笔记内容转载自 AcWing 的 Web 应用课讲义,课程链接:AcWing Web 应用课。
CONTENTS
- 1. 创建父组件
- 2. 从上往下传递数据
- 3. 传递子节点
- 4. 从下往上调用函数
- 5. 兄弟组件间传递消息
- 6. 无状态函数组件
- 7. 组件的生命周期
本节内容是组件与组件之间的组合,例如用不同组件构成 DOM 树,以及给不同的组件传递数据或者调用不同组件的方法,还有不同组件的生命周期。
1. 创建父组件
我们还是继续在之前的 Box 组件上进行操作,首先创建一个 Boxes 组件,其中包含一系列 Box 组件。
在 components 目录中创建 boxes.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';class Boxes extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<h1>Boxes</h1>);}
}export default Boxes;
然后修改一下 index.js:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css';
import Boxes from './components/boxes';const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<Boxes />);
现在我们在 Boxes 中加入多个 Box,当一个组件中包含多个并列元素的时候,需要用一个标签将他们括起来,可以使用 React 中的一个虚拟标签 <React.Fragment>:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><Box /><Box /><Box /></React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
为了方便也可以用一个数组来表示,将 Box 的信息存到 state 里,由于 React 组件如果有若干个儿子那么他们的 key 需要不一样,因此还需要存一个唯一的 id:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 0},{id: 3, x: 0},{id: 4, x: 0},]} render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id} />))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
2. 从上往下传递数据
通过 this.props 属性可以从上到下传递数据。例如我们在 Boxes 中传递 x:
...class Boxes extends Component {state = { ...} render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id} x={box.x} name='yyj' />))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
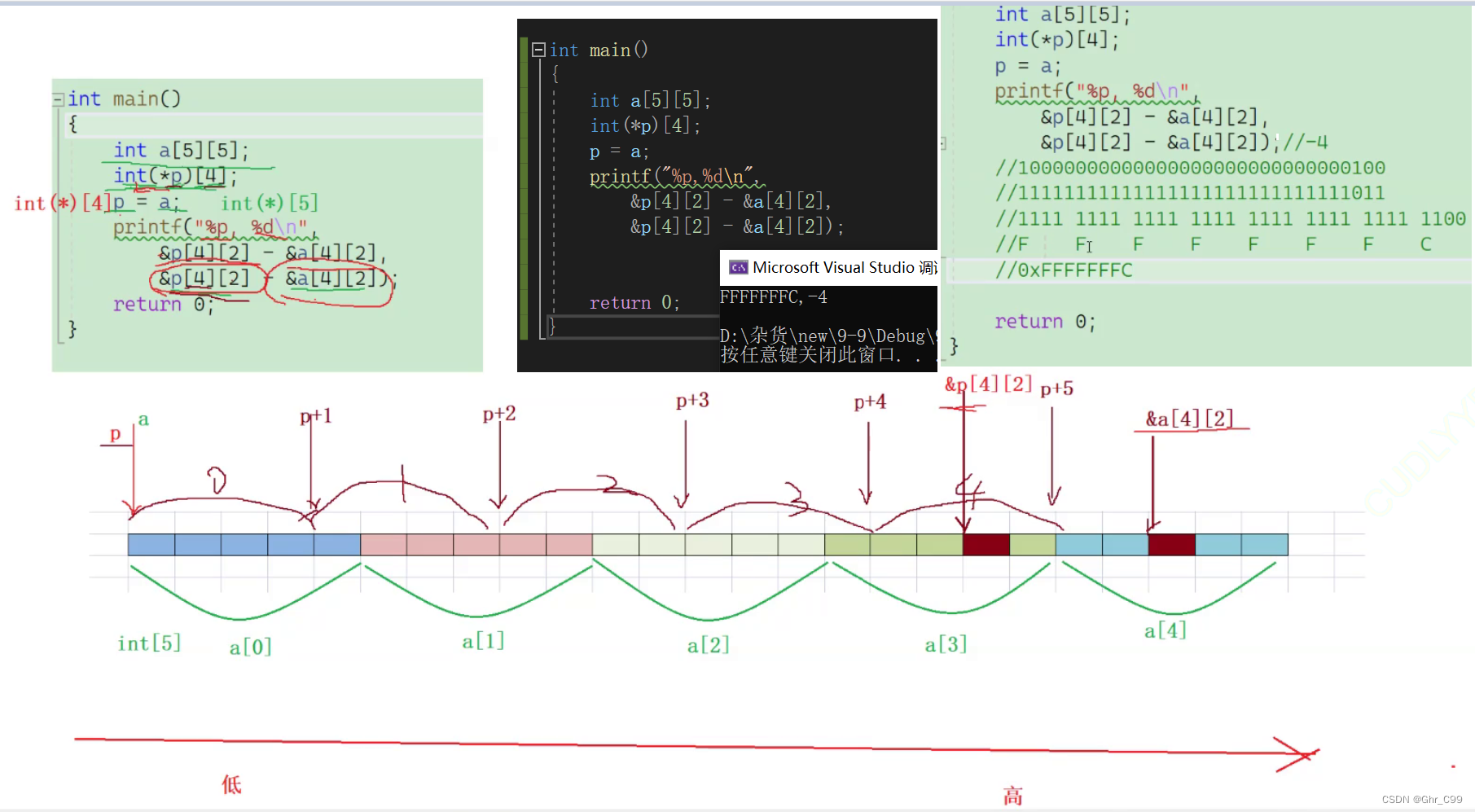
可以在 Box 中输出信息 console.log(this.props); 查看内容:
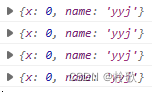
修改 Box 中的 x:
import React, { Component } from 'react'; // 输入imrc即可补全class Box extends Component { // 输入cc即可补全state = { x: this.props.x,};...
}export default Box;
3. 传递子节点
可以将标签写成 <Box></Box> 的形式,然后在标签中添加子标签:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 0},{id: 3, x: 0},{id: 4, x: 0},]} render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id} x={box.x} name='yyj'><h1>Title</h1></Box>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
这样 this.props 中会多一个属性 children,可以使用 [] 单独访问某个子标签。我们可以将这个传过来的值定义在任何地方,例如可以放到每个 Box 组件的最上方:
import React, { Component } from 'react'; // 输入imrc即可补全class Box extends Component { // 输入cc即可补全state = { x: this.props.x,};handleClickLeft = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x - step});}handleClickRight = (step) => {this.setState({x: this.state.x + step});}handleClickLeftTmp = () => {this.handleClickLeft(10);}render() { // Component类的函数,用来返回当前组件最后渲染的HTML结构是什么console.log(this.props);return (// HTML标签中可以使用{}写一个表达式<React.Fragment>{this.props.children}<div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.state.x}</div><button onClick={this.handleClickLeftTmp} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>Left</button><button onClick={() => this.handleClickRight(10)} className='btn btn-success m-2'>Right</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {...}
}export default Box;
4. 从下往上调用函数
父元素可以通过 this.props 向子元素传递信息,子元素也可以使用函数向父元素传递信息。假设我们需要实现通过点击删除按钮删除某个 Box,其信息保存在 Boxes 的 state 中,但是我们点击触发事件是在 Box 中(注意:每个组件的 this.state 只能在组件内部修改,不能在其他组件内修改)。
我们可以在父元素中定义好函数,然后将函数传给子元素:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 0},{id: 3, x: 0},{id: 4, x: 0},]}handleDelete = (boxId) => {// 遍历一遍state.boxes,将box.id不为传入的参数boxId的数据保留下来const res = this.state.boxes.filter(box => box.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: res});}render() { return (<React.Fragment>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id} id={box.id} x={box.x} name='yyj'onDelete={this.handleDelete}/>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
这样子元素就能调用函数对父元素进行操作了:
import React, { Component } from 'react'; // 输入imrc即可补全class Box extends Component { // 输入cc即可补全...render() { // Component类的函数,用来返回当前组件最后渲染的HTML结构是什么console.log(this.props);return (// HTML标签中可以使用{}写一个表达式<React.Fragment>...<button onClick={() => this.props.onDelete(this.props.id)} className='btn btn-danger m-2'>Delete</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {...}
}export default Box;
现在我们在 Boxes 中实现一个 Reset 按钮实现清空所有 Box 的 x:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 1},{id: 3, x: 2},{id: 4, x: 3},]}handleDelete = (boxId) => {...}handleReset = () => {const res = this.state.boxes.map(box => {return {id: box.id,x: 0,}});this.setState({boxes: res});}render() {console.log(this.state.boxes);return (<React.Fragment><buttononClick={this.handleReset}style={{marginBottom: '15px'}}className='btn btn-info'>Reset</button>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id} id={box.id} x={box.x} name='yyj'onDelete={this.handleDelete}/>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
在控制台观察时可以发现点击 Reset 按钮后 x 确实置零了,但是 Box 显示出来的 x 并没有改变,这是因为 state 值不能在外部修改,因此我们可以将 Box 中的 state 删掉,需要在该组件中渲染外面的 state 的值。
每个维护的数据仅能保存在一个 this.state 中,不要直接修改 this.state 的值,因为 setState 函数可能会将修改覆盖掉。
修改 Boxes,将之前 Box 中操作 state 的函数转移过来:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 1},{id: 3, x: 2},{id: 4, x: 3},]}handleDelete = (boxId) => {// 遍历一遍state.boxes,将box.id不为传入的参数boxId的数据保留下来const res = this.state.boxes.filter(box => box.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: res});}handleReset = () => {const res = this.state.boxes.map(box => {return {id: box.id,x: 0,}});this.setState({boxes: res});}// 需要知道修改的是哪个boxhandleClickLeft = (box) => {const boxes = [...this.state.boxes]; // 浅拷贝一份const k = boxes.indexOf(box); // 传入的box是引用,找出其在boxes中的下标kboxes[k] = {...boxes[k]}; // 再clone一遍,相当于创建新的state,深拷贝boxes[k].x--;this.setState({boxes: boxes});}handleClickRight = (box) => {const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box);boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x++;this.setState({boxes: boxes});}render() {return (<React.Fragment><buttononClick={this.handleReset}style={{marginBottom: '15px'}}className='btn btn-info'>Reset</button>{this.state.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id} id={box.id} x={box.x} name='yyj'onDelete={this.handleDelete}onClickLeft={() => this.handleClickLeft(box)}onClickRight={() => this.handleClickRight(box)}/>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
然后修改 Box,将 this.state 替换成父组件传递过来的 props:
import React, { Component } from 'react'; // 输入imrc即可补全class Box extends Component { // 输入cc即可补全render() { // Component类的函数,用来返回当前组件最后渲染的HTML结构是什么return (// HTML标签中可以使用{}写一个表达式<React.Fragment><div style={this.getStyles()}>{this.props.x}</div><button onClick={this.props.onClickLeft} className='btn btn-primary m-2'>Left</button><button onClick={this.props.onClickRight} className='btn btn-success m-2'>Right</button><button onClick={() => this.props.onDelete(this.props.id)} className='btn btn-danger m-2'>Delete</button></React.Fragment>);}getStyles() {let styles = {width: '50px',height: '50px',backgroundColor: 'lightblue',color: 'white',textAlign: 'center',lineHeight: '50px',borderRadius: '5px',position: 'relative',left: this.props.x};if (this.props.x === 0) {styles.backgroundColor = 'orange';}return styles;}
}export default Box;
5. 兄弟组件间传递消息
如果组件的结构关系更为复杂,那么就需要将多个组件共用的数据存放到最近公共祖先的 this.state 中。
我们创建一个 App 组件,其包含两个子组件 NavBar(导航栏)和 Boxes,这两个组件为兄弟组件。
首先是 navbar.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';class NavBar extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<nav className="navbar bg-body-tertiary"><div className="container-fluid"><a className="navbar-brand" href="/">Navbar</a></div></nav>);}
}export default NavBar;
然后是 app.jsx:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Boxes from './boxes';class App extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<React.Fragment><div className='container'><NavBar /><Boxes /></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
现在假设我们要在 NavBar 中存放 Boxes 中有几个 Box 的信息,那么只能把信息放到这两个组件的最近公共祖先 App 中。
我们将 Boxes 中与 state 有关的内容都移到 App 中:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Box from './box';class Boxes extends Component {render() {return (<React.Fragment><buttononClick={this.props.onReset}style={{marginBottom: '15px'}}className='btn btn-info'>Reset</button>{this.props.boxes.map(box => (<Box key={box.id} id={box.id} x={box.x} name='yyj'onDelete={this.props.onDelete}onClickLeft={() => this.props.onClickLeft(box)}onClickRight={() => this.props.onClickRight(box)}/>))}</React.Fragment>);}
}export default Boxes;
移动后的 App 如下:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Boxes from './boxes';class App extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 1},{id: 3, x: 2},{id: 4, x: 3},]}handleDelete = (boxId) => {// 遍历一遍state.boxes,将box.id不为传入的参数boxId的数据保留下来const res = this.state.boxes.filter(box => box.id !== boxId);this.setState({boxes: res});}handleReset = () => {const res = this.state.boxes.map(box => {return {id: box.id,x: 0,}});this.setState({boxes: res});}// 需要知道修改的是哪个boxhandleClickLeft = (box) => {const boxes = [...this.state.boxes]; // 浅拷贝一份const k = boxes.indexOf(box); // 传入的box是引用,找出其在boxes中的下标kboxes[k] = {...boxes[k]}; // 再clone一遍,相当于创建新的state,深拷贝boxes[k].x--;this.setState({boxes: boxes});}handleClickRight = (box) => {const boxes = [...this.state.boxes];const k = boxes.indexOf(box);boxes[k] = {...boxes[k]};boxes[k].x++;this.setState({boxes: boxes});}render() { return (<React.Fragment><div className='container'><NavBarboxesCount={this.state.boxes.length} // 将长度传给NavBar/><Boxesboxes={this.state.boxes}onReset={this.handleReset}onClickLeft={this.handleClickLeft}onClickRight={this.handleClickRight}onDelete={this.handleDelete}/></div></React.Fragment>);}
}export default App;
现在即可在 NavBar 中读取 Boxes 的长度信息了:
import React, { Component } from 'react';class NavBar extends Component {state = { } render() { return (<nav className="navbar bg-body-tertiary"><div className="container-fluid"><a className="navbar-brand" href="/">Navbar <span>Boxes Count: {this.props.boxesCount}</span></a></div></nav>);}
}export default NavBar;
6. 无状态函数组件
当组件中没有用到 this.state 时,可以简写为无状态的函数组件。类相对于函数最大的好处就是可以很方便地维护状态(局部变量)。
无状态函数组件(Stateless Funtion Component),输入 sfc 即可自动补全出来。函数组件相当于只有 render 函数的类组件。注意:函数的传入参数为 props 对象:
import React from 'react';const NavBar = (props) => {return (<nav className="navbar bg-body-tertiary"><div className="container-fluid"><a className="navbar-brand" href="/">Navbar <span>Boxes Count: {props.boxesCount}</span></a></div></nav>);
}export default NavBar;
7. 组件的生命周期
Mount周期(挂载,表示对象被创建出来),执行顺序(按顺序执行三个函数):constructor() -> render() -> componentDidMount()Update周期(修改,例如点击按钮),执行顺序:render() -> componentDidUpdate()Unmount周期(删除),执行顺序:componentWillUnmount()
其中,componentDidUpdate 函数有两个参数,分别表示更新前的 props 和 state:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import NavBar from './navbar';
import Boxes from './boxes';class App extends Component {state = { boxes: [{id: 1, x: 0},{id: 2, x: 1},{id: 3, x: 2},{id: 4, x: 3},]}componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {console.log('App - Update');console.log(prevProps, this.props);console.log(prevState, this.state);}...render() {console.log('App - Render');return (...);}
}export default App;
输出的 state 内容如下:
{boxes: Array(4)}boxes: Array(4)0: {id: 1, x: 0}1: {id: 2, x: 1}2: {id: 3, x: 2}3: {id: 4, x: 3}length: 4[[Prototype]]: Array(0)[[Prototype]]: Object{boxes: Array(4)}boxes: Array(4)0: {id: 1, x: 1} (此处有区别)1: {id: 2, x: 1}2: {id: 3, x: 2}3: {id: 4, x: 3}length: 4[[Prototype]]: Array(0)[[Prototype]]: Object
![[杂谈]-从硬件角度理解二进制数](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/02bcfebc19c94ac786d4fad8ec49c110.png#pic_center)


![[libc-2.31 off_by_null] N0wayBack ezheap练习](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/18c2e9f5c29c4ea1b197cf08bb39bf19.png)