1.红黑树的迭代器与改造
①红黑树的迭代器
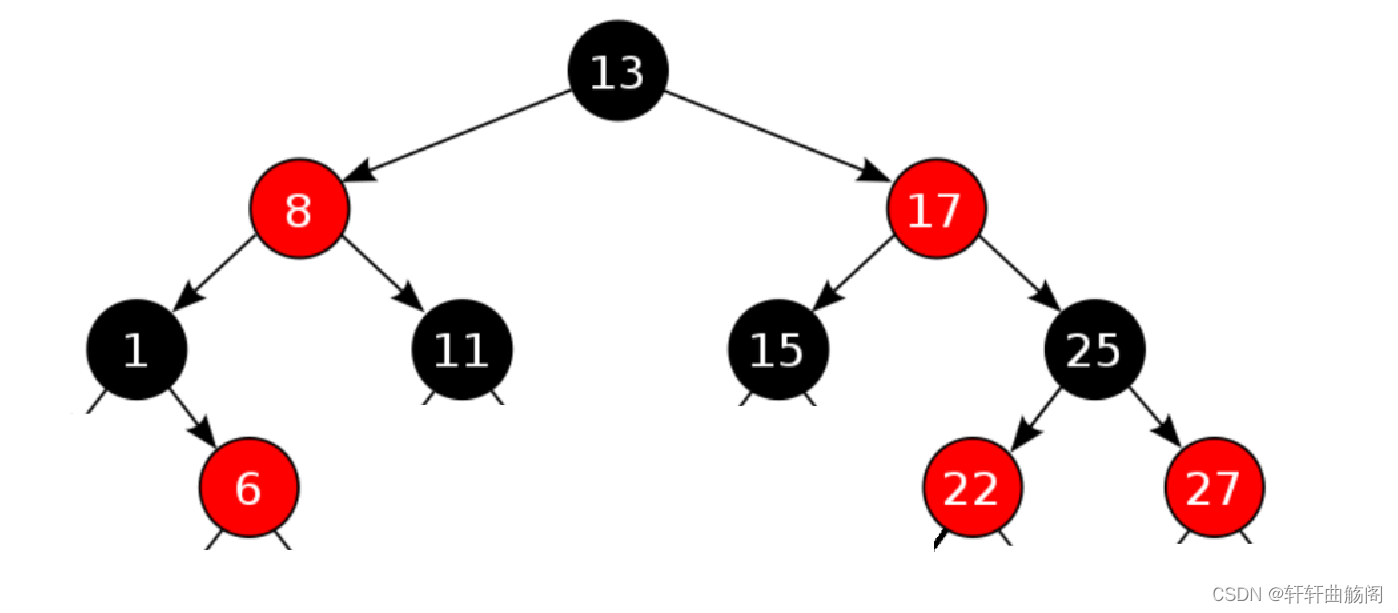
对于上面这棵红黑树,我们可以很容易得知道begin()是红黑树的最左节点,end()应该是一个空节点。即
iterator begin()
{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return cur;
}iterator end()
{return iterator(nullptr);
}接下来定义iterator及其具体操作
template<class T>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T> Self;RBTreeIterator(Node* node): _node(node){}// 让迭代器具有类似指针的行为T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// 迭代器可以移动:前置/后置++ Self& operator++(){// 这里的++是为了找到下一个比当前节点大的位置// 结合图像具体来看就是两种情况// 第一种是如果当前节点有右子树,// 那么下一个节点就是右子树中的最左节点// 第二种是如果当前节点没有右子树,// 那么下一个节点就是“当前节点是父亲的左子树”的节点// 如果不是的话就继续向上更新,直到更新到根节点if (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;while (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}if (parent && cur == parent->_left)_node = parent;else_node = nullptr;}return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);++(*this);return tmp;}// 迭代器可以移动:前置/后置-- Self& operator--(){// 这里的大致逻辑与++类似if (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}if (parent && cur == parent->_right)_node = parent;else_node = nullptr;}return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);--(*this);return tmp;}// 让迭代器可以比较bool operator!=(const Self& s)const{return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s)const{return _node == s._node;}Node* _node;
};②红黑树的改造
// set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
// map->RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
template<class K, class T, class KeyofT>
class RBTree
{
public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T*, T&> iterator;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T*, const T&> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return (iterator)cur;}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return (const_iterator)cur;}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}Node* Find(const T& data){KeyofT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(data) < kot(cur->_data)){cur = cur->_left;}else if (data > kot(cur->_data)){cur = cur->_right;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyofT kot;if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_color = BLACK;return make_pair((iterator)_root, true);}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;// 寻找要插入的位置while (cur){if (kot(data) < kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(data) > kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return make_pair((iterator)cur, false);}}// 到此处cur已经指向了应该插入的位置,// 然后判断应该插入到parent的哪边cur = new Node(data);if (kot(data) > kot(parent->_data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;// 插入完成后判断一下// 若父节点是黑就无需调整// 而当父节点是红就需要进行调整while (parent && parent->_color == RED){Node* grandpa = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandpa->_left){Node* uncle = grandpa->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){uncle->_color = parent->_color = BLACK;grandpa->_color = RED;cur = grandpa;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (uncle == nullptr){if (parent->_left == cur){// grandpa// parent//curRotateR(grandpa);grandpa->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;}else{// grandpa// parent// curRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandpa);cur->_color = BLACK;grandpa->_color = RED;}}else // uncle存在且为黑{if (parent->_left == cur){// grandpa// parent//curRotateR(grandpa);grandpa->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;}else{// grandpa// parent// curRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandpa);cur->_color = BLACK;grandpa->_color = RED;}}break;}}else // parent == grandpa->_right{Node* uncle = grandpa->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){uncle->_color = parent->_color = BLACK;grandpa->_color = RED;cur = grandpa;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (uncle == nullptr){if (parent->_left == cur){//grandpa// parent//curRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandpa);cur->_color = BLACK;grandpa->_color = RED;}else{//grandpa// parent// curRotateL(grandpa);grandpa->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;}}else // uncle存在且为黑{if (parent->_left == cur){//grandpa// parent//curRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandpa);cur->_color = BLACK;grandpa->_color = RED;}else{//grandpa// parent// curRotateL(grandpa);grandpa->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;}}break;}}}if (cur->_parent == nullptr){cur->_color = BLACK;}return make_pair((iterator)cur, true);}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* cur = parent->_right; // 记录当前节点Node* curleft = cur->_left; // 记录当前节点的左节点// 如果当前节点的左节点为空说明是h为0的情况// 不为空时就要进行节点间的连接if (curleft){curleft->_parent = parent;}parent->_right = curleft;cur->_left = parent;// 此时需要确定parent是否属于子树if (parent == _root){_root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}else // 此时parent以下的节点属于子树{cur->_parent = parent->_parent;// 确认parent与其父节点间的关系// 然后将cur与parent的父节点连接起来if (parent->_parent->_left == parent){parent->_parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_parent->_right = cur;}}parent->_parent = cur;}void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* cur = parent->_left; // 记录当前节点Node* curright = cur->_right; // 记录当前节点的右节点// 如果当前节点的右节点为空说明是h为0的情况// 不为空时就要进行节点间的连接if (curright){curright->_parent = parent;}parent->_left = curright;cur->_right = parent;// 此时需要确定parent是否属于子树if (parent == _root){_root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}else // 此时parent以下的节点属于子树{cur->_parent = parent->_parent;// 确认parent与其父节点间的关系// 然后将cur与parent的父节点连接起来if (parent->_parent->_left == parent){parent->_parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_parent->_right = cur;}}parent->_parent = cur;}private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};2.map的模拟实现
namespace my_map
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}3.set的模拟实现
namespace my_set
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}// 使用iterator RBTree::const_iterator时,有// 无法从“std::pair<RBTreeIterator<T,T *,T &>,bool>”// 转换为“std::pair<RBTreeIterator<T,const T *,const T &>,bool>”// pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)// {// return _t.Insert(key);// }pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){// 将插入后的结果用一个key类型的pair接收pair<typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(key);// 用ret的的元素构造key的特定pair// 目的:这里的iterator实际是const_iterator, // 转换之后可以使key的第一个元素不被修改return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}4.测试
#include "my_map.h"
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include "my_set.h"//int main()
//{
// RBTree<int, int, pair<int, int>> t;
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
// {
// t.Insert(i);
// }
//
// RBTree<int, int, pair<int, int>>::iterator it = t.begin();
// while (it != t.end())
// {
// cout << *it << " ";
// it++;
// }
//
// return 0;
//}//int main()
//{
// my_set::set<int> st;
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
// {
// st.insert(i);
// }
//
// auto it = st.begin();
// while (it != st.end())
// {
// cout << *it << " ";
// ++it;
// }
//
// return 0;
//}//int main()
//{
// my_set::set<int> st;
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
// {
// st.insert(i);
// }
//
// my_set::set<int>::iterator it = st.begin();
// while (it != st.end())
// {
// //if (*it % 2 == 0)
// //{
// // *it += 10;
// //}
// cout << *it << " ";
// ++it;
// }
//
// return 0;
//}//int main()
//{
// my_map::map<string, string> st;
// string s1 = "a";
// string s2 = "b";
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
// {
// st.insert(make_pair(s1, s2));
// s1[0]++;
// s2[0]++;
// }
//
// my_map::map<string, string>::iterator it = st.begin();
// while (it != st.end())
// {
// //if (*it % 2 == 0)
// //{
// // *it += 10;
// //}
// cout << (*it).first << ":"<< (*it).second << " "<<endl;
// ++it;
// }
//
// return 0;
//}int main()
{my_map::map<string, string> dict;dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "xxx"));dict["left"]; // 插入for (const auto& kv : dict){cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}cout << endl;dict["left"] = "左边"; // 修改dict["sort"] = "排序"; // 修改dict["right"] = "右边"; // 插入+修改for (const auto& kv : dict){cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}cout << endl;return 0;
}