一、初识 MQ
1. 同步通讯
时效性强,立即获取结果
微服务间基于 Feign 的调用就属于同步
方式,存在一些问题:
① 耦合度高
② 性能和吞吐能力不如异步
③ 额外资源消耗
④ 级联失败问题
2. 异步通讯
异步调用常见实现就是事件驱动模式
优点:
① 服务解耦
② 性能提升,吞吐量提高
③ 服务没有强依赖,不担心级联问题
④ 流量削峰
缺点
① 依赖 Broker(事件代理者) 的可靠性、
安全性、吞吐能力
② 架构复杂的情况下,业务没有明显
的流程线,不好追踪管理
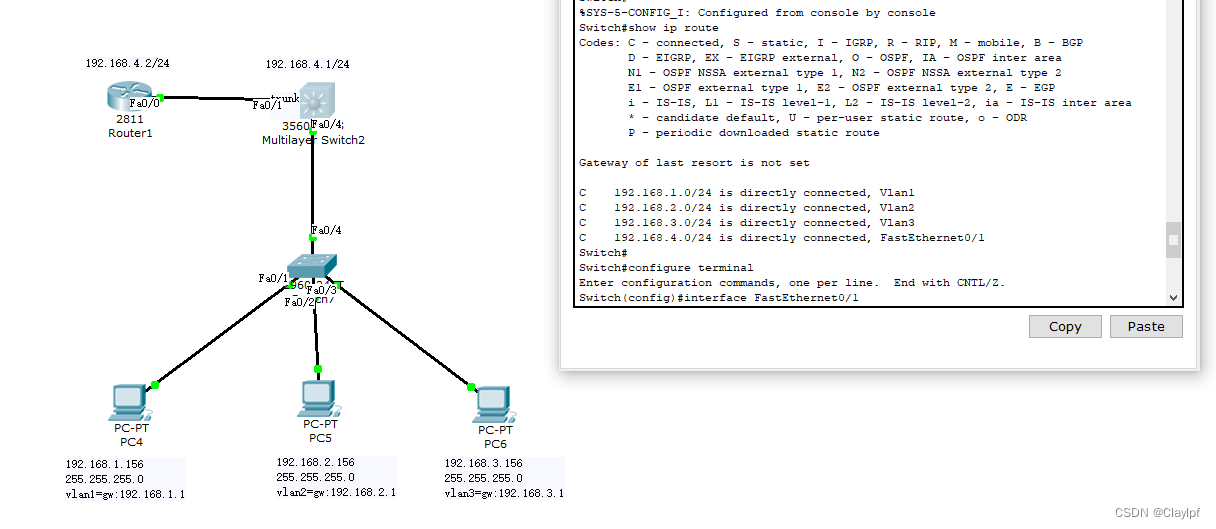
3. MQ 常见框架
MQ (MessageQueue),中文是消息队列,
字面来看就是存放消息的队列,也就是事
件驱动架构中的 Broker
二、RabbitMQ 快速入门
1. RabbitMQ 概述
RabbitMQ 是基于 Erlang 语言开发的开源
消息通信中间件
官网地址:https://www.rabbitmq.com/
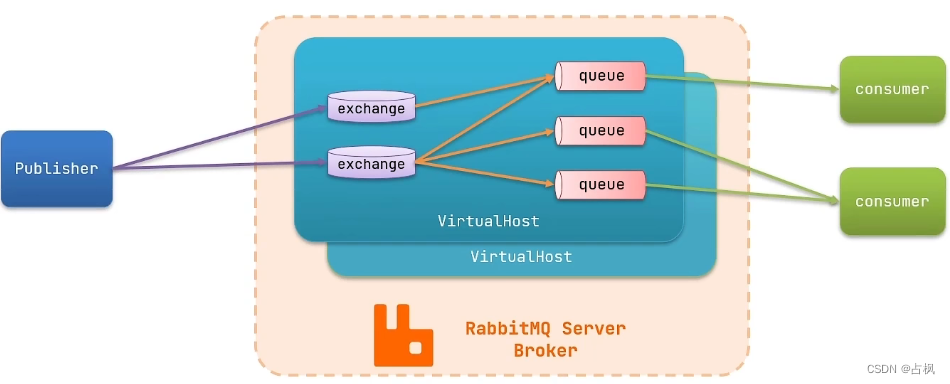
channel(通道):操作 MQ 的工具
exchange(交换机):路由消息到队列中
queue(队列):缓存消息
virtual host:虚拟主机,是对 queue、
exchange 等资源的逻辑分组
2. 常见消息模型
(1) 基本消息队列(BasicQueue)
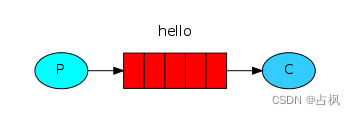
1) 官方的 HelloWorld 是基于最基础的
消息队列模型来实现的,只包括三个
角色:
publisher:消息发布者,将消息发送到队列
queue queue:消息队列,负责接受并缓存消息
consumer:订阅队列,处理队列中的消息

2) 基本消息队列的消息发送流程:
① 建立 connection
② 创建 channel
③ 利用 channel 声明队列
④ 利用 channel 向队列发送消息
3) 基本消息队列的消息接收流程:
① 建立 connection
② 创建 channel
③ 利用 channel 声明队列
④ 定义 consumer 的消费行为
handleDelivery()
⑤ 利用 channel 将消费者与队列
绑定
(2) 工作消息队列(WorkQueue)

可以提高消息处理速度,避免队列消
息堆积
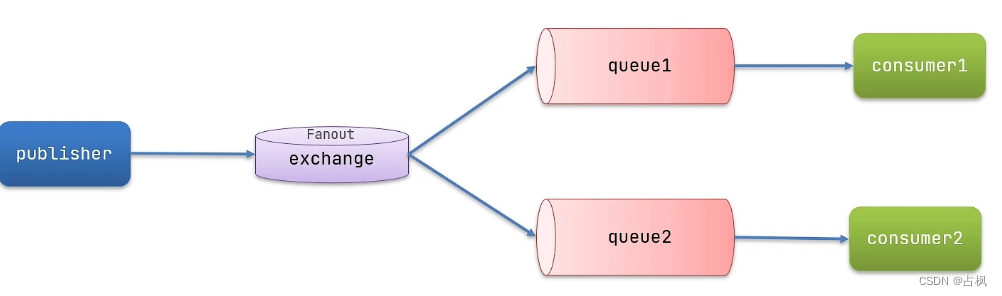
(3) 发布订阅(Publish、Subscribe)
允许将同一消息发送给多个消费者
实现方式是加入了 exchange(交换机)
注意:exchange 负责消息路由,而
不是存储,路由失败则消息丢失
根据交换机类型不同分为三种:
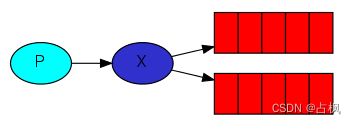
1) Fanout Exchange:广播
将接收到的消息广播到每一个跟其
绑定的 queue
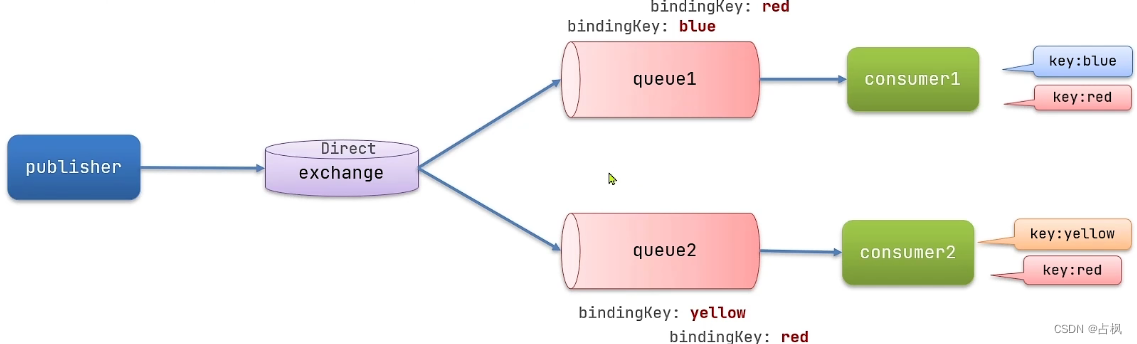
2) Direct Exchange:路由
将接收到的消息根据规则路由到指定
的 Queue,因此称为路由模式(routes)
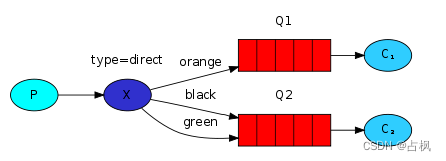
① 每一个 Queue 都与 Exchange 设置
一个 BindingKey
② 发布者发送消息时,指定消息的
RoutingKey
③ Exchange 将消息路由到 BindingKey
与消息 RoutingKey 一致的队列
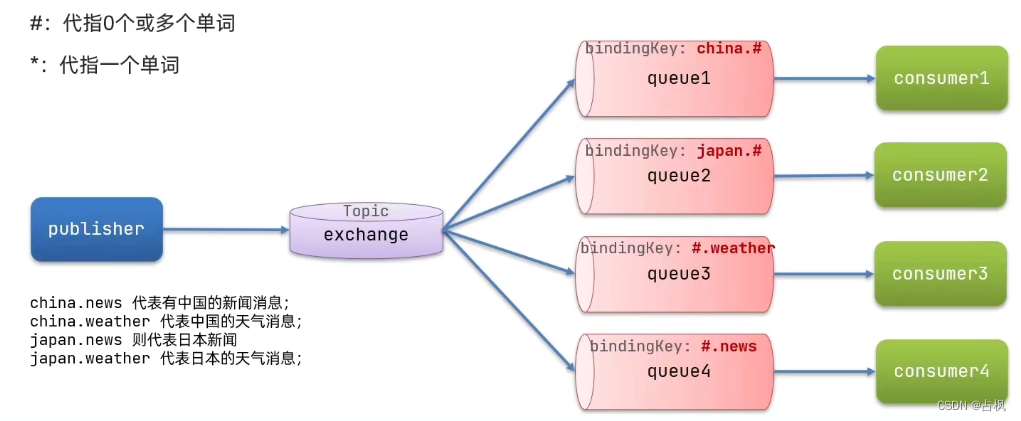
3) Topic Exchange:主题
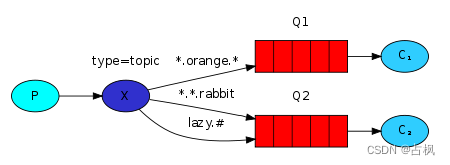
TopicExchange 与 DirectExchange 类
似,区别在于 routingKey 必须是多个
单词的列表,并且以 . 分割
Queue 与 Exchange 指定 BindingKey 时
可以使用通配符:
#:代指0个或多个单词
*:代指一个单词
三、SpringAMQP
SpringAmqp 的官方地址:
https://spring.io/projects/spring-amqp
AMQP,即 Advanced Message Queuing
Protocol,一个提供统一消息服务的应用
层标准高级消息队列协议,基于此协议的
客户端与消息中间件可传递消息,并不受
客户端/中间件不同产品,不同的开发语言
等条件的限制
Spring AMQP 项目将核心 Spring 概念应
用于基于 AMQP 的消息传递解决方案的
开发的一套 API 规范,它提供了一个模板
作为发送和接收消息的高级抽象
其中 spring-amqp 是基础抽象,
spring-rabbit 是底层的默认实现
1. 利用 SpringAMQP 实现 HelloWorld 中的基
础消息队列功能
(1) 在父工程中引入 spring-amqp 的依赖
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ-->
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
(2) 在 publisher 服务中利用 RabbitTemplate
发送消息到 simple.queue 这个队列
① 在 publisher 服务中编写 application.yml,
添加 mq 连接信息:
spring:rabbitmq:host: 192.168.150.110 # 主机名port: 5672 # 端口virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机username: rootpassword: 123456
② 在 publisher 服务中新建一个测试类,
编写测试方法:
public class PublisherTest {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@Testpublic void testSimpleQueue() {String queueName = "simple.queue";String message = "hello, spring amqp";rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message);}
}
(3) 在 consumer 服务中编写消费逻辑,绑定
simple.queue 这个队列
① 在 consumer 服务中编写 application.yml,
添加 mq 连接信息:
spring:rabbitmq:host: 192.168.150.110 # 主机名port: 5672 # 端口virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机username: rootpassword: 123456② 在 consumer 服务中新建一个类,编写消
费逻辑:
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {@RabbitListener(queues = {"simple.queue"})public void listenSimpleQueue(String msg) {System.out.println(msg);}
}
注意:消息一旦消费就会从队列删除,
RabbitMQ 没有消息回溯功能
2. 使用 WorkQueue 实现一个队列绑定多个
消费者
(1) 生产者循环发送消息到 simple.queue
@Test
public void testSimpleQueue() throws InterruptedException {String queueName = "simple.queue";String message = "hello, spring amqp";for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message + i);Thread.sleep(20);}
}
(2) 编写两个消费者,都监听 simple.queue
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {@RabbitListener(queues = {"simple.queue"})public void listenSimpleQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("消费者1" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());Thread.sleep(20);}@RabbitListener(queues = {"simple.queue"})public void listenSimpleQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {System.err.println("消费者2" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());Thread.sleep(200);}
}
AMQP 有一个消息预取机制,设置 preFetch
这个值,可以控制预取消息的上限:
spring:rabbitmq:host: 190.92.246.107 # 主机名port: 5672 # 端口virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机username: rootpassword: 123456listener:simple:prefetch: 1
3. FanoutExchange 的使用
(1) 在 consumer 服务中,利用代码声明队
列、交换机,并将两者绑定
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {@Beanpublic FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {return new FanoutExchange("root.fanout");}@Beanpublic Queue fanoutQueue1() {return new Queue("fanout.queue1");}@Beanpublic Queue fanoutQueue2() {return new Queue("fanout.queue2");}@Beanpublic Binding bindQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanoutExchange);}@Beanpublic Binding bindQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanoutExchange);}
}
(2) 在 consumer 服务中,编写两个消费者
方法,分别监听 fanout.queue1 和
fanout.queue2
@RabbitListener(queues = {"fanout.queue1"})
public void listenFanoutQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("fanout.queue1消费者" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
}@RabbitListener(queues = {"fanout.queue2"})
public void listenFanoutQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {System.err.println("fanout.queue2消费者" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
}
(3) 在 publisher 中编写测试方法,向
itcast.fanout 发送消息
@Test
public void testSendFanoutExchange() {String exchangeName = "root.fanout";String message = "hello everyone";rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "", message);
}
交换机的作用:
① 接收 publisher 发送的消息
② 将消息按照规则路由到与之绑定的
队列
③ 不能缓存消息,路由失败,消息丢
失
④ FanoutExchange 的会将消息路由
到每个绑定的队列
声明队列、交换机、绑定关系的 Bean:
Queue
FanoutExchange
Binding
4. DirectExchange 的使用
(1) 利用 @RabbitListener 声明 Exchange、
Queue、RoutingKey
(2) 在 consumer 服务中,编写两个消费者
方法,分别监听 direct.queue1 和
direct.queue2
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "root.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),key = {"blue","red"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg) {System.err.println("direct.queue1消费者" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());}@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "root.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),key = {"yellow","red"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg) {System.err.println("direct.queue2消费者" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());}
(3) 在 publisher 中编写测试方法,向 itcast.
direct发送消息
@Test
public void testSendDirectExchange() {String exchangeName = "root.direct";String message = "hello red";rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "red", message);
}
Direct 交换机与 Fanout 交换机的差异:
① Fanout 交换机将消息路由给每一个
与之绑定的队列
② Direct 交换机根据 RoutingKey 判断
路由给哪个队列
③ 如果多个队列具有相同的 RoutingKey,
则与 Fanout 功能类似
5. TopicExchange 的使用
(1) 利用 @RabbitListene r声明 Exchange、
Queue、RoutingKey
(2) 在 consumer 服务中,编写两个消费者方
法,分别监听topic.queue1和topic.queue2
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue1"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "root.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),key = {"china.#"}
))
public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg) {System.err.println("topic.queue1消费者" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue2"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "root.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),key = {"#.news"}
))
public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg) {System.err.println("topic.queue2消费者" + "【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
}
(3) 在 publisher 中编写测试方法,向 itcast.
topic 发送消息
@Test
public void testSendTopicExchange() {String exchangeName = "root.topic";String message = "hello world";rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "china.news", message);
}
6. 消息转换器
在 SpringAMQP 的发送方法中,接收消息
的类型是 Object,也就是说我们可以发送
任意对象类型的消息,SpringAMQP 会帮
我们序列化为字节后发送
SpringAMQP 中消息的序列化和反序列化
是利用 MessageConverter 实现的,默认
是 JDK 的序列化,其中发送方与接收方必
须使用相同的 MessageConverter
推荐用 JSON 方式序列化:
① 先在 publisher 服务引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
② 在 publisher 服务声明 MessageConverter
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter() {return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
③ 在 consumer 服务引入 Jackson 依赖:
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
④ 在 consumer 服务定义 MessageConverter:
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter() {return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
⑤ 定义一个消费者,监听 object.queue 队列
并消费消息:
@RabbitListener(queues = "object.queue")
public void listenObjectQueue(Map<String, Object> msg) {System.out.println("收到消息:【" + msg + "】");
}