ChibiOS简介2/5
- 1. 源由
- 2. ChibiOS基础知识2/5
- 2.4 Chapter 4 - ChibiOS General Architecture
- 2.4.1 The Big Picture(总体框图)
- 2.4.2 Embedded Components(嵌入式组件)
- 2.4.3 Application Model(应用模型)
- 2.4.4 Code(代码)
- 2.4.4.1 Application(应用代码)
- 2.4.4.2 Startup Code(启动代码)
- 2.4.4.3 ChibiOS/RT
- 2.4.4.4 ChibiOS/HAL
- 2.5 Chapter 5 - Introduction to the RT Kernel
- 2.5.1 Designed Concepts(设计概念)
- 2.5.2 Coding Conventions(编码约定)
- 2.5.2.1 Code Style
- 2.5.2.2 Naming Conventions
- 2.5.3 Architecture
- 2.5.4 System States
- 2.5.5 API Classes
- 2.5.6 Thread Working Areas
- 2.5.7 Thread States
- 2.6 Chapter 6 - RT System Layer
- 3. 参考资料
1. 源由
作为后续研读Ardupilot的ChibiOS的垫脚石,先了解下ChibiOS系统。
Ardupilot ChibiOS项目: https://github.com/ArduPilot/ChibiOS
Artery(AT32) porting项目: //Artery官网没有相关porting动作,不过开源github有相关项目。
- https://github.com/dron0gus/artery
- https://github.com/dron0gus/ChibiOS
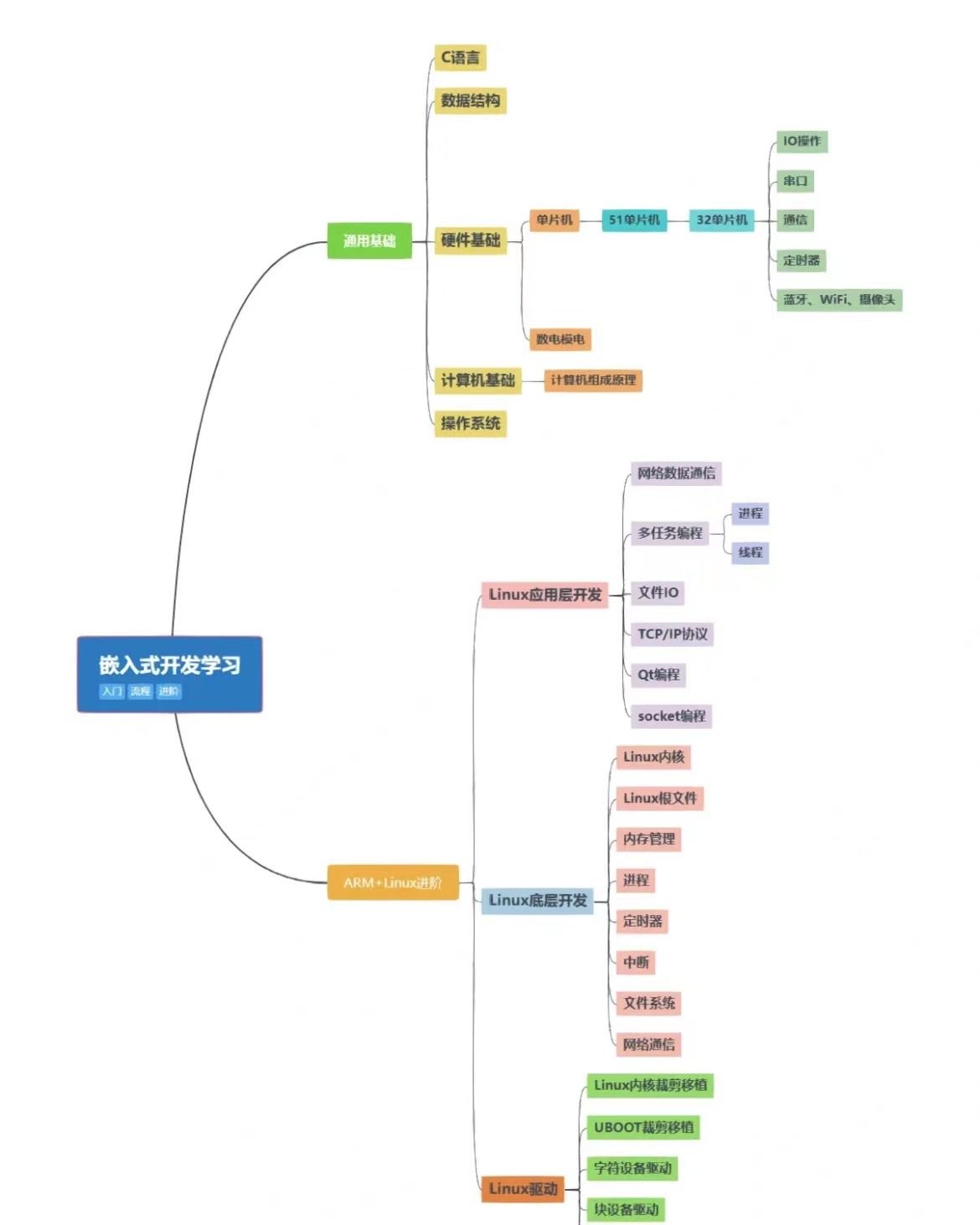
2. ChibiOS基础知识2/5
2.4 Chapter 4 - ChibiOS General Architecture
2.4.1 The Big Picture(总体框图)
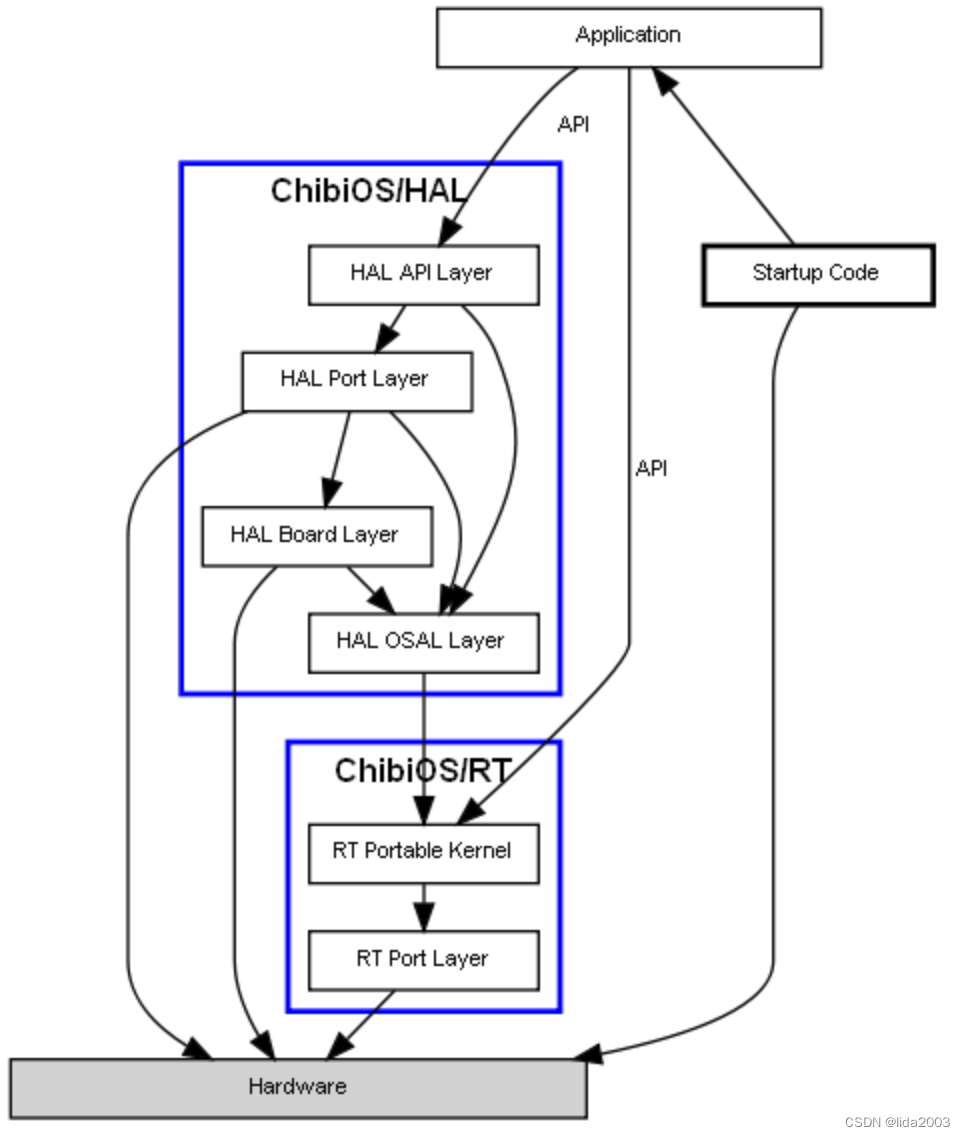
2.4.2 Embedded Components(嵌入式组件)
- RT, the RTOS scheduler. RT is a very high performance RTOS with a complete set of features and small footprint. It is what we cover in this book.
- NIL, an alternate RTOS. NIL is compatible with RT but its internal architecture is completely different, It is designed for minimal code size.
- OSLIB, an RTOS extension library. It sits on top of RT or NIL and adds an incredible set of higher level services.
- HAL, the Hardware Abstraction Layer enclosing abstract drivers for most common peripherals.
- SB, an extension for RT or NIL offering isolated sandboxes where to run “unsafe” code. The code in the sandbox is unable to crash the whole system.
2.4.3 Application Model(应用模型)
Single Application with Multiple Threads. This means:
- The runtime environment is trusted, the application does not need to defend from itself. Non-trusted code can be handled using the SB subsystem.
- Multiple threads are part of the application and share the address space. There is no protection between thread and thread and no virtualization.
- Application and Operating System are linked together into a single memory image, a single program.
- There is no concept of “loading an application”.
2.4.4 Code(代码)
2.4.4.1 Application(应用代码)
It is the user code, ChibiOS provides a simple template of main() function, everything else starts from there.
2.4.4.2 Startup Code(启动代码)
In ChibiOS the startup code is provided with the OS and is located under ./os/common/startup for the various supported architectures and compilers, scatter files and everything else is required for system startup are also provided.
- Core initialization.
- Stacks initialization.
- C Runtime initialization.
- Calling the main() function.
2.4.4.3 ChibiOS/RT
The RT scheduler kernel which is divided in two internal layers:
- RT Portable Kernel. It is the part of the RTOS kernel which is architecture and compiler independent. The RT code is located under
./os/rt. - RT Port Layer. It is the part of the RTOS kernel specific for one architecture and one or more compilers. The RT port code is located under
./os/common/ports.
2.4.4.4 ChibiOS/HAL
HAL is the acronym for Hardware Abstraction Layer, a set of device drivers for the peripherals most commonly found in micro-controllers. The HAL is split in several layers:
- HAL API Layer. This layer contains a series of portable device drivers. The HAL portable code is located under
./os/hal. - HAL Port Layer. This is the device driver implementations for a specific micro-controller or family of micro-controllers. The HAL port code is located under
./os/hal/ports. - HAL Board Layer. This module contains all details of a specific board mounting the micro-controller. Board level initialization is performed in this module. The HAL boards code is located under
./os/hal/boards. - HAL OSAL Layer. This is the Operating System Abstraction Layer. The HAL has to use some RTOS services in order to implement its functionality. The access to the RTOS services is done through this abstraction layer in order to not lock the HAL to a specific RTOS. The HAL OSAL code is located under
./os/hal/osal.
2.5 Chapter 5 - Introduction to the RT Kernel
2.5.1 Designed Concepts(设计概念)
- 【fast】It must be fast, execution efficiency is the main requirement.
- 【size】The code must be optimized for size unless this conflicts with point 1.
- 【RTOS】The kernel must offer a complete set of RTOS features unless this conflicts with requirement 1.
- 【safe】It must be intrinsically safe. Primitives with dangerous corner cases are simply not allowed. The rule is to guide the user to choose a safe approach if possible.
- 【robust】The code base must be elegant, consistent, readable and rules-driven.
- 【handy】This may be subjective but working with the code must be a pleasant experience.
2.5.2 Coding Conventions(编码约定)
这是一个好习惯,是一种研发工程师的素质体现。
2.5.2.1 Code Style
The K&R style (Kernighan & Ritchie Style), this is a small subset:
- Tabs are forbidden.
- Non UTF-8 characters are forbidden.
- C++ style comments are forbidden.
- Indentation is 2 spaces.
- Multiple empty lines are forbidden.
- Insertion of empty lines is regulated.
- The code is written in “code blocks”, blocks are composed by:
An empty line.
A comment describing the block. The comment can be on a single or multiple lines.
One or more code lines.
Comments on the same line of statements are allowed but not encouraged.
- Files are all derived from templates.
- No spaces at the end of lines.
2.5.2.2 Naming Conventions
API Functions
The name of a function meant to be an API is always composed as follow:
ch<subsystem><verb>[<extra>][Timeout][<I|S|X>]()
Where:
- ch. Identifies an ChibiOS/RT API.
- <subsystem> Identifies the subsystem of the kernel where this function belongs. This part also identifies the object type on which the function operates. For example “Sem” indicates that the function operates on a
semaphore_tobject which is passed by pointer as first parameter. - <verb> The action performed by this function.
- <extra> The extra part of the name or other context information.
- [Timeout]. If the function is able to stop the execution of the invoking thread and has a time-out capability.
- <I|S|X>. Optional function class attributes. This attribute, if present, strictly defines the system state compatible with the API function. The “API Classes” section will describe the relationship between function classes and the system state.
Variables, Fields and Structures
Names must be fully written in lower case, underscore is used as separator.
Types
Simple or structured type follow the same convention, the symbol must be written all in lower case, underscore is used as separator and an “_t” is added at the end.
examples:
thread_t, semaphore_t.
Macros
Macros are written fully in upper case. A “CH_” prefix is encouraged but not enforced. A common prefix for grouped macros is mandatory.
examples:
CH_IRQ_EPILOGUE(), THD_FUNCTION().
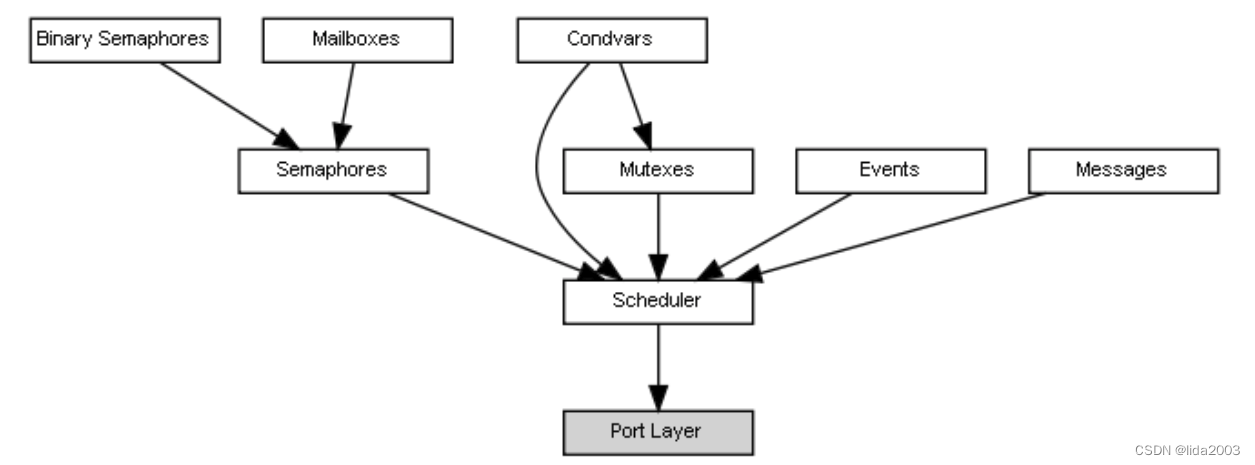
2.5.3 Architecture
All kernel services are build around the central scheduler module. The scheduler exports a low level API that allows to build virtually any kind of synchronization primitive, other modules are built using the scheduler services and have no interactions.
2.5.4 System States
One important concept in ChibiOS/RT are the so called System States, the global behavior of the system is regulated by an high level state machine:
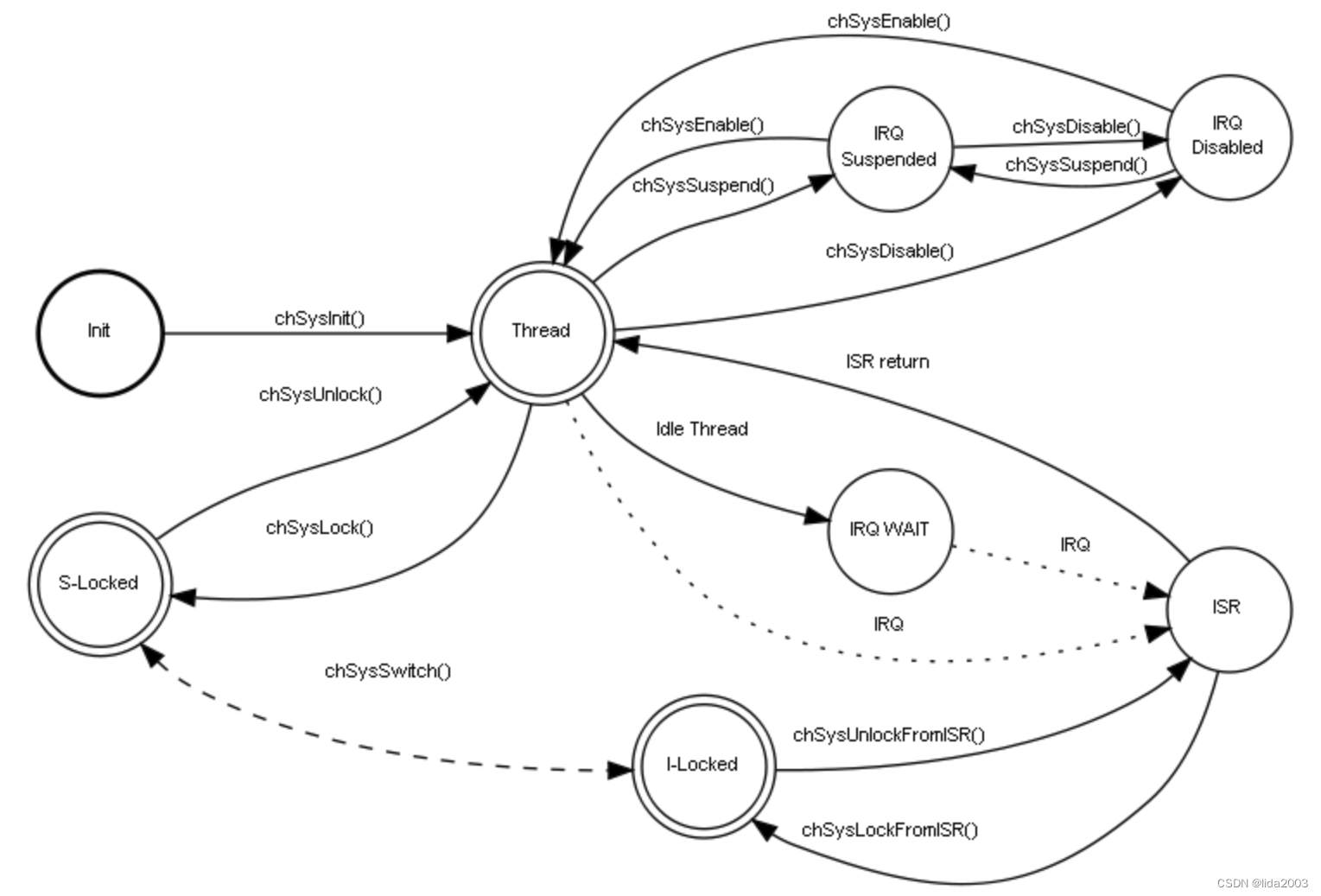
The states have a strong meaning and must be understood in order to utilize the RTOS correctly:
- Init. This state represents the execution of code before the RTOS is initialized using chSysInit(). The only kind of OS functions that can be called in the “Init” state are object initializers.
- Thread. This state represents the RTOS executing one of its threads. Normal APIs can be called in this state.
- Suspended. In this state all the OS-IRQs are disabled but Fast-IRQs are still served.
- Disabled. In this state all interrupt sources are disabled.
- S-Locked. This is the state of critical sections in thread context.
- I-Locked. This is the state of critical sections in ISR context.
- IRQ WAIT. When the system has no threads ready for execution it enters a state where it just waits for interrupts. This state can be mapped on a low power state of the host architecture.
- ISR. This state represents the execution of ISR code.
There are some additional states not directly related to the RTOS activity but still important from the system point of view:
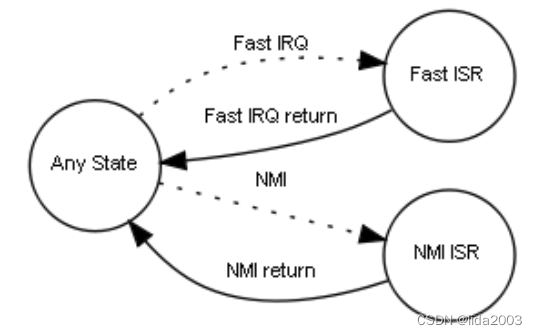
- Fast ISR. This state represents the execution of ISR code of a fast IRQ source.
- NMI. This state represents the execution of ISR code of a non-maskable interrupt source.
2.5.5 API Classes
- Normal Functions, Normal functions have no suffix and can only be invoked from the “Thread” state unless the documentation of the function states further restrictions or defines a special context.
- S-Class Functions, Functions with suffix “S” can only be invoked from the “S-Locked” state, this means that this class of functions are meant to be called in a thread-level critical section. This class of functions can reschedule internally if required.
- I-Class Functions, Functions with suffix “I” can be called either in the “I-Locked” state and in the “S-Locked” state. Both ISR-level and thread-level critical sections are compatible with this class. Note that this class of functions never reschedule internally, if called from “S-Locked” state an explicit reschedule must be performed.
- X-Class Functions, This class of functions has no special requirements and can be called from any context where API functions can be called: “Thread”, “S-Locked” and “I-Locked”.
- Special Functions, Special functions have no specific suffix but have special execution requirements specified in their documentation.
- Object Initializers, This kind of functions are meant for objects initialization and can be used in any context, even before the kernel is initialized. Initialized objects themselves are “passive” until referred by some other function. Note that most kernel objects have also static initializers, macros that allocate objects and initialize them using a static variable initialization.
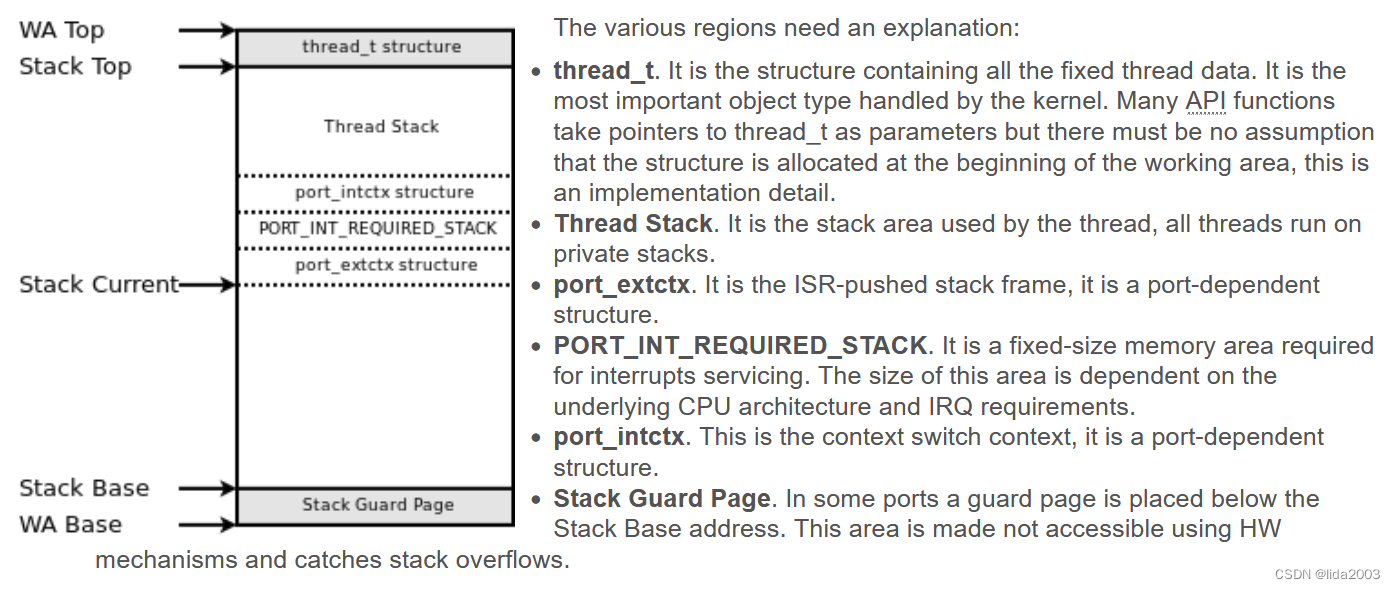
2.5.6 Thread Working Areas
In ChibiOS/RT threads occupy a single, contiguous region of memory called Thread Working Area. Working areas can be statically or dynamically allocated and are always aligned using the same alignment required for stack pointers.
2.5.7 Thread States
During their life cycle threads go through several states, the state machine is regulated by the API and events in the kernel:
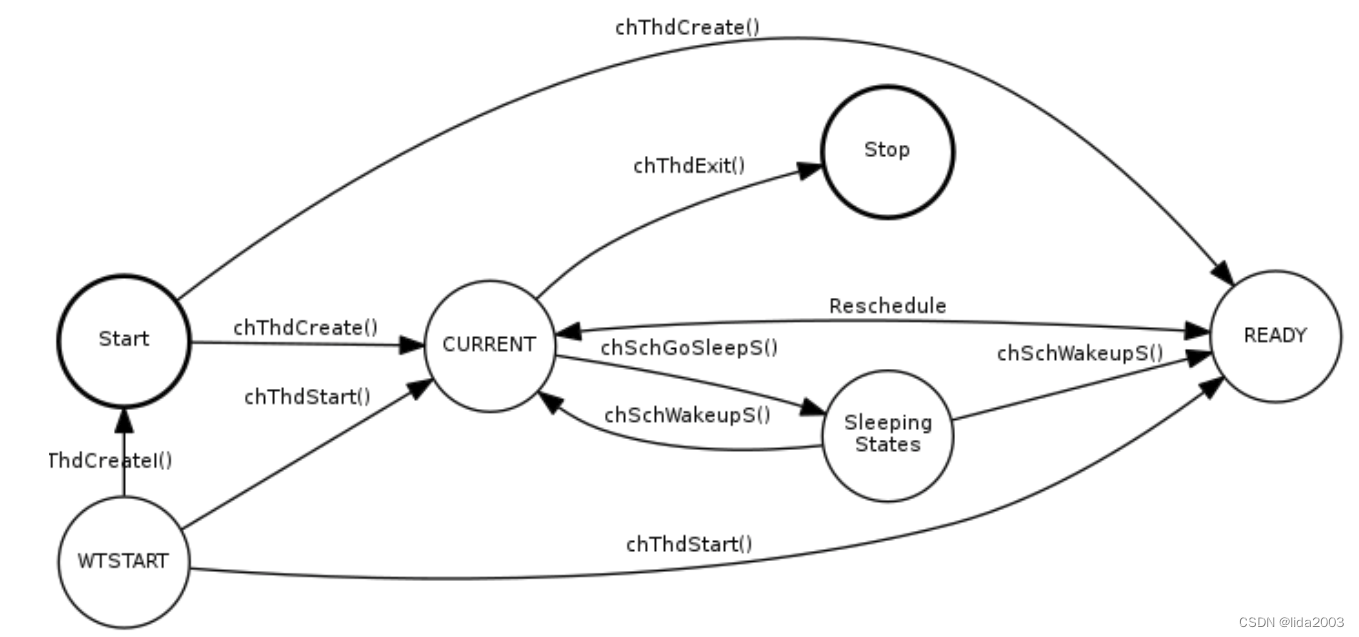 Note that in ChibiOS/RT there are multiple sleeping states that are indicated on the diagram as a single state. Each synchronization object has its own sleeping states, this is done in order to understand on which kind of object the thread is sleeping on.
Note that in ChibiOS/RT there are multiple sleeping states that are indicated on the diagram as a single state. Each synchronization object has its own sleeping states, this is done in order to understand on which kind of object the thread is sleeping on.
2.6 Chapter 6 - RT System Layer
The System Layer is the most fundamental part of the RT kernel, it lies just above the port layers and provides a series of important services:
- Initialization.
- Abnormal Termination.
- Interrupts Handling.
- Critical Sections.
- Power Management.
- Realtime Counter.
This service handles the system initialization: chSysInit() //Starts the RT kernel. This function must be called once from the main() function.
3. 参考资料
【1】ArduPilot开源飞控系统之简单介绍
【2】Ardupilot开源飞控之ChibiOS简介
【3】 ChibiOS官方文档