf.d/proxy-nginx.conf <<-EOF
upstream back_end {server 121.42.11.34:8080 weight=2 max_conns=1000 fail_timeout=10s max_fails=3;keepalive 32;keepalive_requests 80;keepalive_timeout 20s;
}server {listen 80;server_name proxy.lion.club;location /proxy {proxy_pass http://back_end/proxy;}
}
EOF
分析:
- 当访问 proxy.lion.club/proxy 时,通过 upstream 的配置找到 121.42.11.34:8080 ;
- 因此访问地址变为 http://121.42.11.34:8080/proxy ;
- 连接到 121.42.11.34 服务器,找到 8080 端口提供的 server ;
- 通过 server 找到 /usr/share/nginx/html/proxy/index.html 资源,最终展示出来。

location实例演示
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.nginx-test.com;#只有当访问 www.nginx-test.com/match_all/ 时,才会匹配到/usr/share/nginx/html/match_all/index.htmllocation = /match_all/ {root /usr/share/nginx/htmlindex index.html}#当访问 www.nginx-test.com/1.jpg 等路径时,会去 /usr/share/nginx/images/1.jpg 找对应的资源location ~ \.(jpeg|jpg|png|svg)$ {root /usr/share/nginx/images;}#当访问 www.nginx-test.com/bbs/ 时,会匹配上 /usr/share/nginx/html/bbs/index.htmllocation ^~ /bbs/ {root /usr/share/nginx/html;index index.html;}
}
server_name实例演示
因为虚拟域名进行测试,因此需要配置本地 DNS 解析,如果使用阿里云上购买的域名,则需要在阿里云上设置好域名解析。
#配置本地 DNS 解析 hosts
121.42.11.34 www.nginx-test.com
121.42.11.34 www.nginx-test.org
121.42.11.34 www.nginx-test.cn
121.42.11.34 mail.nginx-test.com
121.42.11.34 doc.nginx-test.com
121.42.11.34 fe.nginx-test.club
配置 nginx.conf 的 server 配置
# 完全匹配
server {listen 80;server_name www.nginx-test.com;root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/all-match/;location / {index index.html;}
}# 左匹配
server {listen 80;server_name *.nginx-test.com;root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/left-match/;location / {index index.html;}
}# 右匹配
server {listen 80;server_name www.nginx-test.*;root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/right-match/;location / {index index.html;}
}# 正则匹配
server {listen 80;server_name ~^.*\.nginx-test\..*$;root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/reg-match/;location / {index index.html;}
}
访问分析
- 当访问 <www.nginx-test.com> 时,都可以被匹配上,因此选择优先级最高的“完全匹配”;
- 当访问 <mail.nginx-test.com> 时,会进行“左匹配”;
- 当访问 <doc.nginx-test.com> 时,会进行“左匹配”;
- 当访问 <www.nginx-test.org> 时,会进行“右匹配”;
- 当访问 <www.nginx-test.cn> 时,会进行“右匹配”;
- 当访问 <fe.nginx-test.club> 时,会进行“正则匹配”;
内置变量实例演示
server{listen 8081;server_name var.lion-test.club;root /usr/share/nginx/html;location / {return 200 "remote_addr: $remote_addrremote_port: $remote_portserver_addr: $server_addrserver_port: $server_portserver_protocol: $server_protocolbinary_remote_addr: $binary_remote_addrconnection: $connectionuri: $urirequest_uri: $request_urischeme: $schemerequest_method: $request_methodrequest_length: $request_lengthargs: $argsarg_pid: $arg_pidis_args: $is_argsquery_string: $query_stringhost: $hosthttp_user_agent: $http_user_agenthttp_referer: $http_refererhttp_via: $http_viarequest_time: $request_timehttps: $httpsrequest_filename: $request_filenamedocument_root: $document_root";}
}
当我们访问 http://var.lion-test.club:8081/test?pid=121414&cid=sadasd 时,由于 Nginx 中写了 return 方法,因此 chrome 浏览器会默认为我们下载一个文件,下面展示的就是下载的文件内容:
remote_addr: 27.16.220.84
remote_port: 56838
server_addr: 172.17.0.2
server_port: 8081
server_protocol: HTTP/1.1
binary_remote_addr: 茉
connection: 126
uri: /test/
request_uri: /test/?pid=121414&cid=sadasd
scheme: http
request_method: GET
request_length: 518
args: pid=121414&cid=sadasd
arg_pid: 121414
is_args: ?
query_string: pid=121414&cid=sadasd
host: var.lion-test.club
http_user_agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.182 Safari/537.36
http_referer:
http_via:
request_time: 0.000
https:
request_filename: /usr/share/nginx/html/test/
document_root: /usr/share/nginx/html
Via
- https://www.cnblogs.com/ratelcloud/p/18595015
- https://www.cnblogs.com/lywJ/p/10710361.html