目录
一 . 底层结构--哈希
1.直接定址法
2. 除留余数法 + 哈希桶
3. 一些定义
二 . 模拟实现哈希表
1.哈希表框架
编辑
2.插入
3.查找
4 . 删除
5.解决使用问题
6.完整代码
三 .实现unordered_map, unordered_set
1. 初步实现unordered_map, unordered_set
2.加上迭代器(自行理解)
3.测试用例
一 . 底层结构--哈希
哈希思想:构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素。
哈希方法构造出来的结构称为哈希表(Hash Table)(或者称散列表)
1.直接定址法
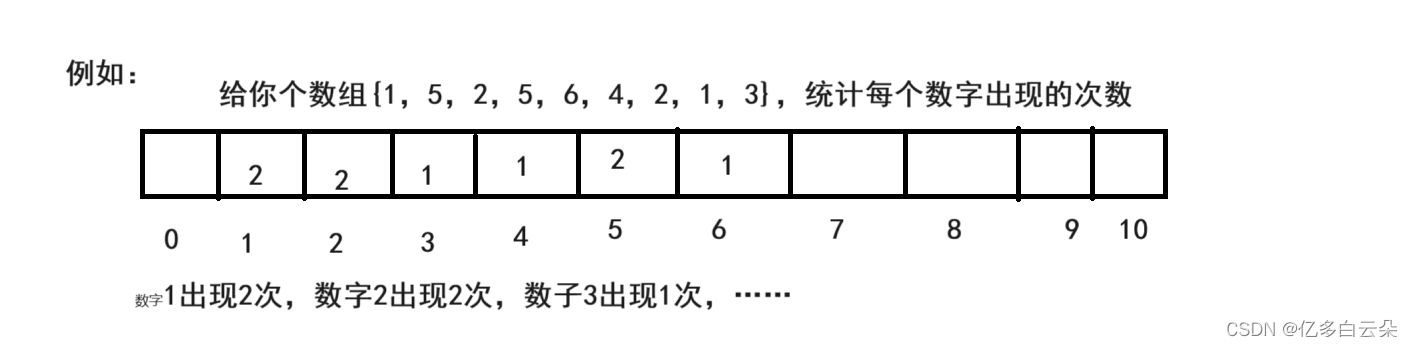
2. 除留余数法 + 哈希桶
如果数据过多,并且数据很散,直接定址法不适合。
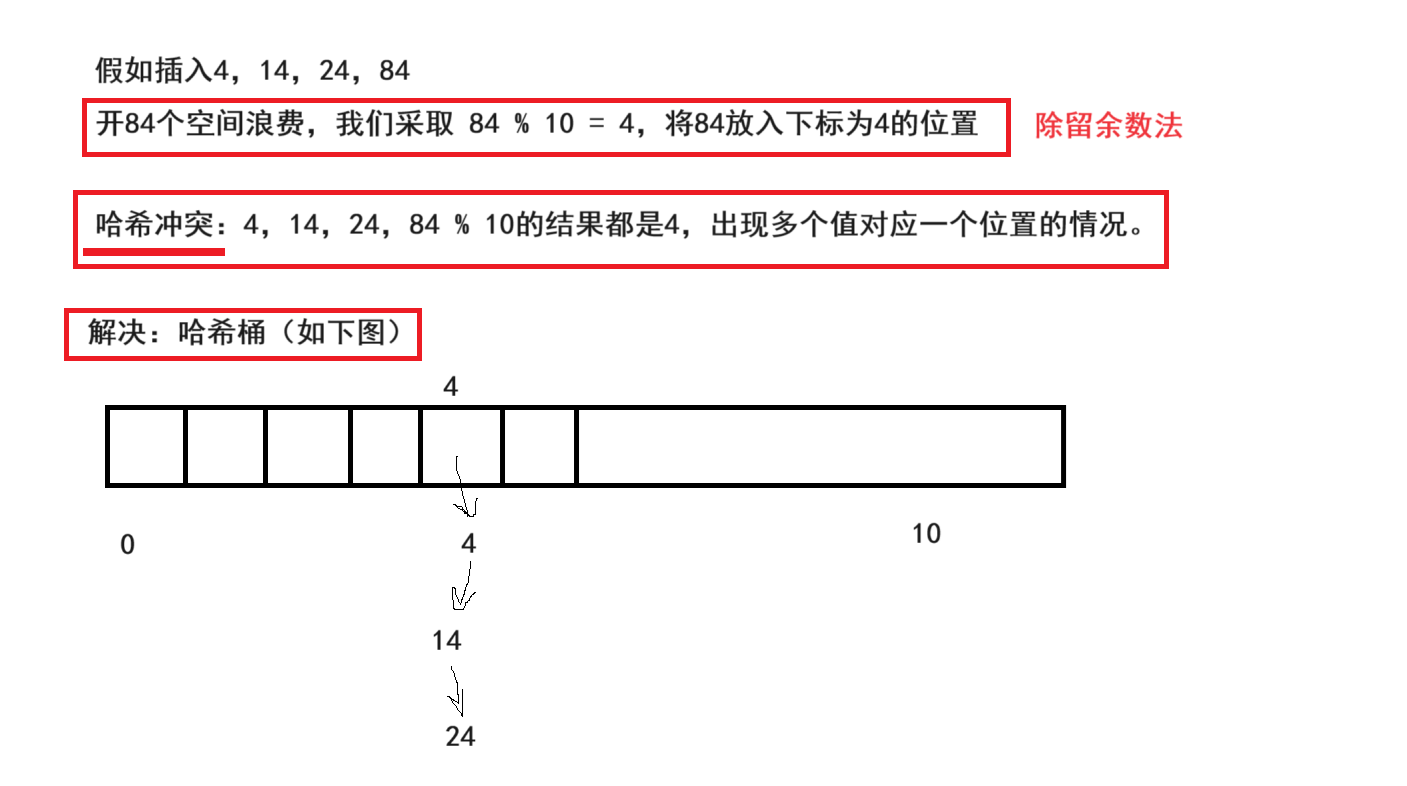
3. 一些定义
不同关键字(4,14,24,84)通过相同的方法(% 10)计算出相同的哈希地址,该种现象称为哈希冲突或哈希碰撞。
解决哈希冲突两种常见的方法是:闭散列和开散列
闭散列:也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有
空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去
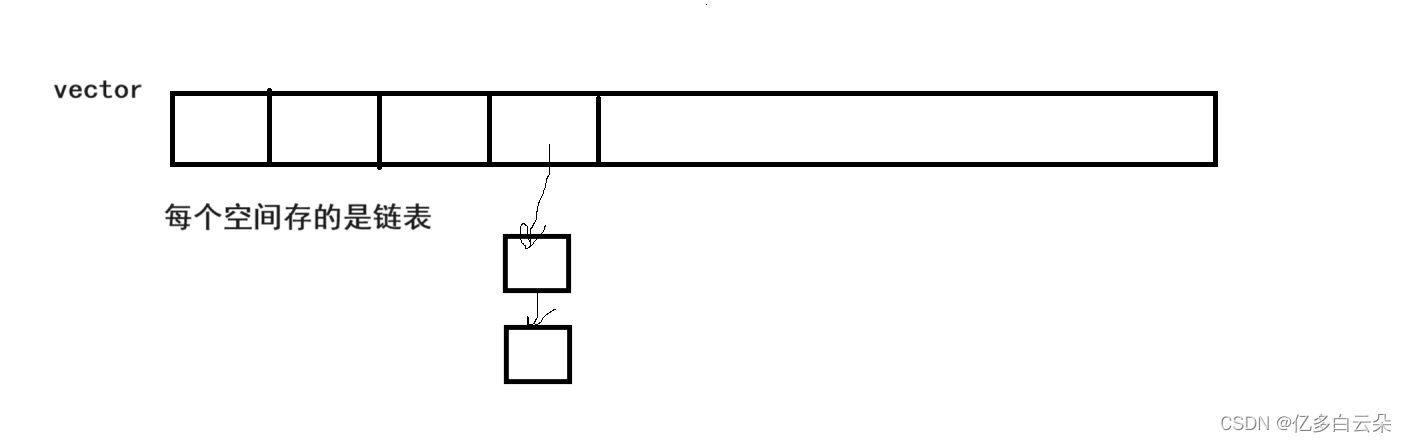
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法):首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地
址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链
接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
(我们采用的是开散列法)
二 . 模拟实现哈希表
1.哈希表框架
代码:
//节点
template<class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _next(nullptr){}pair<K, V> _kv;HashNode<K, V>* _next;
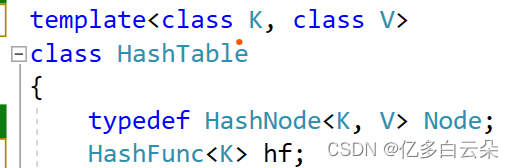
};template<class K, class V>
{typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:HashTable(){_tables.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}}}//删除//插入//查找private:vector<Node*> _tables;size_t _n = 0; // 哈希表实际元素个数
}_n存在的意义:判断_tables什么时候扩容。
开散列最好的情况是:每个哈希桶中刚好挂一个节点,再继续插入元素时,每一次都会发生哈希冲突,因此,在元素个数刚好等于桶的个数时,可以给哈希表增容。
2.插入

bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if(Find(kv.first))return false;//扩容if (_n / _tables.size() == 1){size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newTables;newTables.resize(newSize, nullptr);for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % newTables.size();cur->_next = newTables[hashi];newTables[hashi] = cur;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newTables);}size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();Node* newnode = new Node(kv);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;_n++;return false;}3.查找
Node* Find(const K& key){size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();//找到插入位置Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){return cur;}cur = cur->_next;}return nullptr;}4 . 删除
bool erase(const K& key){size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;if (cur->_kv.first == key){_tables[hashi] = nullptr;return true;}while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){prev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return false;}5.解决使用问题

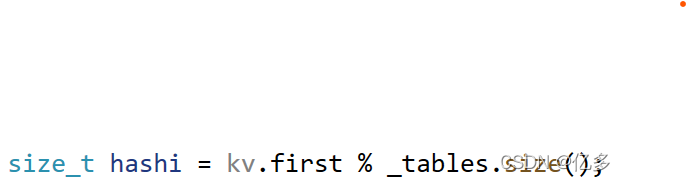
如果kv.first为string或者其他类型,就会出问题。
解决:
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t sum = 0;for (auto& e : key){sum *= 31;sum += e;}return sum;}
};接着把所有用除留余数法的部分进行修改:

6.完整代码
#pragma oncetemplate<class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _next(nullptr){}pair<K, V> _kv;HashNode<K, V>* _next;
};template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t sum = 0;for (auto& e : key){sum *= 31;sum += e;}return sum;}
};//哈希桶
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;Hash hf;
public:HashTable(){_tables.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}}}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if(Find(kv.first))return false;//扩容if (_n / _tables.size() == 1){size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newTables;newTables.resize(newSize, nullptr);for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){size_t hashi = hf(cur->_kv.first) % newTables.size();cur->_next = newTables[hashi];newTables[hashi] = cur;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newTables);}size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _tables.size();Node* newnode = new Node(kv);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;_n++;return false;}Node* Find(const K& key){size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){return cur;}cur = cur->_next;}return nullptr;}bool erase(const K& key){size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;if (cur->_kv.first == key){_tables[hashi] = nullptr;return true;}while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){prev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return false;}private:vector<Node*> _tables;size_t _n = 0;
};三 .实现unordered_map, unordered_set
1. 初步实现unordered_map, unordered_set
这部分内容类似红黑树封装map,set。
unordered_set.h
#pragma oncetemplate<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{struct KeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:bool insert(const K& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}HashNode<K>* find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}private:HashTable<K, K, KeyOfT> _ht;
};unordered_map.h
#pragma oncetemplate<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{struct KeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:bool insert(const pair<K, V>& key){return _ht.Insert(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}HashNode<pair<K, V>>* find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}private:HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, KeyOfT> _ht;
};HashTable.h
#pragma oncetemplate<class T>
struct HashNode
{HashNode(const T& data):_data(data), _next(nullptr){}T _data;HashNode<T>* _next;
};template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t sum = 0;for (auto& e : key){sum *= 31;sum += e;}return sum;}
};//哈希桶
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{typedef HashNode<T> Node;HashFunc<K> hf;KeyOfT kot;
public:HashTable(){_tables.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}}}bool Insert(const T& data){if(Find(kot(data)))return false;//扩容if (_n / _tables.size() == 1){size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newTables;newTables.resize(newSize, nullptr);for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();cur->_next = newTables[hashi];newTables[hashi] = cur;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newTables);}size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % _tables.size();Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;_n++;return false;}Node* Find(const K& key){size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return cur;}cur = cur->_next;}return nullptr;}bool Erase(const K& key){size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;if (kot(cur->_data) == key){_tables[hashi] = nullptr;return true;}while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){prev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return false;}private:vector<Node*> _tables;size_t _n = 0;
};2.加上迭代器(自行理解)
unordered_map.h
#pragma oncetemplate<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{struct KeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
public:typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfT, Hash>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}const V& operator[](const K& key) const{pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.Erase(key);}private:HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};unordered_set.h
#pragma oncetemplate<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{struct KeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename HashTable<K, K, KeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename HashTable<K, K, KeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;const_iterator begin() const{return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _ht.end();}pair<const_iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){auto ret = _ht.Insert(key);return pair<const_iterator, bool>(const_iterator(ret.first._node, ret.first._pht, ret.first._hashi), ret.second);}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.Find(key);}private:HashTable<K, K, KeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};HashTable.h
#pragma oncetemplate<class T>
struct HashNode
{HashNode(const T& data):_data(data), _next(nullptr){}T _data;HashNode<T>* _next;
};template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t sum = 0;for (auto& e : key){sum *= 31;sum += e;}return sum;}
};//前置声明
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable;//迭代器
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
struct _HTIterator
{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;Node* _node;size_t _hashi;const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* _pht;_HTIterator(Node* node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* pht, size_t hashi):_node(node), _hashi(hashi), _pht(pht){}_HTIterator(Node* node, const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* pht, size_t hashi):_node(node), _hashi(hashi), _pht(pht){}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next){_node = _node->_next;}else//需要哈希表{++_hashi;while (_hashi < _pht->_tables.size()){if (_pht->_tables[_hashi]){_node = _pht->_tables[_hashi];break;}++_hashi;}if (_hashi == _pht->_tables.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->_data);}};//哈希桶
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:typedef HashNode<T> Node;//为了访问HashTable的私有成员template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>friend struct _HTIterator;typedef _HTIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;typedef _HTIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;Hash hf;KeyOfT kot;HashTable(){_tables.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}}}iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){if (_tables[i]){return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);}}return end();}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);}const_iterator begin() const{for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){if (_tables[i]){return const_iterator(_tables[i], this, i);}}return end();}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr, this, -1);}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){iterator it = Find(kot(data));if (it != end())return make_pair(it, false);//扩容if (_n / _tables.size() == 1){size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newTables;newTables.resize(newSize, nullptr);for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();cur->_next = newTables[hashi];newTables[hashi] = cur;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newTables);}size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % _tables.size();Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newnode;_n++;return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this, hashi), true);}iterator Find(const K& key){size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return iterator(cur, this, hashi);}cur = cur->_next;}return end();}bool Erase(const K& key){size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;if (kot(cur->_data) == key){_tables[hashi] = nullptr;return true;}while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){prev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return false;}private:vector<Node*> _tables;size_t _n = 0;
};3.测试用例
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<assert.h>
#include<utility>using namespace std;
#include"HashTable.h"
#include"myunordered_set.h"
#include"myunordered_map.h"void test()
{//HashTable<string, int> ht;//ht.Insert(make_pair("西瓜", 1));//HashNode<string, int>* ret = ht.Find("西瓜");//ret->_kv.second++;//cout << ret->_kv.first << ":" << ret->_kv.second << endl;;//ht.Insert(make_pair("桃子", 1));//ht.Insert(make_pair("桃子", 2));//ht.Insert(make_pair("苹果", 1));
}//void testset()
//{
// unordered_set<string> us;
// us.insert("西瓜");
// us.insert("香蕉");
// us.insert("苹果");
// us.insert("西瓜");
//
// us.erase("西瓜");
// HashNode<string>* ret = us.find("香蕉");
// cout << ret->_data << endl;
//}//void testmap()
//{
// string arr[] = { "西瓜", "香蕉", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "西瓜", "香蕉", "西瓜" };
// unordered_map<string, int> up;
// for (auto e : arr)
// {
// HashNode<pair<string, int>>* ret = up.find(e);
// if (ret)
// {
// ret->_data.second++;
// cout << ret->_data.first << ":" << ret->_data.second << endl;
//
// }
// else
// {
// up.insert(make_pair(e, 1));
// }
// }
//
//}void test_set()
{// 17:05unordered_set<int> us;us.insert(5);us.insert(15);us.insert(52);us.insert(3);unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();while (it != us.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : us){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;
}void test_map()
{//unordered_map<string, string> dict;//dict.insert(make_pair("sort", ""));//dict.insert(make_pair("string", "ַ"));//dict.insert(make_pair("insert", ""));//for (auto& kv : dict)//{// //kv.first += 'x';// kv.second += 'x';// cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;//}//cout << endl;string arr[] = { "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "胡萝卜", "梨子", "橘子", "哈密瓜", "桃子", "西瓜", "西瓜", "梨子" };unordered_map<string, int> count_map;for (auto& e : arr){count_map[e]++;}for (auto& kv : count_map){cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{//test();//testset();//testmap();//test_set();test_map();return 0;
}