先导入模块并创建数据:
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures as PF
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import numpy as nprnd = np.random.RandomState(42) #设置随机数种子
X = rnd.uniform(-3, 3, size=100)
y = np.sin(X) + rnd.normal(size=len(X)) / 3#将X升维,准备好放入sklearn中
X = X.reshape(-1,1)画图:
plt.scatter(X, y,marker='o',c='k',s=20)
plt.show()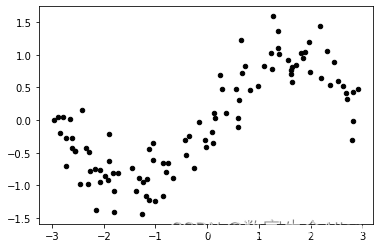
可以看到被画出来了。现在我们来拟合:
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltd=5
#和上面展示一致的建模流程X_ = PF(degree=d).fit_transform(X)
LinearR_ = LinearRegression().fit(X_, y)
line = np.linspace(-3, 3, 1000, endpoint=False).reshape(-1, 1)
line_ = PF(degree=d).fit_transform(line)#放置画布
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1)#将测试数据带入predict接口,获得模型的拟合效果并进行绘制
ax1.plot(line, LinearR_.predict(line_), linewidth=2, color='red',label="Polynomial regression")#将原数据上的拟合绘制在图像上
ax1.plot(X[:, 0], y, 'o', c='k')#其他图形选项
ax1.legend(loc="best")
ax1.set_ylabel("Regression output")
ax1.set_xlabel("Input feature")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()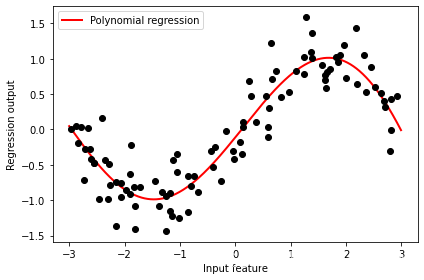
可以看到,多项式回归可以更好地拟合我们的非线性数据。