自己在秋招过程中遇到的算法笔试题,包含中大厂,都附解析!
汽水瓶
如果汽水瓶数目为1或者0,那么一瓶都喝不到
如果汽水瓶数目为2或者3,那么只能喝到一瓶
如果为2,喝到一瓶后手里一个瓶子都没有了,没法继续循环下去
如果为3,喝到一瓶后手里只剩一个瓶子,没法继续循环下去
如果汽水瓶数目大于3,每次耗费三个瓶子喝到一瓶,然后多了一个瓶子,即每一轮耗费两个瓶子
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
unsigned int sln(unsigned int N){if (N == 2 || N == 3) {return 1;}if (N <= 1){return 0;}unsigned int Total = 0;while (N > 3) {N -= 2;Total++;if (N == 2){Total++;N = 0;}if (N == 3){Total++;N = 1;}}return Total;
}
int main(){unsigned int N;while (cin >> N) {if (N == 0) break;cout << sln(N) << endl;}return 0;
}明明的随机数
//方法一: 暴力版本
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;int main() {int n;cin>>n;int m;vector<int>v;while(n--){cin>>m;v.push_back(m);}sort(v.begin(),v.end());cout<<v[0]<<endl;for(int i=1;i<v.size();i++){if(v[i]!=v[i-1]){cout<<v[i]<<endl;}}
}
//方法二:STL(set)版本
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int main() {int n;cin>>n;int m;set<int>us;//插入有序while(n--){cin>>m;us.insert(m);}for(auto &i:us){cout<<i<<endl;}
}
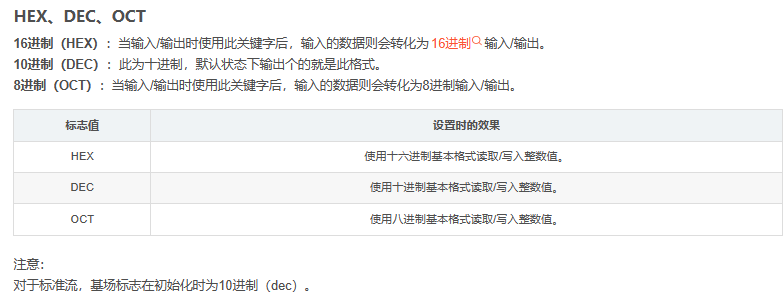
**进制转换
**
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int a;while (cin >> hex>> a) { // 注意 while 处理多个 casecout << a << endl;}
}
Words

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int main(){string str="";while(getline(cin,str)){int n=str.size();int countspace=0;double ans=0;for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++){if(str[i]==' '){countspace++;} }ans=1.0*(n-countspace)/(1.0*(countspace+1));cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<ans<<endl;} return 0;
}
Vowel

#include<set>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main(){string str="";string ans="";set<char>se;se.insert('a');se.insert('e');se.insert('i');se.insert('o');se.insert('u');se.insert('A');se.insert('E');se.insert('I');se.insert('O');se.insert('U');while(getline(cin,str)){for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++){if(se.find(str[i])==se.end()){ans.push_back(tolower(str[i]));}else{ans.push_back(toupper(str[i])); }}cout<<ans; } return 0;
}
计算字符串重新排列数

栈数据合并


整体代码
#include <iostream>
#include<stack>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;//没有消除时,栈里面大小一直是1
int main() {stack<int> s;string input;//输入:10 20 50 80 1 1//输出:2 160getline(cin, input);istringstream iss(input);//输入的一行挨个读取int num;while (iss >> num) {if (s.empty()) {s.push(num);continue;//关键}int sum = num;while (!s.empty() && s.top() <= num) {int top = s.top();s.pop();sum += top;if (sum == top * 2) {sum = top * 2;continue;//关键}if (!s.empty() && sum == top * 2 + s.top()) {sum = top * 2 + s.top();s.pop();}break;}s.push(sum);}while (!s.empty()) {cout << s.top() << " ";s.pop();}return 0;
}
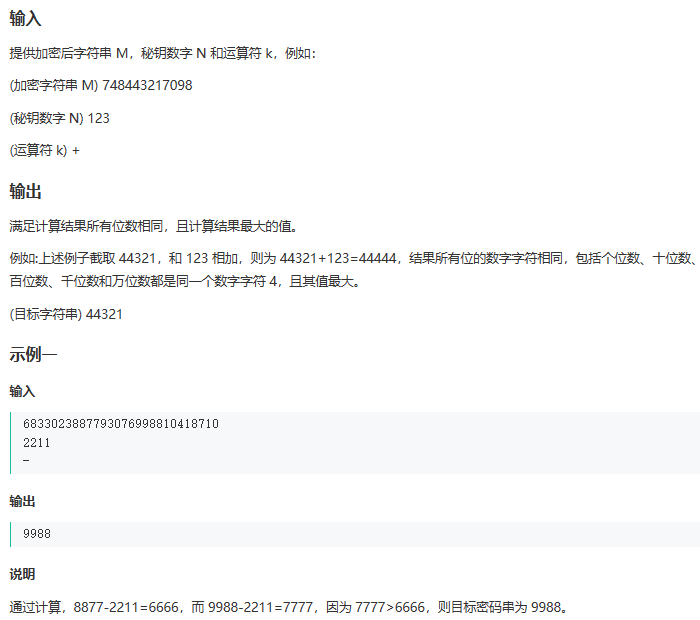
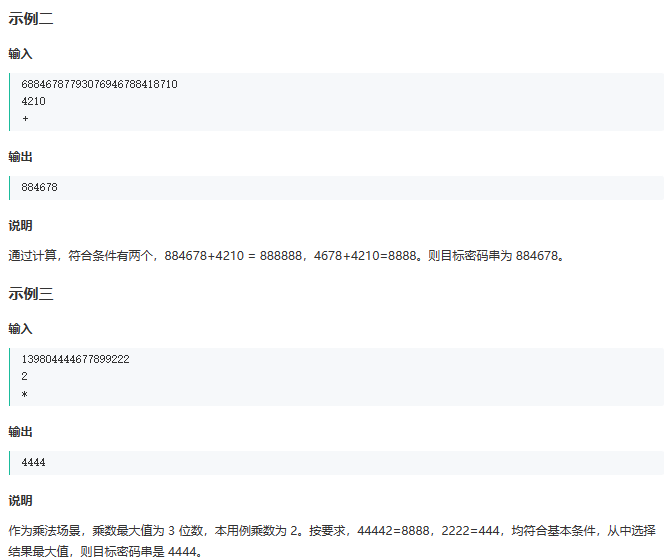
寻找密码串
C++字符串转数字: stoi C语言字符串转数字:atoi(s.c_str())
C++数字转字符串to_string

整体代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<set>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;bool is_valid(string s) {return set<char>(s.begin(), s.end()).size() == 1;
}int main() {string a, c;long long b;cin >> a >> b >> c;long long size = a.length();long long ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {for (int len = 0; len < 13; len++) {if (i + len >= size) {break;}long long now = stoll(a.substr(i, len + 1));if (c == "+") {if (is_valid(to_string(now + b))) {ans = max(ans, now);}}else if (c == "-") {if (is_valid(to_string(now - b))) {ans = max(ans, now);}}else {if (is_valid(to_string(now * b))) {ans = max(ans, now);}}}}cout << ans << endl;return 0;
}
染色服务器,最短耗费时间走完所有的服务器-5.10



#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <climits>using namespace std;int main() {int n;cin >> n;//几个服务器int m;cin >> m;//几条路径unordered_map<int, int> sysTime;unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> nxs;//m条路径从哪到哪,耗时多久for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {int s, d, t;cin >> s >> d >> t;if (s != d)nxs[s].push_back({ d, t });elsesysTime[s] = t;}//从哪个服务器开始int start;cin >> start;priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> h;h.push({ 0, start });vector<int> dis(n + 1, INT_MAX);dis[start] = 0;while (!h.empty()) {int time = h.top().first;int node = h.top().second;h.pop();for (auto& nx : nxs[node]) {int nxNode = nx.first;int nxTime = nx.second;if (dis[nxNode] > time + sysTime[nxNode] + nxTime) {h.push({ time + sysTime[nxNode] + nxTime, nxNode });dis[nxNode] = min(dis[nxNode], time + sysTime[nxNode] + nxTime);}}}int cnt = 0, res = 0;for (int d : dis) {if (d != INT_MAX) {cnt++;res = max(res, d);}}cout << cnt << " " << res << endl;return 0;
}
小美的送花路线
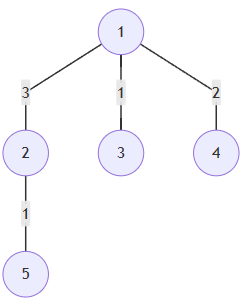
根据题设,考虑树状结构。求:
sum1:从花店到所有客户地址的距离之和;
sum2:骑手实际走的最短路程,且最后一趟不需再返回。
求sum1:
根据输入的u、v、w,对于任意节点都能写出dp[v]=dp[u]+w,从而得到sum1。
对于例子1来说,sum1+=dp[v]。如dp[5]=dp[2]+1=3+1=4。sum1=3+1+2+4=10。
求sum2:
要求最短路径,根据最后一趟不需返回,可知最后一趟一定是从花店到最远的客户地址处,这部分距离只需计算一次,其余的到其他客户地址的距离需要计算往返路程。因此sum2+=2×w,还要-maxlen,其中maxlen是dp[v]中的最大值。
对于例子1来说,离花店最远的客户地址是5,路程中还途径了客户1。因此,sum2=2×(3+1+2+1)-(3+1)=10。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;int main(){int n;cin>>n;vector<int>dp(n,0);int sum1 = 0,maxlen = 0,sum2 = 0;int u,v,w;for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){cin>>u>>v>>w;dp[v] = dp[u]+w;sum2 += w*2;maxlen = max(dp[v],maxlen);sum1 += dp[v];}cout << sum1 << " " << sum2-maxlen;
}
小美的评分计算器
需注意的点:
①输入的是1星到5星的评价的数量;
②两个整数相除还是整数,需要用强制转换成小数;
③需要考虑输出为0.0的情况。
④不四舍五入的小数去尾的实现:乘整十(一位小数)向下取整再除十,使用fixed和setprecision控制实数部分及小数部分精度
fixed 和 setprecision 是用来控制输出浮点数精度和格式的两个重要工具。
fixed 是一个 C++ 标准库中的输出流修饰符,它用于指示输出的浮点数使用定点表示法而非默认的科学计数法。使用 fixed 后,输出的浮点数会以固定的小数位数格式进行输出。
fixed 是一个全局性质的修饰符,一旦使用,它会一直生效,直到被另外的修饰符覆盖为止。
setprecision 是另一个输出流修饰符,用于指定输出浮点数的小数位数。
向上取整:ceil,向下取整:floor,四舍五入:round
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){int n1,n2,n3,n4,n5;cin>>n1>>n2>>n3>>n4>>n5;double rate = 0;rate = (double)(1*n1+2*n2+3*n3+4*n4+5*n5)/(n1+n2+n3+n4+n5);if(n1==0&&n2==0&&n3==0&&n4==0&&n5==0){cout<<"0.0";}else{cout<<fixed<<setprecision(1)<<floor(rate*10.0)/10.0; }
}
小美的外卖省钱计划
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int n;cin>>n;int x=0, y=0;int sum1=0,sum2=0;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>x>>y;if(x>y){sum2+=(x-y);sum1+=x;}else{sum1+=y;}}cout<<sum1<<" "<<sum2;
}
小美的代金券要过期啦
例子中是从后向前进行消消乐的,因此考虑使用栈结构,将序列元素入栈后,当栈顶元素和序列中元素相等时,将输入的x+1。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int main(){ int n;int x = 0;cin>>n;int* s = new int[n];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){cin>>s[i];}stack<int> nums;nums.push(s[0]);for(int i=1;i<n;i++){while(!nums.empty()&&s[i]==nums.top()){nums.pop(); s[i]++;x++;} nums.push(s[i]);}cout<<x;
}
字符分割
如给你一串字符“path=/chat.openai.com, language=c++, path=baidu.com",
输入 2 path language,输出 baidu.com c++
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>using namespace std;int main() {string str;getline(cin, str);unordered_map<string, string> mmap;//字符分割for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {int start = i;while (start < str.size() && str[start] != '=') {start++;}string str2 = str.substr(i, start - i);int start2 = start + 1;while (start2 < str.size() && str[start2] != ',') {start2++;}string str3 = str.substr(start + 1 , start2 - start - 1);i = start2;//此处说相同的key取后者的value,应该直接替代是没有问题的mmap[str2] = str3;}//输入验证int n;cin >> n;string str4;vector<string> vec;while (n > 0 && cin >> str4) {vec.push_back(str4);n--;}for (string& strTmp : vec) {if (mmap.count(strTmp) >= 1) {cout << mmap[strTmp] << endl;}else {cout << "EMPTY" << endl;}}return 0;
}
美味值数组
给你一个每一天糖果的美味值数组,只能隔天吃,但也可以反悔,有K次反悔机会
- 思路:先用打家劫舍的方法,然后对没有选的取k个最大值
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>using namespace std;
int maxTaste(int k, vector<int>& vec) {int len = vec.size();vector<int> dp(len);dp[0] = vec[0];if (len == 1) {return dp[0];}vector<bool> used(len, false);if (len >= 2) {dp[1] = max(dp[0], vec[1]);if (len == 2) {if (k > 0) {return vec[0] + vec[1];}else {return dp[1];}}}for (int i = 2; i < len; i++) {dp[i] = max(dp[i - 2] + vec[i], dp[i - 1]);}//判断最后一个选了没bool jus;if (dp[len - 3] + vec[len - 1] > dp[len - 2]) {jus = true;}else {jus = false;}priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> pq;if (!jus) {for (int i = len - 1; i > 0; i = i - 2) {pq.push(vec[i]);}}else {for (int i = len - 2; i > 0; i = i - 2) {pq.push(vec[i]);}}int res = dp[len - 1];for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {res += pq.top();pq.pop();}return res;
}int main() {//反悔次数int k;cin >> k;//输入美味值int n; //天数cin >> n;vector<int> vec;int num;while (n > 0 && cin >> num) {vec.push_back(num);n--;}cout << maxTaste(k, vec) << endl;return 0;
}
0-1背包问题
n块巧克力板,边长为a[i], 重量为a[i]*a[i], m 个背包, 可以装重量为b[i], 求每个背包最多可以装多少?
- 思路: 可以对巧克力板按重量从小到大排序,前缀和即可
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>using namespace std;int large(vector<int>& a, int b) {int sum = 0;int len = a.size();int i;for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {sum += a[i];if (sum > b) {break;}}return i;
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<int> a, b;int ins;while (n > 0 && cin >> ins) {a.push_back(ins * ins);n--;}while (m > 0 && cin >> ins) {b.push_back(ins);m--;}sort(a.begin(), a.end());for (int tmp : b) {cout << large(a, tmp)<< " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
用O(n)写一个数组的第K大数
快速选择算法的基本思想是通过每次选取一个基准元素,将数组分为两个部分,小于基准元素的部分和大于基准元素的部分。然后根据基准元素所在位置和K的关系,决定在哪个部分继续查找
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>// 快速选择算法
int quickSelect(std::vector<int>& nums, int left, int right, int k) {// 选取基准元素int pivot = nums[left];int i = left + 1;int j = right;// 将大于基准元素的数移到右侧,小于基准元素的数移到左侧while (i <= j) {if (nums[i] < pivot && nums[j] > pivot) {std::swap(nums[i], nums[j]);i++;j--;}if (nums[i] >= pivot) {i++;}if (nums[j] <= pivot) {j--;}}// 将基准元素放在正确的位置std::swap(nums[left], nums[j]);// 判断基准元素的位置与K的关系int pos = j - left + 1;if (pos == k) {return nums[j];}else if (pos > k) {return quickSelect(nums, left, j - 1, k);}else {return quickSelect(nums, j + 1, right, k - pos);}
}// 找出数组的第K大数
int findKthLargest(std::vector<int>& nums, int k) {int n = nums.size();return quickSelect(nums, 0, n - 1, k);
}int main() {std::vector<int> nums = { 3, 1, 5, 2, 4 };int k = 2;int kthLargest = findKthLargest(nums, k);std::cout << "第" << k << "大数是:" << kthLargest << std::endl;return 0;
}
合并有序数组
class Solution {
public:void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {int p1=m-1;int p2=n-1;int tail=p1+p2+1;int cur;while(p1>=0||p2>=0){if(p1==-1){cur=nums2[p2--];}else if(p2==-1){cur=nums1[p1--];}else if(nums1[p1]>nums2[p2]){cur=nums1[p1--];}else{cur=nums2[p2--];}nums1[tail--]=cur;}}
};
输入一堆数,每个数都是出现 4 次,只有一个数出现三次,找出这个数。时间复杂度 O(nlogn),空间复杂度 O(logn)
1)手撕快排再遍历
2)一直异或,最后异或的结果一定是那个数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//时间复杂度O(N)
int main() {vector<int>nums{ 1,1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,3,6,6,6,6,5,5,5,5};int ans = nums[0];for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {ans = ans ^ nums[i];}cout << ans << endl;return 0;
}
手写生产者消费者模型
为应对系统的通信上消息收发的高耦合度,在接受和发送消息后设计一个缓存队列,并使用多线程生产者-消费者来进行收发解耦。避免通信上的拥堵情况。
class MyTest{
private:std::deque<T> queue_; //缓存队列size_t size_limit_; //缓存队列大小的限制std::mutex lock_; //互斥锁std::condition_variable empty_, full_; //并发条件变量类std::atomic<int> producer_num_; //生产者数量
};
实现思路是:当缓存队列满的时候,生产者将被挂起,直到队列重新拥有空间。但缓存队列为空时,消费者线程将被挂起,直到有“商品”被放入队列之中。
void Productor(T& item) {{std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(lock_); //加锁防止冲突while (queue_.size() >= size_limit_) {full_.wait(lk);}queue_.emplace_back(item);}empty_.notify_one();
}
full_.wait(lk)在queue队列满时将会把Productor挂起,直到queue有空间放入新的item。notify_one方法任意从WAITTING状态的线程中挑选一个进行通知,使得调用wait()方法的线程从等待队列移入到同步队列中,等待有机会再一次获取到锁,从而使得调用wait()方法的线程能够从wait()方法处退出。
bool Consumer(T& item) {{std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(lock_);while (queue_.empty() && (producer_num_ != 0)) {empty_.wait(lk);}if (queue_.empty() && (producer_num_ == 0)) {return false;} else {item = std::move(queue_.front());queue_.pop_front();full_.notify_one();return true;}}}
同理,empty_.wait(lk)会在生产者数量为0或者队列queue为空的时候,将Consumer挂起。直到有商品进入到队列中。这样就可以实现一个简单的生产者消费者。
二叉树层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode*root) {queue<TreeNode*>que;if(root==NULL) return root;que.push(root);vector<vector<int>>ans;while(!que.empty()){int n=que.size();vector<int>path;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){TreeNode*node=que.front();que.pop_back();path.push_back(node->val);if(node->left) que.push(node->left);if(node->right) que.push(node->right);}ans.push_back(path);}return ans;
}
输入高维张量,返回shape
import numpy as np
def get_shape(tensor):shape = np.shape(tensor)return shape
# 示例输入一个3维张量
tensor = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
shape = get_shape(tensor)
print(shape)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;template<typename T>
vector<size_t> getShape(const vector<T>& tensor) {vector<size_t> shape;size_t size = tensor.size();while (size > 0) {shape.push_back(size);size /= tensor[0].size();}return shape;
}int main() {vector<vector<vector<int>>> tensor{{{1, 2}, { 3, 4 }},{ {5, 6}, {7, 8} }};vector<size_t> shape = getShape(tensor);cout << "Shape: ";for (size_t dim : shape) {std::cout << dim << " ";}cout << std::endl;return 0;
}
GPU内存结构
- 全局内存(Global Memory):全局内存是GPU中最大的内存池,通常具有较大的容量。它用于存储核心数据结构、变量和计算结果等。全局内存对于所有线程可见,但相对于其他内存层级而言,它的访问速度较慢。
- 共享内存(Shared Memory):共享内存是位于GPU的多处理器(Multiprocessor)中的每个线程块(Thread Block)之间共享的内存区域。它的访问速度非常快,可以在同一线程块的线程之间共享数据。共享内存主要用于线程之间的通信和协作,以提高性能。
- 常量内存(Constant Memory):常量内存用于存储在执行期间不会发生改变的常量数据。它在访问速度上比全局内存快,但容量较小。常量内存对于所有线程可见,可以通过缓存机制提高访问效率。
- 纹理内存(Texture Memory):纹理内存是专门用于图形渲染的内存区域,具有高速缓存和过滤器等功能。它主要用于存储纹理数据,并提供一些特殊的访问方式,如双线性插值和边界处理等。
- 寄存器文件(Register File):寄存器文件是GPU中每个线程的私有内存空间。它用于存储线程的局部变量、中间计算结果和函数调用参数等。寄存器的访问速度非常快,但容量有限。对于某些计算密集型任务,寄存器的使用可能需要精心管理以避免资源耗尽。
CUDA三维结构好还是二维好
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture)是NVIDIA提供的用于GPU编程的并行计算平台和编程模型。在CUDA中,既可以使用二维结构(二维线程块和二维网格)也可以使用三维结构(三维线程块和三维网格)。选择使用二维还是三维结构取决于问题的特性和并行计算的需求。
二维结构:
- 二维结构适用于处理具有二维或类似矩阵的数据结构。例如,图像处理中的像素数据可以组织为二维数组,因此使用二维结构可以方便地处理图像。
- 二维结构可以更好地利用数据的空间局部性。相邻的线程可以访问相邻的数据,这有助于减少全局内存访问和数据传输的次数,提高数据访问的效率。
三维结构: - 三维结构适用于处理具有三维特性的数据结构,例如体积数据或具有复杂三维结构的数据集。
- 使用三维结构可以更好地描述和组织三维数据,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
- 在某些情况下,三维结构可以提供更好的并行计算的均匀性和负载平衡,特别是当问题具有三维的均匀性或对称性时。
总体而言,选择二维结构还是三维结构应根据问题的特性、数据的组织方式以及并行计算的需求来决定。如果问题可以自然地映射到二维结构,并且能够充分利用二维数据的空间局部性,那么二维结构可能更合适。如果问题具有三维特性或需要更好的均匀性和负载平衡,则可以考虑使用三维结构。在实际使用中,可以通过实验和性能分析来确定最适合问题的结构。
tensor core 了解吗
Tensor Core提供了高度优化的矩阵乘法和累积运算功能,能够在相对较短的时间内执行大规模矩阵运算,从而加速深度学习模型的训练和推理过程。
Tensor Core的主要特点包括:
- 数值精度:Tensor Core支持半精度浮点数(FP16)运算,它将浮点运算的计算精度降低一半,但同时大大增加了计算性能。在深度学习中,使用半精度计算通常可以满足训练和推理的准确性要求,能够显著提升计算速度。
- 矩阵乘法:Tensor Core使用特定的算法和硬件电路来加速矩阵乘法运算,尤其是小批量(mini-batch)矩阵乘法。它能够同时执行多个矩阵乘法操作,并且支持半精度累积运算,使得在一个时钟周期内可以完成更多的计算。
- 混合精度计算:Tensor Core可以与其他精度计算单元结合使用,如32位浮点数(FP32)和整数计算单元。这种混合精度计算的方法能够在保持准确性的同时提高计算性能,常用于深度学习的训练和推理过程。
Tensor Core广泛应用于深度学习框架和库,如TensorFlow和PyTorch等,以加速深度神经网络的计算。它可以显著提高模型训练的速度,并在一定程度上降低对计算资源的需求。然而,使用Tensor Core需要特定的软件支持和配置,以确保正确地利用它的性能优势。
ReduceSum怎么优化
- 数据布局优化:调整数据的布局方式,以便在内存访问和数据传输方面更加高效。例如,优化数据的连续性和缓存友好性,可以利用缓存和向量化指令集提高访问效率。
- 并行化:使用并行计算技术,如线程、向量化和GPU并行处理等,将ReduceSum操作分布到多个计算单元上并发执行,以提高计算效率。
3.** 数据复用**:尽可能地复用数据,减少不必要的读取和写入操作。可以通过共享内存、寄存器或缓存等机制来缓存中间计算结果,以减少数据的重复读取和写入。 - 剪枝和分解:对于大规模ReduceSum操作,可以考虑使用剪枝和分解等技术将其分解为更小的子任务,以降低每个子任务的计算负载,并充分利用并行性。
- 异步计算:使用异步计算技术,如CUDA流或异步任务队列,将ReduceSum操作与其他计算任务重叠,以充分利用计算和数据传输之间的隐藏延迟,提高整体性能。
- 内存访问优化:通过合理地利用局部性原则、数据对齐和访问模式等技术,优化内存访问方式,减少数据传输次数和延迟,提高数据吞吐量。
- 分级存储:对于大规模ReduceSum操作,可以使用分级存储策略,将数据分为多个层级,并使用不同的存储介质来适应不同的访问需求。例如,结合全局内存、共享内存和寄存器等多级存储来提高性能。
- 算法选择:根据实际需求,选择适合的ReduceSum算法。不同的算法可能有不同的计算复杂度和内存访问模式,选择合适的算法可以提高性能。
异构设备内存局部性怎么优化
- 内存访问模式优化:调整数据的访问模式,以提高内存局部性。例如,尽量保证线程对内存的访问是连续的、对齐的,避免随机的、不规则的内存访问。
- 数据布局优化:重组数据的存储方式,以提高内存局部性。例如,将相关的数据项存储在相邻的内存位置,或者使用数据结构和算法来组织数据,以充分利用局部性原则。
- 数据复用:尽量复用已经从内存加载到高速缓存的数据,减少对主存的访问。可以使用缓存、共享内存或寄存器等层级存储来存储中间计算结果,以避免重复的内存访问。
- 数据预取:利用硬件的数据预取机制,提前将需要使用的数据从主存加载到高速缓存,以减少访问延迟。可以使用编译器指令、预取指令或手动编码来控制数据的预取行为。
- 空间局部性优化:利用数据的空间局部性原则,以减少数据的移动和传输。例如,通过使用局部变量、循环展开、数据重用等技术来减少内存的读写操作。
- 访问模式分析和优化:通过对代码进行访问模式分析,了解内存访问的模式和特点,进而针对性地进行优化。可以使用工具、分析器或性能剖析器来帮助确定访问模式和性能瓶颈,并针对性地进行优化。
- 数据压缩和存储优化:在某些情况下,可以使用数据压缩技术来减少内存占用和传输带宽。通过压缩算法、数据压缩库或自定义的数据存储方案等方式,将数据压缩后存储在内存中,然后在需要使用时进行解压缩。
K 个一组翻转链表
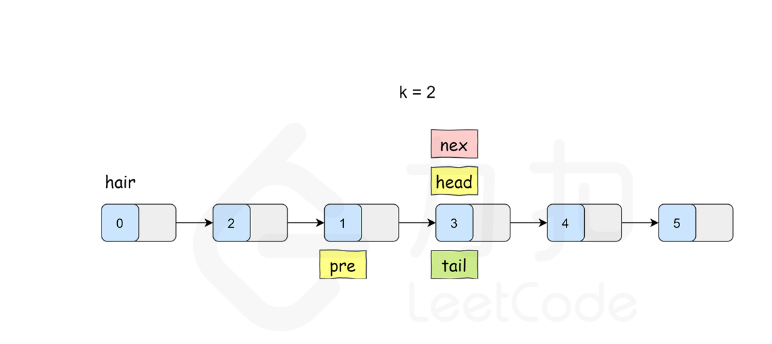
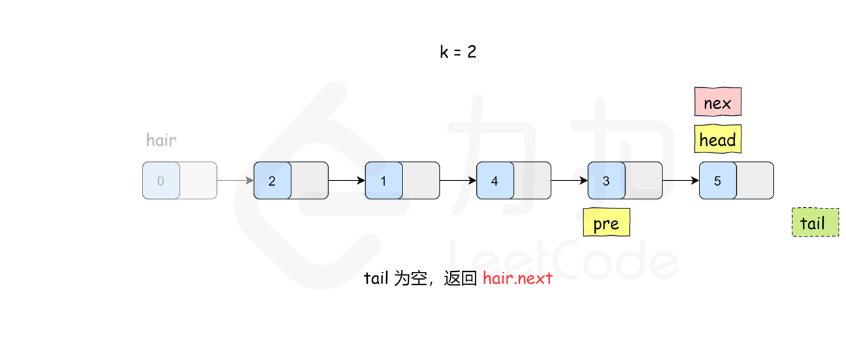
class Solution {
public:
// 翻转一个子链表,并且返回新的头与尾
pair<ListNode*, ListNode*> myReverse(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) {ListNode* prev = tail->next;ListNode* p = head;while (prev != tail) {ListNode* nex = p->next;p->next = prev;prev = p;p = nex;}return {tail, head};
}ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {ListNode* hair = new ListNode(0);hair->next = head;ListNode* pre = hair;while (head) {ListNode* tail = pre;// 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 kfor (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {tail = tail->next;if (!tail) {return hair->next;}}ListNode* nex = tail->next;// 这里是 C++17 的写法,也可以写成// pair<ListNode*, ListNode*> result = myReverse(head, tail);// head = result.first;// tail = result.second;tie(head, tail) = myReverse(head, tail);// 把子链表重新接回原链表pre->next = head;tail->next = nex;pre = tail;head = tail->next;}return hair->next;}
};
最长回文子串:中心扩散法
class Solution {
public:pair<int, int> expandAroundCenter(const string& s, int left, int right) {while (left >= 0 && right < s.size() && s[left] == s[right]) {--left;++right;}return {left + 1, right - 1};}string longestPalindrome(string s) {int start = 0, end = 0;for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {auto [left1, right1] = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);auto [left2, right2] = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);if (right1 - left1 > end - start) {start = left1;end = right1;}if (right2 - left2 > end - start) {start = left2;end = right2;}}return s.substr(start, end - start + 1);}
};
字符串首次出现3次的字符
哈希表就行,遍历字符串,存放在map中,并判断value==3就返回key
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;string str;
cin>>str;
unordered_map<char,int>um;
for(auto &i:str){um[i]++;if(i.second==3){cout<<i.first<<endl;}
}
数组中只出现一次的数字
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {unordered_map<int,int>mp;int ans=0;for(auto &i:nums){mp[i]++;} for(auto &i:mp){if(i.second==1){ans=i.first;}}//for(auto &[key,value]:mp){// if(value==1){// ans=key;// break;// }//}return ans;}
};
合并2个有序数组
法一排序
将nums2放到nums1中,直接排序
class Solution {
public:void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {for(int i=0;i<n;i++){nums1[m++]=nums2[i]; }sort(nums1.begin(),nums1.end());}
};
法二,双指针
逆向双指针,尾部覆盖
class Solution {
public:void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {int p1=m-1,p2=n-1;int tail=m+n-1;while(p1>=0||p2>=0){if(p1==-1){nums1[tail--]=nums2[p2--];}else if(p2==-1){nums1[tail--]=nums1[p1--];}else if(nums1[p1]<nums2[p2]){nums1[tail--]=nums2[p2--];}else{nums1[tail--]=nums1[p1--];}}}
};
435.不重叠区间
先计算不重叠的区间数,然后用总的区间数—重叠的=要去掉的,记得自定义排序规则
class Solution {
public:/// static bool cmp(vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b){// return a[1]<b[1];//}int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {//sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end(),cmp);sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end(),[](const auto &a,const auto &b){return a[1]<b[1];});int count=1;int right=intervals[0][1];for(int i=1;i<intervals.size();i++){if(intervals[i][0]>=right){count++;right=intervals[i][1];}}return intervals.size()-count;}
};
73.矩阵置零
2个标记数组,如果有元素为0,元素所在的行列所对应的标记数组的位置置true,用标记数组更新原数组
class Solution {
public:void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int m=matrix.size();int n=matrix[0].size();vector<bool>row(m),col(n);for(int i=0;i<m;i++){for(int j=0;j<n;j++){if(!matrix[i][j]){row[i]=col[j]=true;}}} for(int i=0;i<m;i++){for(int j=0;j<n;j++){if(row[i]||col[j]){matrix[i][j]=0;}}}}
};
分割字符串,知道字符数量
输入一个字符串,求[“xiao”,“mi”]的组和有多少种
比如 输入:“I love xiaomi, I think mi com is the best"
输出:2
计算输入字符串中指定子字符串组的数量
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>//s输入字符串
int countSubstringGroups(const std::string& s, const std::vector<std::string>& substrings) {int count = 0;size_t startIndex = 0;while (true) {bool found = false;//遍历目标串for (const auto& substring : substrings) {size_t index = s.find(substring, startIndex);if (index != std::string::npos) {found = true;startIndex = index + substring.length();break;}}if (!found) {break;}bool allNotFound = true;for (const auto& substring : substrings) {if (s.find(substring, startIndex) != std::string::npos) {allNotFound = false;break;}}if (allNotFound) {count++;}}return count;
}int main() {// 输入字符串std::string inputStr = "I love xiaomi, I think mi com is the best";// 目标子字符串列表std::vector<std::string> targetSubstrings = {"xiao", "mi"};// 计算组数int result = countSubstringGroups(inputStr, targetSubstrings);// 输出结果std::cout << result << std::endl;return 0;
}划分3*3矩阵
有一个m*n的字符矩阵,
要求:3*3的连续子矩阵里面x,a,o,m至少出现1次,i至少出现2次
求这样的3*3的矩阵有多少?比如输入4*4的话
x i a q
o i m e
x a i c
c a d f输出结果为2,有2个符合条件的连续子矩阵
x i a
o i m
x a io i m
x a i
c a d #include <iostream>
#include <vector>using namespace std;bool isValidSubmatrix(const vector<vector<char>>& matrix, int startRow, int startCol) {int count_x = 0, count_a = 0, count_o = 0, count_m = 0, count_i = 0;for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; ++i) {for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; ++j) {char currentChar = matrix[i][j];if (currentChar == 'x') count_x++;else if (currentChar == 'a') count_a++;else if (currentChar == 'o') count_o++;else if (currentChar == 'm') count_m++;else if (currentChar == 'i') count_i++;else{continue;}}}return (count_x >= 1 && count_a >= 1 && count_o >= 1 && count_m >= 1 && count_i >= 2);
}int countSubmatrices(const vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {int m = matrix.size();int n = matrix[0].size();int count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < m - 2; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < n - 2; ++j) {if (isValidSubmatrix(matrix, i, j)) {count++;}}}return count;
}int main() {// 示例 4x4 的字符矩阵vector<vector<char>> matrix = {{'x', 'i', 'a', 'q'},{'o', 'i', 'm', 'e'},{'x', 'a', 'i', 'c'},{'c', 'a', 'd', 'f'}};int result = countSubmatrices(matrix);cout << "满足条件的3x3子矩阵数量为: " << result << endl;return 0;
}42.接雨水
动态规划
1)统计每个下标左边的最大值,正向遍历
2)统计每个下标右边的最大值,反向遍历
3)计算每个下标的储水量,累加
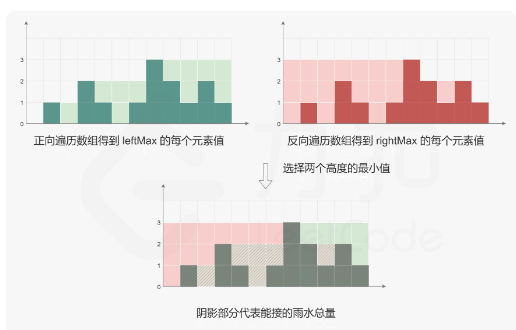
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)class Solution {
public:int trap(vector<int>& height) {if(height.size()<=2) return 0;vector<int>leftHeight(height.size(),0);vector<int>rightHeight(height.size(),0);int size=rightHeight.size();leftHeight[0]=height[0];for(int i=1;i<size;i++){leftHeight[i]=max(height[i],leftHeight[i-1]);}rightHeight[size-1]=height[size-1];for(int i=size-2;i>=0;i--){rightHeight[i]=max(height[i],rightHeight[i+1]);}int sum=0;for(int i=0;i<size;i++){int h=min(leftHeight[i],rightHeight[i])-height[i];if(h>0) sum+=h;}return sum;}
};
有序链表
法一,先放到数组
class Solution
{
public:ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {if(head==nullptr) return head;vector<ListNode*>v;ListNode*cur=head;while(cur){v.push_back(cur);cur=cur->next;}sort(v.begin(),v.end(),[](ListNode*a,ListNode*b){return a->val<b->val;});cur=v[0];for(int i=1;i<v.size();++i){cur->next=v[i];cur=v[i];}cur->next=nullptr;return v[0];}
};
法二:合并2个有序链表,中点划分链表
class Solution
{
public:ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {return sortList(head,nullptr);}ListNode*sortList(ListNode*head,ListNode*tail){if(head==nullptr){return head;}if(head->next==tail){head->next=nullptr;return head;}//找中点,以中点位2分界拆分成2个子链表,快慢指针ListNode*slow=head,*fast=head;while(fast!=tail){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next;if(fast!=tail){fast=fast->next;}}ListNode*mid=slow;return merge(sortList(head,mid),sortList(mid,tail));}//合并两个有序链表ListNode*merge(ListNode*head1,ListNode*head2){ListNode*dummyHead=new ListNode(0);ListNode*temp=dummyHead,*temp1=head1,*temp2=head2;while(temp1!=nullptr&&temp2!=nullptr){if(temp1->val<=temp2->val){temp->next=temp1;temp1=temp1->next;}else{temp->next=temp2;temp2=temp2->next;}temp=temp->next;}if(temp1!=nullptr){temp->next=temp1;}if(temp2!=nullptr){temp->next=temp2;}return dummyHead->next;}
};
一个数恰好等于它的因子之和
比如6=1+2+3,称为完数,问1-10000有多少个完数
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>//找因子
std::vector<int> findFactors(int num) {std::vector<int> factors = {1}; // 1 是所有正整数的因子for (int i = 2; i <= num / 2; ++i) {if (num % i == 0) {factors.push_back(i);}}return factors;
}//找出所有完数
std::vector<int> findPerfectNumbers(int limit) {std::vector<int> perfectNumbers;for (int num = 2; num <= limit; ++num) {if (std::find(perfectNumbers.begin(), perfectNumbers.end(), num) != perfectNumbers.end()) {continue; // 避免重复计算已经找到的完数}std::vector<int> factors = findFactors(num);int sum = 0;for (int factor : factors) {sum += factor;}if (sum == num) {perfectNumbers.push_back(num);}}return perfectNumbers;
}int main() {int limit = 10000;std::vector<int> perfectNumbersList = findPerfectNumbers(limit);std::cout << "在1到" << limit << "之间有" << perfectNumbersList.size() << "个完数,它们分别是:" << std::endl;for (int num : perfectNumbersList) {std::cout << num << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}大数相减
// 函数用于模拟字符串相加,包括进位处理
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {int carry = 0;string result;// 让两个字符串等长,短的字符串前面补0int len = max(num1.length(), num2.length());num1 = string(len - num1.length(), '0') + num1;num2 = string(len - num2.length(), '0') + num2;for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {int digit1 = num1[i] - '0';int digit2 = num2[i] - '0';int sum = digit1 + digit2 + carry;carry = sum / 10;result += to_string(sum % 10);}if (carry > 0) {result += to_string(carry);}reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // 反转结果字符串return result;
}浮点数相加
//字符串转浮点stod
//自定义函数用于将浮点数字符串转换为 double
double stringToDouble(const std::string& str) {double result = 0.0;bool isNegative = false;bool isFraction = false;double fractionMultiplier = 0.1;for (char ch : str) {if (ch == '-') {isNegative = true;} else if (ch == '.') {isFraction = true;} else {if (isFraction) {result += (ch - '0') * fractionMultiplier;fractionMultiplier *= 0.1;} else {result = result * 10 + (ch - '0');}}}return isNegative ? -result : result;
}统计元音字母个数
对偶性质
class Solution {
public:long long countVowels(string word) {int n = word.size();unordered_set<char> vowels = {'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'};long long ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (vowels.count(word[i])) {ans += (long long)(i + 1) * (n - i);}}return ans;}
};双链表模拟
假设双链表把一个 q 所指新结点作为非空双向链表中的 p 所指结点的前驱结点插入到该双链表中,算法步骤。
q->Link=p->prev;
p->Link=q;
q->Rink=p;
q->Link->Rlink=q;
输入的句子使用find函数找出NiuNiu,没有则输出-1;限定Python语言
input_sentence = input("请输入句子:") # 获取用户输入的句子# 使用find方法查找子字符串
index = input_sentence.find("NiuNiu")if index != -1:print("NiuNiu 在句子中的索引是:", index)
else:print("NiuNiu 未在句子中找到")字符串排序
2.给定几个字符串,请你分类,对于同一类字符串,可以通过N次交换其中的元素变为一样的,如ABCD和CDBA,不限定交换次数;输入
4
ABCD
BCDA
ACBD
CDAB
输出
1#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>int classifyStrings(std::vector<std::string> strings) {std::set<std::string> sortedStrings;for (const std::string& str : strings) {std::string sortedStr = str;std::sort(sortedStr.begin(), sortedStr.end());sortedStrings.insert(sortedStr);}return sortedStrings.size();
}int main() {int n;std::cin >> n;std::vector<std::string> strings(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {std::cin >> strings[i];}int result = classifyStrings(strings);std::cout << result << std::endl;return 0;
}
105.岛屿的最大面积
class Solution {int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int cur_i, int cur_j) {if (cur_i < 0 || cur_j < 0 || cur_i == grid.size() || cur_j == grid[0].size() || grid[cur_i][cur_j] != 1) {return 0;}grid[cur_i][cur_j] = 0;int di[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};int dj[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};int ans = 1;for (int index = 0; index != 4; ++index) {int next_i = cur_i + di[index], next_j = cur_j + dj[index];ans += dfs(grid, next_i, next_j);}return ans;}
public:int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i != grid.size(); ++i) {for (int j = 0; j != grid[0].size(); ++j) {ans = max(ans, dfs(grid, i, j));}}return ans;}
};
641.双端队列模拟
class MyCircularDeque {
private:vector<int> elements;int rear, front;int capacity;public:MyCircularDeque(int k) {capacity = k + 1;rear = front = 0;elements = vector<int>(k + 1);}bool insertFront(int value) {if (isFull()) {return false;}front = (front - 1 + capacity) % capacity;elements[front] = value;return true;}bool insertLast(int value) {if (isFull()) {return false;}elements[rear] = value;rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;return true;}bool deleteFront() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}front = (front + 1) % capacity;return true;}bool deleteLast() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}rear = (rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity;return true;}int getFront() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return elements[front];}int getRear() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return elements[(rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity];} bool isEmpty() {return rear == front;}bool isFull() {return (rear + 1) % capacity == front;}
};
141.环形链表
判断是否有环
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode*slow=head,*fast=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;if(slow==fast){return true;}}return false;}
};
142.环形链表 II
判断环的位置
相遇之后,slow指针回到出发点,一起走就行
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode*fast=head,*slow=head;while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL){fast=fast->next->next;slow=slow->next;if(slow==fast){ListNode*cur=slow;ListNode*temp=head;while(cur!=temp){temp=temp->next;cur=cur->next;}return temp;}}return NULL; }
};
怎么判断顺子5个
1)法一,先sort,然后遍历从第2个开始,看当前的是不是等于前一个+1
2)法二:放到set里面,判断最大值-最小值<5,且set的size=5
83.删除链表中的重复元素
1-2-2删除后为1-2
法一, 借助数组
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {vector<int>ans;ListNode*cur=head;while(cur){ans.push_back(cur->val);cur=cur->next;}ans.erase(unique(ans.begin(),ans.end()),ans.end());ListNode*dummyNode=new ListNode(0);ListNode*now=dummyNode;for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++){now->next=new ListNode(ans[i]);now=now->next;}return dummyNode->next;}
};
法二,一次遍历
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL){return head;}ListNode*cur=head;while(cur->next!=NULL){if(cur->val==cur->next->val){cur->next=cur->next->next;}else{cur=cur->next;}}return head;}
};
82.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
删除链表中所有重复出现过的数,即1-2-2删除后为1
//一次遍历
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {if (!head) {return head;}ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);ListNode* cur = dummy;while (cur->next && cur->next->next) {if (cur->next->val == cur->next->next->val) {int x = cur->next->val;while (cur->next && cur->next->val == x) {cur->next = cur->next->next;}}else {cur = cur->next;}}return dummy->next;}
};
//哈希集合
class Solution
{
public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head){unordered_set<int>us;ListNode*s=head;//将链表中的重复元素的值放入哈希集合while(s!=NULL&&s->next!=NULL){if(s->val==s->next->val)us.insert(s->val); s=s->next;}//遍历链表,与哈希集合比较,重复则删除ListNode* prehead=new ListNode(-1);prehead->next=head;ListNode*pre=prehead;s=head;while(s!=NULL){if(us.find(s->val)==us.end())//没有重复结点{s=s->next;pre=pre->next; }else{pre->next=s->next;s=s->next; }}return prehead->next;}
};
已经排好序的数组,找两个和为num的数字
//二分查找
//数组中的元素最多遍历一次,时间复杂度为 O(n*log(n))。
//只使用了两个额外变量,空间复杂度为 O(1)。
class Solution
{
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& numbers, int target) {for (int i=0;i<numbers.size();++i){int low=i+1,high=numbers.size()-1; //细节i+1 while(low<=high){int mid=low+(high-low)/2;if(numbers[mid]==target-numbers[i]){return {i+1,mid+1};}else if(numbers[mid]>target-numbers[i]){high=mid-1;}else{low=mid+1;}}} return {-1,-1};}
};补充知识
set_union并集
求两个有序序列的并集,合并结果包含所有的不重复元素,并拷贝到一个新的序列,前提是这两个序列的排序规则一样。
set_intersection交集
求两个有序序列的交集,合并结果是两个集合重合的元素,并拷贝到一个新的序列,前提是这两个序列的排序规则一样。
set_difference差集
求两个有序序列的差集,合并结果是在第一个集合中存在而在第二个集合中不存在的元素,并拷贝到一个新的序列,前提是这两个序列的排序规则一样。
set_symmetric_difference异或集
求两个有序序列的异或集,合并结果是两个序列合并后去除重合的元素,并拷贝到一个新的序列,前提是这两个序列的排序规则一样。