面向过程语言:C ——> 重视求解过程
面向对象语言:C++ ——> 重视求解的方法
面向对象的三大特征:封装、继承和多态
C 和 C++ 在语法上的区别
1、命名空间(用于解决命名冲突问题)
2、函数重载和运算符重载(一名多用)
3、引用(和指针类似)
4、面向对象的特征(封装、继承和多态)
5、泛式编程(👈 安全链接,请放心跳转)
6、模板编程
7、STL 标准模板库
8、赋值操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{int a(1); // int a = 1;cout << a << endl;int b(a); // int b = a;cout << b << endl;int c(a+b); // int c = a + b;cout << c << endl;return 0;
}
在 C++11 中对上述写法又进行了升级。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{int a(1); // int a = 1;cout << a << endl;double b = 3.14;int b1 = b; // 3 数据窄化int b2(b);int b3{b}; // 升级:对数据窄化提出警告cout << b << endl;cout << b1 << endl;cout << b2 << endl;cout << b3 << endl;return 0;
}

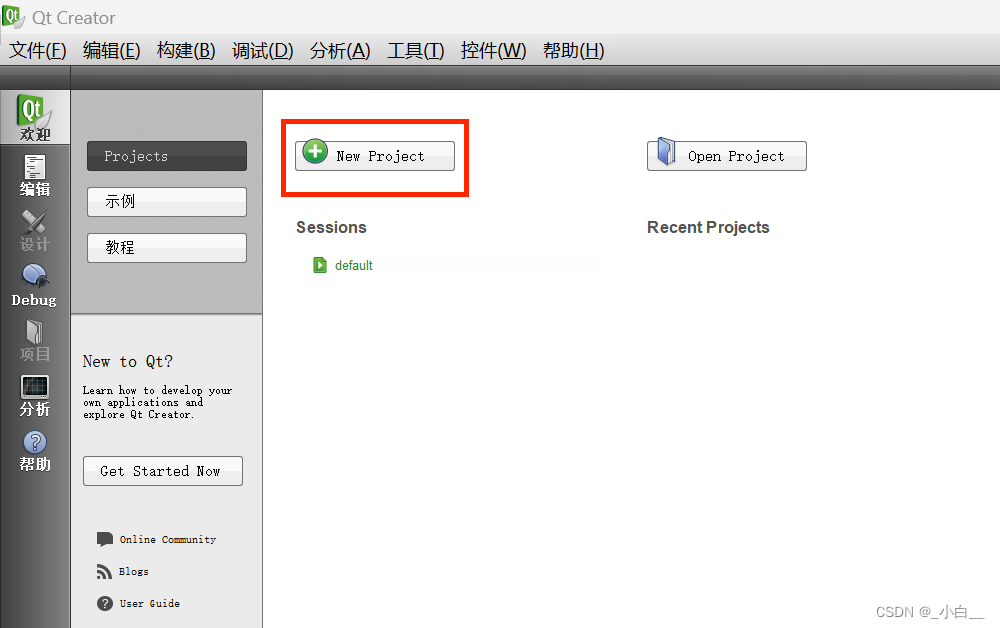
Qt creator
创建桌面快捷方式
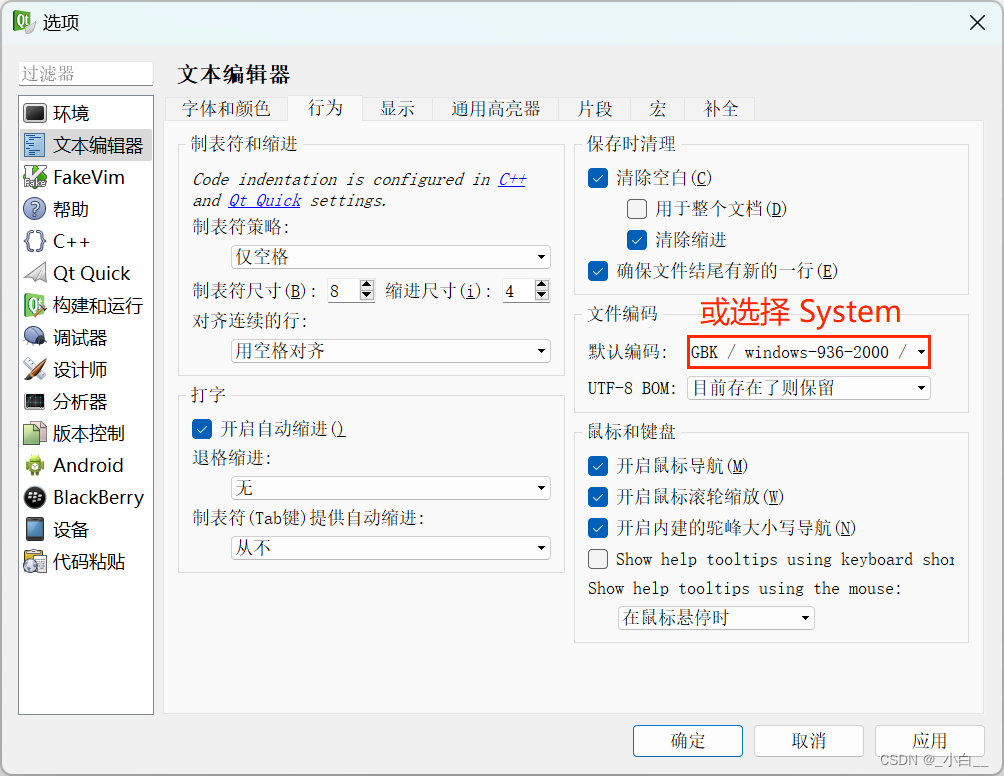
修改编码格式以支持中文
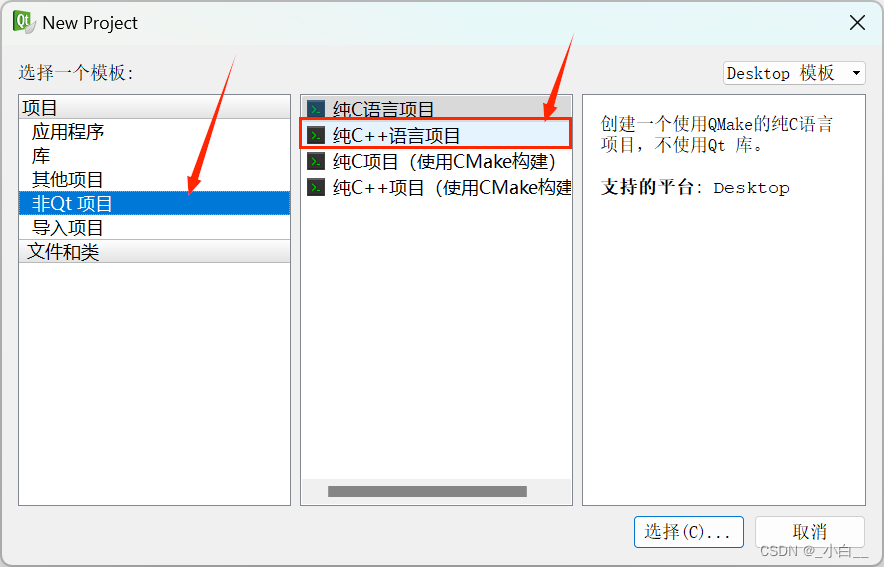
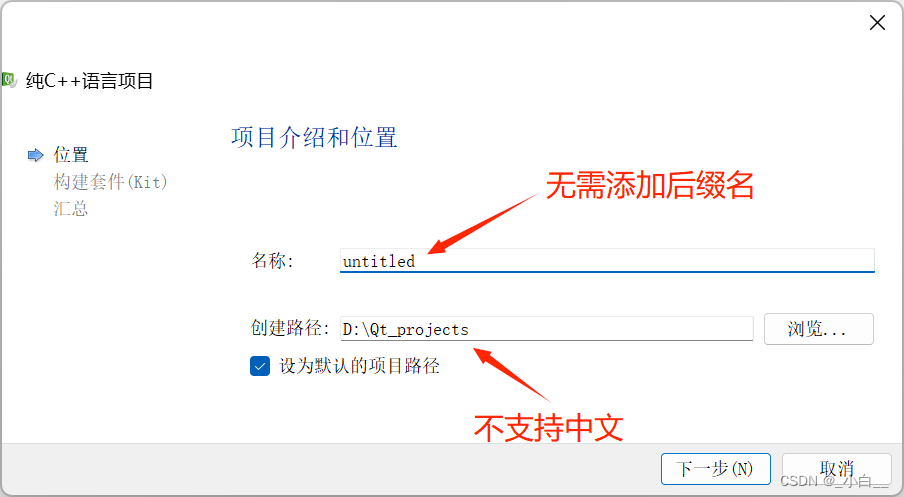
创建 C++ 项目
第一个 C++ 程序
后缀名、编译方式
C 文件: 以 .c 结尾,使用 gcc 编译
C++ 文件: 以 .cpp 或 .C 结尾,使用 g++ 编译(g++也可编译 .c 文件)
C++ 对 C 的兼容
C++ 支持几乎所有的 C 语言语法;
若要在 C++ 文件中引用 C 中的头文件,一般去掉 .h,在头文件前加上c;
#include <cstdio> 等价于 #include <stdio.h> 。
g++ 可以编译 C 程序,但是 gcc 不能编译 C++ 程序。
Hello world
#include <iostream>
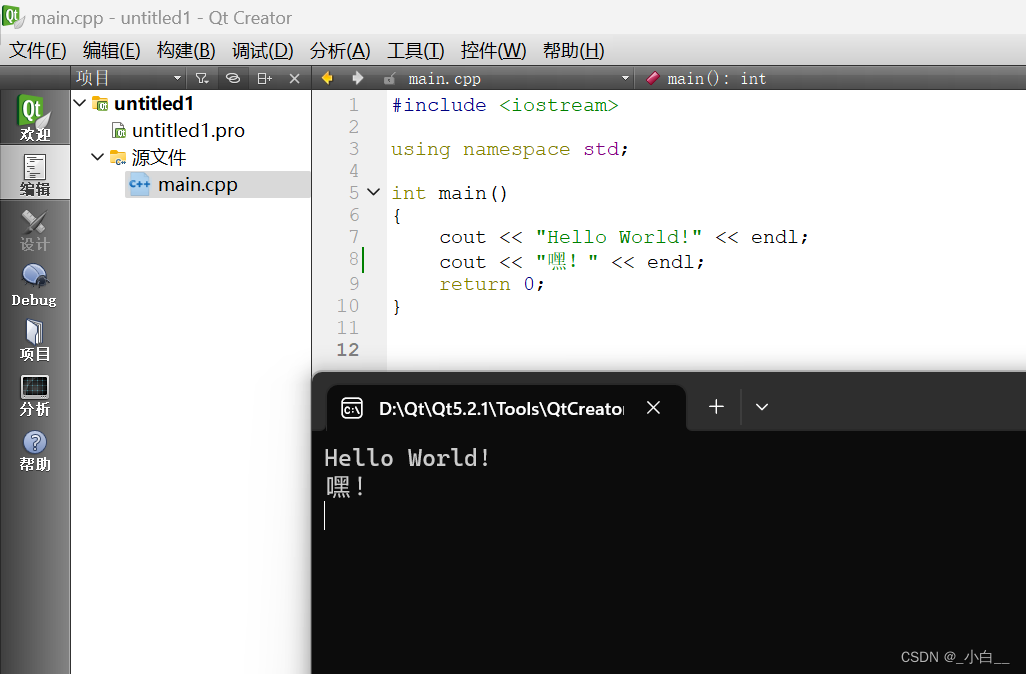
// 导入头文件,导入 istream 和 ostreamusing namespace std; // 使用标准命名空间 stdint main()
{cout << "Hello world!" << endl;cout << "嘿!" << endl;// cout 是一个标准输出流对象// endl 换行// << 插入运算符的重载return 0;
}
标准输出流对象 cout 与 格式化输出 printf
printf() 在输出时,可以使用格式符:%d, %f, %c, %#x, %s…
cout 在输出时,不需要任何格式符,cout 会自动推导输出的类型。
cout 的级联使用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
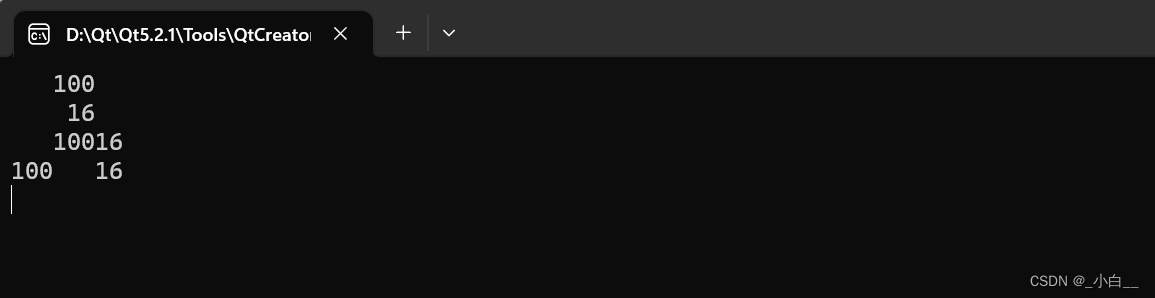
{int a = 100;int b = 16;cout << "a=" << a << endl; // 级联使用 cout // 显示 a=100return 0;
}
cout 输出十六进制、八进制数据
使用关键字(hex、dec、oct)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{int a = 100;int b = 16;// 关键字实现 cout 的输出cout << "十六进制 a: ";cout << hex << a << endl; // 64cout << "b = " << b << endl; // 10 ,因为上一句已经修改过 cout 的输出格式cout << dec << "十进制 b: " << b << endl;return 0;
}
运行结果如下:

使用函数实现格式化输出n进制(setbase(n))
如果使用函数,需要导入头文件<iomanip>。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip> // 使用函数改变 cout 的输出格式
using namespace std;int main()
{int a = 100;int b = 16;// 通过函数实现格式化的输出cout << "八进制 b: ";cout << setbase(8) << b << endl; // 20cout << "a = " << a << endl; // 144 ,因为上一句已经修改过 cout 的输出格式cout << setbase(10) << "十进制 a: " << a << endl; return 0;
}
运行结果如下:

cout 实现对齐输出(setw(n))
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip> // 使用函数改变 cout 的输出格式
using namespace std;int main()
{int a = 100;int b = 16;// cout 实现对齐输出cout << setw(6) << a << endl;cout << setw(6) << b << endl; // setw() 默认右对齐cout << setw(6) << a << b << endl; // 如果想要两个都右对齐,b 的前面也要加 setw(n)cout << setw(6) << left << a << b << endl; // 想要恢复右对齐,只需要把 left 改成 rightreturn 0;
}
运行结果如下:
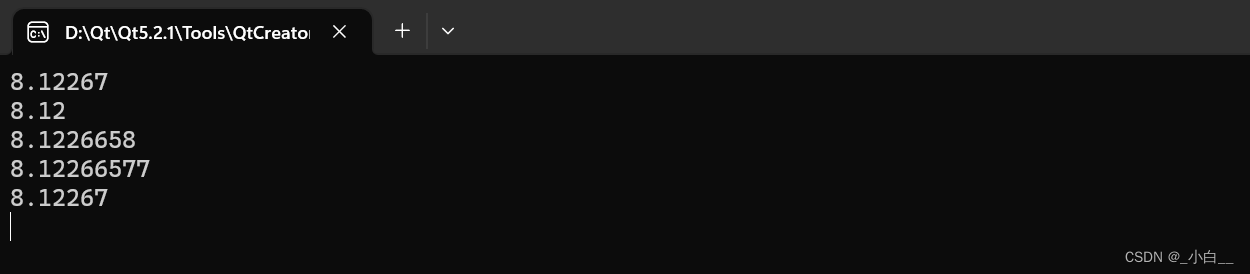
cout 输出浮点型数据(setprecision(n))
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip> // 使用函数改变 cout 的输出格式
using namespace std;int main()
{cout << 8.12266577 << endl; // cout 在输出浮点型数据时,把小数点计入输出位数(默认6位)cout << setprecision(3) << 8.12266577 << endl; // 四舍五入,整数位+小数位共 3 位cout << setprecision(8) << 8.12266577 << endl; // 整数位+小数位共 8 位// 加上 fixed 关键字,小数位 8 位cout << setprecision(8) << fixed << 8.12266577 << endl;// 没有办法取消 fixed 输出格式,但是可以通过 setprecision(5) 以默认格式输出(小数位 5 位)cout << setprecision(5) << 8.12266577 << endl;return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
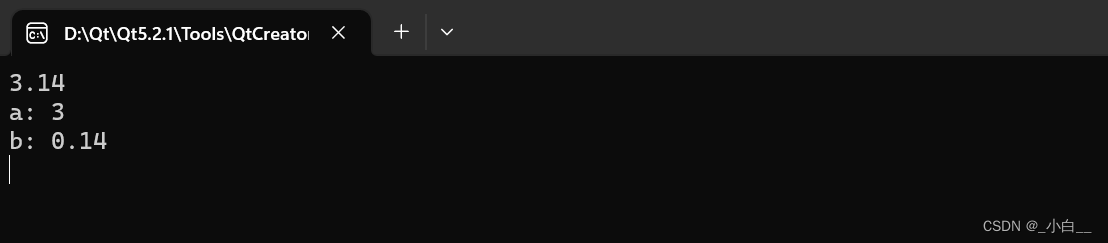
标准输入流对象 cin 与 格式化输入 scanf
cin 是 istream 类的一个类对象,自动推导输入变量的类型。
终端输入和源代码中的输入格式必须严格对应!!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{int a;float b;cin >> a >> b; // cin也可以级联使用,但不能加 endl// cin 会自动控制格式,要求:用户输入和源代码中的输入格式必须严格对应// 比如给整型数据,输入3.14,还在缓冲区的0.14被赋值给下一个浮点型变量,只能输入一次cout << "a: " << a << endl << "b: " << b << endl;return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
命名空间
用于解决 命名冲突/命名污染 的问题。
标准命名空间 std
cout、endl、cin
如果代码中没有 using namespace std,cin、cout 和 endl 会报错。
(可以用 std::cin、std::cout、std::endl 来解决)
命名空间的定义
命名空间中可以存放标识符:变量名、函数名、结构体名、枚举名…
namespace 命名空间名
{
// 定义变量;
// 函数声明; // 只能是函数声明,不能是函数定义
// 结构体名; // 可以直接定义结构体
···
};
命名空间中只能存放函数的声明,不能放函数的定义!
(域限定符 ::)使用某命名空间中的标识符
全局导入整体命名空间
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace mySpace {char str[32] = {};void reverse();
}
using namespace mySpace;int main()
{...}
全局导入部分标识符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace mySpace {char str[32] = {};void reverse();
}
using mySpace::str; // 注意此行int main()
{...}
局部导入标识符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace mySpace {char str[32] = {}; // 命名空间内可以对变量初始化int func();
}int mySpace::func()
{cout << "This is my function. " << endl;return 99;
}int main()
{cout << mySpace::func << endl; // 注意此行cout << mySpace::func() << endl;return 0;
}

局部导入整体命名空间
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace mySpace {char str[32] = {};void reverse();
}void mySpace::reverse()
{...}void myFunc()
{using namespace mySpace; // 局部导入整体命名空间cin.get(str, 32); // 这里的数字要 <= 上面定义时的数字reverse();
}int main()
{myFunc();cout << mySpace::str << endl; // 局部导入标识符
}
命名冲突问题(ambiguous)
两个命名空间中标识符冲突
两个命名空间中有同名成员。
解决方法:
1、命名空间名 + 域限定符;
2、只导入一个命名空间,代码就只能访问所导入的命名空间中的标识符。
局部变量和命名空间中标识符冲突
代码不会报错,但是只能默认访问局部变量。
想要访问命名空间中的标识符:命名空间名 + 域限定符。
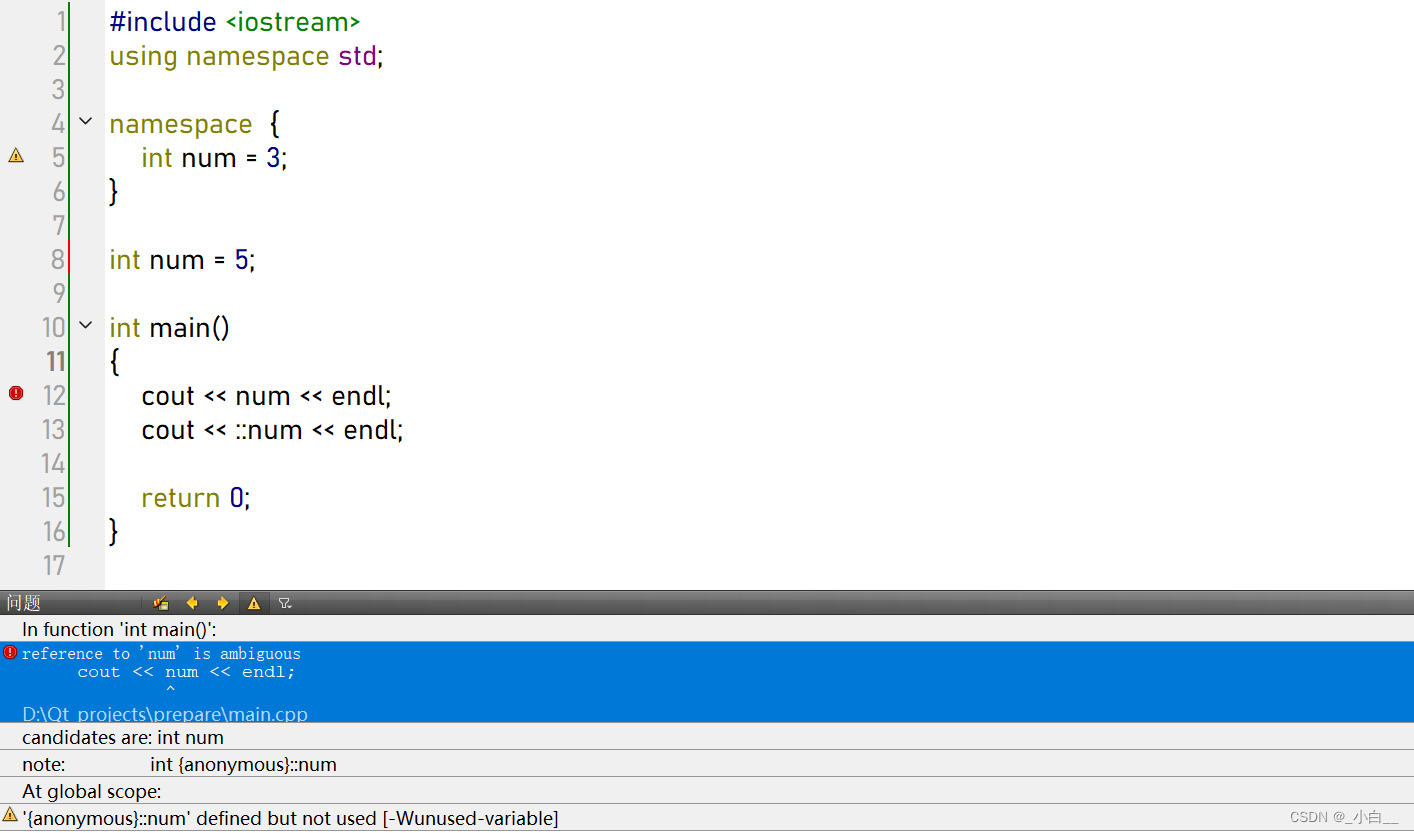
全局变量和命名空间标识符冲突
访问全局变量:在标识符前只加域限定符(::var)
访问命名空间中标识符:命名空间名 + 域限定符。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int a = 1000; // 定义了一个全局变量a
namespace mySpace
{int a = 90;char c = 'v';float p = 3.14;void func();
};void mySpace::func()
{...}int main()
{// 在使用的位置使用域限定符mySpace::func();cout << ::a << endl; // 加上域限定符访问全局变量的 a,与下面的匿名空间访问标识符做好区分// 因为全局变量默认在匿名空间中cout << "mySpace 中的 a = " << mySpace::a << endl;return 0;
}
匿名空间
没有名字的命名空间,就是匿名空间。
匿名空间中的标识符的访问方式:::<标识符名>
注意:匿名空间中的标识符尽量不要和全局变量冲突!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace { // 匿名空间,int num = 3; // 此变量与全局变量同名,不可被访问
}int num = 5; // 全局变量int main()
{
// cout << num << endl; // 报错cout << ::num << endl; // 显示 5return 0;
}
嵌套的命名空间
一个命名空间定义在另一个命名空间内,访问时需要逐层查找。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace space1 {int num1 = 10;int num2 = 30;namespace space2{int num1 = 1;int num2 = 90;int x = 7;};
};using namespace space1;
using namespace space1::space2;int main()
{cout << space1::space2::num1 << endl; // 访问 space2 中的 num1// cout << num2 << endl; // 一定会构成命名冲突问题cout << space1::num2 << endl; // 访问 space1 中的 num2cout << space2::x << endl; // 访问 space2 中的 xreturn 0;
}

给命名空间重命名
namespace <新名字> = <旧名字>;
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
namespace space1 {int num1 = 10;int num2 = 30;namespace space2{int num1 = 1;int num2 = 90;int x = 7;};
};using namespace space1;
using namespace space1::space2;namespace space0 = space1; // 注意此行int main()
{cout << space1::space2::num1 << endl;cout << space0::space2::num1 << endl; // 两句话等价return 0;
}
using 用于类型重定义
C++ 11 标准才能使用 using 实现类型重定义。
typedef int arr[5]; <===> arr相当于int [5]
typedef int *p; <===> p后面就相当于int *
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{using INT = int;// 使用 using 把 int 重命名为 INT,此后使用两者中的任意一个都可以定义整型变量INT a = 90;cout << a << endl;cout << sizeof(a) << endl;cout << sizeof(INT) << endl;return 0;
}
运行结果如下:

C++ 风格的字符串
C++ 中字符串并不严格需要 ‘\0’。
string 不是 C++ 的基本数据类,而是一个 C++ 标准库中的字符串类,使用时需要(非必要)引入头文件 #include <string> ,而不是<string.h>。
string 在绝大多数情况下可以替换 C 语言中字符串,不必担心内存是否足够长等等,其中内部还包含了很多字符串处理函数,可以完成各种情况下的字符串处理。
string 和 C 语言相同,字符串使用的是 ASCII 编码,不支持中文。
定义与初始化
string str = "hi"; // 隐式调用构造函数
string str1("hello"); // 显式调用构造函数
string str2(5, 'v'); // vvvvv
string str3(str1); // 显示调用拷贝构造函数
string str4 = str1; // 隐式调用拷贝构造函数string str5("ABCDEFG", 3); // str5 == "ABC",源字符串:char *
string str6(str1, 2); // str6 == "he",源字符串:std::string
赋值和比较
str = str1 + str2; // 使用已有的两个字符串 str1、str2 拼接给新的字符串 str 赋值
if(str > str1) {...} // 可以使用比较运算符,对几个字符串进行比较,== != >= <= > <
C++ 风格和 C 风格字符串的转换
C 风格字符串向 C++ 风格字符串转化,无需任何操作。
C++ 风格字符串向 C 风格字符串转化,需要借助 成员函数 data() 和 c_str()。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // 导入 C 中 string.h 头文件
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;int main()
{char str1[] = "hello";char str2[16] = "cat";strcat(str2, str1); // 把 str1 拼接到 str2 的后面string s1 = str2;cout << "s1 =" << s1 << endl; // cathellocout << "str2 =" << str2 << endl; // cathellochar str3[16];char str4[16];strcpy(str3, str2);// strcpy(str3, s1); // error:C++ 风格的字符串不能直接转换为 C 语言风格的字符串// data 和 c_str 叫做 s1 的成员函数strcpy(str3, s1.data());// 使用 data 函数,实现 C++ 风格字符串向 C 语言风格字符串的转换// printf("%s\n", s1); // error:C++ 风格的字符串不能直接转换为 C 语言风格的字符串printf("%s\n", s1.c_str());//使用 c_str 成员函数,实现 C++ 风格的字符串向 C 语言风格字符串的转换printf("%s\n", s1.data());//使用 data 成员函数,实现 C++ 风格的字符串向 C 语言风格字符串的转换strcpy(str4, s1.c_str());cout << strlen(str3) << "\t" << strlen(str4) << endl;cout << sizeof(str3) << "\t" << sizeof(str4) << endl;return 0;
}

常用的函数
data() 、c_str()
两者都返回一个 const char * 类型的指针。
在所有 C++ 标准中,c_str() 函数都保证返回的指针指向以空字符 ‘\0’ 结尾的数组。
C++11 之前的标准中,data() 函数返回的指针可以不指向以空字符 ‘\0’ 结尾的数组。但是在C++11 标准之后,data() 函数与 c_str() 函数的功能相同,都返回一个以空字符 ‘\0’ 结尾的字符数组指针。
at(index)
使用方式: 变量名.at(下标) ;
作用: 访问指定下标的元素;
注意: at() 函数 会自动检查越界问题,如果访问越界,则退出程序不再向后执行。
在 C++ 中更推荐使用 at 函数。原因是 at 函数更安全,但是 [ ] 的方式效率更高。
在 C++ 中,通过数组下标越界访问数组元素,不报段错误,但是会 输出一个’\0’换行。
empty()
返回值是 bool 类型,判断字符串是否为空。
size() / length()
返回字符串的实际长度,不包括’\0’。
两者的源代码一模一样,length 是因为沿用 C 语言的习惯而保留下来的,
string 类最初只有 length,引入 STL 之后,为了兼容又加入了 size,size 是作为 STL 容器的属性存在的,便于符合 STL 的接口规则,以便用于 STL 的算法。
clear()
清空字符串。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s = "dfgh";cout << s << endl;s.clear();cout << s << endl;return 0;
}

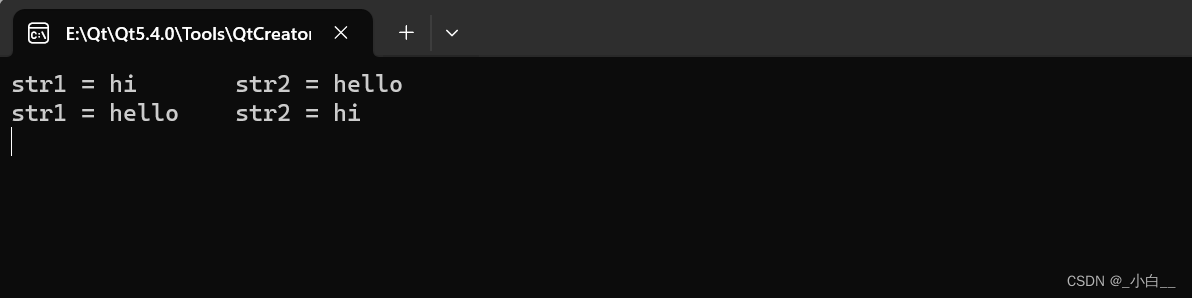
swap(str1, str2)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string str1 = "hi";string str2("hello");cout << "str1 = " << str1 << "\tstr2 = " << str2 << endl;swap(str1, str2);cout << "str1 = " << str1 << "\tstr2 = " << str2 << endl;return 0;
}
append()
见名知义,向后追加字符串。
push_back(char ch)
向后追加单个字符。
insert(index, str)
在指定位置插入字符串。
erase(index, count)
删除指定位置后 count 个字符。
copy(arr, count, index_of_src)
将 C++风格的源串 的 count 个字符,拷贝到 C 风格的目标串。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string str1 = "hi";string str2("hello");str1.append("gh");cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;str1.insert(1, "e");cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;str1.push_back('t');cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;str2.erase(4, 1);cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;char arr[20] = {0};str2.copy(arr, 2, 1);cout << "arr = " << arr << endl;return 0;
}

字符串的输入
1、cin,不能获取带空格的字符串
2、getline(),可以获取带空格的字符串,getline(cin, string类型的字符串首地址);
3、cin.get(),可以获取带空格的字符串,cin.get(字符串首地址, size);
4、cin.getline(),可以获取带空格的字符串,cin.getline(字符串首地址, size);
cin.get() 通常用于字符的输入。
cin.getline() 函数会读取输入流中的字符直到遇到换行符 ‘\n’ 或者读取到最大字符数(包括终止符)为止,并将换行符从输入流中提取出来,会在读取到最大字符数之后,添加一个字符串终止符 ‘\0’ ,即自动在字符数组的末尾添加一个空字符。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{char str1[32];char str2[32] = "hello";string s1 = str2;// cout << s1[6] << endl; // 可以通过下标访问字符串中的字符,但下标访问不能检查越界问题cout << s1.at(1) << endl;// 访问 string 类型的变量时,通常使用 at函数,可以进行越界检查getline(cin, s1); // getline 需要两个参数,cin 输入流 和 字符串变量名cout << s1 << endl;// getline(cin, str1); // 报错,使用 getline 只能输入 string 类型的字符串cin.getline(str1, sizeof(str1)); // 这样可以cout << str1 << endl;cin.get(str1, 32); // cin.get 需要两个参数,字符串变量名 和 所输入字符串大小// 所输入字符串大小 必须小于等于 字符数组定义时的长度cout << str1 << endl;return 0;
}
字符串的遍历
string 类支持多种遍历方式:for 循环、while 循环、do-while 循环、for-each 循环。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string str = "helloworld";// for 循环遍历输出字符串for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){cout << str.at(i);}cout << endl;// for each 的方式进行循环遍历字符串for(char i : str){cout << i;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
C++ 中的 bool 类型
C 中不直接支持 bool 类型,但是 C++ 中支持 bool 类型。
1、bool 在 C++ 中可以直接使用,默认值为 0,默认输出形式为数字;
2、bool 类型的变量在赋值时,可以使用数字,也可以使用 true 和 false;
3、bool 类型可以以字母的形式输出,需要加上 boolalpha,如果要取消,加上 noboolalpha;
4、bool 类型的大小是 1Byte。
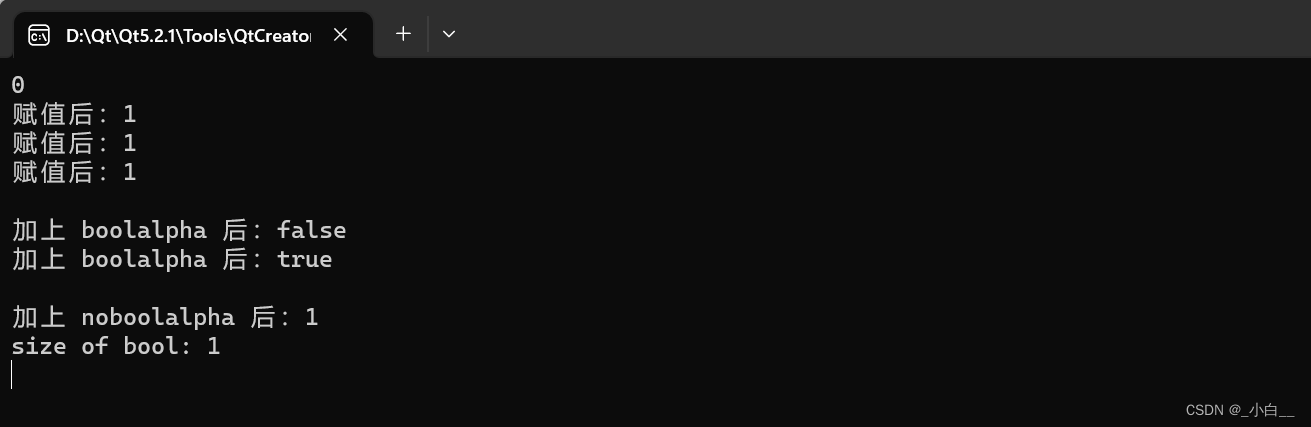
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{bool c;cout << c << endl; // C++ 中 bool 类型的默认值为 0c = true; // 使用单词给 bool 类型的变量赋值// bool 类型默认输出为数字的形式cout << "赋值后:" << c << endl;c = -10;cout << "赋值后:" << c << endl;c = 3.5;cout << "赋值后:" << c << endl;// 转换为字母形式的输出cout << boolalpha << endl;c = 0;cout << "加上 boolalpha 后:" << c << endl;c = 1;cout << "加上 boolalpha 后:" << c << endl;// 取消字母表示 cout << noboolalpha << endl;cout << "加上 noboolalpha 后:" << c << endl;cout << "size of bool: " << sizeof(bool) << endl; // 1return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
nullptr
NULL 在源码当中就是个 0,因此可能会存在二义性的问题。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;void func(int a)
{cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}void func(char *b)
{cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}int main()
{func(NULL); // a = 0return 0;
}

在 C++11 中使用 nullptr 代替了 NULL,来作为空指针的表示方式。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;void func(int a)
{cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}void func(char *b)
{cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}int main()
{func(nullptr); // b = return 0;
}

类型推导
auto 关键字
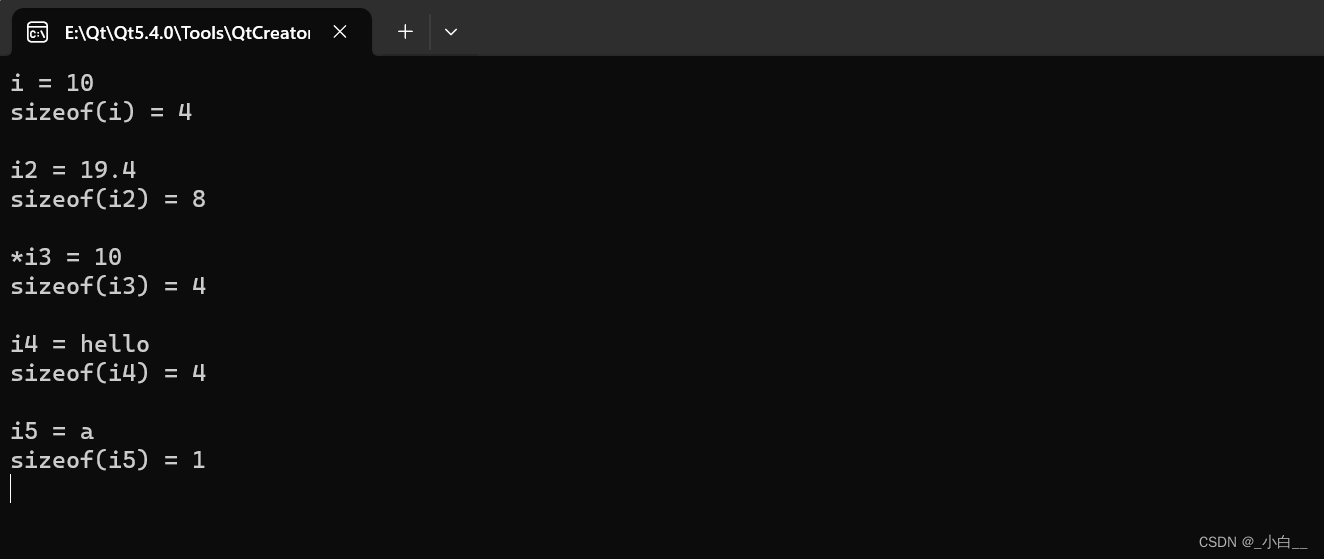
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{auto i = 10;cout << "i = " << i << endl;cout << "sizeof(i) = " << sizeof(i) << endl << endl;auto i2 = 19.4;cout << "i2 = " << i2 << endl;cout << "sizeof(i2) = " << sizeof(i2) << endl << endl;auto i3 = new auto(10);cout << "*i3 = " << *i3 << endl;cout << "sizeof(i3) = " << sizeof(i3) << endl << endl;auto i4 = "hello";cout << "i4 = " << i4 << endl;cout << "sizeof(i4) = " << sizeof(i4) << endl << endl;auto i5 = 'a';cout << "i5 = " << i5 << endl;cout << "sizeof(i5) = " << sizeof(i5) << endl;delete i3;return 0;
}
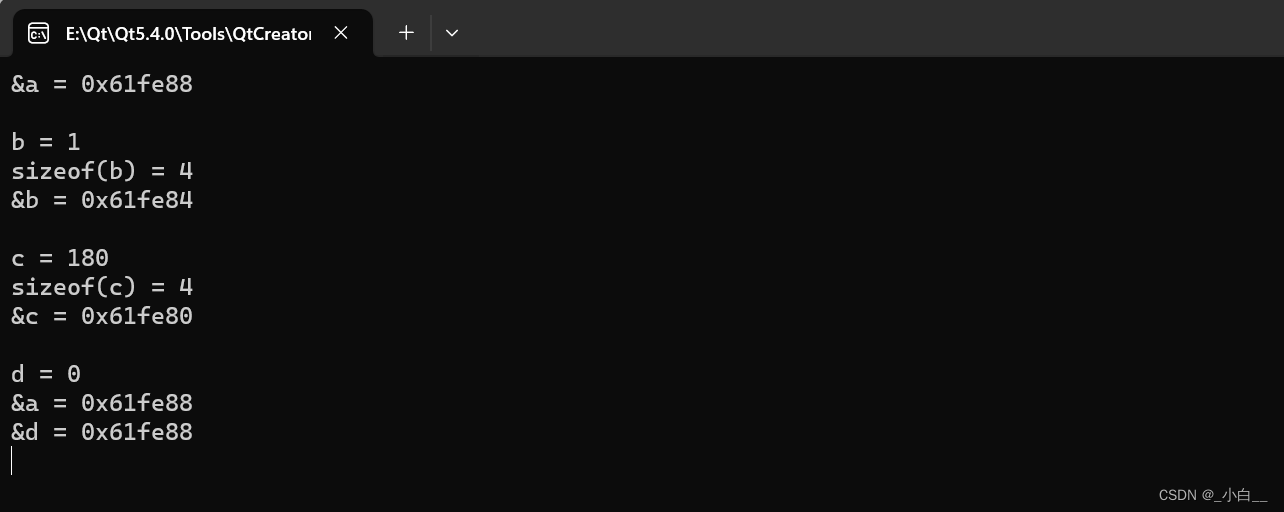
decltype
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int func(int str1, int str2)
{return str1 + str2;
}int main()
{int a = 0;cout << "&a = " << &a << endl << endl;decltype(a) b = 1.5; // b 的类型为 intcout << "b = " << b << endl;cout << "sizeof(b) = " << sizeof(b) << endl;cout << "&b = " << &b << endl << endl;decltype(func(3.14, 6.28)) c = 180.5; // c 的类型为 intcout << "c = " << c << endl;cout << "sizeof(c) = " << sizeof(c) << endl;cout << "&c = " << &c << endl << endl;decltype((a)) d = a; // d 的类型为 int&cout << "d = " << d << endl;cout << "&a = " << &a << endl;cout << "&d = " << &d << endl;return 0;
}
练习:
定义一个命名空间 Myspace,包含以下函数:将一个字符串进行翻转,并输出翻转后的结果,在主函数内测试该函数。
// 只能输入一次#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;namespace mySpace {char str[32] = {};void reverse();
}void mySpace::reverse()
{char *p = str;char *head = p;char *tail = NULL;while (*(p+1) != '\0')p++;tail = p;while (head < tail){*head ^= *tail;*tail ^= *head;*head++ ^= *tail--;}
}using namespace mySpace;int main()
{cin.get(str, 32);reverse();cout << str << endl;return 0;
}
// 只能输入一次#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace mySpace {char str[32] = {};void reverse();
}void mySpace::reverse()
{char *p = str;char *head = p;char *tail = NULL;while (*(p+1) != '\0')p++;tail = p;while (head < tail){*head ^= *tail;*tail ^= *head;*head++ ^= *tail--;}
}void myFunc()
{using namespace mySpace;cin.get(str, 32); // 这里的数字要 <= 上面定义时的数字reverse();
}int main()
{myFunc();cout << mySpace::str << endl;return 0;
}
// 可以循环输入#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace mySpace {void reverse(string &str);
}void mySpace::reverse(string &str)
{int end = str.size()-1;for (int begin = 0; begin < end; begin++, end--){char temp;temp = str.at(begin);str.at(begin) = str.at(end);str.at(end) = temp;}
}using namespace mySpace;int main()
{string s;while (1){getline(cin, s);reverse(s);cout << s << endl;}return 0;
}