目录
1. 线性表
2. 顺序表
接口的实现
3. ArrayList简介
3.1 ArrayList介绍
3.2 ArrayList的构造方法
4. ArrayList的扩容机制
5. ArrayList的常见操作
6. ArrayList的遍历
7. 例题
8. ArrayList的具体使用
8.1 简单的洗牌算法
8.2 杨辉三角
9. ArrayList的问题及思考
1. 线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。

2. 顺序表
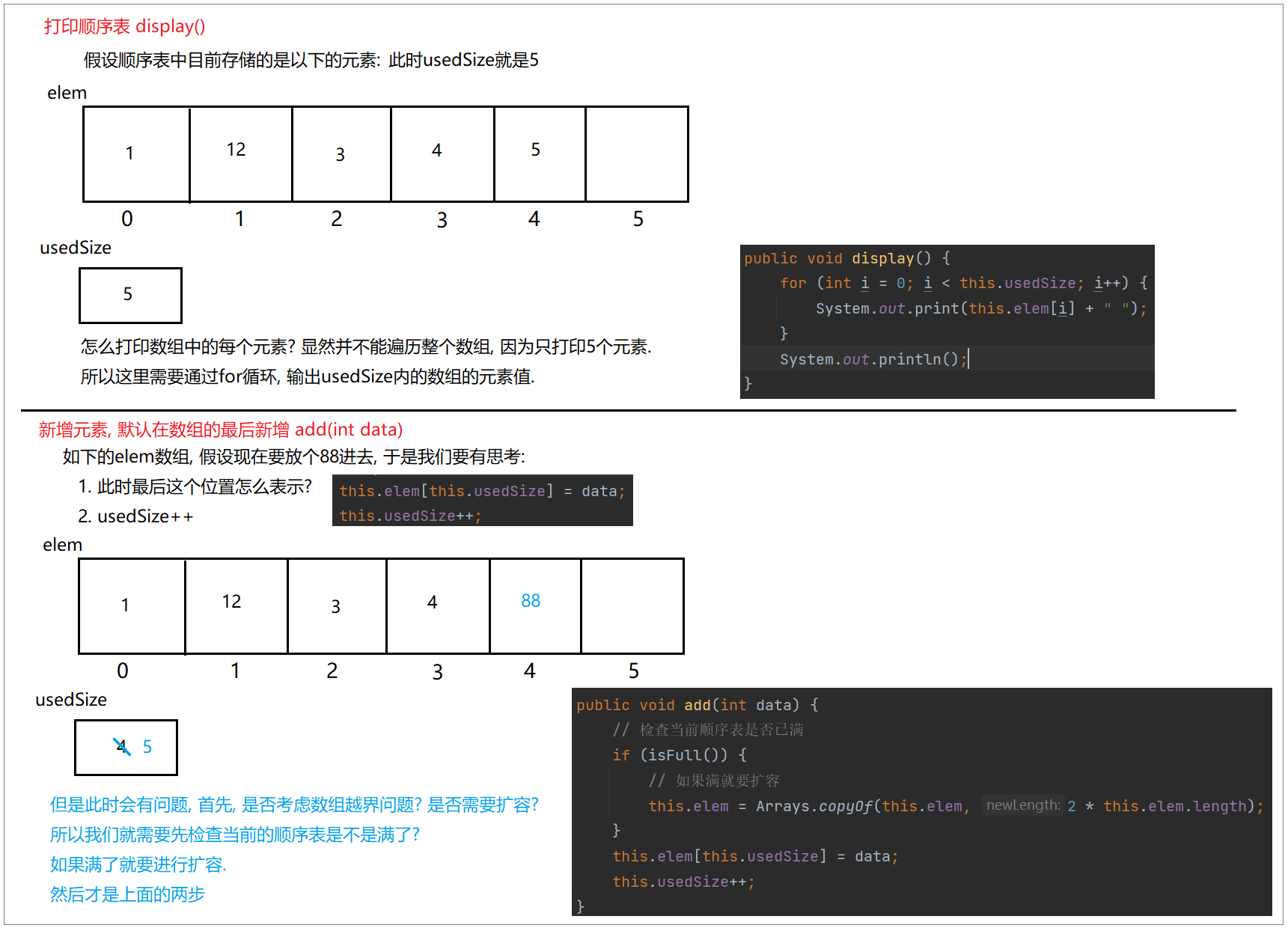
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元一次存储数据的线性结构,一般采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
接口的实现
public class MyArrayList {// 这个类所操作的全部都是数组, 是提供一些方法用于操作private int[] elem; // 数组private int usedSize; // 记录有效的数据的个数private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;// 提供一个构造方法public MyArrayList() {this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE]; // 对 elem 进行初始化}// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的public void display() {for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");}System.out.println();}// 新增元素, 默认在数组最后新增public void add(int data) {// 检查当前顺序表是否已满if (isFull()) {// 如果满就要扩容this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * this.elem.length);}this.elem[this.usedSize] = data;this.usedSize++;}public boolean isFull() {/*if(size() >= this.elem.length){return true;}return false;*/return size() >= this.elem.length;}// 获取顺序表长度public int size() {return this.usedSize;}
}
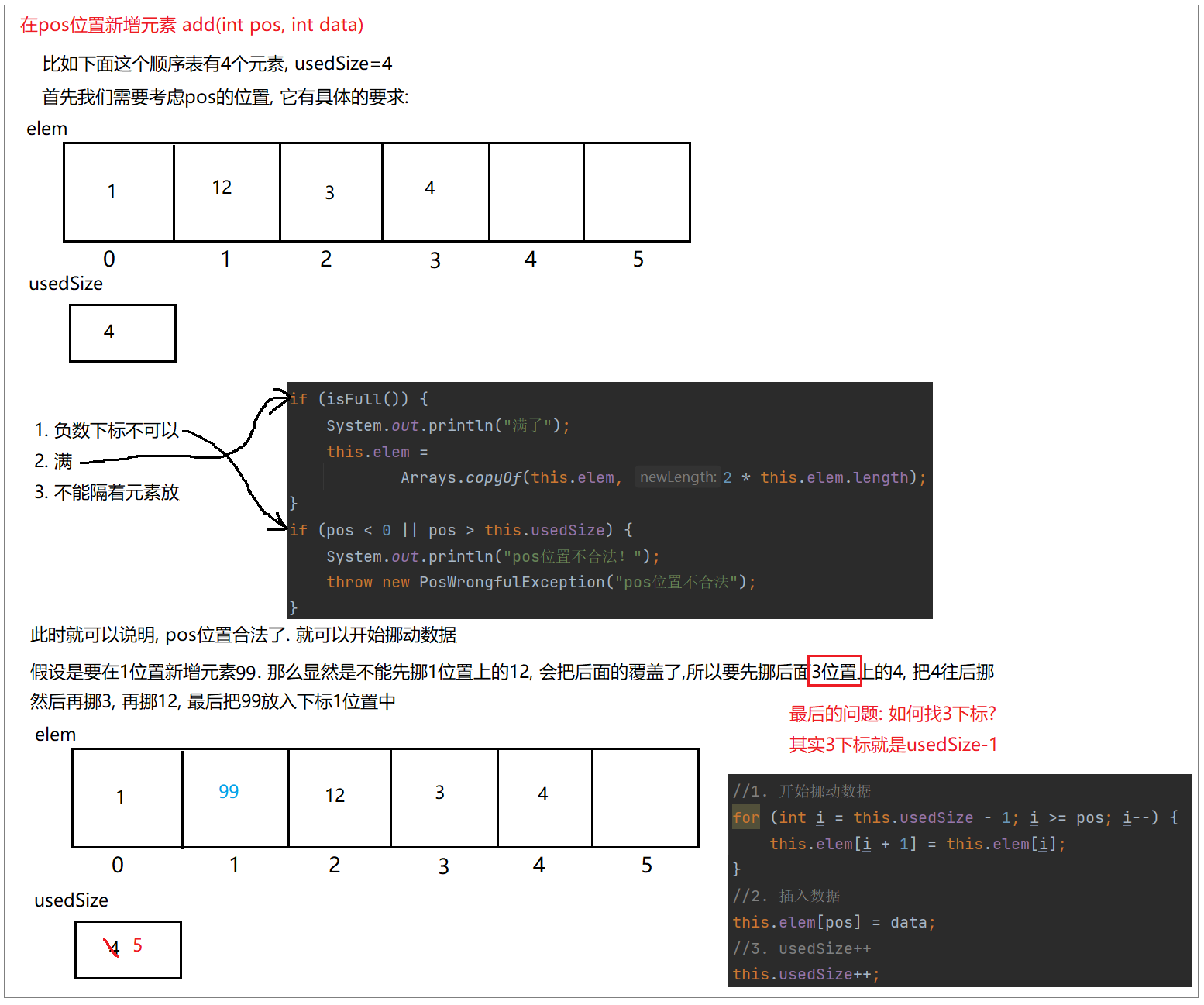
// 在 pos 位置新增元素.// 如果pos下标不合法,那么就会抛出一个 PosWrongfulExceptionpublic void add(int pos, int data) throws PosWrongfulException {if (isFull()) {System.out.println("满了");this.elem =Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * this.elem.length);}if (pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize) {System.out.println("pos位置不合法!");throw new PosWrongfulException("pos位置不合法");}//pos一定是合法的//1. 开始挪动数据for (int i = this.usedSize - 1; i >= pos; i--) {this.elem[i + 1] = this.elem[i];}//2.插入数据this.elem[pos] = data;//3. usedSize++this.usedSize++;}// pos 位置不合法的异常
public class PosWrongfulException extends RuntimeException{public PosWrongfulException() {}public PosWrongfulException(String message) {super(message);}
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素public boolean contains(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.size(); i++) {if (this.elem[i] == toFind) {return true;}}return false;}// 查找某个元素对应的位置public int indexOf(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < this.size(); i++) {if (this.elem[i] == toFind) {return i;}}return -1;}// 获取 pos 位置的元素public int get(int pos) {if (isEmpty()) {throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");}if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {throw new PosWrongfulException("get获取元素的时候,pos不合法异常!");}return this.elem[pos];}public boolean isEmpty() {return size() == 0;}// 给 pos 位置的元素 更新 为 valuepublic void set(int pos, int value) {if (isEmpty()) {throw new EmptyException("当前顺序表为空!");}if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {throw new PosWrongfulException("set获取元素的时候,pos不合法异常!");}this.elem[pos] = value;}public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{public EmptyException() {}public EmptyException(String message) {super(message);}
} //删除第一次出现的关键字keypublic void remove(int key) {if (isEmpty()) {throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!");}int index = this.indexOf(key);if (index == -1) {System.out.println("没有这个数字");return;}for (int i = index; i < size() - 1; i++) {this.elem[i] = this.elem[i + 1];}this.usedSize--;}
// 清空顺序表public void clear() {this.usedSize = 0;}3. ArrayList简介
3.1 ArrayList介绍
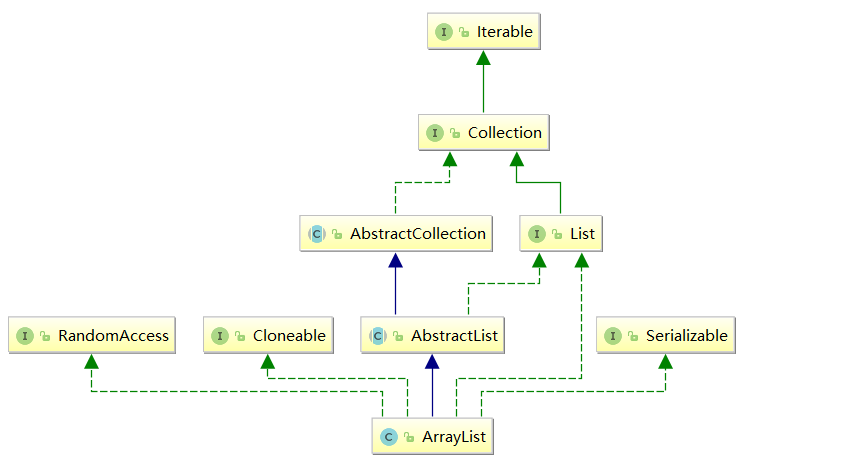
ArrayList是Java里面的一个集合类,这是一个具体的实现类叫做ArrayList,那么它实际上实现了许多接口:
【说明】
1. ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
2. ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
3. ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
4. 和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
5. ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
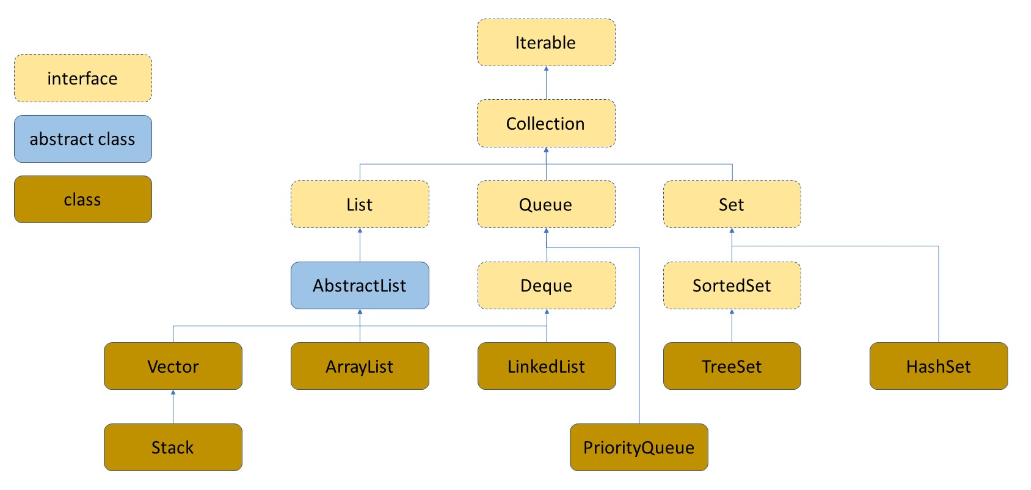
上图中,我们可以看到,ArrayList类继承了一个抽象类AbstractList,然后实现类List接口,List接口又扩展了Collection接口,Collection接口又扩展了Iterable接口,那么不管怎么样呢最重要的还是List接口。
我们需要跟着源码来学习其集合类,所以看一下ArrayList的源码。
首先,Java的集合类一般都在java.util包里面,这里可以通过编译器看到:
当我们点进查看ArrayList的源码的时候就可以看见ArrayList实现的接口:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{//..
}3.2 ArrayList的构造方法

其中,第二个的使用要注意:

注意不能把String类型的arrayList3放进Integer类型的arrayList4中,因为使用第二个构造方法时只能只能用E或者E的子类,因为arrayList3并不是arrayList4的子类类型。
4. ArrayList的扩容机制
我们来看ArrayList的不带参数的构造方法:
public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA为0}接着看DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA:
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 指定默认容量为10private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 空数组private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认空数组transient Object[] elementData; // 类似于顺序表代码里背后的数组private int size; //有效数据个数这个构造方法中, DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA为0, 并没有分配数组内存,那么引出一个问题:既然没有大小,那么是怎么把数据放进顺序表的?
这个时候看我们的测试方法。
public class Test {public static void main1(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> arrayList1 = new ArrayList<>(); // 这行构造方法中没有找到实际调用将元素放进去的方式,那么目光往下看add方法。arrayList1.add(1); // 将数据存储于ArrayList中, 下面同理arrayList1.add(2);System.out.println(arrayList1);
}看add方法的源码:
public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 假定size=0elementData[size++] = e; // 存储的时候放在最后一个元素后边return true;}再看其中第一行ensureCapacityInternal的源码:
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { // minCapacity = size + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));}ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); // elementData = 0}再接着往下看calculateCapacity方法:
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { // 0 == 0return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); // DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10, minCapacity=1}return minCapacity; // 10}在这个方法里可以了解到做了一个求最大值的方法, 这里为10, 那么往上返回到ensureCapacityInternal中,再进入方法ensureExplicitCapacity中:
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { // minCapacity = 10modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) // 10 - 0 > 0grow(minCapacity);}看到又调用了grow:
private void grow(int minCapacity) { // minCapacity = 10// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 0int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 0 + 0 / 2 = 0if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 0 - 10 < 0newCapacity = minCapacity; // 10if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 很大这里进不来newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); //真正分配内存了}所以,当我们调用不带参数的构造方法的时候,只有第一个add的时候,我们才会分配大小为10的内存。
由grow()中的 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);可知, 在放第11个的时候,采用1.5倍扩容. 总结:
1. 检测是否真正需要扩容,如果是调用grow准备扩容
2. 预估需要库容的大小
初步预估按照1.5倍大小扩容
如果用户所需大小超过预估1.5倍大小,则按照用户所需大小扩容
真正扩容之前检测是否能扩容成功,防止太大导致扩容失败
3. 使用copyOf进行扩容
5. ArrayList的常见操作
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
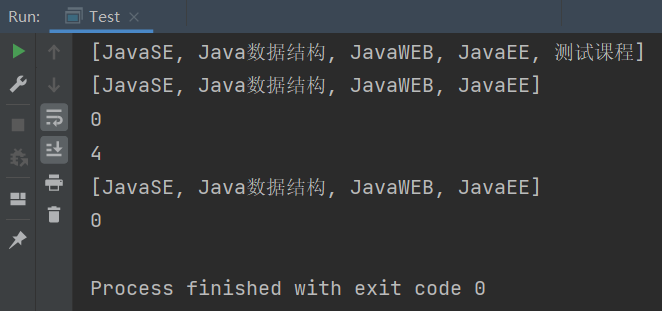
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("JavaSE");list.add("JavaWeb");list.add("JavaEE");list.add("JVM");list.add("测试课程");System.out.println(list);// 获取list中有效元素个数System.out.println(list.size());// 获取和设置index位置上的元素,注意index必须介于[0, size)间System.out.println(list.get(1));list.set(1, "JavaWEB");System.out.println(list.get(1));// 在list的index位置插入指定元素,index及后续的元素统一往后搬移一个位置list.add(1, "Java数据结构");System.out.println(list);// 删除指定元素,找到了就删除,该元素之后的元素统一往前搬移一个位置list.remove("JVM");System.out.println(list);// 删除list中index位置上的元素,注意index不要超过list中有效元素个数,否则会抛出下标越界异常list.remove(list.size()-1);System.out.println(list);// 检测list中是否包含指定元素,包含返回true,否则返回falseif(list.contains("测试课程")){list.add("测试课程");}// 查找指定元素第一次出现的位置:indexOf从前往后找,lastIndexOf从后往前找list.add("JavaSE");System.out.println(list.indexOf("JavaSE"));System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("JavaSE"));// 使用list中[0, 4)之间的元素构成一个新的ArrayList返回List<String> ret = list.subList(0, 4);System.out.println(ret);list.clear();System.out.println(list.size());
}
6. ArrayList的遍历
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();arrayList.add(1);arrayList.add(2);arrayList.add(3);arrayList.add(4);arrayList.add(5);int size = arrayList.size();// 通过for循环的遍历for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {System.out.print(arrayList.get(i) + " ");}System.out.println();// 增强for遍历for (int x : arrayList) {System.out.print(x + " ");}System.out.println();// 迭代器遍历Iterator<Integer> it = arrayList.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}}
}
7. 例题
1. 一个班级有若干(3个)学生,这些学生的信息有,姓名,年龄,分数(小数),考试结束后,每个学生都有分数等信息。已知每个学生对象都在ArrayList当中存放,请输出每个学生的信息?
Collections是一个用来操作集合的工具类,这个类里有非常多的方法,在里面我们用的最多的是排序方法.
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {return (int)(this.score - o.score);}private int age;private String name;private double score;public Student(int age, String name, double score) {this.age = age;this.name = name;this.score = score;}/** 此处省略Setter和Getter, 以及toString() */}public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();arrayList.add(new Student(10, "小王", 49.9));arrayList.add(new Student(50, "小红", 19.9));arrayList.add(new Student(10, "大胖", 89.9));for (Student s : arrayList) {System.out.println(s);}System.out.println("==========================");Collections.sort(arrayList);for (Student s : arrayList) {System.out.println(s);}}
}运行结果:

通过这个题我们可以总结:
(1) 我们可以在ArrayList中 存放自定义的类型
(2) 我们可以对集合进行排序, 也就是使用Collections.sort()方法
2. 给你两个字符串。
str1:"welcome to bit";
str2:"come";
请删除第一个字符串当中,出现的第二个字符串当中的字符。
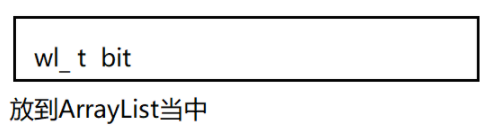
预期结果:
wl t bit
要求:请使用集合ArrayList来完成
解释:
public class Test {public static ArrayList<Character> func(String str1, String str2) {ArrayList<Character> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {char ch = str1.charAt(i);if (!str2.contains(ch + "")) { // 转为字符串arrayList.add(ch);}}return arrayList;}public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Character> ret = func("welcome to bit","come");
// System.out.println(ret);for (int i = 0; i < ret.size(); i++) {System.out.print(ret.get(i));}}
}8. ArrayList的具体使用
8.1 简单的洗牌算法
需求: 通过代码买一副扑克牌, 没有大小王, 也没有AJQK, 只有数字1~13, 共有四种花色, 所以一共52张牌. 然后把洗牌, 将顺序打乱, 让三个人轮流揭5张牌.
(1)设计对象 - 一副牌
public class Poker {private String suit; // 花色private int rank; // 数字// 提供 Getter 和 Setterpublic String getSuit() {return suit;}public void setSuit(String suit) {this.suit = suit;}public int getRank() {return rank;}public void setRank(int rank) {this.rank = rank;}// 提供构造方法, 构造一张牌public Poker(String suit, int rank) {this.suit = suit;this.rank = rank;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return suit + " " + rank;}
}(2) 买牌、洗牌、揭牌
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;public class Pokers {public static final String[] SUITS = {"♥", "♠", "♣", "♦"}; // 花色// 通过这个方法买一副扑克牌, 此时是有序的public static List<Poker> buyPokers() {List<Poker> pokerList = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 花色有 4个for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) { // 每一种花色有 13张String suit = SUITS[i];Poker poker = new Poker(suit, j);pokerList.add(poker);}}return pokerList;}// 交换public static void swap(List<Poker> pokerList, int i, int j) {Poker tmp = pokerList.get(i);pokerList.set(i, pokerList.get(j)); // 把j下标的值给到i下标pokerList.set(j, tmp);}// 洗牌public static void shuffle(List<Poker> pokerList) {Random random = new Random();for (int i = pokerList.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {int index = random.nextInt(i); // 假设生成的随机数为 4swap(pokerList, i, index); // 那么4下标和i下标交换即可}}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Poker> pokerList = buyPokers();System.out.println("买牌:" + pokerList);shuffle(pokerList);System.out.println("洗牌:" + pokerList);// 揭牌: 3个人 每个人 轮流抓5张牌// 1. 描述3个人List<Poker> hand1 = new ArrayList<>();List<Poker> hand2 = new ArrayList<>();List<Poker> hand3 = new ArrayList<>();// 2. 区分 往哪个人手里放牌List<List<Poker>> hand = new ArrayList<>();hand.add(hand1);hand.add(hand2);hand.add(hand3);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {List<Poker> handTmp = hand.get(j); // 来确定是谁的手, 在 hamdTmp 中放一张牌handTmp.add(pokerList.remove(0)); // 每次都是0下标}}for (int i = 0; i < hand.size(); i++) {System.out.println("第" + (i + 1) + "个人的牌是:" + hand.get(i));}System.out.println("剩余的牌:" + pokerList);}
}
8.2 杨辉三角
理论上说我们可以把杨辉三角的图化成下图:

而在OJ中我们可以看到, 它的返回值为List<List<Integer>>, 也就是:

class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();list1.add(1); // 先安排第一行, 只有一个1ret.add(list1);// 上述第一行只有1个1, 已经添加到了ret当中. 接下来我们需要从第2行开始计算for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>(); // 当前行curRow.add(1); // 是当前行的第一个元素, 1// 中间位置 需要计算List<Integer> prevRow = ret.get(i - 1); //前一行for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {int num = prevRow.get(j) + prevRow.get(j - 1);curRow.add(j, num);}curRow.add(1); // 是当前行结束元素, 1ret.add(curRow); // 当前行加入ret中, 即结果List<List<Integer>>}return ret;}
}9. ArrayList的问题及思考
对于顺序表ArrayList来说, 它底层是一个数组, 那么它放满了之后, 就需要扩容, 它就会产生一些问题.
比如有放满了10个元素的顺序表, 但是总共要放11个元素, 此时就需要进行一个1.5倍的扩容, 这个顺序表就变成15了, 但是只需要放11个元素, 那么就浪费了4个元素的内存空间.
所以在这里ArrayList所带来的第一个问题就是, 扩容之后, 可能会带来空间的浪费.
第二, 当前顺序表 在每次删除一个元素或者插入一个元素的时候(比如删除插入都是第一个元素), 都需要移动元素. 我们会发现它的时间复杂度达到了O(n).
于是我们就会想, 能不能有一种数据结构, 能够随用随取, 插入,删除元素的时候, 不去移动元素?
是有的, 就是链表.
1. 顺序表中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
2. 扩容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
3. 扩容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
ArrayList 不适合使用在频繁的插入和删除的场景. 它适合给定下标位置进行查找 元素。此时可以达到O(1).