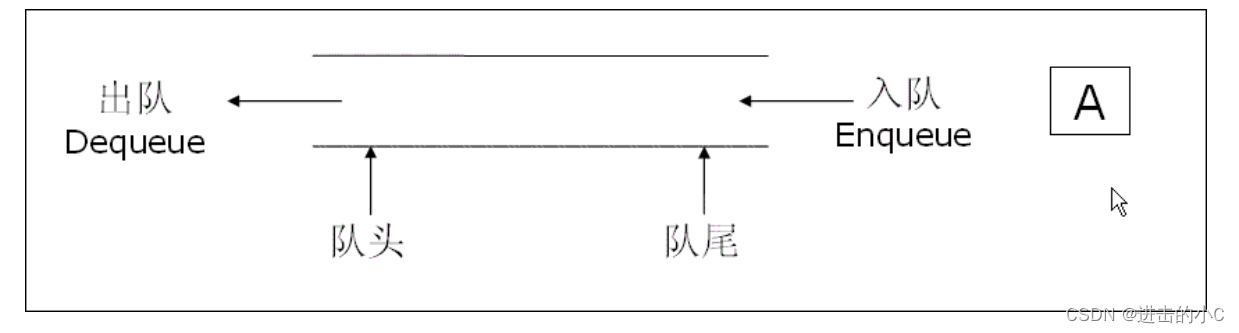
1.队列的概念及结构
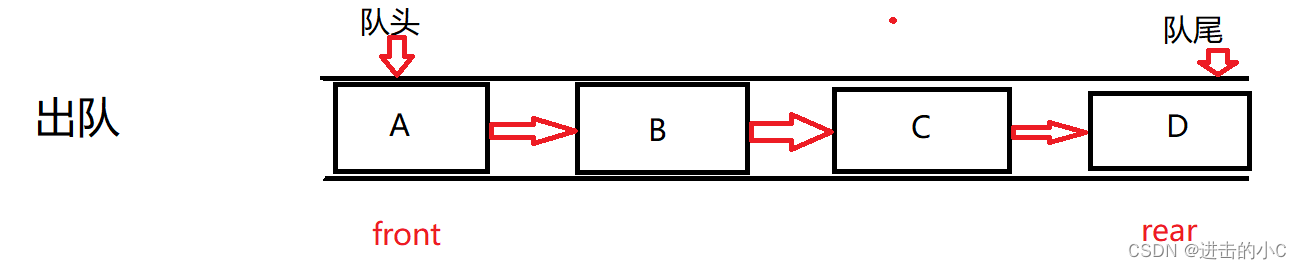
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头.
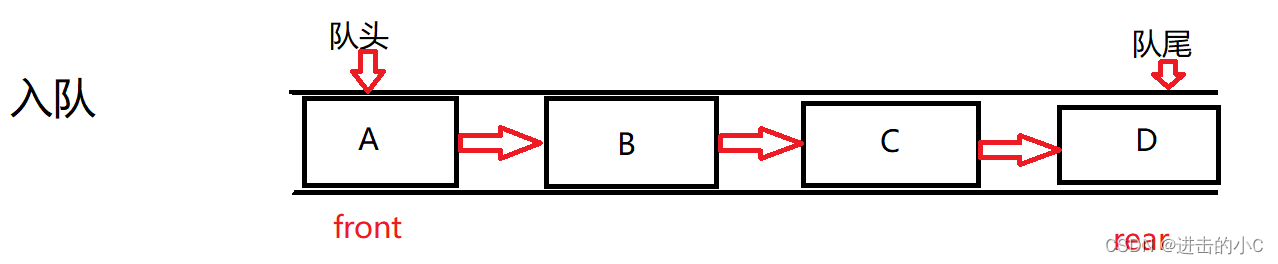
2.队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。

2.1定义队列
多个值我们使用两个结构体来封装,方便找头和尾。
typedef int QDataType;
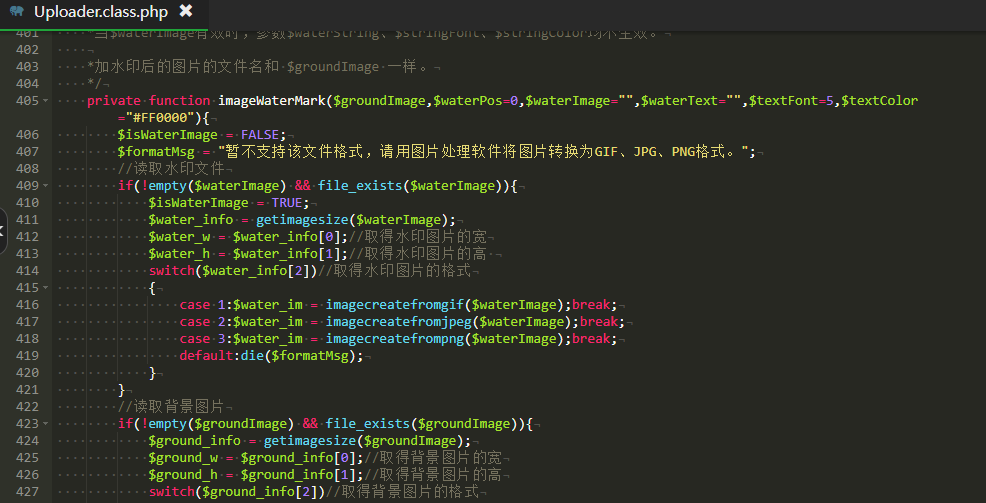
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;2.2初始化队列
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->size = 0;pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}2.3销毁队列
销毁队列需要遍历,并且需要提前保存下一个节点的地址。
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
2.3数据入队列
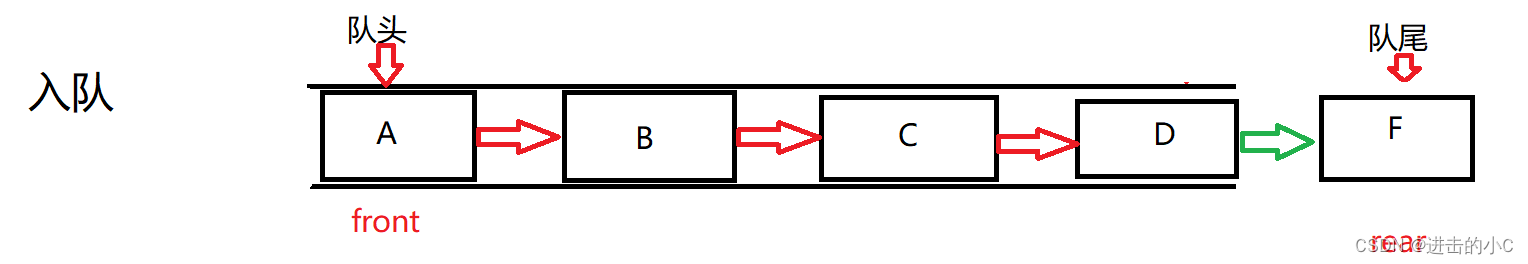
首先为新节点malloc一块空间,将data赋值,然后将此节点的next置空。开始入对列,这时需要注意,如果队列为空,则此节点就同时是头和尾,如果不为空,则链接在tail的后面,在将新节点置为tail,最后size++。
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* tmp = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (tmp == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}tmp->data = x;tmp->next = NULL;if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = tmp;}else{pq->tail->next = tmp;pq->tail = tmp;}pq->size++;
}2.4数据出队列
队列是先入先出,所以数据是从头节点出去,使用断言此队列不为空,在判断是不是只有一个节点,如果是就直接free掉这个节点即可,再将tai和head置空。如果不止一个节点,则需要保存第二个节点,free掉head,再将head置为下一个节点,最后size--。
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}2.5取队列的头部数据
直接返回head的data即可。
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}2.6取队列的尾部数据
返回tail的data即可。
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}2.7判断队列是否为空
使用bool的返回值。
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}2.8队列的数据个数
返回size即可。
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}今天的分享到这里就结束啦!谢谢老铁们的阅读,让我们下期再见。