3.Gin 框架中的路由简要说明
Gin 框架中的路由
路由概述
路由(Routing)是由一个 URI(或者叫路径)和一个特定的 HTTP 方法(GET、POST 等)
组成的,涉及到应用如何响应客户端对某个网站节点的访问。
RESTful API 是目前比较成熟的一套互联网应用程序的 API 设计理论,所以我们设计我们的路
由的时候建议参考 RESTful API 指南。
在 RESTful 架构中,每个网址代表一种资源,不同的请求方式表示执行不同的操作:
| GET(SELECT) | 从服务器取出资源(一项或多项) |
|---|---|
| POST(CREATE) | 在服务器新建一个资源 |
| PUT(UPDATE) | 在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变后的完整资源) |
| DELETE(DELETE) | 从服务器删除资源 |
简单的路由配置
简单的路由配置
GET 请求示例
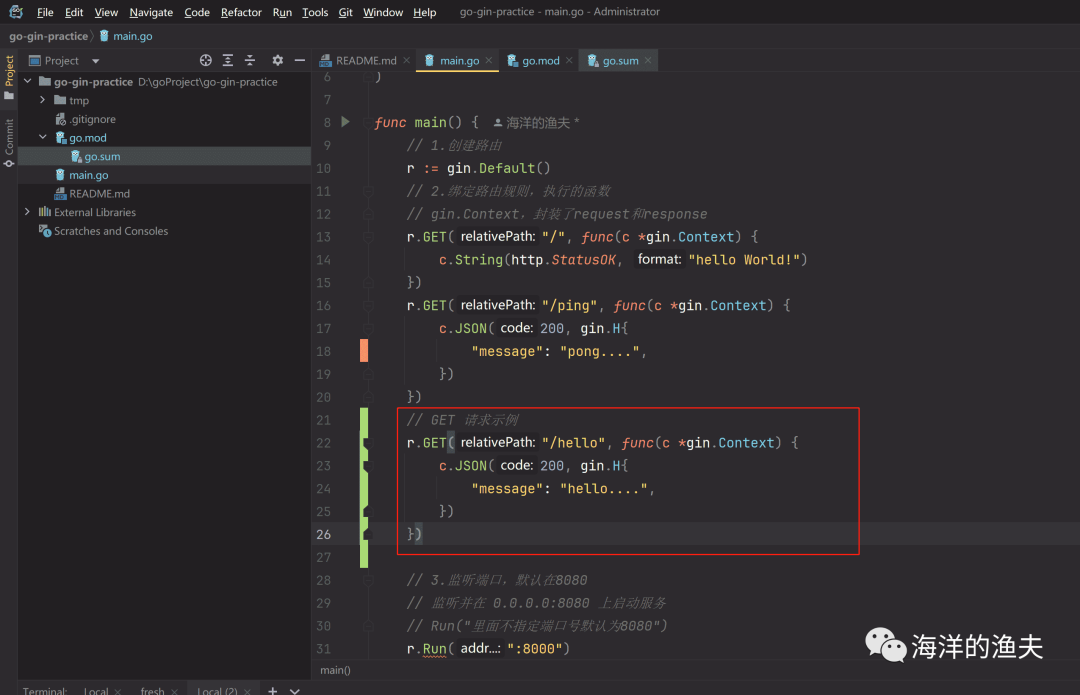
// GET 请求示例
r.GET("/hello", func(c *gin.Context) {c.JSON(200, gin.H{"message": "hello....",})
})测试如下:
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/hello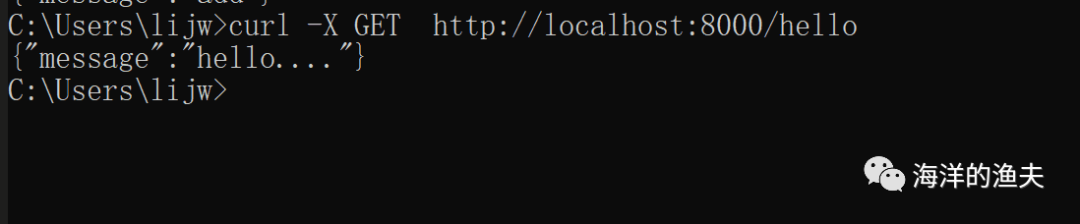
POST请求示例
// POST 请求示例
r.POST("/add", func(c *gin.Context) {c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "add",})
})测试如下:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8000/add
PUT请求示例
// PUT 请求示例
r.PUT("/put", func(c *gin.Context) {c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "put",})
})测试如下:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8000/put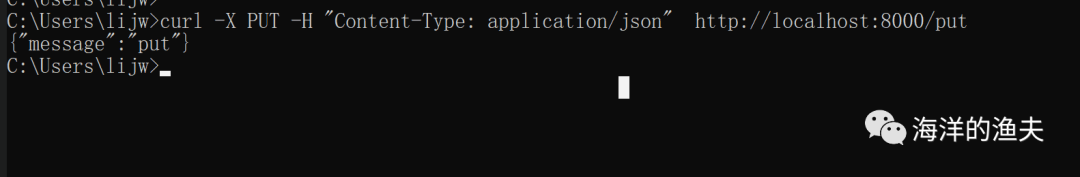
DELETE请求
// DETELE 请求示例
r.DELETE("/delete", func(c *gin.Context) {c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "delete",})
})测试如下:
curl -X DELETE -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8000/delete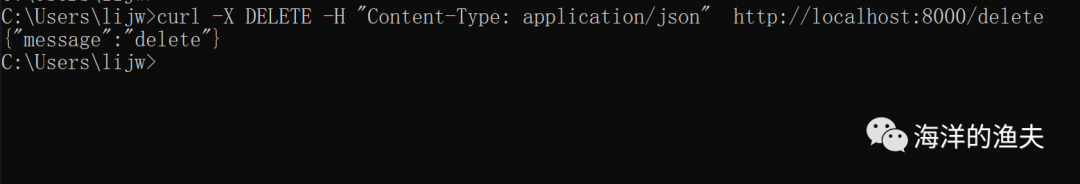
获取query参数、路径参数
路由里面获取 Query 参数
// GET 获取query参数示例
r.GET("/user", func(c *gin.Context) {// 获取query参数uid := c.Query("uid")// 返回响应信息c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": fmt.Sprintf("uid=%s", uid),})
})测试如下:
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/user?uid=test001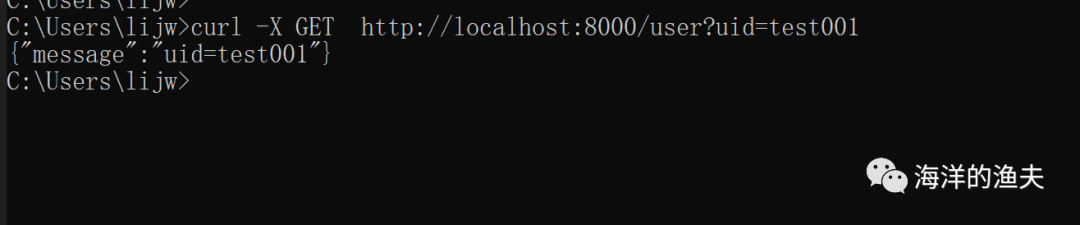
获取动态路由的路径参数
// GET 获取path路径参数
r.GET("/book/:bid", func(c *gin.Context) {// 获取path参数bid := c.Param("bid")// 返回响应信息c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": fmt.Sprintf("bid=%s", bid),})
})测试 如下:
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/book/bid001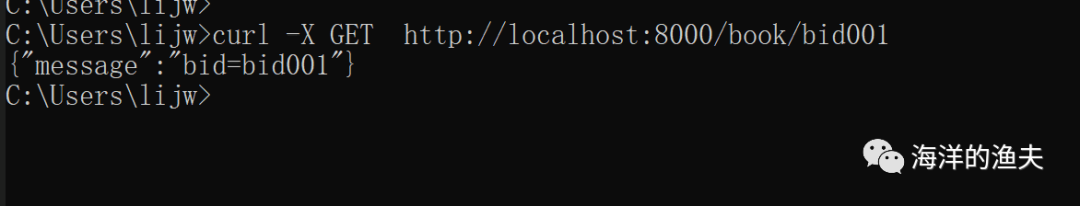
路由响应数据:c.String() c.JSON() c.JSONP() c.XML() c.HTML()
c.String() 返回一个字符串
“在上面的代码示例中,其实已经使用过了。
”
// c.String 响应内容为字符串
r.GET("/news", func(c *gin.Context) {// 获取参数aid := c.Query("aid")// 返回字符串c.String(http.StatusOK, "aid=%s", aid)
})测试如下:
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/news?aid=aid001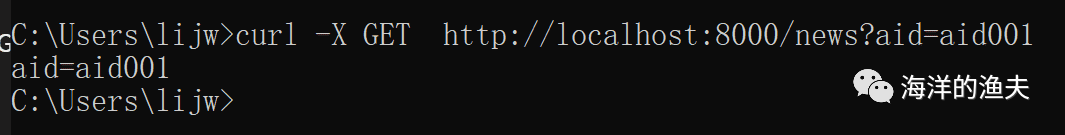
c.JSON() 返回 JSON 字符串
r.GET("/json1", func(c *gin.Context) {// 使用 map[string]any 返回json内容c.JSON(200, map[string]any{"code": 0,"data": "json1",})
})r.GET("/json2", func(c *gin.Context) {// gin.H 是 map[string]any的缩写c.JSON(200, gin.H{"code": 0,"data": "json2",})
})r.GET("/json3", func(c *gin.Context) {// 使用结构体设置JSON结构var msg struct {Name string `json:"user"` // 使用`json:"user"` 定义json字符串返回的别名,例如Name在json字符串中为userMessage string `json:"message"`Age int `json:"age"`}msg.Name = "lijw"msg.Message = "Hello world!"msg.Age = 18// 使用结构体对象,返回JSON数据c.JSON(http.StatusOK, msg)
})测试如下:
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/json1
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/json2
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/json3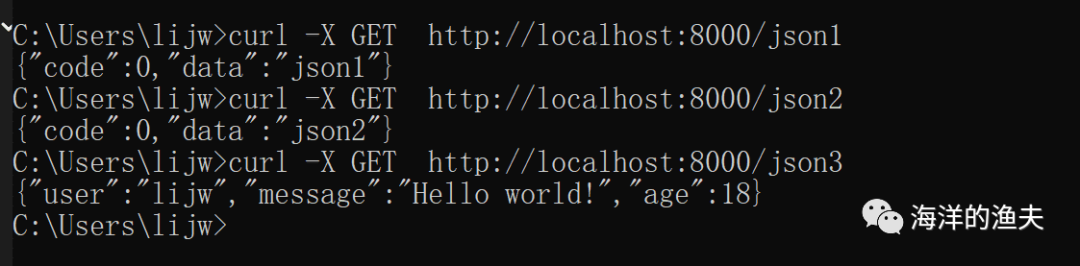
c.JSONP() 返回回调JSON
// c.JSONP() 返回回调JSON
r.GET("/JSONP", func(c *gin.Context) {data := map[string]interface{}{ "foo": "bar", }// /JSONP?callback=x// 将输出:x({\"foo\":\"bar\"})c.JSONP(http.StatusOK, data)
})测试如下:
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/JSONP
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/JSONP?callback=x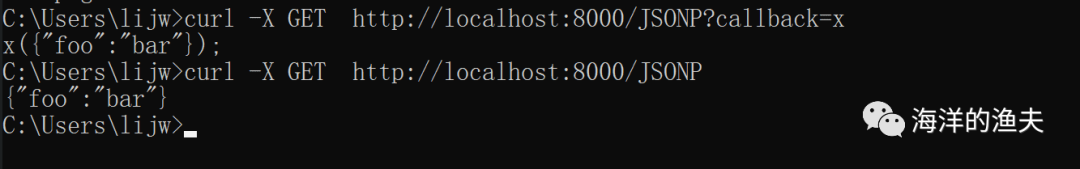
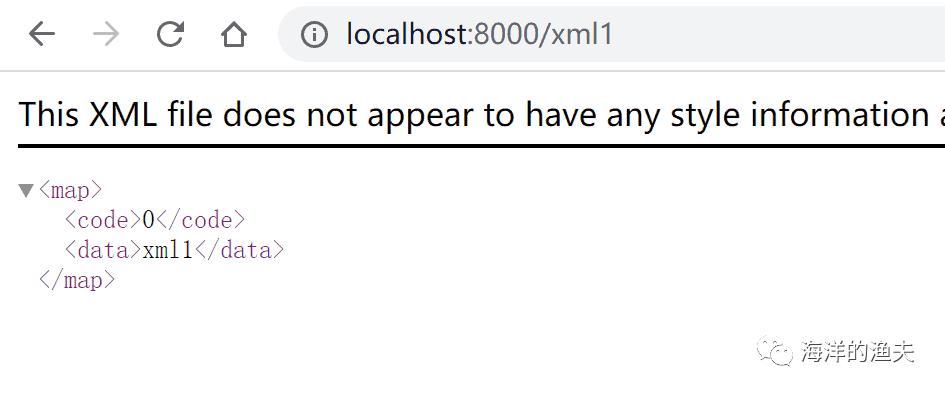
c.XML() 返回 XML 数据
// c.XML() 返回 XML 数据
r.GET("/xml1", func(c *gin.Context) {// 方式一:手动拼接JSONc.XML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 0,"data": "xml1",})
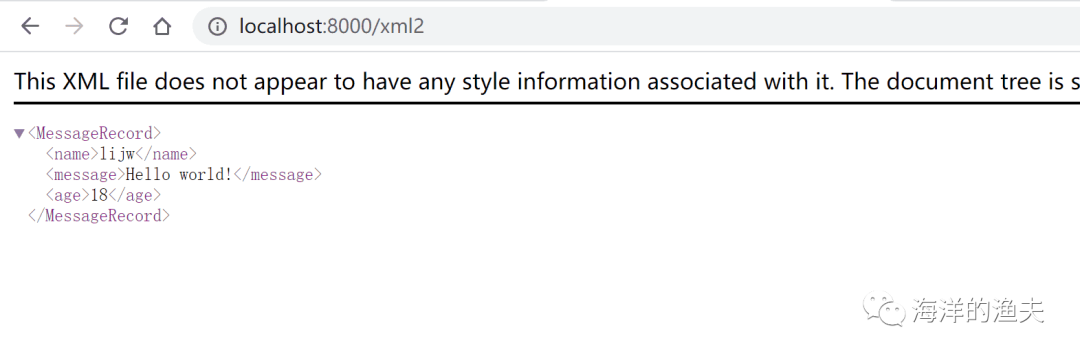
})r.GET("/xml2", func(c *gin.Context) {// 方法二:使用结构体type MessageRecord struct {Name string `xml:"name"`Message string `xml:"data"`Age int `xml:"age"`}var msg MessageRecordmsg.Name = "lijw"msg.Message = "Hello world!"msg.Age = 18// 返回XML格式内容c.XML(http.StatusOK, msg)
})测试如下:
http://localhost:8000/xml1
http://localhost:8000/xml2
c.HTML 渲染模板
创建用于渲染的模板html
templates/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title>
</head>
<body><h1>index</h1><h2>渲染的内容: {{.title}}</h2>
</body>
</html>templates/goods.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title>
</head>
<body><h1>商品页面</h1><h2>渲染的内容: {{.title}}</h2>
</body>
</html>路由加载模板文件
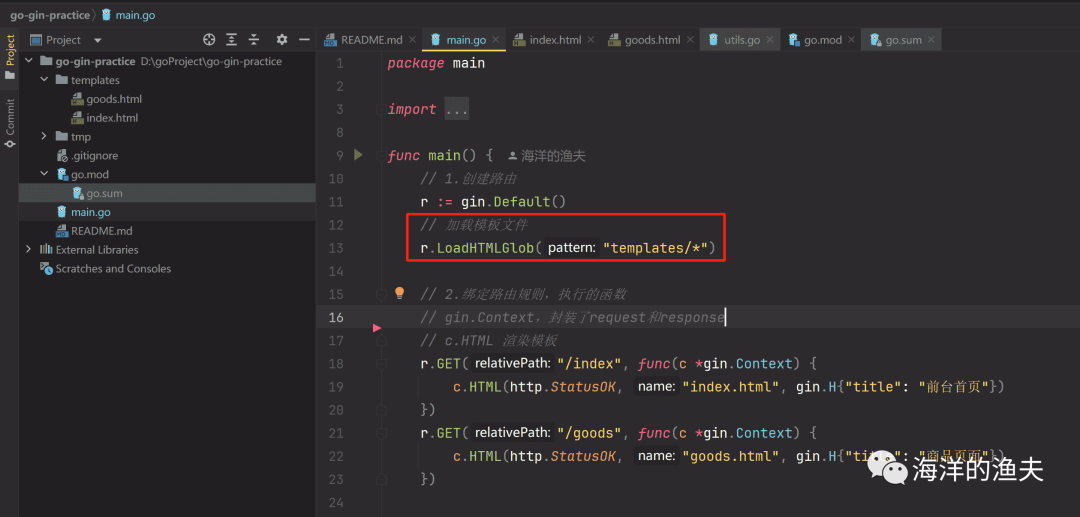
// 加载模板文件
r.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")渲染模板
// c.HTML 渲染模板
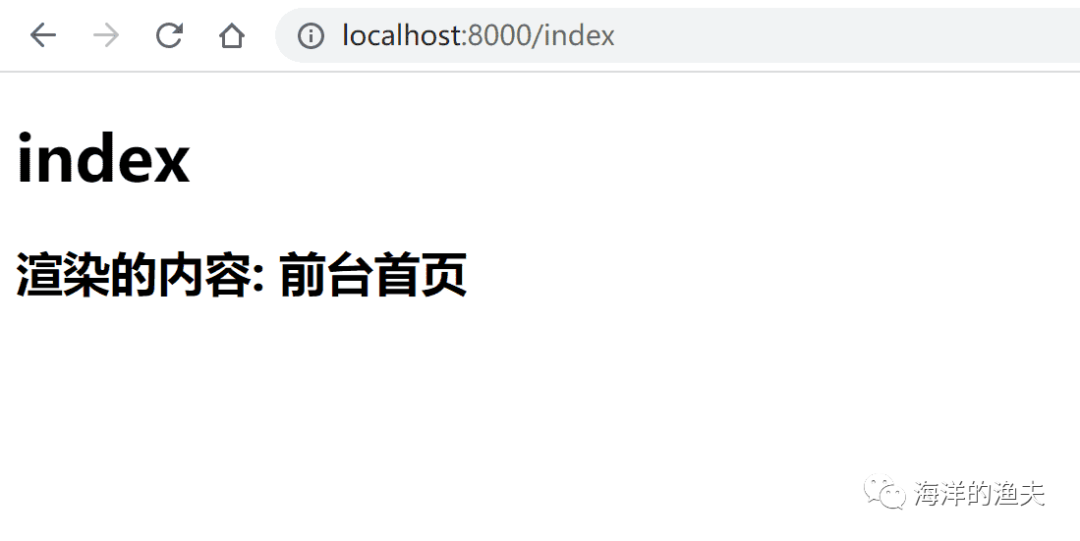
r.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{"title": "前台首页"})
})
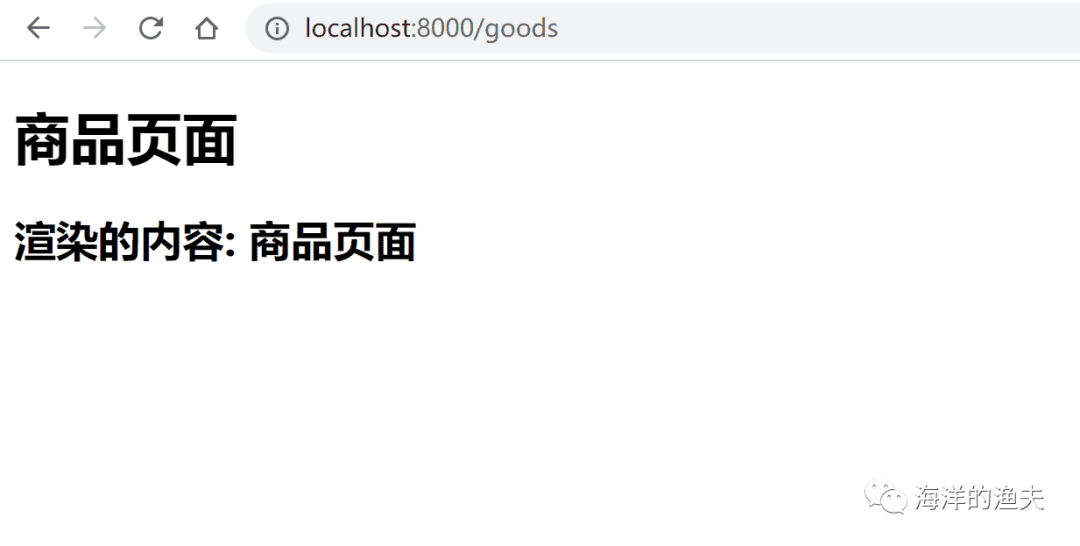
r.GET("/goods", func(c *gin.Context) {c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "goods.html", gin.H{"title": "商品页面"})
})测试如下
访问 http://localhost:8000/index
访问 http://localhost:8000/goods

![④【Set】Redis常用数据类型: Set [使用手册]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20a7f1b58dfb4660b75d7f021c157d57.png#pic_center)