文章目录
- 链表结构(LinkedList)
- 链表以及数组的缺点
- 数组
- 链表的优势
- 什么是链表?
- 封装链表相关方法
- 源码
- 链表常见面试题
- 237-删除链表中的节点
- 206 - 反转链表
- 数组和链表的复杂度对比
链表结构(LinkedList)
链表以及数组的缺点
- 链表和数组一样,可以用于存储一系列的元素,但是链表和数组的实现机制完全不同。
- 这一章中,我们就来学习一下另外一种非常常见的用于存储数据的线性结构:链表。
数组
- 要存储多个元素,数组(或称为链表)可能是最常用的数据结构。
- 我们之前说过,几乎每一种编程语言都有默认实现数组结构。
但是数组也有很多缺点
- 数组的创建通常需要申请一段连续的内存空间(一整块的内存),并且大小是固定的(大多数编程语言数组都是固定的),所以当当前数组不能满足容量需求时,需要扩容。(一般情况下是申请一个更大的数组,比如2倍。然后将原数组中的元素复制过去
- 而且在数组开头或中间位置插入数据的成本很高,需要进行大量元素的位移。
- 尽管JavaScript的Array底层可以帮我们做这些事,但背后的原理依然是这样。
链表的优势
要存储多个元素,另外一个选择就是链表
但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中不必是连续的空间。
- 链表的每个元素有一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(有些语言称为指针或者链接)组成。
相对于数组,链表的优势:
-
内存空间不是必须连续的。
√可以充分利用计算机的内存,实现灵活的内存动态管理。
-
链表不必再创建时就确定大小,并且大小可以无限的延伸下去。
-
链表在插入和删除数据时,时间复杂度可以达到O(1)
√相对数组效率高很多
相对数组,链表的缺点:
- 链表访问任何一个位置的元素时,都要从头开始访问。(无法跳过第一个元素访问任何一个元素)。
- 无法通过下标直接访问元素,需要从头一个个访问,直到找到对应元素。
什么是链表?
- 其实上面我们已经简单的提过了链表的结构,我们这里更加详细的分析一下。
- 链表类似于火车:有一个火车头,火车头会连接一个节点,节点上有乘客(类似于数据),并且这个节点会连接下一个节点,以此类推。
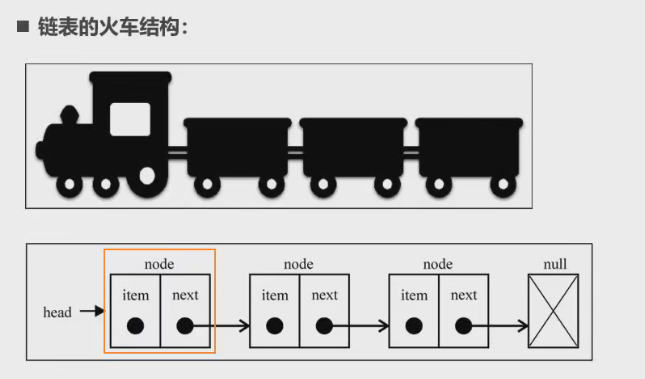
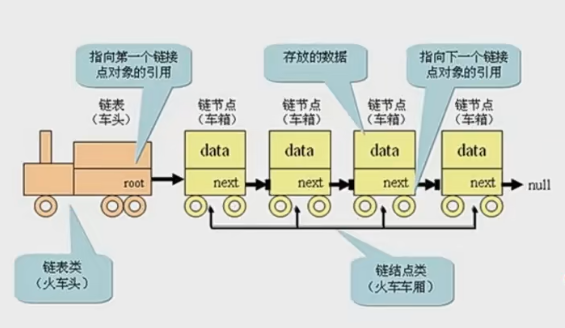
封装链表相关方法
我们先来认识一下,链表中应该有哪些常见的操作
append(element):向链表尾部添加一个新的项
insert(position,element):向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项。
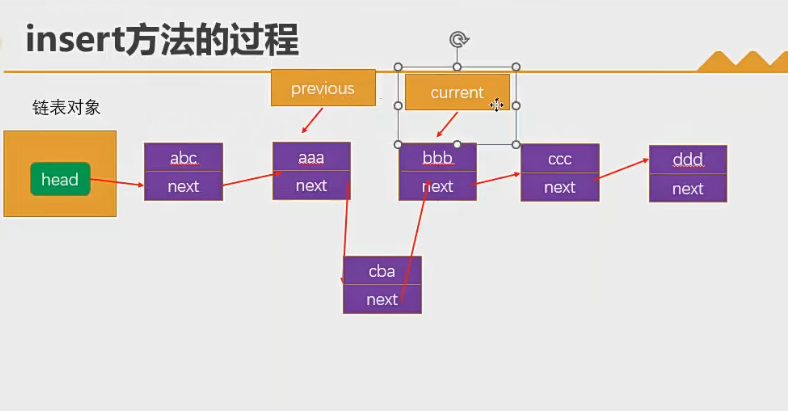
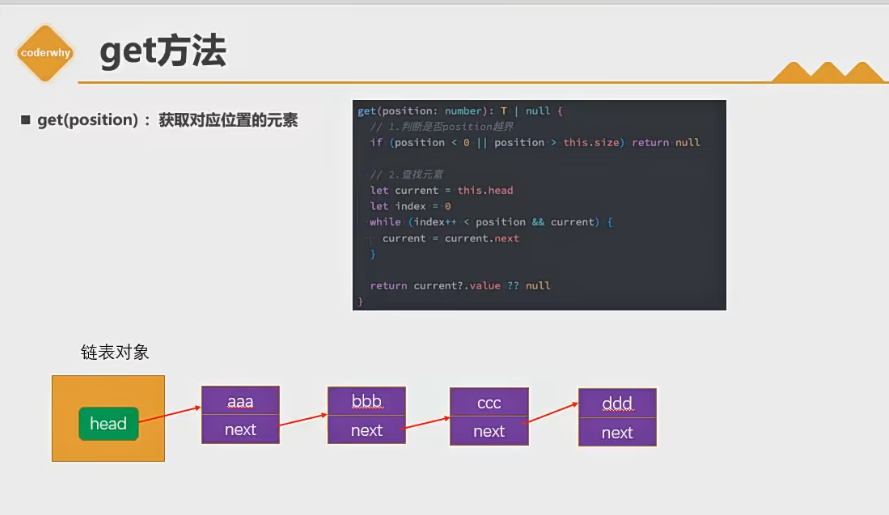
get(position):获取对应位置的元素
indexOf(element):返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素则返回-1。
update(position,element):修改某个位置的元素
removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一项。
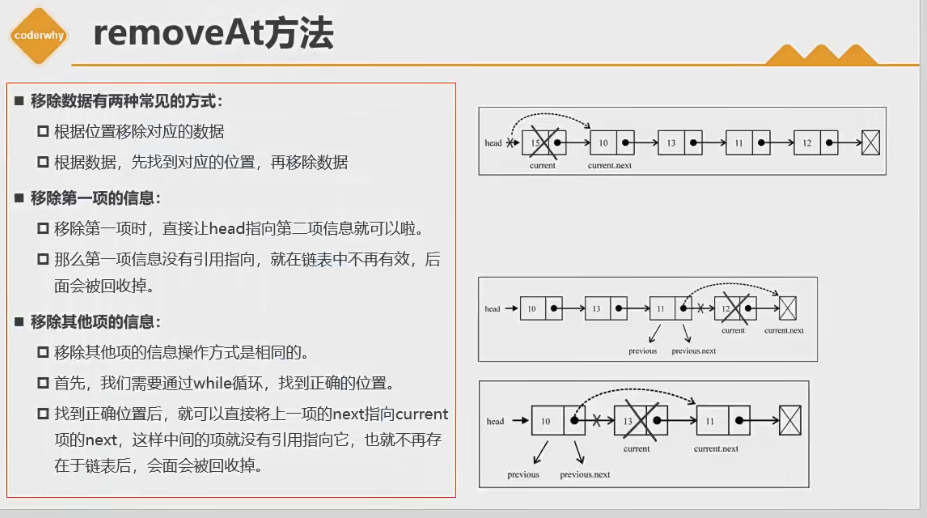
remove(element):从链表中移除一项。
isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0则返回false。
size():返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似。
源码
// 1.创建Node节点类
class Node<T> {value: T;next: Node<T> | null = null;constructor(value: T) {this.value = value;}
}// 2.创建LinkedList的类
class LinkedList<T> {private head: Node<T> | null = null;private size: number = 0;get length() {return this.size;}// 封装私有方法// 根绝positon获取当前的节点(不是节点的value,而是获取节点)private getNode(position: number): Node<T> | null {let index = 0;let current = this.head;while (index++ < position && current) {current = current.next;}return current;}// 追加节点append(value: T) {// 1.根据value新建一个Node节点const newNode = new Node(value);// 2.if (!this.head) {this.head = newNode;} else {let current = this.head;while (current.next) {current = current.next;}// current肯定指向最后一个节点current.next = newNode;}// 3.size++this.size++;}// 遍历链表的方法traverse() {const values: T[] = [];let current = this.head;while (current) {values.push(current.value);current = current.next;}console.log(values.join(" -> "));}//链表插入元素的方法insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {// 1.越界判断if (position < 0 || position > this.size) return false;// 2.根据value创建新的节点const newNode = new Node(value);/* 3.判断* 是否插入头部* 否则就找到需要插入的位置,然后记录前一个节点和当前节点,在前一个节点的next等于newNode,newNode的next等于后一个节点*/if (position === 0) {newNode.next = this.head;this.head = newNode;} else {const previous = this.getNode(position - 1);newNode.next = previous!.next;previous!.next = newNode;}this.size++;return true;}//链表插入元素的方法removeAt(position: number): T | null {// 1.越界判断if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return null;let current = this.head;if (position === 0) {this.head = current?.next ?? null;} else {const previous = this.getNode(position - 1);previous!.next = previous?.next?.next ?? null;}this.size--;return current?.value ?? null;}// 获取方法get(position: number): T | null {if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return null;return this.getNode(position)?.value ?? null;}// 更新方法update(value: T, position: number): boolean {if (position < 0 || position >= this.size) return false;const currentNode = this.getNode(position);currentNode!.value = value;return true;}// 根据值获取该值位置索引indexOf(value: T): number {let current = this.head;let index = 0;while (current) {if (current.value === value) {return index;}index++;current = current.next;}return -1;}// 删除方法,根据value删除remove(value: T): T | null {const index = this.indexOf(value);return this.removeAt(index);}// 判断单链表是否为空的方法isEmpty() {return this.size === 0;}
}export {};链表常见面试题
237-删除链表中的节点
- https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
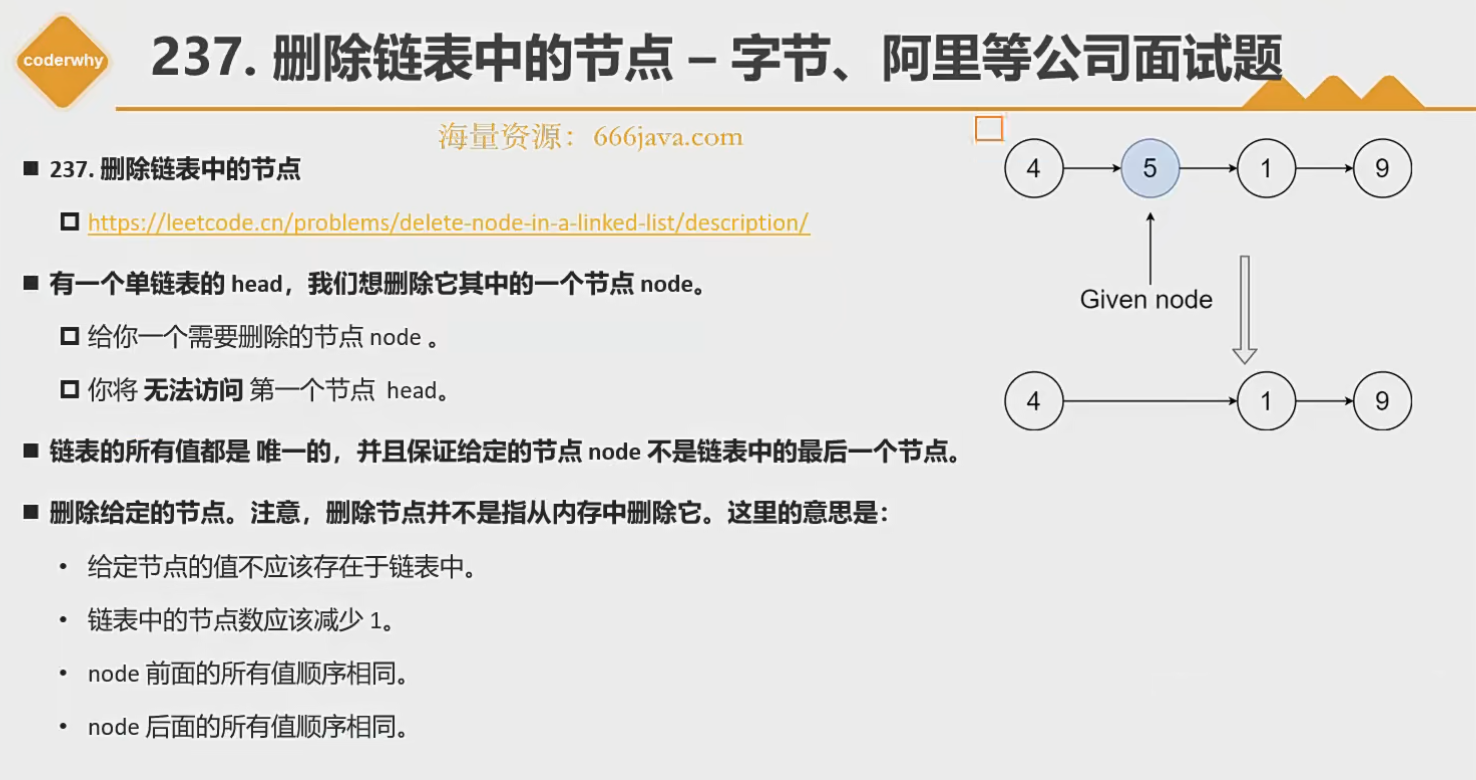
解题
// Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode {val: number;next: ListNode | null;constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;}
}/**Do not return anything, modify it in-place instead.*/
function deleteNode(node: ListNode | null): void {node!.val = node!.next!.valnode!.next = node!.next!.next
}206 - 反转链表
- https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/

- 用栈结构解决
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {if(head === null) return nullif(head.next === null) return headconst stack:ListNode[] = []let current:ListNode | null = headwhile(current) {stack.push(current)current = current.next}const newHead:ListNode = stack.pop()!let newHeadCurrent = newHeadwhile(stack.length) {const node = stack.pop()!newHeadCurrent.next = nodenewHeadCurrent = newHeadCurrent.next}newHeadCurrent.next = nullreturn newHead
};
- 用非递归解题
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {if (head === null || head.next === null) return head;let newHead: ListNode | null = null;// 1.next = 2, 2.next = 3, 3.next = 4while (head) {// 让current指向下一个节点// 目的:保留下个节点的引用,可以拿到,并且不会销毁(current = 2)const current= head.next;// 改变head当前指向的节点,指向newHead// 这里反转链表对于第一节点来说,指向newHead就是null(1.next = null)head.next = newHead;// 让newhead指向head节点// 这里开始准备反转新的节点,目的是下一次遍历时,可以让下一个节点指向第一个节点(newHead = 1)newHead = head;// 让head指向下个节点也就是current(head = 2)head = current;}return newHead;
}

- 用递归方案解题
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {// 递归停止条件,当递归到最后一个节点时停止if (head === null || head.next === null) return head;// 一直递归循环直到符合head === null 时停止递归// 那么拿到的就是链表倒数第二个节点const newHead = reverseList(head.next ?? null)// 反转链表,让最后一个节点指向head开始正式反转head.next.next = head// 让倒数第二个节点的next指向nullhead.next = null// 最后递归完了就是反转后的链表了return newHead
}
数组和链表的复杂度对比
接下来,我们使用大O表示法来对比一下数组和链表的时间复杂度:
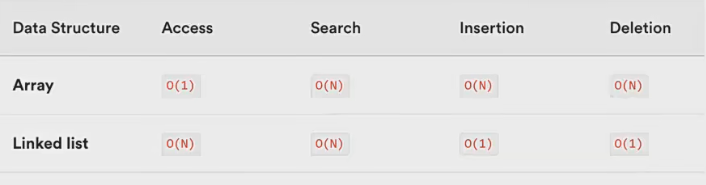
-
数组是一种连续的存储结构,通过下标可以直接访问数组中的任意元素。
-
时间复杂度:对于数组,随机访问时间复杂度为o(1),插入和删除操作时间复杂度为o(n)。
-
空间复杂度:数组需要连续的存储空间,空间复杂度为o(n)。
-
链表是一种链式存储结构,通过指针链接起来的节点组成,访问链表中元素需要从头结点开始遍历。
-
时间复杂度:对于链表,随机访问时间复杂度为o(n),插入和删除操作时间复杂度为o(1)。
-
空间复杂度:链表需要为每个节点分配存储空间,空间复杂度为O(n)。
-
在实际开发中,选择使用数组还是链表需要根据具体应用场景来决定。
-
如果数据量不大,且需要频繁随机访问元素,使用数组可能会更好。
-
如果数据量大,或者需要频繁插入和删除元素,使用链表可能会更好。