1,标准流布局
标准流,也称文档流或普通流,是所有元素默认的布局方式。 在标准流中,元素按照其在 HTML 中出现的顺序,自上而下依次排列,并占据其父容器内的可用空间。 标准流中的元素按照其自然尺寸和位置进行布局,不会特意改变元素的属性或位置。
2,非标准流布局
(1)相对定位:
是指将一个元素从它的标准流中所处的位置进行向上,向下,向左,向右偏移,这种偏移不会影响周围元素的位置,周围元素还是位于自己原来的标准流中的位置。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style type="text/css">.A{width: 500px;height: 500px;background: #ccc;margin-top: 100px;overflow: hidden;}.B{width: 100px;height: 100px;background: red;position: relative;left: 100px;top: 70px;}.C{width: 100px;height: 100px;background: blue;margin-top: 70px;color: #000;}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="A"><div class="B"></div><div class="C"></div></div>
</body>
</html>结果: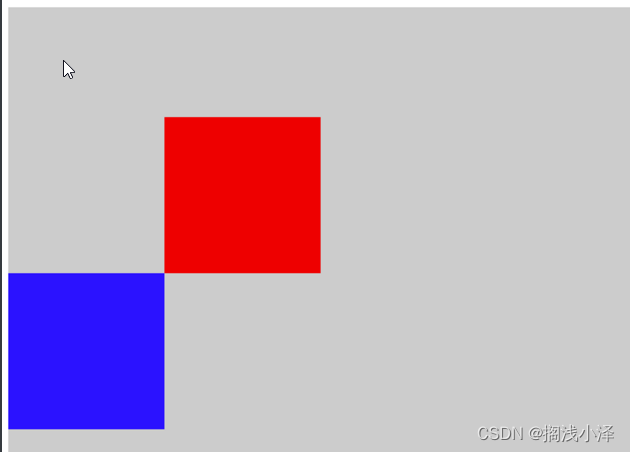
(2)绝对定位:
是指将一个元素完全脱离标准流,浏览器完全忽略掉该元素所占据的空间,该元素向上,向下,向左,向右偏移是相对于浏览器窗口,或者向上追溯到第一个已经定位的父级元素作为参照物。
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title>
</head>
<style type="text/css">.A{width: 500px;height: 500px;background: #ccc;margin-top: 100px;position: relative;overflow: hidden;}.B{width: 100px;height: 100px;background: red;position: absolute;left: 100px;top: 70px;}.C{width: 100px;height: 100px;background: blue;margin-top: 70px;color: #000;}
</style>
<body><div class="A"><div class="B"></div><div class="C"></div></div>
</body>
</html>结果: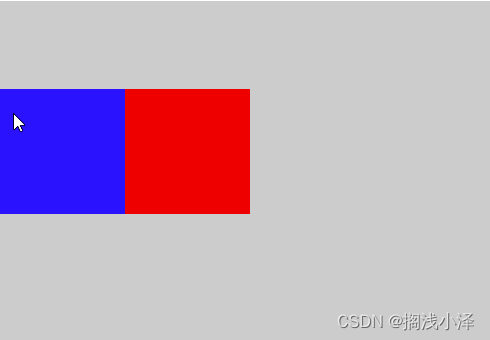
3,其核心知识点还需要自己去理解。

![[HCIE] IPSec-VPN (IKE自动模式)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6fe35169573e49659bbf4a457236cf5b.png)