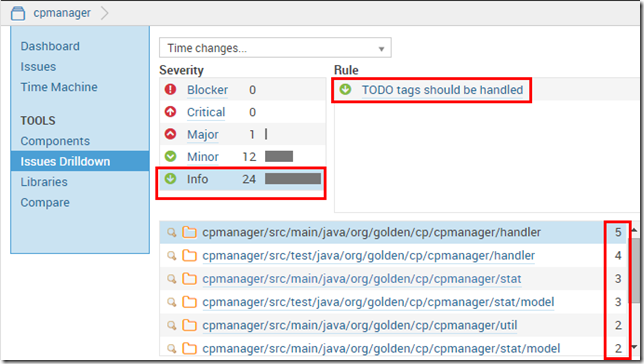
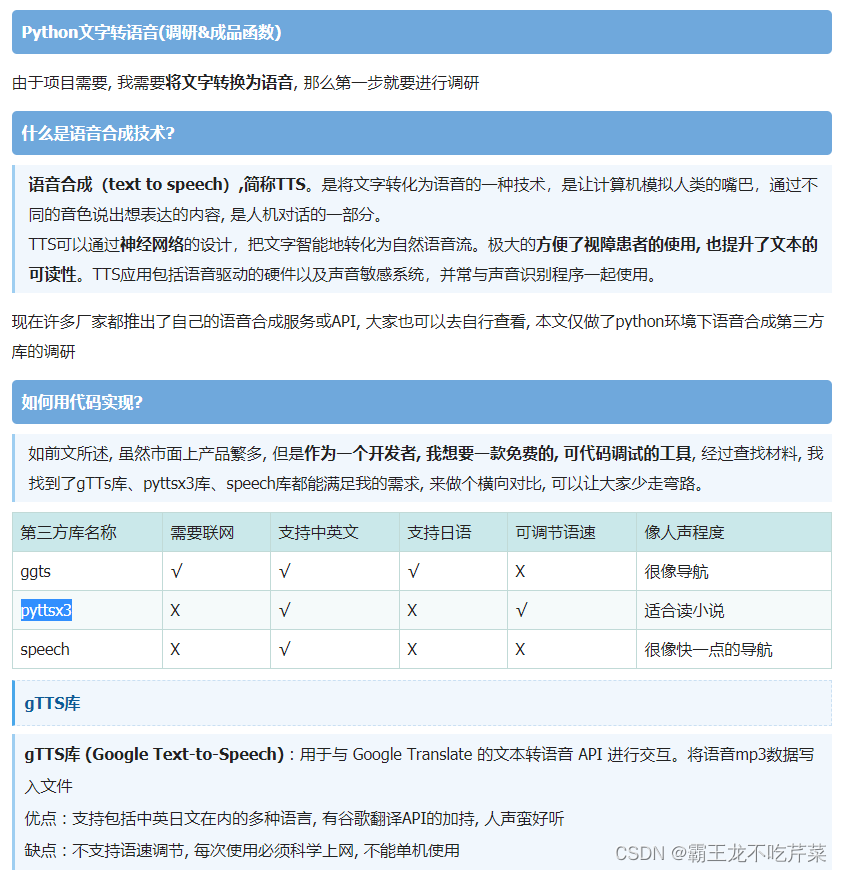
对于1-4问针对的是附录1 中的数据
clc;
close all;
clear;
% 图像文件夹路径
folder_path = 'E:/新建文件夹/yatai/Attachment/Attachment 1/';
% 图像文件列表
image_files = dir(fullfile(folder_path, '*.jpg')); % 假设所有图片都是jpg格式% 解析文件名中的数字,并转换为数值类型
numbers = cellfun(@(x) sscanf(x, '%d.jpg'), {image_files.name});% 根据解析出的数字对文件列表进行排序
[~, sorted_idx] = sort(numbers);
image_files = image_files(sorted_idx);
% 存储每张图片苹果数量的数组
apple_counts = zeros(length(image_files), 1);1,需要对原始的数据预操作,进行数据增强增强
% 应用Retinex算法sigma = 150; % 高斯滤波器的标准差,可以调整enhanced_img = singleScaleRetinex(img, sigma);2.转换色彩空间 进行直方图均值化
% 转换到YCbCr色彩空间进行直方图均衡化
img_ycbcr = rgb2ycbcr(enhanced_img);
Y_channel = img_ycbcr(:,:,1); % Y通道
img_ycbcr(:,:,1) = histeq(Y_channel); % 对Y通道进行直方图均衡化3.LAb色彩空间
% 将处理后的图像转换回RGB色彩空间img_eq = ycbcr2rgb(img_ycbcr);% 转换到LAB色彩空间img_lab = rgb2lab(img);% 分别获取L*, a*, b*通道L_channel = img_lab(:,:,1); % L* 亮度通道a_channel = img_lab(:,:,2); % a* 通道,从绿色到红色b_channel = img_lab(:,:,3); % b* 通道,从蓝色到黄色4.k-means聚类
% 使用k-means算法在a_channel进行颜色聚类numOfClusters = 2; % 你想要的聚类数量[cluster_idx, cluster_center] = kmeans(a_channel_reshape, numOfClusters, 'Distance', 'sqEuclidean', 'Replicates', 3);% 将聚类索引重塑回图像的大小clustered_img = reshape(cluster_idx, rows, cols);clustered_img_color = label2rgb(clustered_img);
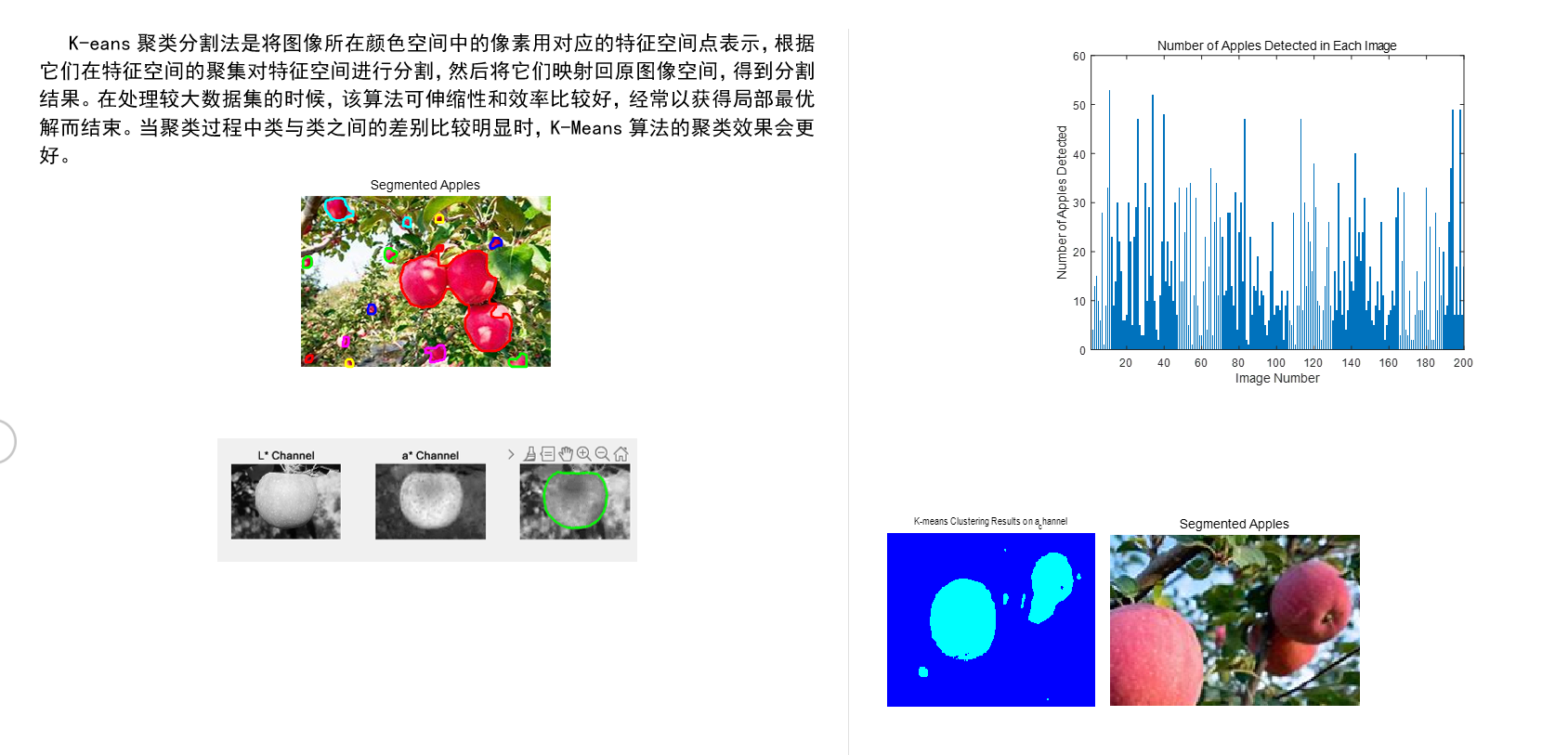

基于1-4问生成的附录2 中的训练集标签用于后续yolov5对苹果的分割检测