综合案例,全球GDP排行榜
1、知识点补充:sort()方法
sort()方法: 列表.sort(key=选择排序依据的函数,reverse=True|False)
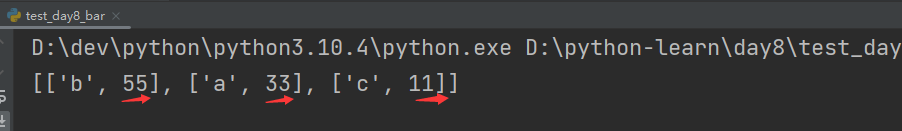
my_list = [['a', 33], ['b', 55], ['c', 11]]def choose_sort_key(element):return element[1] # 列表中每个元素传进来,按照元素下标1排序# 逆序
my_list.sort(key=choose_sort_key, reverse=True) # 注意此处调用函数方式
print(my_list)
匿名函数写法
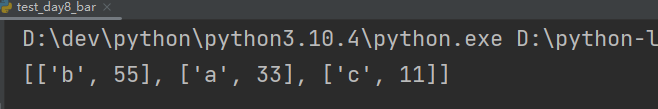
my_list = [['a', 33], ['b', 55], ['c', 11]]
my_list.sort(key=lambda element: element[1], reverse=True)
print(my_list)
2、实战案例 ,全球GDP数据可视化
导包
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.options import *
from pyecharts.globals import *
数据准备
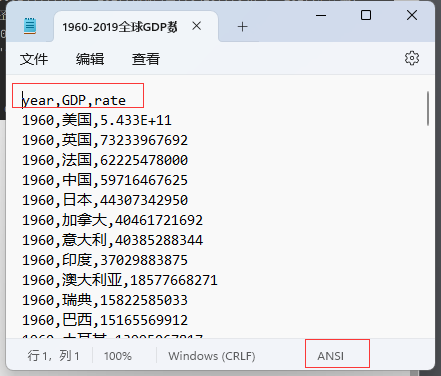
f = open("D:/1960-2019全球GDP数据.csv", "r", encoding="ansi") # 本机编码为GB2312
data = f.readlines() # readlines()返回列表,read()返回字符串
f.close()
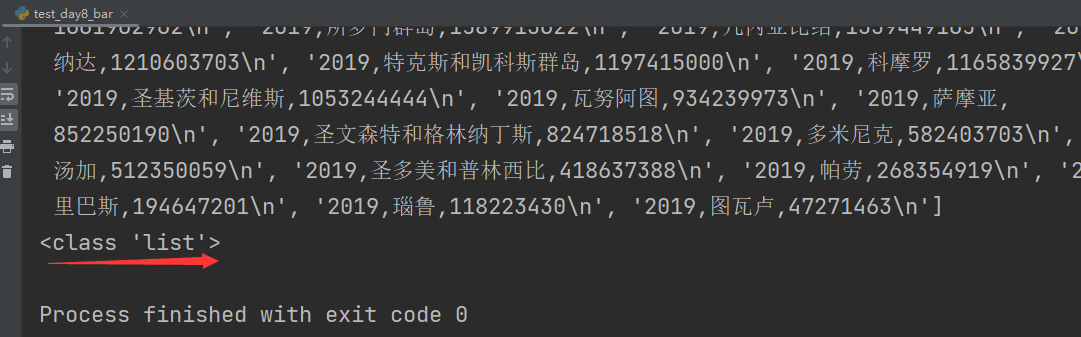
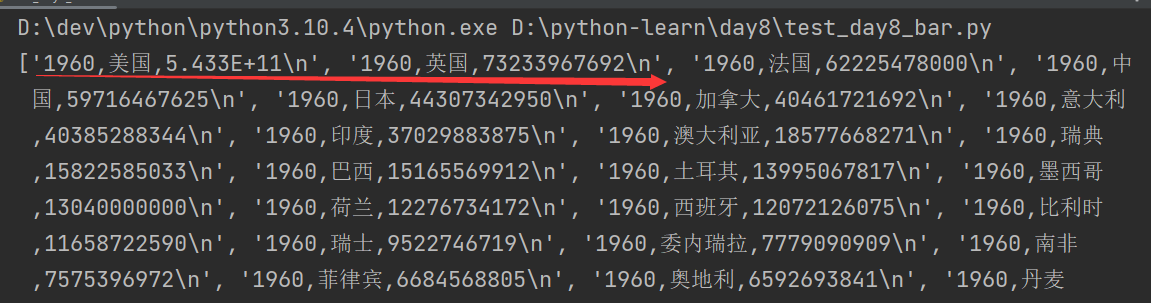
print(data)
print(type(data))
第一行为标头,非数据,使用pop()方法去除
data.pop(0)
print(data)
将数据转为字典格式
错误思路
{年份:[国家,GDP],年份:[国家,GDP],int:[str,float]…} ,实际上,同年应有多个国家GDP数据,故此格式错误
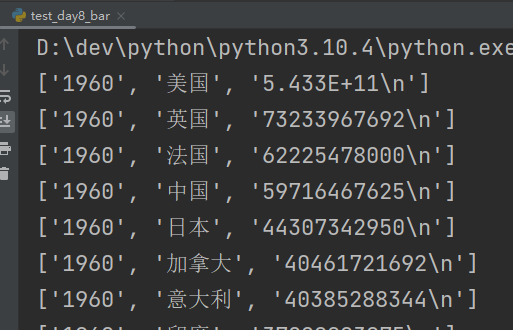
for element in data:element = element.strip()element = element.split(',')print("element:",element)
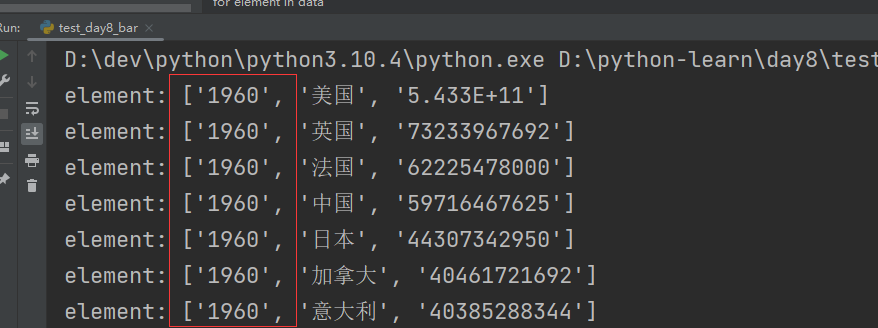
此方法错误,年份key相同时,为更新value操作!!!!!严重丢失数据!!!
data_dict = {}
# {年份:[国家,GDP],年份:[国家,GDP],int:[str,float]......},实际上,同年应有多个国家GDP数据,故此格式错误
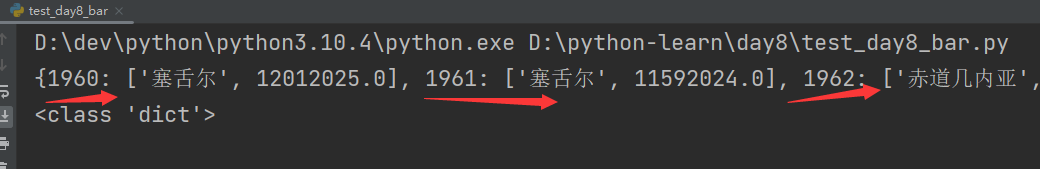
for element in data:element = element.strip()element = element.split(',')# print("element:",element)# 注意字典添加/更新数据方式:my_dict[key] = value# 此方法错误,年份key相同时,为更新value操作!!!!!严重丢失数据!!!# data_dict = {element[0]: [element[1], element[2]]}data_dict[int(element[0])] = [element[1], float(element[2])]
print(data_dict)
print(type(data_dict))
正确思路
{年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],…],年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],…],int:[[str,float],[str,float],…],…}
正确数据格式,年份:value,而value是一个列表,包含不同国家的数据,其中每个元素又是一个列表;而某一国家具体数据列表为[国家,GDP]。
data_dict = {}
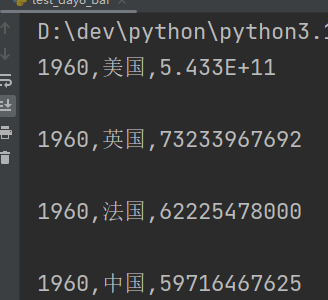
for line in data:print(line)
print(type(line))
print(line.split(',')) # ['2018', '巴巴多斯', '5086500000\n']
split()方法生成列表,取0号索引元素为年份,1号索引元素为国家,2号索引元素为GDP
data_dict = {}
# {年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],int:[[str,float],[str,float],......],......},正确数据格式,年份:value,而value是一个列表,包含不同国家的数据,其中每个元素又是一个列表;而某一国家具体数据列表为[国家,GDP]。
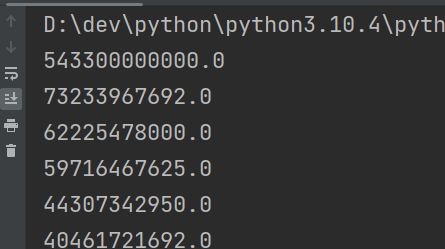
for line in data:# print(line)# print(type(line))# print(line.split(',')) # ['2018', '巴巴多斯', '5086500000\n']# split()方法生成列表,取0号索引元素为年份,1号索引元素为国家,2号索引元素为GDPyear = int(line.split(',')[0])country = line.split(',')[1]GDP = float(line.split(',')[2]) # 换行符消失 543300000000.0print(GDP)
注意此处灵活使用try捕获异常语句,妙
"""{key:value} --> value = [元素一,元素二,......] --> 元素一 = [country,GDP]try:无异常的情况,向列表(value)中使用append()方法追加元素(list)data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])except:出现异常情况,data_dict[year]此时无对应value,构建空列表,再向列表中追加元素data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])"""
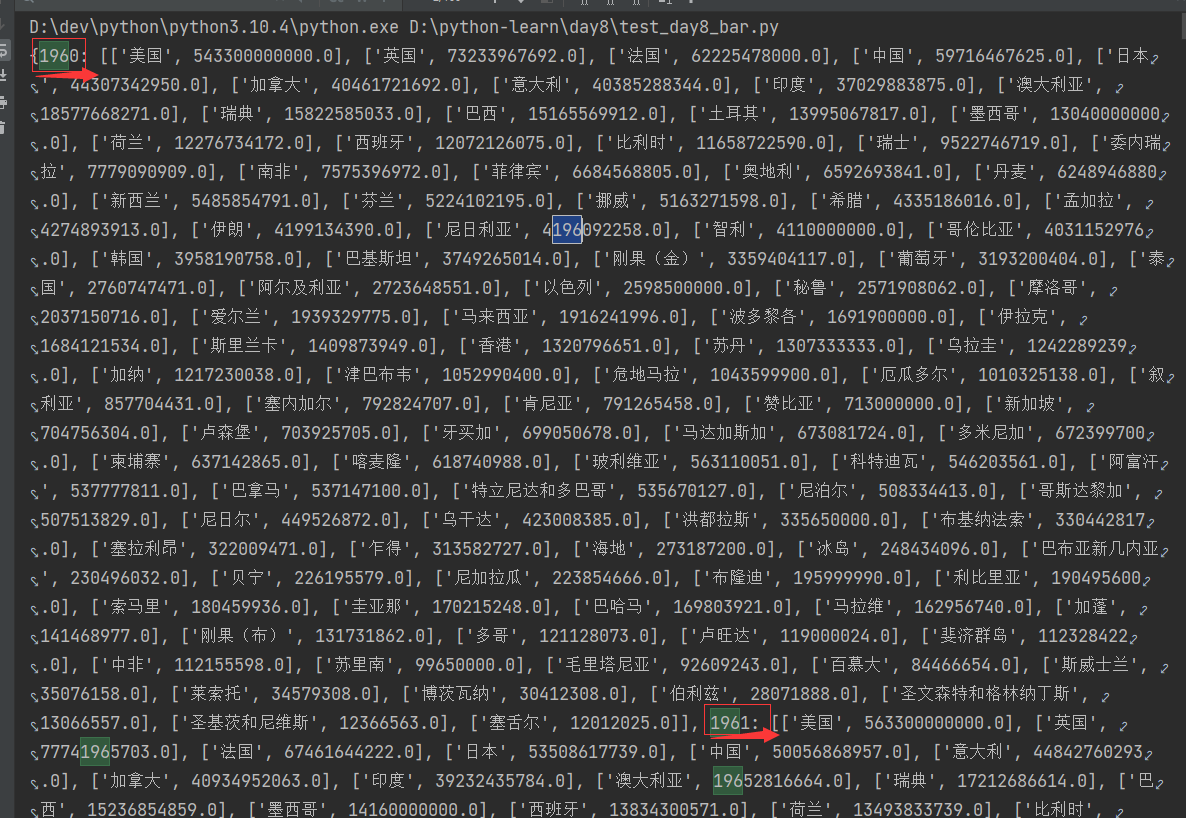
try:data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])except:data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])print(data_dict)
print(type(data_dict))
将数据转为字典格式完整代码
# 将数据转为字典格式"""
data_dict = {}
# {年份:[国家,GDP],年份:[国家,GDP],int:[str,float]......},实际上,同年应有多个国家GDP数据,故此格式错误
for element in data:element = element.strip()element = element.split(',')# print("element:",element)# 注意字典添加/更新数据方式:my_dict[key] = value# 此方法错误,年份key相同时,为更新value操作!!!!!严重丢失数据!!!# data_dict = {element[0]: [element[1], element[2]]}data_dict[int(element[0])] = [element[1], float(element[2])]
print(data_dict)
print(type(data_dict))
"""data_dict = {}
# {年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],int:[[str,float],[str,float],......],......},正确数据格式,年份:value,而value是一个列表,包含不同国家的数据,其中每个元素又是一个列表;而某一国家具体数据列表为[国家,GDP]。
for line in data:# print(line)# print(type(line))# print(line.split(',')) # ['2018', '巴巴多斯', '5086500000\n']# split()方法生成列表,取0号索引元素为年份,1号索引元素为国家,2号索引元素为GDPyear = int(line.split(',')[0])country = line.split(',')[1]GDP = float(line.split(',')[2]) # 换行符消失 543300000000.0# print(GDP)# 注意此处灵活使用try捕获异常语句,妙"""{key:value} --> value = [元素一,元素二,......] --> 元素一 = [country,GDP]try:无异常的情况,向列表(value)中使用append()方法追加元素(list)data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])except:出现异常情况,data_dict[year]此时无对应value,构建空列表,再向列表中追加元素data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])"""try:data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])except:data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])# print(data_dict)
# print(type(data_dict))
可转为json,放入格式化工具查看一下
data_json = json.dumps(data_dict)
print(data_json)
print(type(data_json))
时间线柱状图timeline的时间节点应有序,故先对年份进行排序(实际上字典中year(key)已是升序)
sorted_year_list = sorted(data_dict.keys()) # keys()方法取出字典所有关键字,可用for循环遍历字典
print(sorted_year_list)
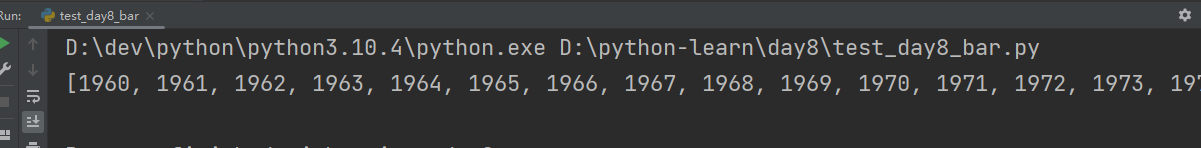
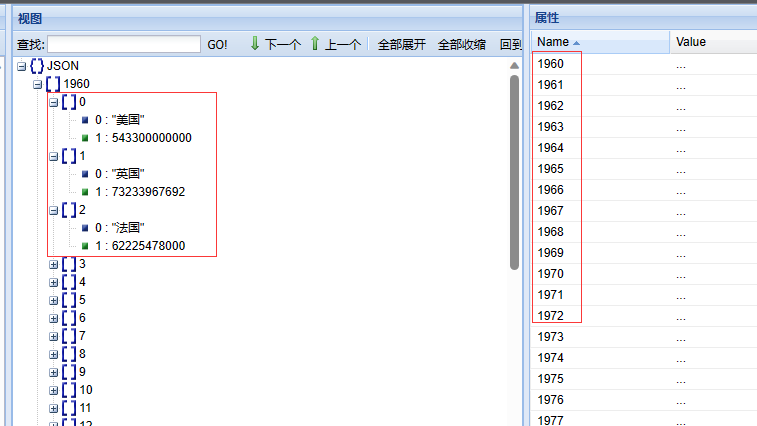
每年国家数量非常多,取GDP排名前十作柱状图
print(data_dict[1960]) # 每年国家数量非常多,取GDP排名前十作柱状图
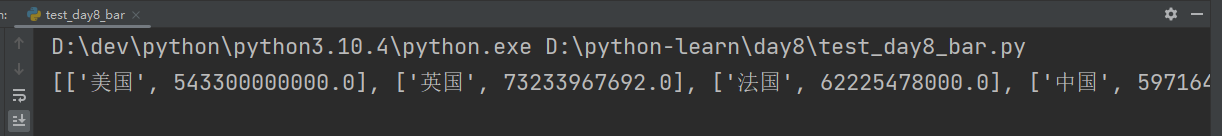
构建时间线对象
timeline = Timeline({"theme": ThemeType.LIGHT} # 设置主题
)
每年GDP降序排序
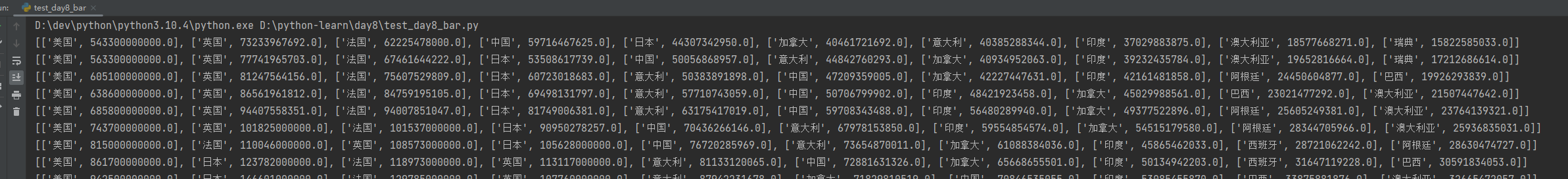
for year in sorted_year_list:data_dict[year].sort(key=lambda element: element[1],reverse=True) # sort()方法: 列表.sort(key=选择排序依据的函数,reverse=True|False)print(data_dict[year]) # [['美国', 543300000000.0], ['英国', 73233967692.0], ['法国', 62225478000.0], ['中国', 59716467625.0],......]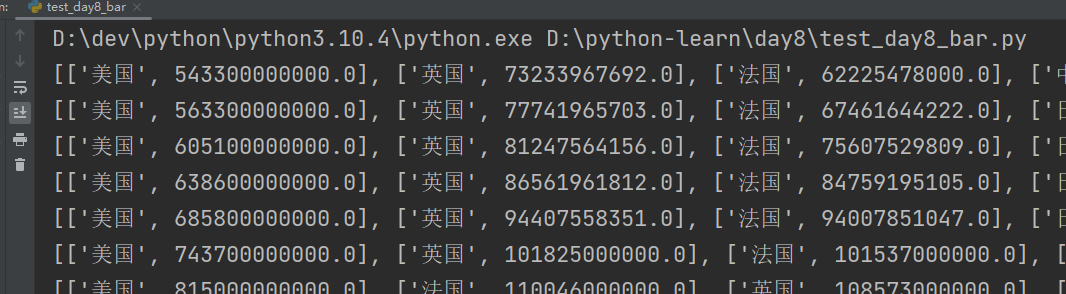
取出本年度GDP前十的国家, 数据类型为列表,可通过切片[::],取出前十名
print(type(data_dict[year])) # 数据类型为列表,可通过切片[::],取出前十名prior_gdp = data_dict[year][0:10]
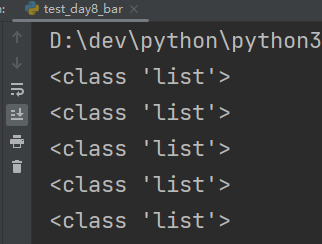
每一年都构建一个柱状图
# 创建两个列表分别存放X轴数据与Y轴数据x_data = []y_data = []
前十名
print(prior_gdp)
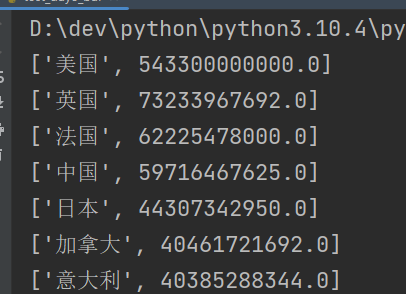
取国家名存入列表作为X轴数据,取GDP值存入列表作为Y轴数据
for country_gdp in prior_gdp:print(country_gdp) # ['美国', 17527200000000.0]x_data.append(country_gdp[0])y_data.append(country_gdp[1] / 100000000)
print(x_data) # ['美国', '英国', '法国', '中国', '日本', '加拿大', '意大利', '印度', '澳大利亚', '瑞典']print(y_data) # [5433.0, 732.33967692, 622.25478, 597.16467625, 443.0734295, 404.61721692, 403.85288344, 370.29883875, 185.77668271, 158.22585033]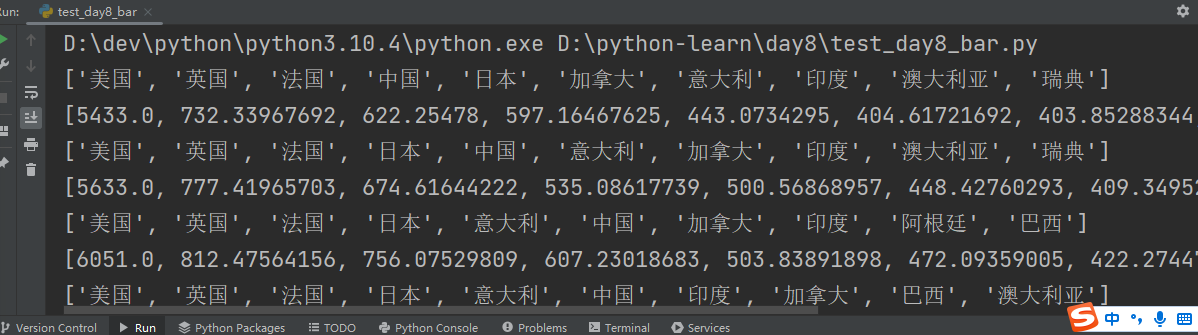
构建柱状图对象
反转X轴与Y轴,此操作导致GDP高的国家在最下面,故上方使用reverse()方法逆置X轴与Y轴数据
# 构建柱状图对象bar = Bar()# 逆置X轴与Y轴数据,使GDP值高的排在前面x_data.reverse()y_data.reverse()bar.add_xaxis(x_data)# Y轴设置图例,数据,以及数据在右侧显示bar.add_yaxis("GDP(亿元)", y_data, label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))bar.reversal_axis() # 反转X轴与Y轴,此操作导致GDP高的国家在最下面,故上方使用reverse()方法逆置X轴与Y轴数据设置每年图的标题
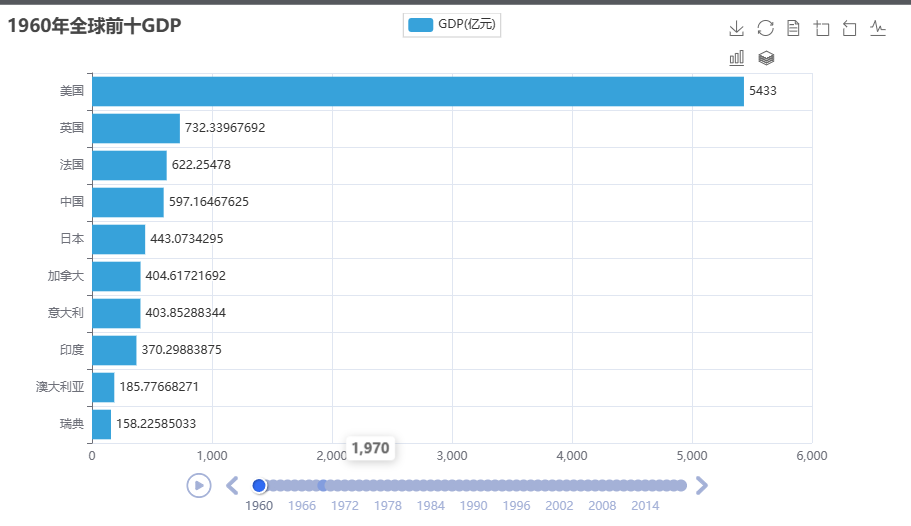
bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=TitleOpts(title=f"{year}年全球前十GDP"),toolbox_opts=ToolboxOpts(is_show=True))timeline.add(bar, str(year)) # 要求为字符串
设置自动播放
timeline.add_schema(play_interval=500,is_loop_play=False,is_auto_play=True,is_timeline_show=True
)
绘图
timeline.render("GDP排行榜.html")
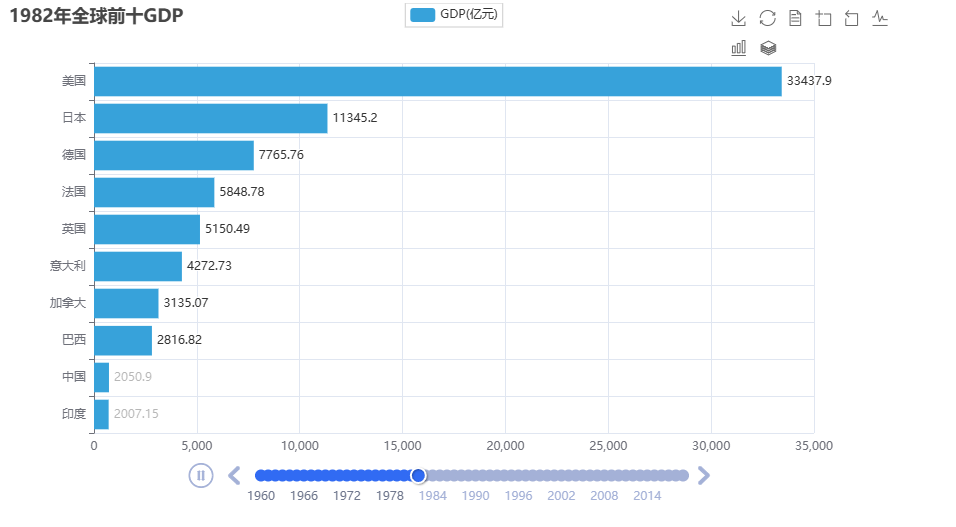
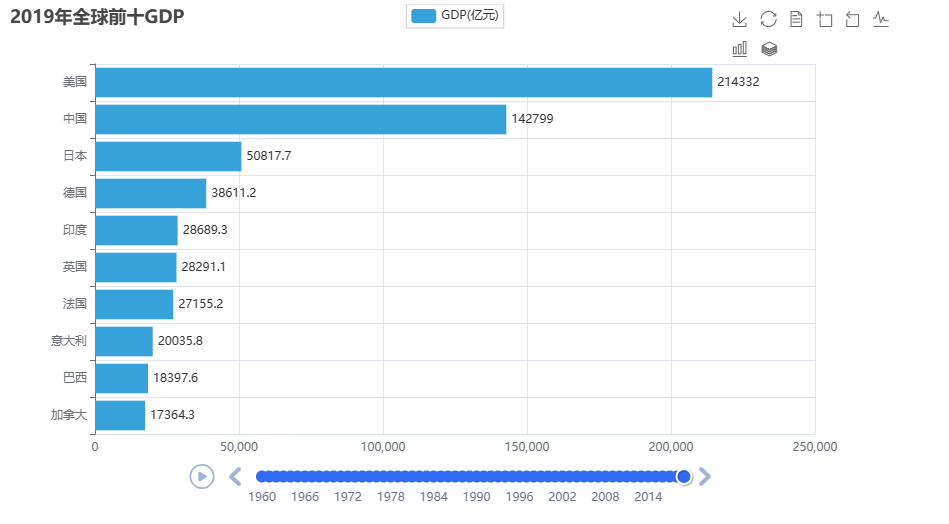

PS完整代码(含思路注释版)
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.options import *
from pyecharts.globals import *
import json# 实战案例 ,全球GDP数据可视化# 数据准备
f = open("D:/1960-2019全球GDP数据.csv", "r", encoding="ansi") # 本机编码为GB2312
data = f.readlines() # readlines()返回列表,read()返回字符串
f.close()
# print(data)
# print(type(data))# 第一行为标头,非数据,使用pop()方法去除
data.pop(0)
# print(data)# 将数据转为字典格式"""
data_dict = {}
# {年份:[国家,GDP],年份:[国家,GDP],int:[str,float]......},实际上,同年应有多个国家GDP数据,故此格式错误
for element in data:element = element.strip()element = element.split(',')# print("element:",element)# 注意字典添加/更新数据方式:my_dict[key] = value# 此方法错误,年份key相同时,为更新value操作!!!!!严重丢失数据!!!# data_dict = {element[0]: [element[1], element[2]]}data_dict[int(element[0])] = [element[1], float(element[2])]
print(data_dict)
print(type(data_dict))
"""data_dict = {}
# {年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],int:[[str,float],[str,float],......],......},正确数据格式,年份:value,而value是一个列表,包含不同国家的数据,其中每个元素又是一个列表;而某一国家具体数据列表为[国家,GDP]。
for line in data:# print(line)# print(type(line))# print(line.split(',')) # ['2018', '巴巴多斯', '5086500000\n']# split()方法生成列表,取0号索引元素为年份,1号索引元素为国家,2号索引元素为GDPyear = int(line.split(',')[0])country = line.split(',')[1]GDP = float(line.split(',')[2]) # 换行符消失 543300000000.0# print(GDP)# 注意此处灵活使用try捕获异常语句,妙"""{key:value} --> value = [元素一,元素二,......] --> 元素一 = [country,GDP]try:无异常的情况,向列表(value)中使用append()方法追加元素(list)data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])except:出现异常情况,data_dict[year]此时无对应value,构建空列表,再向列表中追加元素data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])"""try:data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])except:data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])# print(data_dict)
# print(type(data_dict))# 可转为json,放入格式化工具查看一下
# data_json = json.dumps(data_dict)
# print(data_json)
# print(type(data_json))# 时间线柱状图timeline的时间节点应有序,故先对年份进行排序(实际上字典中year(key)已是升序)
sorted_year_list = sorted(data_dict.keys()) # keys()方法取出字典所有关键字,可用for循环遍历字典
# print(sorted_year_list)# print(data_dict[1960]) # 每年国家数量非常多,取GDP排名前十作柱状图# 构建时间线对象
timeline = Timeline({"theme": ThemeType.LIGHT} # 设置主题
)for year in sorted_year_list:data_dict[year].sort(key=lambda element: element[1],reverse=True) # sort()方法: 列表.sort(key=选择排序依据的函数,reverse=True|False)# print(data_dict[year]) # [['美国', 543300000000.0], ['英国', 73233967692.0], ['法国', 62225478000.0], ['中国', 59716467625.0],......]# 取出本年度GDP前十的国家# print(type(data_dict[year])) # 数据类型为列表,可通过切片[::],取出前十名prior_gdp = data_dict[year][0:10]# 每一年都构建一个柱状图# 创建两个列表分别存放X轴数据与Y轴数据x_data = []y_data = []# print(prior_gdp)for country_gdp in prior_gdp:# print(country_gdp) # ['美国', 17527200000000.0]x_data.append(country_gdp[0])y_data.append(country_gdp[1] / 100000000)# print(x_data) # ['美国', '英国', '法国', '中国', '日本', '加拿大', '意大利', '印度', '澳大利亚', '瑞典']# print(y_data) # [5433.0, 732.33967692, 622.25478, 597.16467625, 443.0734295, 404.61721692, 403.85288344, 370.29883875, 185.77668271, 158.22585033]# 构建柱状图对象bar = Bar()# 逆置X轴与Y轴数据,使GDP值高的排在前面x_data.reverse()y_data.reverse()bar.add_xaxis(x_data)# Y轴设置图例,数据,以及数据在右侧显示bar.add_yaxis("GDP(亿元)", y_data, label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))bar.reversal_axis() # 反转X轴与Y轴,此操作导致GDP高的国家在最下面,故上方使用reverse()方法逆置X轴与Y轴数据# bar.render()# 设置每年图的标题bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=TitleOpts(title=f"{year}年全球前十GDP"),toolbox_opts=ToolboxOpts(is_show=True))timeline.add(bar, str(year)) # 要求为字符串# 设置自动播放
timeline.add_schema(play_interval=500,is_loop_play=False,is_auto_play=True,is_timeline_show=True
)
# 绘图
timeline.render("GDP排行榜.html")PS完整代码(清爽版)
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.options import *
from pyecharts.globals import *# 实战案例 ,全球GDP数据可视化# 数据准备
f = open("D:/1960-2019全球GDP数据.csv", "r", encoding="ansi") # 本机编码为GB2312
data = f.readlines() # readlines()返回列表,read()返回字符串
f.close()# 第一行为标头,非数据,使用pop()方法去除
data.pop(0)# 将数据转为字典格式
data_dict = {}
# {年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],年份:[[国家,GDP],[国家,GDP],......],int:[[str,float],[str,float],......],......},正确数据格式,年份:value,而value是一个列表,包含不同国家的数据,其中每个元素又是一个列表;而某一国家具体数据列表为[国家,GDP]。
for line in data:# split()方法生成列表,取0号索引元素为年份,1号索引元素为国家,2号索引元素为GDPyear = int(line.split(',')[0])country = line.split(',')[1]GDP = float(line.split(',')[2]) # 换行符消失 543300000000.0# 注意此处灵活使用try捕获异常语句,妙"""{key:value} --> value = [元素一,元素二,......] --> 元素一 = [country,GDP]try:无异常的情况,向列表(value)中使用append()方法追加元素(list)data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])except:出现异常情况,data_dict[year]此时无对应value,构建空列表,再向列表中追加元素data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country,GDP])"""try:data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])except:data_dict[year] = []data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])# 时间线柱状图timeline的时间节点应有序,故先对年份进行排序(实际上字典中year(key)已是升序)
sorted_year_list = sorted(data_dict.keys()) # keys()方法取出字典所有关键字,可用for循环遍历字典# 构建时间线对象
timeline = Timeline({"theme": ThemeType.LIGHT} # 设置主题
)for year in sorted_year_list:data_dict[year].sort(key=lambda element: element[1],reverse=True) # sort()方法: 列表.sort(key=选择排序依据的函数,reverse=True|False)# 取出本年度GDP前十的国家prior_gdp = data_dict[year][0:10]# 每一年都构建一个柱状图# 创建两个列表分别存放X轴数据与Y轴数据x_data = []y_data = []for country_gdp in prior_gdp:x_data.append(country_gdp[0])y_data.append(country_gdp[1] / 100000000)# 构建柱状图对象bar = Bar()# 逆置X轴与Y轴数据,使GDP值高的排在前面x_data.reverse()y_data.reverse()bar.add_xaxis(x_data)# Y轴设置图例,数据,以及数据在右侧显示bar.add_yaxis("GDP(亿元)", y_data, label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))bar.reversal_axis() # 反转X轴与Y轴,此操作导致GDP高的国家在最下面,故上方使用reverse()方法逆置X轴与Y轴数据# 设置每年图的标题bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=TitleOpts(title=f"{year}年全球前十GDP"),toolbox_opts=ToolboxOpts(is_show=True))timeline.add(bar, str(year)) # 要求为字符串# 设置自动播放
timeline.add_schema(play_interval=500,is_loop_play=False,is_auto_play=True,is_timeline_show=True
)
# 绘图
timeline.render("GDP排行榜.html")