目录
- 1.解题思路
- 2.代码实现
1.解题思路
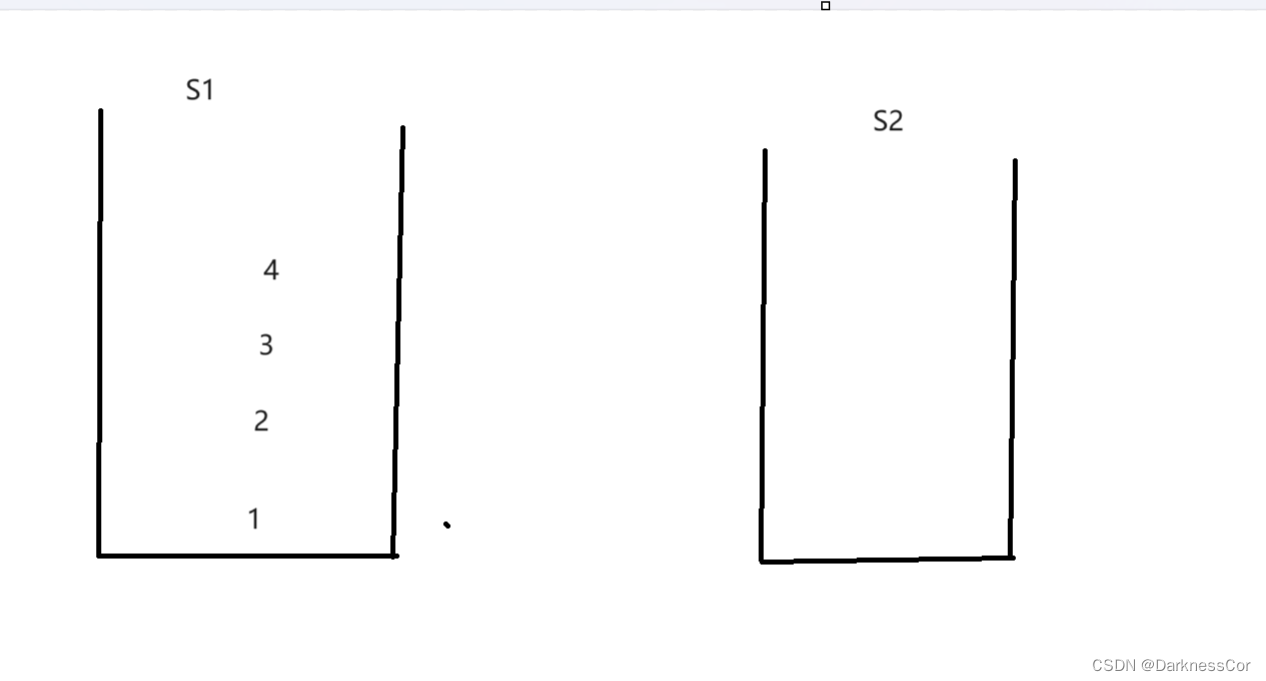
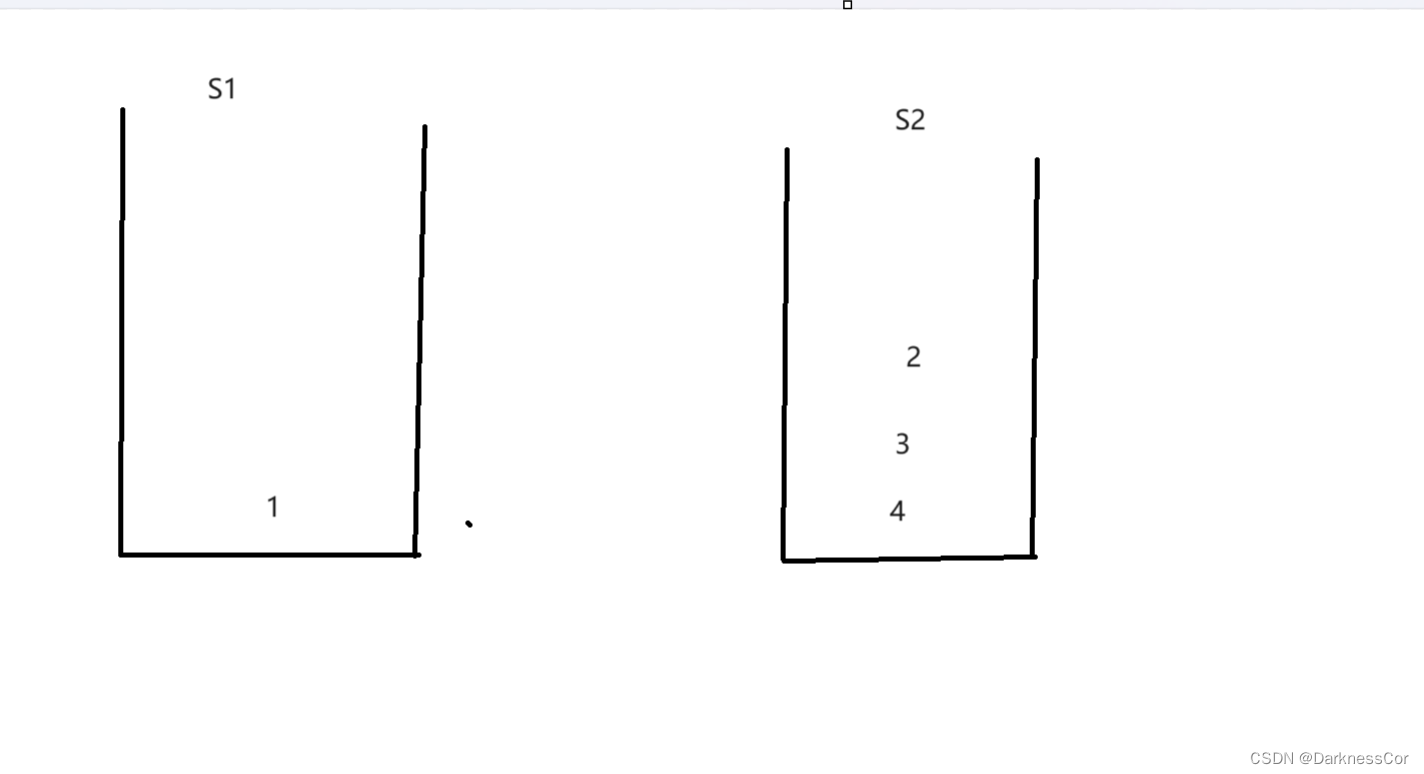
利用两个栈,设栈s1为入栈,s2为出栈,则当s2为空时,出队列只能将s1的后N-1项挪到s2后剩下的就为出栈的项,但如果s2不为空那就说明此时s2栈中的元素就已经是按照队列的顺序排好了,直接出栈即可.
2.代码实现
栈的实现代码:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* _a;int _top; // 栈顶int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->_a = NULL;ps->_capacity = 0;ps->_top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->_top == pst->_capacity){int newcapacity = pst->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->_capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->_a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->_a = tmp;pst->_capacity = newcapacity;}pst->_a[pst->_top] = x;pst->_top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps->_top > 0);ps->_top--;}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{return ps->_a[ps->_top - 1];}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{return ps->_top;}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{return ps->_top == 0;}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{free(ps->_a);ps->_capacity = 0;ps->_top = 0;}解题代码:
typedef struct {Stack s1;Stack s2;
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue* m = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));StackInit(&m->s1);StackInit(&m->s2);
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {StackPush(&obj->s1, x);}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {if (!StackEmpty(&obj->s2)){int tmp = StackTop(&obj->s2);StackPop(&obj->s2);return tmp;}else{while (StackSize(&obj->s1) > 1){int tmp = StackTop(&obj->s1);StackPush(&obj->s2, tmp);StackPop(&obj->s1);}int tmp1 = StackTop(&obj->s1);StackPop(&obj->s1);return tmp1;}
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {if (!StackEmpty(&obj->s1)){return obj->s1._a[0];}else{return obj->s2._a[obj->s2._top - 1];}}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {if (StackEmpty(&obj->s1) && StackEmpty(&obj->s2))return true;elsereturn false;}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {StackDestroy(&obj->s1);StackDestroy(&obj->s2);}结尾:今天的分享到此结束,喜欢的朋友如果感觉有帮助可以点赞三连支持,咱们共同进步!