前言
VIR-SLAM中VIR_VINS文件夹下是基于VINS-mono的结合UWB传感器的估计器,主要改动的文件在uwb_posegraph,vir_estimator中。其他文件夹完成的是UWB数据的处理问题,比较简单上一节介绍足够,代码也容易看懂。本节介绍的VIR_VINS是VIR-SLAM的核心内容。
1、uwb_posegraph
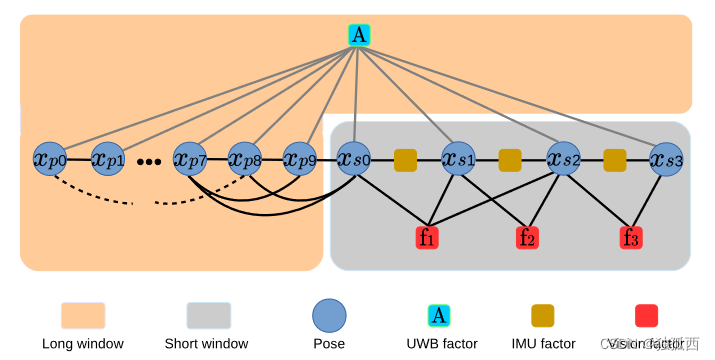
启动uwb_posegraph节点的启动代码在launch(vir_estimator/launch下的launch文件)文件当中。这个文件夹是通过复制修改原本的posegraph得到的,用来添加长窗口的结合UWB约束的全局位姿图优化。
uwb_factor.h
class UWBFactor : public ceres::SizedCostFunction<1,3,3>函数
UWBFactor的代价函数构建,残差维度为1,输入参数为三维位移和三维锚点位置。这个factor面向的是全局位姿图优化,是长窗口对于关键帧之间的估计的优化,因此这里也包含了对于锚点位置的优化。在后面四自由度优化中使用。
class UWBFactor : public ceres::SizedCostFunction<1,3,3>
{public:UWBFactor() = delete;float uwbmeas;UWBFactor(float dist){uwbmeas = dist;}virtual bool Evaluate(double const *const *parameters, double *residuals, double **jacobians) const{Eigen::Vector3d pos(parameters[0][0], parameters[0][1], parameters[0][2]);Eigen::Vector3d anchor_pos(parameters[1][0], parameters[1][1], parameters[1][2]);Eigen::Vector3d tmp(pos-anchor_pos);float predist = tmp.norm();float weight = 1;residuals[0] = weight*(uwbmeas - predist );if(jacobians){jacobians[0][0] = weight*(parameters[1][0]-parameters[0][0])/predist;jacobians[0][1] = weight*(parameters[1][1]-parameters[0][1])/predist;jacobians[0][2] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;jacobians[1][0] = -weight*(parameters[1][0]-parameters[0][0])/predist;jacobians[1][1] = -weight*(parameters[1][1]-parameters[0][1])/predist;jacobians[1][2] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;}//printf(" Meas of uwb is : %f, residual: %f \n", uwbmeas, residuals[0]);return true;}
};
uwb_posegraph_node.cpp
这个文件中含有主函数,完成对关键帧位姿信息和UWB测距信息的接收,以及开启处理函数线程,长窗口长度为2000个数据点。
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{printf("start uwb_posgraph \n");ros::init(argc, argv, "uwb_pose_graph");ros::NodeHandle n("~");posegraph.registerPub(n);// read paramros::Subscriber sub_pose = n.subscribe("/vins_estimator/keyframe_pose", 2000, pose_callback);ros::Subscriber sub_uwb = n.subscribe("/uwb/corrected_range", 2000, uwb_callback);std::thread measurement_process;measurement_process = std::thread(process);ros::spin();return 0;
}
void pose_callback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr &pose_msg)函数
位姿信息保存入栈函数
void pose_callback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr &pose_msg)
{m_buf.lock();pose_buf.push(pose_msg);m_buf.unlock();
}
void uwb_callback(const geometry_msgs::PointStamped &pos_msg)
UWB测量信息保存入栈函数,根据主函数可知这里保存的是经过预处理后的距离测量信息。
void uwb_callback(const geometry_msgs::PointStamped &pos_msg)
{m_buf.lock();uwb_buf.push_back(pos_msg);m_buf.unlock();
}
void process()
主线程处理函数,process中的核心操作,就是根据estimator节点当中发送的关键帧位姿来创建“符合条件”的新关键帧添加到位姿图当中。这里添加的关键帧数据主要是UWB测量值,根据时间戳来确定关键帧的UWB信息,找时间上接近关键帧位姿的UWB测量值添加为关键帧数据,超过1秒舍弃该关键帧。
void process()
{if (!UWB_POSEGRAPH)//判断是否使能UWB全局位姿图优化return;while (true){geometry_msgs::PointStampedPtr uwb_msg = NULL;nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr pose_msg = NULL;double uwb_curRange = -1;// find out the messages with same time stampm_buf.lock();if(!pose_buf.empty()){pose_msg = pose_buf.front();while (!pose_buf.empty())pose_buf.pop();}m_buf.unlock();if (pose_msg != NULL)// when receive the key pose topic, means this is the keyFrame.{m_buf.lock();double t_time;t_time = pose_msg->header.stamp.toSec();// Find the uwb measurement for the poseif (!uwb_buf.empty() && uwb_buf.back().header.stamp.toSec()>=t_time){//find the first time smaller than pose timefor (std::deque<geometry_msgs::PointStamped>::reverse_iterator it = uwb_buf.rbegin(); it!=lastUwbIt; it++){if (it->header.stamp.toSec()<t_time && it->header.stamp.toSec()>t_time-1){uwb_curRange = it->point.x;lastUwbIt = it;printf(" received uwb_curRange %f \n", uwb_curRange);break;}else if (it->header.stamp.toSec()<t_time-1){printf(" No approriate UWB measure matched \n");lastUwbIt = it;break;}}}else{printf(" No UWB measure received or no new \n");}m_buf.unlock();// build keyframeVector3d T = Vector3d(pose_msg->pose.pose.position.x,pose_msg->pose.pose.position.y,pose_msg->pose.pose.position.z);Matrix3d R = Quaterniond(pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.w,pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.x,pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.y,pose_msg->pose.pose.orientation.z).toRotationMatrix();KeyFrame* keyframe = new KeyFrame(pose_msg->header.stamp.toSec(), frame_index, T, R); if(uwb_curRange != -1){// add uwb meas to keyframe.keyframe->hasUwbMeas = true;keyframe->uwbMeas = lastUwbIt->point.x;printf(" uwb meas %f \n", lastUwbIt->point.x);}m_process.lock();posegraph.addKeyFrame(keyframe);m_process.unlock();frame_index++;}std::chrono::milliseconds dura(5);std::this_thread::sleep_for(dura);}
}
uwb_posegraph.cpp/.h
uwbPoseGraph::uwbPoseGraph()
为uwbPoseGraph类的构造函数,该函数里自动启动optimize4DoF函数线程,用来对全局信息长窗口进行优化。
uwbPoseGraph::uwbPoseGraph()
{t_optimization = std::thread(&uwbPoseGraph::optimize4DoF, this);t_drift = Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, 0);yaw_drift = 0;r_drift = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();global_index = 0;nav_msgs::Path uwbpg_path;anchor_pos[0]=1.0;anchor_pos[1]=1.0;anchor_pos[2]=1.0;}
void uwbPoseGraph::optimize4DoF()函数
进行位姿图优化是为了将已经产生的所有位姿统一到一个全局一致的配置当中。如VINS论文中所说,参考帧处于世界坐标系下,当相机运动的时候
会相对于参考帧发生变化。而由于重力向量始终不会发生变化,所以从重力方向得到的水平面也不会发生变化,进而该水平面对应的两个向量
也不会发生变换。所以,系统中需要计算并且优化的向量只有
(也就是位置和旋转),这就是4自由度优化的由来。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/moyu123456789/article/details/104041710
这里的optimize4DoF()使用的是UWB测量进行约束优化,而不是VINS中的回环检测优化。
void uwbPoseGraph::optimize4DoF()
{while(true){int cur_index = -1;m_optimize_buf.lock();while(!optimize_buf.empty()){cur_index = optimize_buf.front(); // Triger of real optimization work.while (!optimize_buf.empty()){optimize_buf.pop();}}m_optimize_buf.unlock();if (cur_index != -1){printf("optimize pose graph \n");TicToc tmp_t;m_keyframelist.lock();KeyFrame* cur_kf = getKeyFrame(cur_index);int max_length = cur_index + 1;// w^t_i w^q_idouble t_array[max_length][3];Quaterniond q_array[max_length];double euler_array[max_length][3];ceres::Problem problem;ceres::Solver::Options options;options.linear_solver_type = ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY;//options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = 3;options.max_num_iterations = 50*3;ceres::Solver::Summary summary;ceres::LocalParameterization* angle_local_parameterization =AngleLocalParameterization::Create();list<KeyFrame*>::iterator it;// Add anchor position as parameter in the problem.problem.AddParameterBlock(anchor_pos, 3);int i = 0;for (it = keyframelist.begin(); it != keyframelist.end(); it++){Quaterniond tmp_q;Matrix3d tmp_r;Vector3d tmp_t;(*it)->getVioPose(tmp_t, tmp_r);tmp_q = tmp_r;t_array[i][0] = tmp_t(0);t_array[i][1] = tmp_t(1);t_array[i][2] = tmp_t(2);q_array[i] = tmp_q;Vector3d euler_angle = Utility::R2ypr(tmp_q.toRotationMatrix());euler_array[i][0] = euler_angle.x();euler_array[i][1] = euler_angle.y();euler_array[i][2] = euler_angle.z();problem.AddParameterBlock(euler_array[i], 1, angle_local_parameterization);problem.AddParameterBlock(t_array[i], 3);//add edgefor (int j = 1; j < 5; j++){if (i - j >= 0)// Frame i and previous frame[i-j]{// Calculate the RT from frame i to i-j: last 5 frame.; hardly calculated.Vector3d euler_conncected = Utility::R2ypr(q_array[i-j].toRotationMatrix());Vector3d relative_t(t_array[i][0] - t_array[i-j][0], t_array[i][1] - t_array[i-j][1], t_array[i][2] - t_array[i-j][2]);relative_t = q_array[i-j].inverse() * relative_t;double relative_yaw = euler_array[i][0] - euler_array[i-j][0];ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = FourDOFError::Create( relative_t.x(), relative_t.y(), relative_t.z(),relative_yaw, euler_conncected.y(), euler_conncected.z());problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, NULL, euler_array[i-j], t_array[i-j], euler_array[i], t_array[i]);}}//add loop edge(removed)// add uwb edgeif((*it)->hasUwbMeas && (*it)->uwbMeas>1){float rawdist = (*it)->uwbMeas;int noise = 0.0 ; //rand()%200;UWBFactor* uwb_factor = new UWBFactor(rawdist+noise/1000.0);problem.AddResidualBlock(uwb_factor, NULL, t_array[i], anchor_pos); }if ((*it)->index == cur_index)// add frames untile cur_index.break;i++;}m_keyframelist.unlock();ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);std::cout << summary.BriefReport()<< "\n";if(cur_kf->hasUwbMeas)printf("Anchor: %f, %f, %f \n",anchor_pos[0],anchor_pos[1],anchor_pos[2]);m_keyframelist.lock();i = 0;geometry_msgs::PoseStamped curPose;for (it = keyframelist.begin(); it != keyframelist.end(); it++){Quaterniond tmp_q;tmp_q = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(euler_array[i][0], euler_array[i][1], euler_array[i][2]));Vector3d tmp_t = Vector3d(t_array[i][0], t_array[i][1], t_array[i][2]);Matrix3d tmp_r = tmp_q.toRotationMatrix();(*it)-> updatePose(tmp_t, tmp_r);if ((*it)->index == cur_index)break;i++;}Vector3d cur_t, vio_t;Matrix3d cur_r, vio_r;cur_kf->getPose(cur_t, cur_r);cur_kf->getVioPose(vio_t, vio_r);m_drift.lock();yaw_drift = Utility::R2ypr(cur_r).x() - Utility::R2ypr(vio_r).x();r_drift = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(yaw_drift, 0, 0));t_drift = cur_t - r_drift * vio_t;m_drift.unlock();it++;//update the frames after cur_index that has not optimimzed with drifts.for (; it != keyframelist.end(); it++){Vector3d P;Matrix3d R;(*it)->getVioPose(P, R);P = r_drift * P + t_drift;R = r_drift * R;(*it)->updatePose(P, R);}m_keyframelist.unlock();updatePath();pub_pose(cur_kf);}}
}
剩下的函数是发布优化后的位姿、轨迹用的,还有析构函数保持优化线程的持续、关键帧添加与获取等函数,这里不赘述,这些代码功能比较好理解。
2、vir_estimator
状态估计器,包含VIR-SLAM的完整功能:初始化、位姿图优化等等,经过修改的代码是estimator_node.cpp、estimator.cpp/.h、parameters.cpp/.h、uwb_factor.h。
factor主要用于非线性优化对各个参数块和残差块的定义,VINS采用的是ceres,所以这部分需要对一些状态量和因子进行继承和重写。VIR-SLAM添加了uwb_factor文件用来存放uwb代价函数。
class UWBFactor : public ceres::SizedCostFunction<1,7,3>
{public:UWBFactor() = delete;double uwbmeas;double weight;UWBFactor(double dist, double _weight){uwbmeas = dist;weight = _weight;}virtual bool Evaluate(double const *const *parameters, double *residuals, double **jacobians) const{Eigen::Vector3d pos(parameters[0][0], parameters[0][1], parameters[0][2]);Eigen::Vector3d anchor_pos(parameters[1][0], parameters[1][1], parameters[1][2]);Eigen::Vector3d tmp = pos-anchor_pos;double predist = tmp.norm();residuals[0] = weight*(uwbmeas - predist );if(jacobians){jacobians[0][0] = weight*(parameters[1][0]-parameters[0][0])/predist;jacobians[0][1] = weight*(parameters[1][1]-parameters[0][1])/predist;//jacobians[0][2] = weight*(parameters[1][2]-parameters[0][2])/predist;jacobians[0][2] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;jacobians[0][3] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;jacobians[0][4] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;jacobians[0][5] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;jacobians[0][6] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;if (KNOWN_ANCHOR == 1)//锚点已经固定{jacobians[1][0] = 0.;//jacobians[1][1] = 0.;//jacobians[1][2] = 0.;//}else{ jacobians[1][0] = -weight*(parameters[1][0]-parameters[0][0])/predist;//0.;//jacobians[1][1] = -weight*(parameters[1][1]-parameters[0][1])/predist;//0.;//jacobians[1][2] = -weight*(parameters[1][2]-parameters[0][2])/predist;//0;//}}return true;}
};class UWBAnchorFactor : public ceres::SizedCostFunction<1,3>
{public:UWBAnchorFactor() = delete;double uwbmeas;double weight;Eigen::Vector3d position;UWBAnchorFactor(double dist, double _weight, Eigen::Vector3d _position){uwbmeas = dist;weight = _weight;position = _position;}virtual bool Evaluate(double const *const *parameters, double *residuals, double **jacobians) const{Eigen::Vector3d anchor_pos(parameters[0][0], parameters[0][1], parameters[0][2]);Eigen::Vector3d tmp = position-anchor_pos;double predist = tmp.norm();residuals[0] = weight*(uwbmeas - predist );if(jacobians){jacobians[0][0] = -weight*(parameters[0][0]-position[0])/predist;jacobians[0][1] = -weight*(parameters[0][1]-position[1])/predist;jacobians[0][2] = -weight*(parameters[0][2]-position[2])/predist;//jacobians[0][2] = 0;//-weight*parameters[0][2]/predist;}return true;}
};
initial初始化程序,主要用于初始化,VINS采用的初始化策略是先SfM进行视觉初始化,再与IMU进行松耦合,与VINS-mono一致。
utility,里面放着用于可视化的函数和tictok计时器,与VINS-mono一致。
feature_manager.cpp/.h特征点管理,三角化,关键帧等,与VINS-mono一致。
下面这三个文件相比于VINS-mono进行了修改
estimator_node.cpp
ROS 节点函数,回调函数。
predict()函数:从IMU测量值imu_msg和上一个PVQ递推得到当前PVQ。
update()函数:得到窗口最后一个图像帧的imu项[P,Q,V,ba,bg,a,g],对imu_buf中剩余imu_msg进行PVQ递推。
getMeasurements()函数:对imu和图像数据进行对齐并组合。
imu_callback()函数:imu回调函数,将imu_msg存入imu_buf,递推IMU的PQV并发布"imu_propagate”。
uwb_callback()函数:uwb回调函数,将uwb_msg.point.x存入uwb_buf。
feature_callback()函数:feature回调函数,将feature_msg放入feature_buf。
restart_callback()函数:restart回调函数,收到restart消息时清空feature_buf和imu_buf,估计器重置,时间重置。
relocalization_callback()函数:relocalization回调函数,将points_msg放入relo_buf。
void process(ros::Publisher pub_debug_uwb)函数
VIO主线程,通过while (true)不断循环,主要功能包括等待并获取measurements,计算dt,然后执行以下功能:进行IMU预积分;设置重定位帧;处理图像帧等,VIR-SLAM不同之处在于添加了对于UWB数据的处理。
void process(ros::Publisher pub_debug_uwb)
{while (true){std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> measurements;std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(m_buf);con.wait(lk, [&]{return (measurements = getMeasurements()).size() != 0;});lk.unlock();m_estimator.lock();for (auto &measurement : measurements) 遍历获取的Feature和IMU测量值,对measurements中的每一个measurement组合进行操作{auto img_msg = measurement.second;double dx = 0, dy = 0, dz = 0, rx = 0, ry = 0, rz = 0;for (auto &imu_msg : measurement.first)//IMU预积分处理,某一图像帧下遍历对齐的imu{double t = imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec();double img_t = img_msg->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td;if (t <= img_t)//发送IMU数据进行预积分{ if (current_time < 0)current_time = t;double dt = t - current_time;ROS_ASSERT(dt >= 0);current_time = t;dx = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.x;dy = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.y;dz = imu_msg->linear_acceleration.z;rx = imu_msg->angular_velocity.x;ry = imu_msg->angular_velocity.y;rz = imu_msg->angular_velocity.z;estimator.processIMU(dt, Vector3d(dx, dy, dz), Vector3d(rx, ry, rz));//processIMU()实现了IMU的预积分,通过中值积分得到当前PQV作为优化初值}else// 这就是针对最后一个imu数据,需要做一个简单的线性插值{double dt_1 = img_t - current_time;double dt_2 = t - img_t;current_time = img_t;ROS_ASSERT(dt_1 >= 0);ROS_ASSERT(dt_2 >= 0);ROS_ASSERT(dt_1 + dt_2 > 0);double w1 = dt_2 / (dt_1 + dt_2);double w2 = dt_1 / (dt_1 + dt_2);dx = w1 * dx + w2 * imu_msg->linear_acceleration.x;dy = w1 * dy + w2 * imu_msg->linear_acceleration.y;dz = w1 * dz + w2 * imu_msg->linear_acceleration.z;rx = w1 * rx + w2 * imu_msg->angular_velocity.x;ry = w1 * ry + w2 * imu_msg->angular_velocity.y;rz = w1 * rz + w2 * imu_msg->angular_velocity.z;estimator.processIMU(dt_1, Vector3d(dx, dy, dz), Vector3d(rx, ry, rz));}}// set relocalization frame,设置重定位帧sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr relo_msg = NULL;while (!relo_buf.empty())//取出最后一个重定位帧{relo_msg = relo_buf.front();relo_buf.pop();}if (relo_msg != NULL){vector<Vector3d> match_points;double frame_stamp = relo_msg->header.stamp.toSec();for (unsigned int i = 0; i < relo_msg->points.size(); i++){Vector3d u_v_id;u_v_id.x() = relo_msg->points[i].x;u_v_id.y() = relo_msg->points[i].y;u_v_id.z() = relo_msg->points[i].z;match_points.push_back(u_v_id);}Vector3d relo_t(relo_msg->channels[0].values[0], relo_msg->channels[0].values[1], relo_msg->channels[0].values[2]);Quaterniond relo_q(relo_msg->channels[0].values[3], relo_msg->channels[0].values[4], relo_msg->channels[0].values[5], relo_msg->channels[0].values[6]);Matrix3d relo_r = relo_q.toRotationMatrix();int frame_index;frame_index = relo_msg->channels[0].values[7];estimator.setReloFrame(frame_stamp, frame_index, match_points, relo_t, relo_r); 重定位}ROS_DEBUG("processing vision data with stamp %f \n", img_msg->header.stamp.toSec());TicToc t_s;map<int, vector<pair<int, Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1>>>> image;//建立每个特征点的(camera_id,[x,y,z,u,v,vx,vy])s的map,索引为feature_idfor (unsigned int i = 0; i < img_msg->points.size(); i++)//遍历img_msg里面的每一个特征点的归一化坐标{int v = img_msg->channels[0].values[i] + 0.5;int feature_id = v / NUM_OF_CAM;int camera_id = v % NUM_OF_CAM;double x = img_msg->points[i].x;double y = img_msg->points[i].y;double z = img_msg->points[i].z;double p_u = img_msg->channels[1].values[i];double p_v = img_msg->channels[2].values[i];double velocity_x = img_msg->channels[3].values[i];double velocity_y = img_msg->channels[4].values[i];ROS_ASSERT(z == 1);Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1> xyz_uv_velocity;xyz_uv_velocity << x, y, z, p_u, p_v, velocity_x, velocity_y;image[feature_id].emplace_back(camera_id, xyz_uv_velocity);}if (USE_UWB){// UWB数据处理if (estimator.uwb_buf.empty()){estimator.uwb_keymeas.push_back(-1);}else{ m_buf.lock();// ... fill vec with values (do not use 0; use 0.0)double average = std::accumulate(estimator.uwb_buf.begin(), estimator.uwb_buf.end(), 0.0) / estimator.uwb_buf.size();//对uwb_buf中的uwb数据求和取平均值estimator.uwb_keymeas.push_back(average);//将平均值添加到uwb_keymeasestimator.uwb_buf.clear();//清空uwb_bufm_buf.unlock();geometry_msgs::PointStamped msgnow;msgnow.point.x = average;pub_debug_uwb.publish(msgnow);//发布存下来的当前uwb平均值}if (KNOWN_ANCHOR == 0 && estimator.solver_flag == Estimator::SolverFlag::NON_LINEAR)//锚点没有固定下来时{estimator.uwbMeas4AnchorEst.push_back(estimator.uwb_keymeas.back());//将estimator.uwb_keymeas.back()存入estimator.uwbMeas4AnchorEst}}estimator.processImage(image, img_msg->header);//处理图像特征,处理图像帧:初始化,紧耦合的非线性优化,这里包含了uwb的处理,这是一个非常重要的函数。double whole_t = t_s.toc();printStatistics(estimator, whole_t);std_msgs::Header header = img_msg->header;header.frame_id = "world";
//向RVIZ发送topic,向RVIZ发布里程计信息、关键位姿、相机位姿、点云和TF关系pubOdometry(estimator, header);//"odometry"里程计PVQ信息pubKeyPoses(estimator, header);//"key_poses"关键点三维坐标pubCameraPose(estimator, header);//"camera_pose" 相机位姿pubPointCloud(estimator, header);//"history_cloud" 点云信息pubTF(estimator, header);//"extrinsic" 相机到IMU的外参pubKeyframe(estimator);//"keyframe_point"、"keyframe_pose" 关键帧位姿和点云if (relo_msg != NULL)pubRelocalization(estimator);//"relo_relative_pose" 重定位位姿}m_estimator.unlock();m_buf.lock(); //更新IMU参数m_state.lock();if (estimator.solver_flag == Estimator::SolverFlag::NON_LINEAR)update();//更新IMU参数[P,Q,V,ba,bg,a,g]m_state.unlock();m_buf.unlock();}
}
主函数main()
完成节点订阅与发布,创建VIO主线程。
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{ros::init(argc, argv, "vir_estimator");ros::NodeHandle n("~");ros::console::set_logger_level(ROSCONSOLE_DEFAULT_NAME, ros::console::levels::Debug);readParameters(n);estimator.setParameter();
#ifdef EIGEN_DONT_PARALLELIZEROS_DEBUG("EIGEN_DONT_PARALLELIZE");
#endifROS_WARN("waiting for image and imu...");registerPub(n);ros::Subscriber sub_imu = n.subscribe(IMU_TOPIC, 2000, imu_callback, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());ros::Subscriber sub_image = n.subscribe("/vir_feature_tracker/feature", 2000, feature_callback);ros::Subscriber sub_restart = n.subscribe("/vir_feature_tracker/restart", 2000, restart_callback);ros::Subscriber sub_relo_points = n.subscribe("/pose_graph/match_points", 2000, relocalization_callback);ros::Subscriber sub_uwb = n.subscribe("/uwb/corrected_range", 1000, uwb_callback);ros::Publisher pub_debug_uwb = n.advertise<geometry_msgs::PointStamped>("debug_uwb_keymeas", 1000);std::thread measurement_process{process, pub_debug_uwb};ros::spin();return 0;
}
estimator.cpp/.h
紧耦合的UWB-VIO状态估计器实现,这里存储着实现紧耦合UWB-VIO状态估计的函数,重点是processImage函数,其中含有结合了uwb的优化处理。processImage()->solveOdometry()->optimization(),结合uwb的优化方面主要在optimization()函数中。下一篇博客详细介绍。
函数功能介绍:
void Estimator::setParameter() 设置部分参数
void Estimator::clearState() 清空或初始化滑动窗口中所有的状态量
void Estimator::processIMU() 处理IMU数据,预积分
void Estimator::processImage() 处理图像特征数据
bool Estimator::initialStructure() 视觉的结构初始化
bool Estimator::visualInitialAlign() 视觉惯性联合初始化
bool Estimator::relativePose() 判断两帧有足够视差30且内点数目大于12则可进行初始化,同时得到R和T
void Estimator::solveOdometry() VIO非线性优化求解里程计
void Estimator::vector2double() vector转换成double数组,因为ceres使用数值数组
void Estimator::double2vector() 数据转换,vector2double的相反过程
bool Estimator::failureDetection() 检测系统运行是否失败
void Estimator::optimization() 基于滑动窗口的紧耦合的非线性优化,残差项的构造和求解
void Estimator::slideWindow() 滑动窗口法
void Estimator::setReloFrame() 重定位操作
void Estimator::estimateAnchorPos() 锚点估计函数,同样在imageprocess函数中调用的。
重点是VIR-SLAM中的optimization()以及slideWindow(),下一弹详细介绍estimator.cpp/.h中的函数。
parameters.cpp/.h
处理前端中需要用到的一些参数,根据uwb数据情况进行了修改。