给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
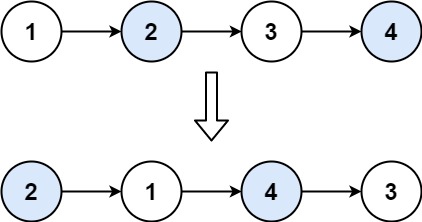
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1] 输出:[1]
解:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {ListNode dumyhead = new ListNode(-1, head); // 设置一个虚拟头结点ListNode cur = dumyhead;ListNode temp; // 临时节点,保存两个节点后面的节点ListNode firstnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第一个节点ListNode secondnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第二个节点while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {temp = cur.next.next.next;firstnode = cur.next;secondnode = cur.next.next;cur.next = secondnode; // 步骤一secondnode.next = firstnode; // 步骤二firstnode.next = temp; // 步骤三cur = firstnode; // cur移动,准备下一轮交换}return dumyhead.next; }
}进而可根据上述过程写出递归的版本:
// 递归版本
class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {// base case 退出提交if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;// 获取当前节点的下一个节点ListNode next = head.next;// 进行递归ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next);// 这里进行交换next.next = head;head.next = newNode;return next;}
}