给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
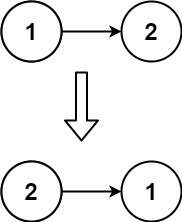
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
方法一
创建一个新链表,遍历旧链表中的数据并将其放入新链表的头部。实现方式如下
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {//创建一个新链表,将旧链表的头部放入新链表头部ListNode o1 = null;ListNode p = head;while(p!=null){o1=new ListNode(p.val,o1);p= p.next;}return o1;}
}方法二
构造一个新链表,从旧链表头部移除节点,添加到新链表头部。与方法一的区别在于,没有新创建节点。
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {//旧节点Link o1 = new Link(head); Link o2 = new Link(null);while(true){ListNode first = o1.removeFirst();if(first==null){break;}o2.addFirst(first);}return o2.head;}static class Link{private ListNode head;public Link(ListNode head){this.head = head;}//传入新链表public void addFirst(ListNode first){first.next=head;head=first;}public ListNode removeFirst(){ListNode first =head;if(first!=null){//说明还存在节点head = head.next;}return first;}}
}方法三
采用递归思想,遍历到最后节点后,将最后一个节点指向上一个节点。
图示如下:

代码实现如下
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head == null||head.next == null){return head;}//list作为头节点ListNode list = reverseList(head.next);//将当前节点作为list的最后一个节点head.next.next = head;//取消掉旧链表中的连接关系head.next =null;return list;}
}方法四
从链表每次拿到第二个节点,将其从链表断开,插入头部,直至它为 null 结束
图示如下
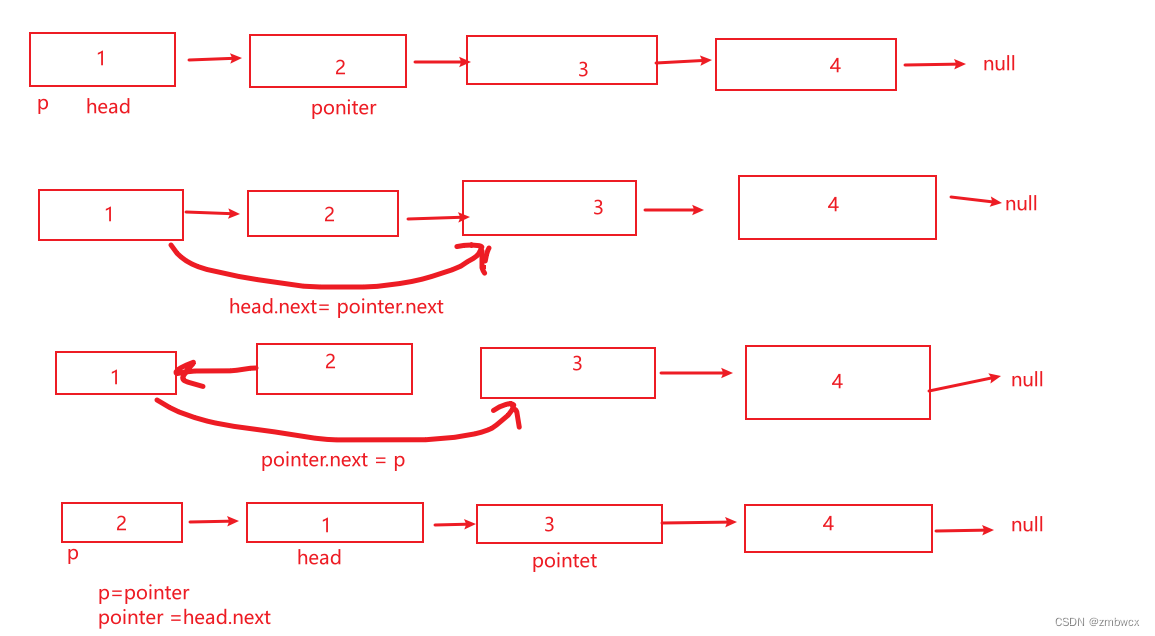
代码实现如下
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head==null || head.next==null){return head;}ListNode poniter = head.next;//用来充当头节点ListNode p = head;//不停的将第二个节点插入该链表的头部while(poniter!=null){//头节点指向第三个节点head.next = poniter.next;//第二个节点更改为头节点poniter.next = p;//将p指向当前链表的头部p = poniter;//pointer指向移动后原链表的第二个节点poniter = head.next;}return p;}
}方法五
把链表分成两部分,思路就是不断从链表2的头,往链表1的头搬移
图示如下:
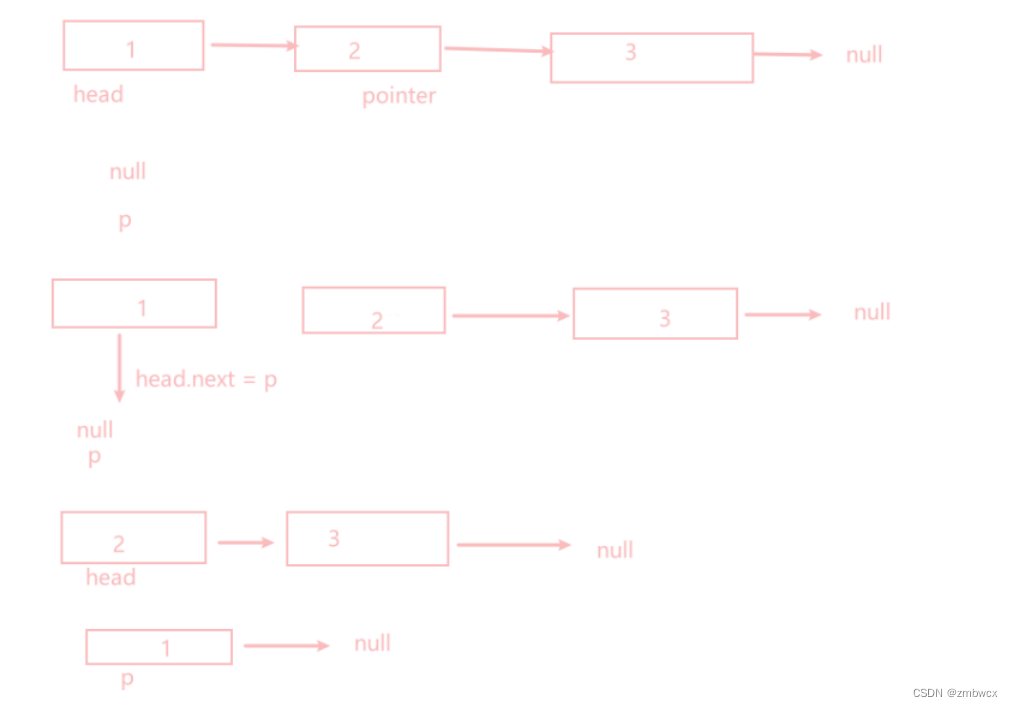
代码实现如下
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head == null){return head;}ListNode p = null;while(head!=null){//第二个节点ListNode pointer = head.next;head.next = p;p = head;head = pointer;}return p;}
}