🕺作者: 主页
我的专栏 C语言从0到1 探秘C++ 数据结构从0到1 探秘Linux 菜鸟刷题集 😘欢迎关注:👍点赞🙌收藏✍️留言
🏇码字不易,你的👍点赞🙌收藏❤️关注对我真的很重要,有问题可在评论区提出,感谢阅读!!!
文章目录
- 前言
- 1 相关概念
- 1.1 条件变量
- 1.2 同步概念与竞态条件
- 1.3 条件变量函数
- 2 实际应用(见见猪跑
- 2.1 模拟加锁未加条件变量(小迷给小芒煮饭且只有一个碗
- 2.2 模拟加锁且加上条件变量
- 2.3 模拟加锁且加条件变量(小迷给多个人做饭 只有一个碗
- 3 条件变量关于等待接口的几个问题
- 3.1 条件变量对的等待接口参数为什么需要互斥锁?
- 3.2 pthread_cond_wait函数的实现原理
- 3.3 线程等待的时候,被唤醒之后需要做什么事?
前言
当谈到多线程编程时,线程同步是一个至关重要的话题。在多线程环境中,我们需要确保不同线程之间的数据访问和操作能够正确、有序地进行,以避免出现竞争条件和数据不一致的情况。因此,线程同步成为了保障多线程程序正确性和可靠性的重要手段。
在本篇博客中,我将深入探讨线程同步的概念、原理和常用的同步机制,帮助读者更好地理解多线程编程中的挑战和解决方案。无论是初学者还是有一定经验的开发人员,都可以通过本文获得对线程同步的全面了解,并学习如何在实际项目中应用这些技术来确保多线程程序的稳定性和性能。
让我们一起深入研究线程同步,探索其中的奥秘,为多线程编程的世界增添一抹精彩的色彩。
1 相关概念
1.1 条件变量
- 当一个线程互斥的访问某个变量时,它可能发现在其他线程改变状态之前,它什么也做不了
- 例如一个线程访问队列时,发现队列为空,它只能等待,只到其他线程将一个节点添加到队列中,这种情况就需要用到条件变量
1.2 同步概念与竞态条件
- 同步:在保证数据安全的前提下,让线程能够按照某种特定顺序访问临界资源,从而有效避免饥饿问题,这叫做同步。
- 竞态条件:因为时序问题,而导致程序异常。我们称之为竞态条件。在线程场景下,这种问题也不难理解
1.3 条件变量函数
- 初始化
动态初始化:
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,const pthread_condattr_t *restrictattr);🔄 ❓
参数:cond:要初始化的条件变量attr:NULL
静态初始化:
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
- 销毁
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond)
- 等待条件满足
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
参数:cond:要在这个条件变量上等待mutex:互斥量,之前的博客解释过
作用:谁调用该接口,就将谁放入PCB等待队列中
- 唤醒等待
唤醒PCB等待队列当中的所有线程:int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
唤醒PCB等待队列当中至少一个线程:int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
2 实际应用(见见猪跑
2.1 模拟加锁未加条件变量(小迷给小芒煮饭且只有一个碗
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;int g_bowl=1;
pthread_mutex_t g_lock;void* Eat(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);g_bowl--;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<"I eat "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);}return NULL;
}void* MakeRice(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);g_bowl++;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<"I make "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);}return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_mutex_init(&g_lock,NULL);pthread_t tid_eat;pthread_t tid_make;int ret = pthread_create(&tid_eat,NULL,Eat,NULL);if(ret<0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}ret = pthread_create(&tid_make,NULL,MakeRice,NULL);if(ret < 0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}while(1){sleep(1);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&g_lock);return 0;
}
结果:
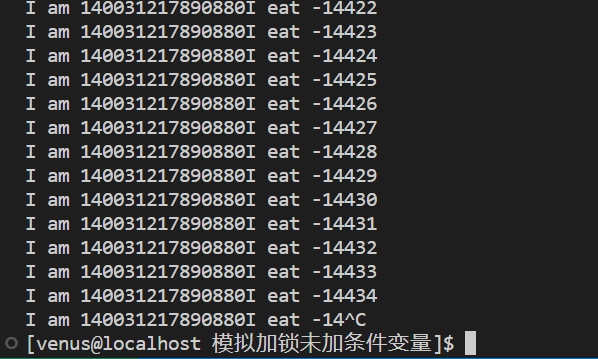
可以观察到bowl已经减为负数,这是因为小芒负责吃,当小芒拿到CPU的资源时,即使碗里面没有饭,它还是持续吃饭,最后居然出现了没有饭还能吃饭的情况,这显然是不合理的所以需要一个条件变量来控制能否吃,以及能否做
2.2 模拟加锁且加上条件变量
给小迷加上条件变量,bowl 里面有饭就不做饭,给小芒加上条件变量,bowl 没有饭就不吃饭。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;int g_bowl=1;
pthread_mutex_t g_lock;pthread_cond_t g_eat_cond;
pthread_cond_t g_make_cond;void* Eat(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);if(g_bowl<=0){pthread_cond_wait(&g_eat_cond,&g_lock);//等待小迷做好饭}g_bowl--;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<"I eat "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);pthread_cond_signal(&g_make_cond);//通知小迷做饭}return NULL;
}void* MakeRice(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);if(g_bowl>=1){pthread_cond_wait(&g_make_cond,&g_lock);//等待小芒吃饭 空出碗}g_bowl++;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<"I make "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);pthread_cond_signal(&g_eat_cond);//通知小芒吃饭}return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_mutex_init(&g_lock,NULL);pthread_cond_init(&g_eat_cond,NULL);pthread_cond_init(&g_make_cond,NULL);pthread_t tid_eat;pthread_t tid_make;int ret = pthread_create(&tid_eat,NULL,Eat,NULL);if(ret<0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}ret = pthread_create(&tid_make,NULL,MakeRice,NULL);if(ret < 0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}while(1){sleep(1);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&g_lock);pthread_cond_destroy(&g_eat_cond);pthread_cond_destroy(&g_make_cond);return 0;
}
结果如下:
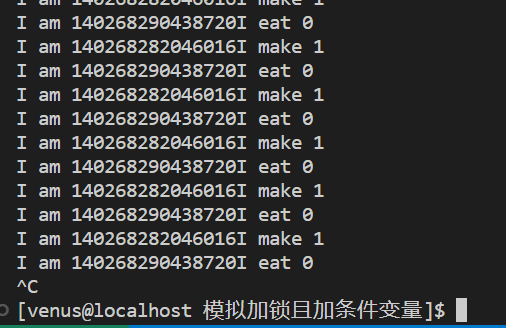
2.3 模拟加锁且加条件变量(小迷给多个人做饭 只有一个碗
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;int g_bowl=1;
pthread_mutex_t g_lock;pthread_cond_t g_eat_cond;
pthread_cond_t g_make_cond;void* Eat(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);if(g_bowl<=0){pthread_cond_wait(&g_eat_cond,&g_lock);}g_bowl--;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<"I eat "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);pthread_cond_signal(&g_make_cond);}return NULL;
}void* MakeRice(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);if(g_bowl>0){pthread_cond_wait(&g_make_cond,&g_lock);}g_bowl++;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<"I make "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);pthread_cond_signal(&g_eat_cond);}return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_mutex_init(&g_lock,NULL);pthread_cond_init(&g_eat_cond,NULL);pthread_cond_init(&g_make_cond,NULL);pthread_t tid_make;int ret = pthread_create(&tid_make,NULL,MakeRice,NULL);if(ret < 0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}for(int i=0;i<3;++i){pthread_t tid_eat;int ret = pthread_create(&tid_eat,NULL,Eat,NULL);if(ret<0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}}while(1){sleep(1);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&g_lock);pthread_cond_destroy(&g_eat_cond);pthread_cond_destroy(&g_make_cond);return 0;
}
结果:
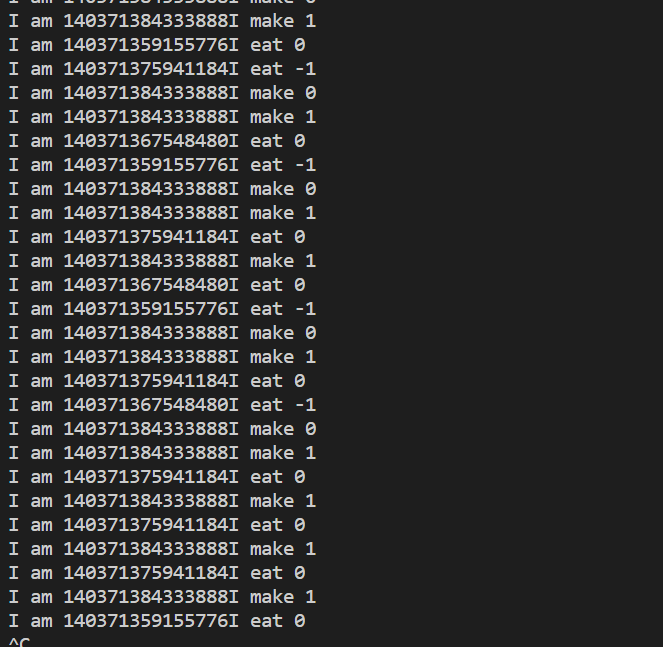
可以看到出现了负数的情况,这是为什么?
这是因为我们是使用if语句来判断条件的,可能线程刚好在这个时候进行了切换,导致多个eat线程拿到了锁,从而发生了这样的现象,想要解决这个问题只需要改为while语句即可
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;int g_bowl=1;
pthread_mutex_t g_lock;pthread_cond_t g_eat_cond;
pthread_cond_t g_make_cond;void* Eat(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);while(g_bowl<=0){pthread_cond_wait(&g_eat_cond,&g_lock);}g_bowl--;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<" I eat "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);pthread_cond_signal(&g_make_cond);}return NULL;
}void* MakeRice(void* arg){(void)arg;while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_lock);while(g_bowl>0){pthread_cond_wait(&g_make_cond,&g_lock);}g_bowl++;cout<<"I am "<<pthread_self()<<" I make "<<g_bowl<<endl;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_lock);pthread_cond_signal(&g_eat_cond);}return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_mutex_init(&g_lock,NULL);pthread_cond_init(&g_eat_cond,NULL);pthread_cond_init(&g_make_cond,NULL);pthread_t tid_make;int ret = pthread_create(&tid_make,NULL,MakeRice,NULL);if(ret < 0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}for(int i=0;i<3;++i){pthread_t tid_eat;int ret = pthread_create(&tid_eat,NULL,Eat,NULL);if(ret<0){cout<<"thread create failed"<<endl;}}while(1){sleep(1);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&g_lock);pthread_cond_destroy(&g_eat_cond);pthread_cond_destroy(&g_make_cond);return 0;
}
结果:
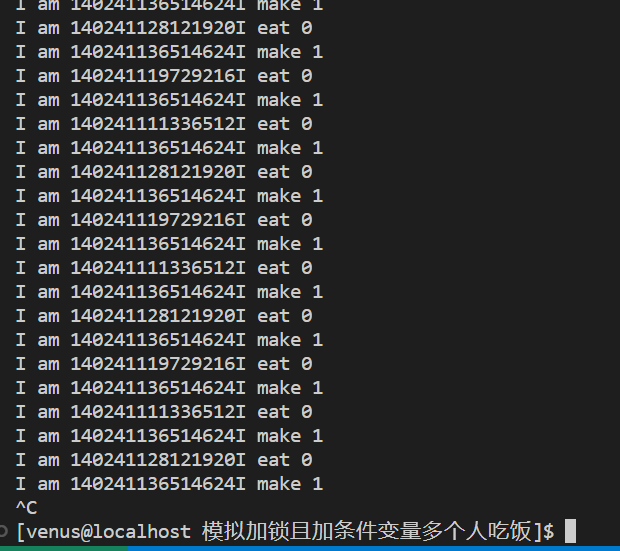
3 条件变量关于等待接口的几个问题
3.1 条件变量对的等待接口参数为什么需要互斥锁?
在pthread_cond_wait函数的内部,需要释放互斥锁。释放之后,其他线程就可以正常加锁操作了。
eg:就像之前小芒发现碗里面没有饭,则需要将自己放到PCB等待队列中,调用了pthread_cond_wait函数之后,需要将拿到互斥锁释放掉,小迷就可以访问到碗这个临界资源开始做饭。
3.2 pthread_cond_wait函数的实现原理
在pthread_cond_wait函数内部,是先释放互斥锁,还是先将PCB放到等待队列中呢?
假设先释放互斥锁,此时可能做饭的小迷就已经将饭做好了,但是小芒还没有到等待队列中,小迷通知小芒吃饭,但是发现等待队列中为空,但是同时发现碗里面有饭,它就会将自己放入等待队列中等待,此时小芒也才将自己放入等待队列中,那么此时小迷和小芒就都在等待队列中进行等待,所以不能先释放互斥锁。
3.3 线程等待的时候,被唤醒之后需要做什么事?
- 移动出PCB等待队列
- 抢互斥锁
- 抢到了:
pthread_cond_wait函数返回了 - 没抢到:
pthread_cond_wait函数没有返回,等待抢锁
- 抢到了: