上文中我们讲了Java库中自带的阻塞队列,并且讲了如何用阻塞队列来实现生产者消费者模型
【Java】用Java库中自带的阻塞队列以及用阻塞队列实现生产者-消费者模型
下面我们来讲如何用代码实现一个阻塞队列
1、实现一个阻塞队列
阻塞队列 = 普通队列 + 线程安全 + 阻塞
(1)首先实现一个普通队列
class MyBlockingQueue{private int head = 0;private int tail = 0;private int size = 0;String[] array;public MyBlockingQueue(){array = new String[1000];}//取出队首元素public String take() throws InterruptedException {//如果队列为空,则返回nullif (size == 0){return null;}//取出队首元素String elem = array[head];//如果head已经到了队尾,那么下一个置0if(head == array.length){head = 0;}head++;size--;return elem;}//放入元素public void put(String elem) throws InterruptedException { if (size == array.length){return;}array[tail] = elem;if (tail == array.length){tail = 0;}tail++;size++;}
}(2)线程安全
由于put()和take()方法中对各个变量都进行了多次修改,因此我们在实现线程安全时,直接对这两段代码加锁
public String take() throws InterruptedException {synchronized{if (size == 0){return null;}String elem = array[head];if(head == array.length){head = 0;}head++;size--;return elem;}} public void put(String elem) throws InterruptedException { synchronized{if (size == array.length){return;}array[tail] = elem;if (tail == array.length){tail = 0;}tail++;size++;}}并且为了防止内存可见性问题和指令重排序问题,我们给三个变量加上volatile关键字进行修饰
(什么是可见性问题和指令重排序问题?)
【Java】volatile-内存可见性问题
【Java】多线程-单例模式/volatile-指令重排序
private volatile int head = 0;
private volatile int tail = 0;
private volatile int size = 0;(3)阻塞
最后再加上阻塞
取队首元素时,如果队列为空,那么我们直接进行阻塞;等到下一次在另一个线程放入元素时将其唤醒
放元素时,如果队列满了,我们将这个线程阻塞;等到队列可用时,我们在另一个线程唤醒
public String take() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){if (size == 0){this.wait();}String elem = array[head];if(head == array.length){head = 0;}head++;size--;this.notify();return elem;}}public void put(String elem) throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){if (size == array.length){this.wait();}array[tail] = elem;if (tail == array.length){tail = 0;}tail++;size++;this.notify();}}
注意他们唤醒的对应关系
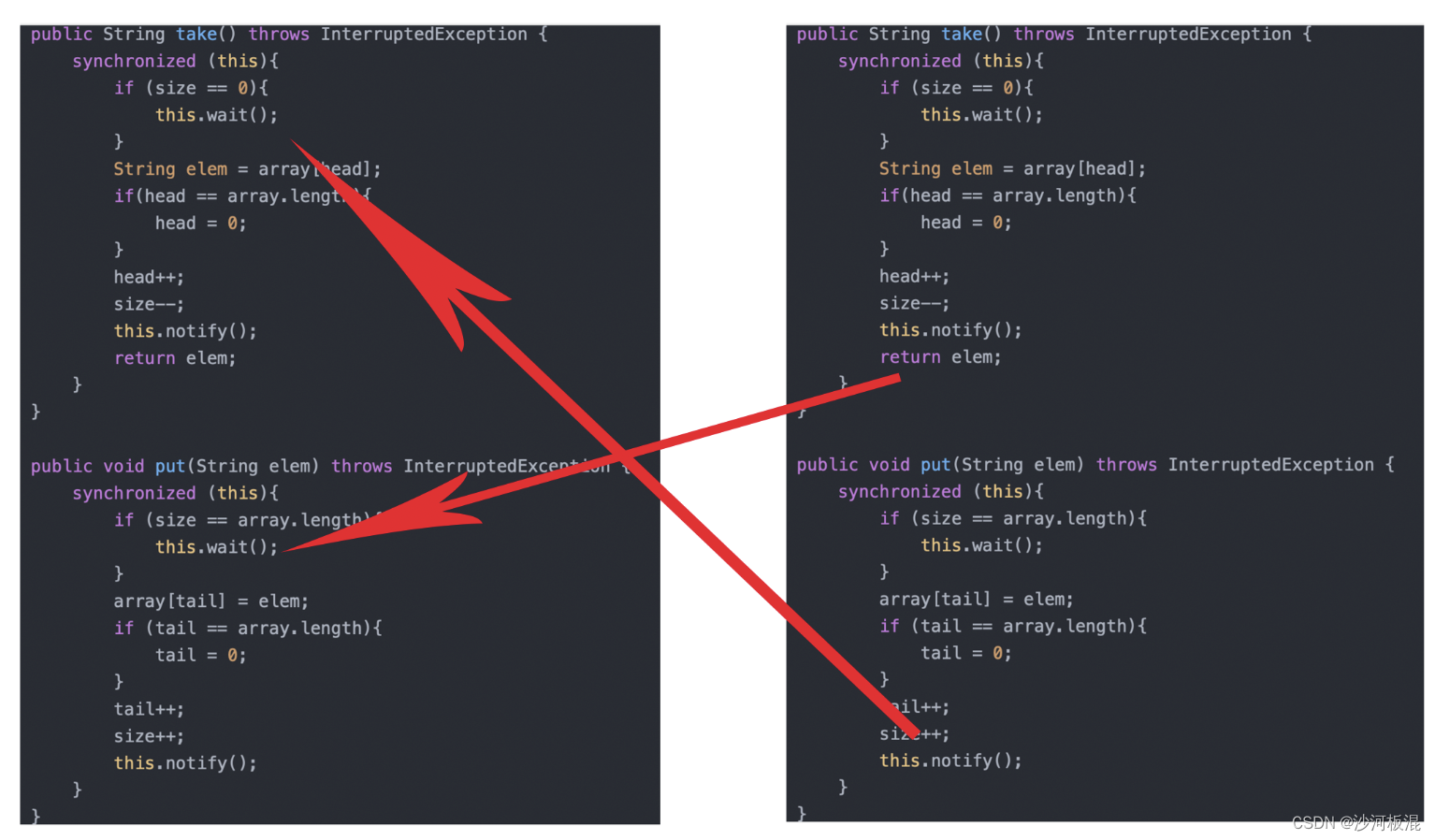
(4)while循环
这其中还存在一个问题,那就是wait()的对象只能被notify()唤醒吗?
答案是不。除了用notify()唤醒,发生InterruptedException异常也可以将对象唤醒
假设队列为空的情况下,发生了InterruptedException异常,对象被唤醒,代码继续往下执行,再想取元素便会出错。因此这种情况下我们还要继续判断队列是否为空
为了解决这个问题,我们将if判断改为while()循环判断,就可以避免上面情况发生
//取出队首元素public String take() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){while (size == 0){this.wait();}String elem = array[head];if(head == array.length){head = 0;}head++;size--;this.notify();return elem;}}//放入元素public void put(String elem) throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){//判断队列是否满了,如果满了则阻塞while (size == array.length){this.wait();}array[tail] = elem;if (tail == array.length){tail = 0;}tail++;size++;this.notify();}}(5)完整代码
实现阻塞队列的完整代码如下
class MyBlockingQueue{private volatile int head = 0;private volatile int tail = 0;private volatile int size = 0;String[] array;public MyBlockingQueue(){array = new String[1000];}//取出队首元素public String take() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){while (size == 0){this.wait();}String elem = array[head];if(head == array.length){head = 0;}head++;size--;this.notify();return elem;}}//放入元素public void put(String elem) throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){//判断队列是否满了,如果满了则阻塞while (size == array.length){this.wait();}array[tail] = elem;if (tail == array.length){tail = 0;}tail++;size++;this.notify();}}
}2、实现生产者-消费者模型
代码如下
class MyBlockingQueue{private volatile int head = 0;private volatile int tail = 0;private volatile int size = 0;String[] array;public MyBlockingQueue(){array = new String[1000];}//取出队首元素public String take() throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){while (size == 0){this.wait();}String elem = array[head];if(head == array.length){head = 0;}head++;size--;this.notify();return elem;}}//放入元素public void put(String elem) throws InterruptedException {synchronized (this){//判断队列是否满了,如果满了则阻塞while (size == array.length){this.wait();}array[tail] = elem;if (tail == array.length){tail = 0;}tail++;size++;this.notify();}}
}public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {MyBlockingQueue myBlockingQueue = new MyBlockingQueue();//生产者Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{int n = 0;while (true){try {myBlockingQueue.put(n +"");} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("生产元素"+n);n++;try {Thread.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});//消费者Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{while (true){try {System.out.println("消费元素" + myBlockingQueue.take());} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});thread1.start();thread2.start();}
}
运行结果如图