RunLoop是什么?
RunLoop是iOS开发中比较重要的知识点,它贯穿程序运行的整个过程。它是线程基础架构的一部分,是一种保障线程循环处理事件而不会退出的机制。同时也负责管理线程需要处理的事件,让线程有事儿时忙碌,没事儿时休眠。
每个线程都有一个关联的RunLoop对象,子线程的RunLoop是需要手动开启的,主线程的RunLoop作为应用启动的一部分由系统自动开启。
iOS提供了NSRunLoop和CFRunLoopRef两个对象,帮助我们配置和管理线程的RunLoop。CFRunLoopRef提供纯C实现并且线程安全的API;NSRunLoop是基于CFRunLoopRef封装的面向对象的API,这个API不是线程安全的。
RunLoop的结构
我们看一下__CFRunLoop的源码:
struct __CFRunLoop {CFRuntimeBase _base;// 获取mode列表的锁pthread_mutex_t _lock; /* locked for accessing mode list */// 唤醒端口__CFPort _wakeUpPort; // used for CFRunLoopWakeUp Boolean _unused;// 重置RunLoop数据volatile _per_run_data *_perRunData; // reset for runs of the run loop//RunLoop所对应的线程pthread_t _pthread;uint32_t _winthread;// 标记为common的mode的集合CFMutableSetRef _commonModes;//commonMode的item集合CFMutableSetRef _commonModeItems;// 当前的modeCFRunLoopModeRef _currentMode;// 存储的是CFRunLoopModeRefCFMutableSetRef _modes;// _block_item链表表头指针struct _block_item *_blocks_head;// _block_item链表表尾指针struct _block_item *_blocks_tail;//运行时间点CFAbsoluteTime _runTime;//睡眠时间点CFAbsoluteTime _sleepTime;CFTypeRef _counterpart;
};
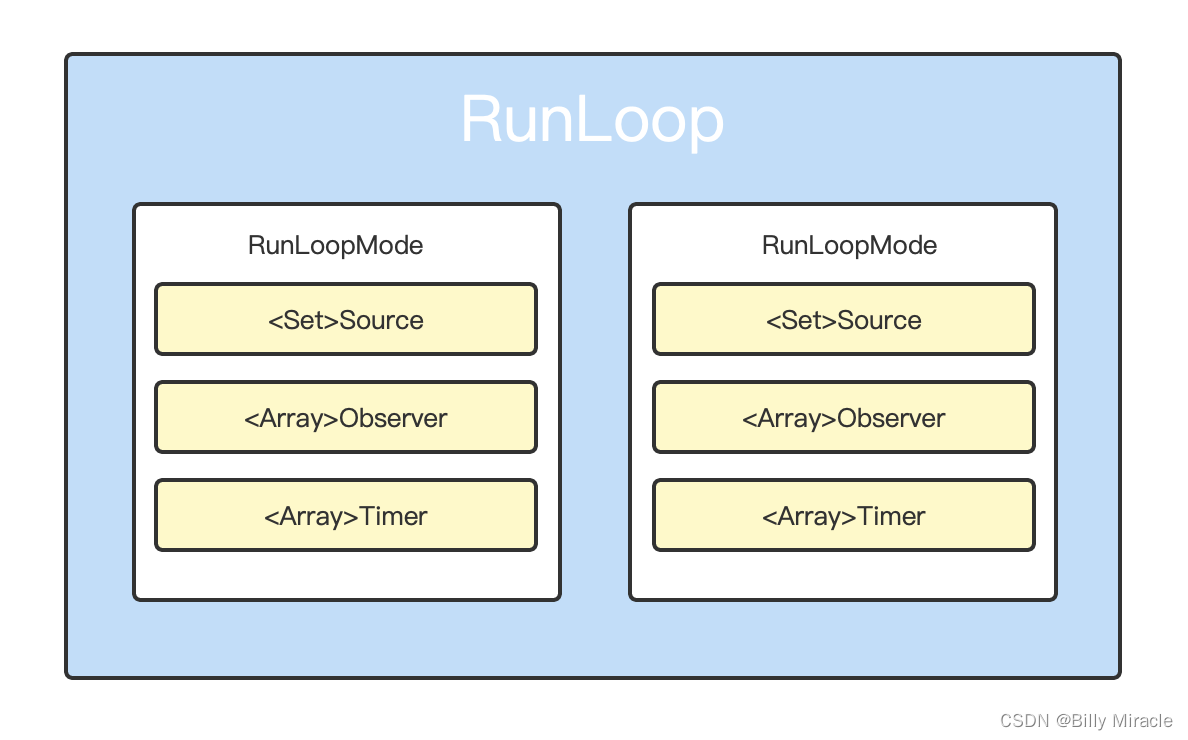
从上面RunLoop的源码可以看出,一个RunLoop对象包含一个线程(_pthread),若干个mode(_modes),若干个commonMode(_commonModes)。
不管是mode还是commonMode都是CFRunLoopMode类型的,只是在处理上有所不同。
RunLoop的相关类
CoreFoundation中与RunLoop有关的5个结构体:
CFRunLoopRef //runLoop对象
CFRunLoopModeRef //runLoop运行的模式
CFRunLoopTimerRef// 基于时间的触发器
CFRunLoopSourceRef//事件源,source0:自定义事件输入源 和 source1 :基于mach内核端口的事件源
CFRunLoopObserverRef //用于监听runLoop运行状态的观察者
CFRunLoopModeRef
// CFRunLoop.c
typedef struct __CFRunLoopMode *CFRunLoopModeRef;struct __CFRunLoopMode {CFRuntimeBase _base;//锁, 必须runloop加锁后才能加锁pthread_mutex_t _lock; /* must have the run loop locked before locking this *///mode的名称CFStringRef _name;//mode是否停止Boolean _stopped;char _padding[3];//sources0事件CFMutableSetRef _sources0;//sources1事件CFMutableSetRef _sources1;//observers事件CFMutableArrayRef _observers;//timers事件CFMutableArrayRef _timers;//字典 key是mach_port_t,value是CFRunLoopSourceRefCFMutableDictionaryRef _portToV1SourceMap;//保存所有需要监听的port,比如_wakeUpPort,_timerPort都保存在这个数组中__CFPortSet _portSet;CFIndex _observerMask;
#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERS//GCD定时器dispatch_source_t _timerSource;//GCD队列dispatch_queue_t _queue;// 当定时器触发时设置为trueBoolean _timerFired; // set to true by the source when a timer has firedBoolean _dispatchTimerArmed;
#endif
#if USE_MK_TIMER_TOOmach_port_t _timerPort;Boolean _mkTimerArmed;
#endif
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWSDWORD _msgQMask;void (*_msgPump)(void);
#endifuint64_t _timerSoftDeadline; /* TSR */uint64_t _timerHardDeadline; /* TSR */
};
// CFRunLoop.h
typedef struct __CFRunLoop * CFRunLoopRef;
从CFRunLoopMode的源码可以看出,一个CFRunLoopMode对象有唯一一个name,若干个sources0事件(一个set),若干个sources1事件(另一个set),若干个timer事件(一个array),若干个observer事件(一个array)和若干port(一个set
),RunLoop总是在某种特定的CFRunLoopMode下运行的,这个特定的mode便是_currentMode。而CFRunloopRef对应结构体的定义知道一个RunLoop对象包含有若干个mode,那么就形成了如下如所示的结构:
关于CFRunLoopMode,苹果提到了5个Model,分别是NSDefaultRunLoopMode、NSConnectionReplyMode、NSModalPanelRunLoopMode、NSEventTrackingRunLoopMode、NSRunLoopCommonModes。
NSDefaultRunLoopMode:默认模式是用于大多数操作的模式。大多数时候使用此模式来启动RunLoop并配置输入源。NSConnectionReplyMode:Cocoa将此模式与NSConnection对象结合使用以监测回应。几乎不需要自己使用此模式。NSModalPanelRunLoopMode:Cocoa使用此模式来识别用于模式面板的事件。NSEventTrackingRunLoopMode:Cocoa使用此模式来限制鼠标拖动loop和其他类型的用户界面跟踪loop期间的传入事件。通常用不到。NSRunLoopCommonModes:是NSDefaultRunLoopMode和NSEventTrackingRunLoopMode集合,在这种模式下RunLoop分别注册了NSDefaultRunLoopMode和UITrackingRunLoopMode。当然也可以通过调用CFRunLoopAddCommonMode()方法将自定义Mode放到kCFRunLoopCommonModes组合。
CFRunLoopSourceRef
// CFRunLoop.h
typedef struct __CFRunLoopSource * CFRunLoopSourceRef;
下面看一下CFRunLoopSource的源码:
// CFRunLoop.c
struct __CFRunLoopSource {CFRuntimeBase _base;//用于标记Signaled状态,source0只有在被标记为Signaled状态,才会被处理uint32_t _bits;pthread_mutex_t _lock;CFIndex _order; /* immutable */CFMutableBagRef _runLoops;//联合体union {CFRunLoopSourceContext version0; /* immutable, except invalidation */CFRunLoopSourceContext1 version1; /* immutable, except invalidation */} _context;
};
根据苹果官方的定义(传送门),CFRunLoopSource是可以放入
RunLoop中的输入源的(source)抽象。输入源通常生成异步事件,例如到达网络端口的消息或用户执行的操作。
source0:是App内部事件,只包含一个函数指针回调,并不能主动触发事件,使用时,你需要先调用CFRunLoopSourceSignal(source),将这个source标记为待处理,然后手动调用CFRunLoopWakeUp(runloop)来唤醒RunLoop,让其处理这个事件。source1:source1包含一个mach_port和一个函数回调指针。source1是基于port的,通过读取某个port上内核消息队列上的消息来决定执行的任务,然后再分发到sources0中处理的。source1只供系统使用,并不对开发者开放。
Source0
CoreFoundation中Source的结构:
typedef struct {CFIndex version;void * info;const void *(*retain)(const void *info);void (*release)(const void *info);CFStringRef (*copyDescription)(const void *info);Boolean (*equal)(const void *info1, const void *info2);CFHashCode (*hash)(const void *info);void (*schedule)(void *info, CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef mode);void (*cancel)(void *info, CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef mode);void (*perform)(void *info);
} CFRunLoopSourceContext;
Source1
Sorce1是基于mach_port的事件,它是内核事件,苹果系统的内核是XNU混合内核,包括了Mach内核和BSD内核,BSD主要提供在Mach之上标准化的API,Mach才是核心,负责线程与进程管理、虚拟内存管理、进程通信与消息传递、任务调度等。
typedef struct {CFIndex version;void * info;const void *(*retain)(const void *info);void (*release)(const void *info);CFStringRef (*copyDescription)(const void *info);Boolean (*equal)(const void *info1, const void *info2);CFHashCode (*hash)(const void *info);
#if (TARGET_OS_MAC && !(TARGET_OS_EMBEDDED || TARGET_OS_IPHONE)) || (TARGET_OS_EMBEDDED || TARGET_OS_IPHONE)mach_port_t (*getPort)(void *info);void * (*perform)(void *msg, CFIndex size, CFAllocatorRef allocator, void *info);
#elsevoid * (*getPort)(void *info);void (*perform)(void *info);
#endif
} CFRunLoopSourceContext1;
基于Source1的事件传递,主要依托于内核接口:
CFRunLoopTimerRef
// CFRunLoop.h
typedef struct CF_BRIDGED_MUTABLE_TYPE(NSTimer) __CFRunLoopTimer * CFRunLoopTimerRef;
这个CFRunLoopTimer是定时器。下面是CFRunLoopTimer的源码:
struct __CFRunLoopTimer {CFRuntimeBase _base;uint16_t _bits;pthread_mutex_t _lock;//timer对应的runloopCFRunLoopRef _runLoop;//timer对应的modeCFMutableSetRef _rlModes;//下一次触发的时间CFAbsoluteTime _nextFireDate;//定时的间隔CFTimeInterval _interval; /* immutable *///定时器允许的误差CFTimeInterval _tolerance; /* mutable */uint64_t _fireTSR; /* TSR units *///优先级CFIndex _order; /* immutable *///任务回调CFRunLoopTimerCallBack _callout; /* immutable *///上下文CFRunLoopTimerContext _context; /* immutable, except invalidation */
};
从上面的代码可以看出,timer是依赖于runloop的,而且有函数指针回调,那么便可以在设定的时间点抛出回调执行任务。同时苹果官方文档(传送门)也有提到CFRunLoopTimer和NSTimer是toll-free bridged的,这就一位着两者之间可以相互转换。在苹果的文档中可以进一步了解桥接的内容。其中的列表显示了CFRunLoopTimer和NSTimer是可以桥接的。(传送门)

CFRunLoopObserverRef
typedef struct __CFRunLoopObserver * CFRunLoopObserverRef;
CFRunLoopObserver是观察者,监测RunLoop的各种状态的变化。下面是CFRunLoopObserver的源码:
struct __CFRunLoopObserver {CFRuntimeBase _base;pthread_mutex_t _lock;//对应的runLoop对象CFRunLoopRef _runLoop;// 当前的观察的runloop个数CFIndex _rlCount;//runloop的状态CFOptionFlags _activities; /* immutable */CFIndex _order; /* immutable *///回调CFRunLoopObserverCallBack _callout; /* immutable *///上下文CFRunLoopObserverContext _context; /* immutable, except invalidation */
};
RunLoop的source事件源用来监测是否有需要执行的任务,而observer则是监测RunLoop本身的各种状态的变化,在合适的时机抛出回调,执行不同类型的任务。RunLoop用于观察的状态如下:
/* Run Loop Observer Activities */
typedef CF_OPTIONS(CFOptionFlags, CFRunLoopActivity) {//即将进入runloopkCFRunLoopEntry = (1UL << 0),//即将处理timer事件kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers = (1UL << 1),//即将处理source事件kCFRunLoopBeforeSources = (1UL << 2),//即将进入休眠kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting = (1UL << 5),//即将唤醒kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting = (1UL << 6),//runloop退出kCFRunLoopExit = (1UL << 7),kCFRunLoopAllActivities = 0x0FFFFFFFU
};
RunLoop底层实现原理
RunLoop启动
RunLoop启动有两个方法可供调用,分别是CFRunLoopRun和CFRunLoopRunInMode。先来看一下这两个方法的源码:
void CFRunLoopRun(void) { /* DOES CALLOUT */int32_t result;do {result = CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);CHECK_FOR_FORK();} while (kCFRunLoopRunStopped != result && kCFRunLoopRunFinished != result);
}SInt32 CFRunLoopRunInMode(CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled) { /* DOES CALLOUT */CHECK_FOR_FORK();return CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), modeName, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled);
}
从上面这两个方法的实现可以看出,CFRunLoopRun方法启动的RunLoop是运行在kCFRunLoopDefaultMode模式下的,即以这种方式启动的RunLoop是在默认模式下运行的。而CFRunLoopRunInMode方法则是需要指定运行的mode。从这里也可以看出来RunLoop虽然有很多的mode,但是RunLoop的运行只能是在一种mode下进行。同时这两个方法都调用了CFRunLoopRunSpecific方法,该方法就是具体启动RunLoop的方法,这个方法的第一个参数就是当前的RunLoop,所以在分析CFRunLoopRunSpecific方法之前,我们需要先了解下是怎么获取到RunLoop的。
获取RunLoop
苹果是不建议我们自己创建RunLoop对象,但是我们可以通过下列方式获取特定线程下的RunLoop对象:
[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop];
[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop];
//CoreFoundation
CFRunLoopGetMain();
CFRunLoopGetCurrent();
它们分别代表着获取当前线程的Runloop对象和获取主线程的RunLoop对象。我们可以查看CFRunLoopRef的关于CFRunLoopGetMain和CFRunLoopGetCurrent的实现:
CFRunLoopGetCurrent
// CFRunloop.c
CFRunLoopRef CFRunLoopGetCurrent(void) {CHECK_FOR_FORK();CFRunLoopRef rl = (CFRunLoopRef)_CFGetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoop);if (rl) return rl;// pthread_self() 获取当前线程return _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_self());
}
该方法内部调用了_CFRunLoopGet0方法,传入的参数是当前线程pthread_self(),由此可见CFRunLoopGetCurrent函数必须要在线程内部调用才能获取到RunLoop对象。
CFRunLoopGetMain
// CFRunloop.c
CFRunLoopRef CFRunLoopGetMain(void) {CHECK_FOR_FORK();static CFRunLoopRef __main = NULL; // no retain needed// pthread_main_thread_np() 获取主线程if (!__main) __main = _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_main_thread_np()); // no CAS neededreturn __main;
}
该方法内部调用了_CFRunLoopGet0方法,传入的参数是主线程pthread_main_thread_np(),由此可见,CFRunLoopGetMain函数不论是在主线程中还是在子线程中都可以获取到主线程的RunLoop。
_CFRunLoopGet0
// 全局`Dictionary`
static CFMutableDictionaryRef __CFRunLoops = NULL;
// 访问`Dictionary`需要的锁
static CFLock_t loopsLock = CFLockInit;// should only be called by Foundation
// t==0 is a synonym for "main thread" that always works
CF_EXPORT CFRunLoopRef _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_t t) {if (pthread_equal(t, kNilPthreadT)) {t = pthread_main_thread_np();}__CFLock(&loopsLock);// `Dictionary`不存在if (!__CFRunLoops) {__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);// 创建局部变量`Dictionary`CFMutableDictionaryRef dict = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, 0, NULL, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);// 【创建主线程的`RunLoop`对象】CFRunLoopRef mainLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(pthread_main_thread_np());// 主线程对象的实际地址,以该地址为`Key`,以`mainLoop`为`Value`存入局部变量`Dictionary`中CFDictionarySetValue(dict, pthreadPointer(pthread_main_thread_np()), mainLoop);//将局部变量`dict`的值 写入全局字典`__CFRunLoops`对应的地址中if (!OSAtomicCompareAndSwapPtrBarrier(NULL, dict, (void * volatile *)&__CFRunLoops)) {CFRelease(dict);}CFRelease(mainLoop);__CFLock(&loopsLock);}// 从全局字典`__CFRunLoops`获取线程对应的`RunLoop`CFRunLoopRef loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);// 如果线程对应的`RunLoop`不存在if (!loop) {// 创建`RunLoop`,取线程对象的实际地址,// 以该地址为`Key`,以`newLoop`为`Value`存入全局变量`__CFRunLoops`中CFRunLoopRef newLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(t);__CFLock(&loopsLock);loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));if (!loop) {CFDictionarySetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t), newLoop);loop = newLoop;}// don't release run loops inside the loopsLock, because CFRunLoopDeallocate may end up taking it// 不要在循环中释放运行循环Lock,因为CFRunLoopDeallocation可能最终会接受它__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);CFRelease(newLoop);}// 是当前线程if (pthread_equal(t, pthread_self())) {// 将`RunLoop`对象以`__CFTSDKeyRunLoop`为`key`,储存到线程的本地(私有)数据空间,// 析构函数为`NULL`_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoop, (void *)loop, NULL);// `CFInternal.h`定了枚举`__CFTSDKeyRunLoop` = 10 与 `__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr` = 11// 如果线程TSD,枚举`__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr` 对应`slot`未存值if (0 == _CFGetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr)) {// 为其存值`PTHREAD_DESTRUCTOR_ITERATIONS-1`,并设置析构函数`__CFFinalizeRunLoop`,// 此举目的是为了:当线程销毁时,实现对`RunLoop`的销毁_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr, (void *)(PTHREAD_DESTRUCTOR_ITERATIONS-1), (void (*)(void *))__CFFinalizeRunLoop);// 如何实现的呢?请继续往下看一探究竟!}}return loop;
}// CFPlatform.c// TSD: Thread Specific Data
// Data structure to hold TSD data, cleanup functions for each
typedef struct __CFTSDTable {uint32_t destructorCount;//`uintptr_t` 存储指针的,无符号整数类型,// 数组个数为`CF_TSD_MAX_SLOTS`uintptr_t data[CF_TSD_MAX_SLOTS];tsdDestructor destructors[CF_TSD_MAX_SLOTS];
} __CFTSDTable;
// For the use of CF and Foundation only
CF_EXPORT void *_CFGetTSD(uint32_t slot) {if (slot > CF_TSD_MAX_SLOTS) {_CFLogSimple(kCFLogLevelError, "Error: TSD slot %d out of range (get)", slot);HALT;}__CFTSDTable *table = __CFTSDGetTable();if (!table) {// Someone is getting TSD during thread destruction. The table is gone, so we can't get any data anymore._CFLogSimple(kCFLogLevelWarning, "Warning: TSD slot %d retrieved but the thread data has already been torn down.", slot);return NULL;}uintptr_t *slots = (uintptr_t *)(table->data);return (void *)slots[slot];
}// For the use of CF and Foundation only
CF_EXPORT void *_CFSetTSD(uint32_t slot, void *newVal, tsdDestructor destructor) {if (slot > CF_TSD_MAX_SLOTS) {_CFLogSimple(kCFLogLevelError, "Error: TSD slot %d out of range (set)", slot);HALT;}__CFTSDTable *table = __CFTSDGetTable();if (!table) {// Someone is setting TSD during thread destruction. The table is gone, so we can't get any data anymore._CFLogSimple(kCFLogLevelWarning, "Warning: TSD slot %d set but the thread data has already been torn down.", slot);return NULL;}void *oldVal = (void *)table->data[slot];table->data[slot] = (uintptr_t)newVal;// 析构函数关联table->destructors[slot] = destructor;return oldVal;
}// Get or initialize a thread local storage. It is created on demand.
static __CFTSDTable *__CFTSDGetTable() {// 通过`CF_TSD_KEY`获取线程对应数据__CFTSDTable *table = (__CFTSDTable *)__CFTSDGetSpecific();// Make sure we're not setting data again after destruction.// 确保销毁后我们不会再次设置数据。if (table == CF_TSD_BAD_PTR) {return NULL;}// Create table on demandif (!table) {// This memory is freed in the finalize function// 此内存在 finalize 函数中释放table = (__CFTSDTable *)calloc(1, sizeof(__CFTSDTable));// Windows and Linux have created the table already, we need to initialize it here for other platforms. On Windows, the cleanup function is called by DllMain when a thread exits. On Linux the destructor is set at init time.///初始化一个键`CF_TSD_KEY`,并关联析构函数/// `CF_TSD_KEY` = 55 ,在不同线程该`Key`值可以共享,但此`Key`对应的值却是不同的。///每个线程都会有自己的`tsd`,它们共用`CF_TSD_KEY`这个`key`/// 线程销毁时苹果系统会调用:/// `_pthread_exit` -> `_pthread_tsd_cleanup` ->///`_pthread_tsd_cleanup_new`->`_pthread_tsd_cleanup_key`///当线程销毁时,会调用关联的析构函数`__CFTSDFinalize`,保证线程对应的私有数据也能销毁///具体可参照函数: _pthread_tsd_cleanup_key/// 函数实现[细节](https://github.com/apple/darwin-libpthread/blob/main/src/pthread_tsd.c)
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINIpthread_key_init_np(CF_TSD_KEY, __CFTSDFinalize);
#endif// 为`CF_TSD_KEY`指定需要存储的数据__CFTSDSetSpecific(table);}return table;
}
//销毁线程对应的TSD
static void __CFTSDFinalize(void *arg) {// Set our TSD so we're called again by pthreads. It will call the destructor PTHREAD_DESTRUCTOR_ITERATIONS times as long as a value is set in the thread specific data. We handle each case below.// 设置我们的 TSD,以便 pthreads 再次调用我们。它将调用析构函数 PTHREAD_DESTRUCTOR_ITERATIONS 次,只要在线程特定数据中设置了值。我们处理以下每个案例。__CFTSDSetSpecific(arg);if (!arg || arg == CF_TSD_BAD_PTR) {// We've already been destroyed. The call above set the bad pointer again. Now we just return.// 我们已经被摧毁了。上面的调用再次设置了错误的指针。现在我们就回来了。return;}__CFTSDTable *table = (__CFTSDTable *)arg;//遍历所有插槽 比如存`RunLoop`的`__CFTSDKeyRunLoop`,也有`__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr`的table->destructorCount++;// On first calls invoke destructor. Later we destroy the data.// Note that invocation of the destructor may cause a value to be set again in the per-thread data slots. The destructor count and destructors are preserved. // This logic is basically the same as what pthreads does. We just skip the 'created' flag.// 在第一次调用时调用析构函数。后来我们销毁了数据。// 请注意,调用析构函数可能会导致在每线程数据槽中再次设置值。将保留析构函数计数和析构函数。 //此逻辑与 pthreads 执行的操作基本相同。我们只是跳过“已创建”标志。for (int32_t i = 0; i < CF_TSD_MAX_SLOTS; i++) {if (table->data[i] && table->destructors[i]) {uintptr_t old = table->data[i];table->data[i] = (uintptr_t)NULL;//遍历到i= 11 =`__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr`时,调用`__CFFinalizeRunLoop`,释放`RunLoop`table->destructors[i]((void *)(old));}}if (table->destructorCount == PTHREAD_DESTRUCTOR_ITERATIONS - 1) { // On PTHREAD_DESTRUCTOR_ITERATIONS-1 call, destroy our datafree(table);// Now if the destructor is called again we will take the shortcut at the beginning of this function.__CFTSDSetSpecific(CF_TSD_BAD_PTR);return;}
}
小结:
RunLoop与线程之间是一一对应的,每条线程都有唯一一个与之对应的RunLoop对象- 当线程需要获取对应的
RunLoop时,才会创建RunLoop对象 - 线程销毁的时候会销毁
RunLoop对象 - 主线程的
RunLoop对象是由系统自动创建好的,在应用程序启动的时候会自动完成启动,而子线程中的RunLoop对象需要我们手动获取并启动。
CFRunLoopRunSpecific
知道了怎么获取RunLoop,接下来继续看CFRunLoopRunSpecific方法。
SInt32 CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled) { /* DOES CALLOUT */CHECK_FOR_FORK();if (__CFRunLoopIsDeallocating(rl)) return kCFRunLoopRunFinished;__CFRunLoopLock(rl);// 根据modeName找到当前的modeCFRunLoopModeRef currentMode = __CFRunLoopFindMode(rl, modeName, false);// 如果没有找到mode或者找到的mode中没有注册事件则退出,不进入循环if (NULL == currentMode || __CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(rl, currentMode, rl->_currentMode)) {Boolean did = false;if (currentMode)__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(currentMode);__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);return did ? kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource : kCFRunLoopRunFinished;}volatile _per_run_data *previousPerRun = __CFRunLoopPushPerRunData(rl);// 取上一次运行的modeCFRunLoopModeRef previousMode = rl->_currentMode;rl->_currentMode = currentMode;int32_t result = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;// 通知observer即将进入RunLoopif (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopEntry )__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopEntry);result = __CFRunLoopRun(rl, currentMode, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled, previousMode);// 通知observer已经退出RunLoopif (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopExit )__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopExit);__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(currentMode);__CFRunLoopPopPerRunData(rl, previousPerRun);rl->_currentMode = previousMode;__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);return result;
}
这个方法需要传入四个参数:
rl:当前运行的RunLoop对象。modeName:指定RunLoop对象的mode的名称。seconds:RunLoop的超时时间returnAfterSourceHandled:是否在处理完事件之后返回。
从上面的代码我们可以获取到如下几点信息:
- RunLoop运行必须要指定一个
mode,否则不会运行RunLoop。 - 如果指定的
mode没有注册时间任务,RunLoop不会运行。 - 通知
observer进入RunLoop,调用__CFRunLoopRun方法处理任务,通知observer退出RunLoop。
__CFRunLoopRun
/* rl, rlm are locked on entrance and exit */
/*** 运行run loop** rl 运行的RunLoop对象* rlm 运行的mode* seconds RunLoop超时时间* stopAfterHandle true: RunLoop处理完事件就退出 false:一直运行直到超时或者被手动终止* previousMode 上一次运行的mode** @return 返回4种状态*/
static int32_t __CFRunLoopRun(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopModeRef rlm, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean stopAfterHandle, CFRunLoopModeRef previousMode) {// 获取系统启动后的CPU运行时间,用于控制超时时间uint64_t startTSR = mach_absolute_time();// 如果RunLoop或者mode是stop状态,则直接return,不进入循环if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(rl)) {__CFRunLoopUnsetStopped(rl);return kCFRunLoopRunStopped;} else if (rlm->_stopped) {rlm->_stopped = false;return kCFRunLoopRunStopped;}// mach端口,在内核中,消息在端口之间传递。 初始为0mach_port_name_t dispatchPort = MACH_PORT_NULL;// 判断是否为主线程Boolean libdispatchQSafe = pthread_main_np() && ((HANDLE_DISPATCH_ON_BASE_INVOCATION_ONLY && NULL == previousMode) || (!HANDLE_DISPATCH_ON_BASE_INVOCATION_ONLY && 0 == _CFGetTSD(__CFTSDKeyIsInGCDMainQ)));// 如果在主线程 && RunLoop是主线程的RunLoop && 该mode是commonMode,则给mach端口赋值为主线程收发消息的端口if (libdispatchQSafe && (CFRunLoopGetMain() == rl) && CFSetContainsValue(rl->_commonModes, rlm->_name)) dispatchPort = _dispatch_get_main_queue_port_4CF();#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERSmach_port_name_t modeQueuePort = MACH_PORT_NULL;if (rlm->_queue) {// mode赋值为dispatch端口_dispatch_runloop_root_queue_perform_4CFmodeQueuePort = _dispatch_runloop_root_queue_get_port_4CF(rlm->_queue);if (!modeQueuePort) {CRASH("Unable to get port for run loop mode queue (%d)", -1);}}
#endif// GCD管理的定时器,用于实现runloop超时机制dispatch_source_t timeout_timer = NULL;struct __timeout_context *timeout_context = (struct __timeout_context *)malloc(sizeof(*timeout_context));// 立即超时if (seconds <= 0.0) { // instant timeoutseconds = 0.0;timeout_context->termTSR = 0ULL;} else if (seconds <= TIMER_INTERVAL_LIMIT) {// seconds为超时时间,超时时执行__CFRunLoopTimeout函数dispatch_queue_t queue = pthread_main_np() ? __CFDispatchQueueGetGenericMatchingMain() : __CFDispatchQueueGetGenericBackground();timeout_timer = dispatch_source_create(DISPATCH_SOURCE_TYPE_TIMER, 0, 0, queue);dispatch_retain(timeout_timer);timeout_context->ds = timeout_timer;timeout_context->rl = (CFRunLoopRef)CFRetain(rl);timeout_context->termTSR = startTSR + __CFTimeIntervalToTSR(seconds);dispatch_set_context(timeout_timer, timeout_context); // source gets ownership of contextdispatch_source_set_event_handler_f(timeout_timer, __CFRunLoopTimeout);dispatch_source_set_cancel_handler_f(timeout_timer, __CFRunLoopTimeoutCancel);uint64_t ns_at = (uint64_t)((__CFTSRToTimeInterval(startTSR) + seconds) * 1000000000ULL);dispatch_source_set_timer(timeout_timer, dispatch_time(1, ns_at), DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER, 1000ULL);dispatch_resume(timeout_timer);} else { // infinite timeout 永不超时seconds = 9999999999.0;timeout_context->termTSR = UINT64_MAX;}// 标志位默认为trueBoolean didDispatchPortLastTime = true;// 记录最后runloop状态,用于returnint32_t retVal = 0;do {
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINIvoucher_mach_msg_state_t voucherState = VOUCHER_MACH_MSG_STATE_UNCHANGED;voucher_t voucherCopy = NULL;
#endif// 初始化一个存放内核消息的缓冲池uint8_t msg_buffer[3 * 1024];
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINImach_msg_header_t *msg = NULL;mach_port_t livePort = MACH_PORT_NULL;
#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWSHANDLE livePort = NULL;Boolean windowsMessageReceived = false;
#endif// 取所有需要监听的port__CFPortSet waitSet = rlm->_portSet;// 设置RunLoop为可以被唤醒状态__CFRunLoopUnsetIgnoreWakeUps(rl);// 2.通知observer,即将触发timer回调,处理timer事件if (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);// 3.通知observer,即将触发Source0回调if (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeSources) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);// 执行加入当前runloop的block__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);//4.处理source0事件//有事件处理返回true,没有事件返回falseBoolean sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSources0(rl, rlm, stopAfterHandle);if (sourceHandledThisLoop) {//执行加入当前runloop的block__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);}// 如果没有Sources0事件处理 并且 没有超时,poll为false// 如果有Sources0事件处理 或者 超时,poll都为trueBoolean poll = sourceHandledThisLoop || (0ULL == timeout_context->termTSR);// 第一次do..whil循环不会走该分支,因为didDispatchPortLastTime初始化是trueif (MACH_PORT_NULL != dispatchPort && !didDispatchPortLastTime) {
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINI// 从缓冲区读取消息msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer;// 5.接收dispatchPort端口的消息,(接收source1事件)if (__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(dispatchPort, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, 0, &voucherState, NULL)) {// 如果接收到了消息的话,前往第9步开始处理msggoto handle_msg;}
#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWSif (__CFRunLoopWaitForMultipleObjects(NULL, &dispatchPort, 0, 0, &livePort, NULL)) {goto handle_msg;}
#endif}didDispatchPortLastTime = false;//6.通知观察者RunLoop即将进入休眠if (!poll && (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting)) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);// 设置RunLoop为休眠状态__CFRunLoopSetSleeping(rl);// do not do any user callouts after this point (after notifying of sleeping)// Must push the local-to-this-activation ports in on every loop// iteration, as this mode could be run re-entrantly and we don't// want these ports to get serviced.__CFPortSetInsert(dispatchPort, waitSet);__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);CFAbsoluteTime sleepStart = poll ? 0.0 : CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent();#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINI
#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERS//这里有个内循环,用于接收等待端口的消息//进入此循环后,线程进入休眠,直到收到新消息才跳出该循环,继续执行RunLoopdo {if (kCFUseCollectableAllocator) {// objc_clear_stack(0);// <rdar://problem/16393959>memset(msg_buffer, 0, sizeof(msg_buffer));}msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer;//7.接收waitSet端口的消息__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY, &voucherState, &voucherCopy);// 收到消息之后,livePort的值为msg->msgh_local_port,if (modeQueuePort != MACH_PORT_NULL && livePort == modeQueuePort) {// Drain the internal queue. If one of the callout blocks sets the timerFired flag, break out and service the timer.while (_dispatch_runloop_root_queue_perform_4CF(rlm->_queue));if (rlm->_timerFired) {// Leave livePort as the queue port, and service timers belowrlm->_timerFired = false;break;} else {if (msg && msg != (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer) free(msg);}} else {// Go ahead and leave the inner loop.break;}} while (1);
#elseif (kCFUseCollectableAllocator) {// objc_clear_stack(0);// <rdar://problem/16393959>memset(msg_buffer, 0, sizeof(msg_buffer));}msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer;__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY, &voucherState, &voucherCopy);
#endif#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS// Here, use the app-supplied message queue mask. They will set this if they are interested in having this run loop receive windows messages.__CFRunLoopWaitForMultipleObjects(waitSet, NULL, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY, rlm->_msgQMask, &livePort, &windowsMessageReceived);
#endif__CFRunLoopLock(rl);__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm);rl->_sleepTime += (poll ? 0.0 : (CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent() - sleepStart));// Must remove the local-to-this-activation ports in on every loop// iteration, as this mode could be run re-entrantly and we don't// want these ports to get serviced. Also, we don't want them left// in there if this function returns.__CFPortSetRemove(dispatchPort, waitSet);__CFRunLoopSetIgnoreWakeUps(rl);// user callouts now OK again// 取消runloop的休眠状态__CFRunLoopUnsetSleeping(rl);// 8.通知观察者runloop被唤醒if (!poll && (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting)) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);// 9.处理收到的消息handle_msg:;__CFRunLoopSetIgnoreWakeUps(rl);#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWSif (windowsMessageReceived) {// These Win32 APIs cause a callout, so make sure we're unlocked first and relocked after__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);if (rlm->_msgPump) {rlm->_msgPump();} else {MSG msg;if (PeekMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE | PM_NOYIELD)) {TranslateMessage(&msg);DispatchMessage(&msg);}}__CFRunLoopLock(rl);__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm);sourceHandledThisLoop = true;// To prevent starvation of sources other than the message queue, we check again to see if any other sources need to be serviced// Use 0 for the mask so windows messages are ignored this time. Also use 0 for the timeout, because we're just checking to see if the things are signalled right now -- we will wait on them again later.// NOTE: Ignore the dispatch source (it's not in the wait set anymore) and also don't run the observers here since we are polling.__CFRunLoopSetSleeping(rl);__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);__CFRunLoopWaitForMultipleObjects(waitSet, NULL, 0, 0, &livePort, NULL);__CFRunLoopLock(rl);__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm); __CFRunLoopUnsetSleeping(rl);// If we have a new live port then it will be handled below as normal}#endifif (MACH_PORT_NULL == livePort) {CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_NOTHING();// handle nothing// 通过CFRunloopWake唤醒} else if (livePort == rl->_wakeUpPort) {CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_WAKEUP();// 什么都不干,跳回2重新循环// do nothing on Mac OS
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS// Always reset the wake up port, or risk spinning foreverResetEvent(rl->_wakeUpPort);
#endif}
#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERSelse if (modeQueuePort != MACH_PORT_NULL && livePort == modeQueuePort) {CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_TIMER();if (!__CFRunLoopDoTimers(rl, rlm, mach_absolute_time())) {// Re-arm the next timer, because we apparently fired early__CFArmNextTimerInMode(rlm, rl);}}
#endif
#if USE_MK_TIMER_TOO// 如果是定时器事件else if (rlm->_timerPort != MACH_PORT_NULL && livePort == rlm->_timerPort) {CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_TIMER();// On Windows, we have observed an issue where the timer port is set before the time which we requested it to be set. For example, we set the fire time to be TSR 167646765860, but it is actually observed firing at TSR 167646764145, which is 1715 ticks early. The result is that, when __CFRunLoopDoTimers checks to see if any of the run loop timers should be firing, it appears to be 'too early' for the next timer, and no timers are handled.// In this case, the timer port has been automatically reset (since it was returned from MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx), and if we do not re-arm it, then no timers will ever be serviced again unless something adjusts the timer list (e.g. adding or removing timers). The fix for the issue is to reset the timer here if CFRunLoopDoTimers did not handle a timer itself. 9308754//9.1处理timer事件if (!__CFRunLoopDoTimers(rl, rlm, mach_absolute_time())) {// Re-arm the next timer__CFArmNextTimerInMode(rlm, rl);}}
#endif// 如果是dispatch到main queue的blockelse if (livePort == dispatchPort) {CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_DISPATCH();__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyIsInGCDMainQ, (void *)6, NULL);
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWSvoid *msg = 0;
#endif// 9.2执行block__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(msg);_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyIsInGCDMainQ, (void *)0, NULL);__CFRunLoopLock(rl);__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm);sourceHandledThisLoop = true;didDispatchPortLastTime = true;} else {CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_SOURCE();// If we received a voucher from this mach_msg, then put a copy of the new voucher into TSD. CFMachPortBoost will look in the TSD for the voucher. By using the value in the TSD we tie the CFMachPortBoost to this received mach_msg explicitly without a chance for anything in between the two pieces of code to set the voucher again.voucher_t previousVoucher = _CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyMachMessageHasVoucher, (void *)voucherCopy, os_release);// Despite the name, this works for windows handles as wellCFRunLoopSourceRef rls = __CFRunLoopModeFindSourceForMachPort(rl, rlm, livePort);// 有source1事件待处理if (rls) {
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINImach_msg_header_t *reply = NULL;//9.2 处理source1事件sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(rl, rlm, rls, msg, msg->msgh_size, &reply) || sourceHandledThisLoop;if (NULL != reply) {(void)mach_msg(reply, MACH_SEND_MSG, reply->msgh_size, 0, MACH_PORT_NULL, 0, MACH_PORT_NULL);CFAllocatorDeallocate(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, reply);}
#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWSsourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(rl, rlm, rls) || sourceHandledThisLoop;
#endif}// Restore the previous voucher_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyMachMessageHasVoucher, previousVoucher, os_release);}
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINIif (msg && msg != (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer) free(msg);
#endif__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);if (sourceHandledThisLoop && stopAfterHandle) {// 进入RunLoop时传入的参数,处理完事件就返回retVal = kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource;} else if (timeout_context->termTSR < mach_absolute_time()) {// RunLoop超时retVal = kCFRunLoopRunTimedOut;} else if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(rl)) {// RunLoop被手动终止__CFRunLoopUnsetStopped(rl);retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;} else if (rlm->_stopped) {// mode被终止rlm->_stopped = false;retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;} else if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(rl, rlm, previousMode)) {// mode中没有要处理的事件retVal = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;}#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINIvoucher_mach_msg_revert(voucherState);os_release(voucherCopy);
#endif// 除了上面这几种情况,都继续循环} while (0 == retVal);if (timeout_timer) {dispatch_source_cancel(timeout_timer);dispatch_release(timeout_timer);} else {free(timeout_context);}return retVal;
}
__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort
在上面的第7步调用了__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort函数,这个函数在RunLoop中起到了至关重要的作用,下面看一下代码:
/*** 接收指定内核端口的消息** port 接收消息的端口* buffer 消息缓冲区* buffer_size 消息缓冲区大小* livePort 暂且理解为活动的端口,接收消息成功时候值为msg->msgh_local_port,超时时为MACH_PORT_NULL* timeout 超时时间,单位是ms,如果超时,则RunLoop进入休眠状态** @return 接收消息成功时返回true 其他情况返回false*/
static Boolean __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(mach_port_name_t port, mach_msg_header_t **buffer, size_t buffer_size, mach_port_t *livePort, mach_msg_timeout_t timeout, voucher_mach_msg_state_t *voucherState, voucher_t *voucherCopy) {Boolean originalBuffer = true;kern_return_t ret = KERN_SUCCESS;for (;;) { /* In that sleep of death what nightmares may come ... */mach_msg_header_t *msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)*buffer;msg->msgh_bits = 0;//消息头的标志位msg->msgh_local_port = port;//源(发出的消息)或者目标(接收的消息)msg->msgh_remote_port = MACH_PORT_NULL;//目标(发出的消息)或者源(接收的消息)msg->msgh_size = buffer_size;//消息缓冲区大小,单位是字节msg->msgh_id = 0;//唯一idif (TIMEOUT_INFINITY == timeout) { CFRUNLOOP_SLEEP(); } else { CFRUNLOOP_POLL(); }//通过mach_msg发送或者接收的消息都是指针,//如果直接发送或者接收消息体,会频繁进行内存复制,损耗性能//所以XNU使用了单一内核的方式来解决该问题,所有内核组件都共享同一个地址空间,因此传递消息时候只需要传递消息的指针ret = mach_msg(msg, MACH_RCV_MSG|(voucherState ? MACH_RCV_VOUCHER : 0)|MACH_RCV_LARGE|((TIMEOUT_INFINITY != timeout) ? MACH_RCV_TIMEOUT : 0)|MACH_RCV_TRAILER_TYPE(MACH_MSG_TRAILER_FORMAT_0)|MACH_RCV_TRAILER_ELEMENTS(MACH_RCV_TRAILER_AV), 0, msg->msgh_size, port, timeout, MACH_PORT_NULL);// Take care of all voucher-related work right after mach_msg.// If we don't release the previous voucher we're going to leak it.voucher_mach_msg_revert(*voucherState);// Someone will be responsible for calling voucher_mach_msg_revert. This call makes the received voucher the current one.*voucherState = voucher_mach_msg_adopt(msg);if (voucherCopy) {if (*voucherState != VOUCHER_MACH_MSG_STATE_UNCHANGED) {// Caller requested a copy of the voucher at this point. By doing this right next to mach_msg we make sure that no voucher has been set in between the return of mach_msg and the use of the voucher copy.// CFMachPortBoost uses the voucher to drop importance explicitly. However, we want to make sure we only drop importance for a new voucher (not unchanged), so we only set the TSD when the voucher is not state_unchanged.*voucherCopy = voucher_copy();} else {*voucherCopy = NULL;}}CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP(ret);// 接收/发送消息成功,给livePort赋值为msgh_local_portif (MACH_MSG_SUCCESS == ret) {*livePort = msg ? msg->msgh_local_port : MACH_PORT_NULL;return true;}// 超出timeout时间没有收到消息,返回MACH_RCV_TIMED_OUT// 此时释放缓冲区,把livePort赋值为MACH_PORT_NULLif (MACH_RCV_TIMED_OUT == ret) {if (!originalBuffer) free(msg);*buffer = NULL;*livePort = MACH_PORT_NULL;return false;}// 如果接收缓冲区太小,则将过大的消息放在队列中,并且出错返回MACH_RCV_TOO_LARGE,// 这种情况下,只返回消息头,调用者可以分配更多的内存if (MACH_RCV_TOO_LARGE != ret) break;// 此处给buffer分配更大内存buffer_size = round_msg(msg->msgh_size + MAX_TRAILER_SIZE);if (originalBuffer) *buffer = NULL;originalBuffer = false;*buffer = realloc(*buffer, buffer_size);}HALT;return false;
}
小结
RunLoop实际很简单,它是一个对象,它和线程是一一对应的,每个线程都有一个对应的RunLoop对象,主线程的RunLoop会在程序启动时自动创建,子线程需要手动获取来创建。
RunLoop运行的核心是一个do..while..循环,遍历所有需要处理的事件,如果有事件处理就让线程工作,没有事件处理则让线程休眠,同时等待事件到来。