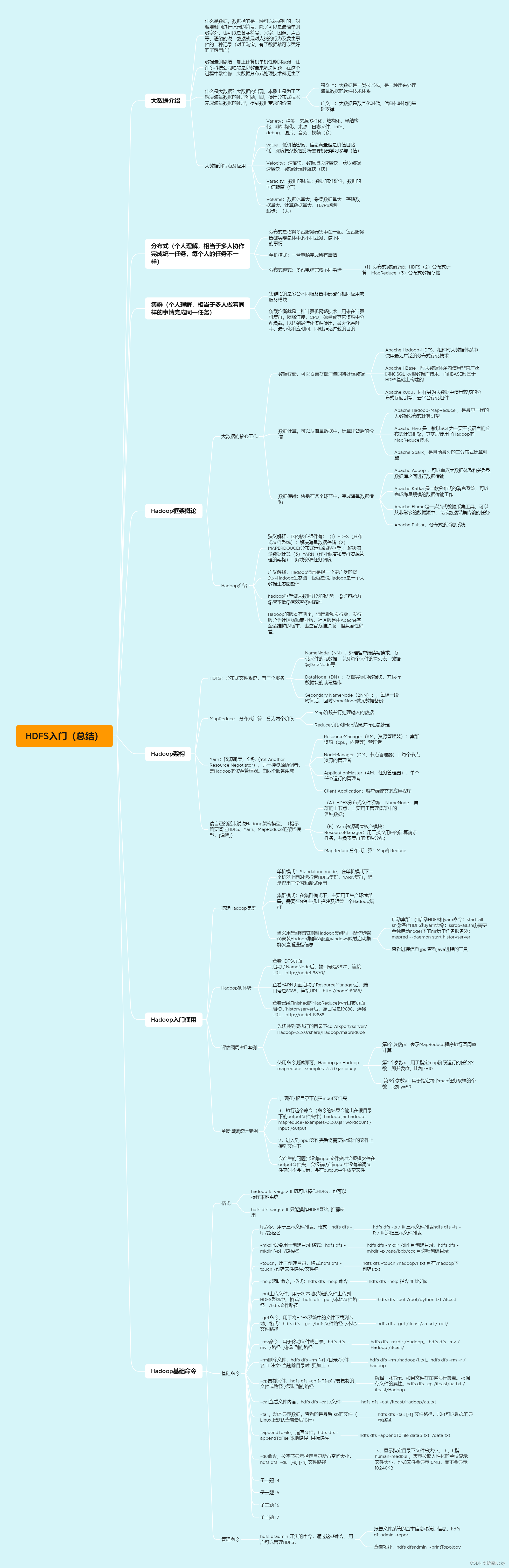
数据结构—— 栈的实现
- 一.栈
- 1.1栈的概念及结构
- 二.栈的实现
- 2.1头文件的实现——(Strck.h)
- 2.2 源文件的实现——(Strck.c)
- 2.3 源文件的实现——(test.c)
- 三.栈的实际数据测试展示
- 3.1正常的后进先出方式
- 3.2 进栈的同时也存在出栈
一.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构


二.栈的实现
2.1头文件的实现——(Strck.h)
Strck.h
#pragma once#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Strck
{STDataType* a;int top; //记录栈顶位置int capacity;
}ST;//初始化/销毁
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);//压栈/出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
//统计栈内元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst);
2.2 源文件的实现——(Strck.c)
Strck.c
#include"Strck.h"//初始化/销毁
void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;}//压栈/出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top == 0;
}
//统计栈内元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
2.3 源文件的实现——(test.c)
test.c
#include"Strck.h"int main()
{ST p;STInit(&p);STPush(&p, 1);STPush(&p, 2);printf("%d ", STTop(&p));STPop(&p);STPush(&p, 3);STPush(&p, 4);printf("%d ", STTop(&p));STPop(&p);STPush(&p, 5);while (!STEmpty(&p)){printf("%d ", STTop(&p));STPop(&p);}STDestroy(&p);return 0;
}
三.栈的实际数据测试展示
1.栈的出栈和入栈的关系是:一对多的关系。
2.元素出入栈满足的方式是:后进先出。
3.1正常的后进先出方式

3.2 进栈的同时也存在出栈