1、使用shared_ptr
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>class Item {
private:std::string name;float price;
public:Item(const std::string& n, float p = 0) :name(n), price(p) {}std::string getName() const {return name;}void setName(const std::string& n) {name = n;}float getPrice() const {return price;}float setPrice(float p) {price = p;return p;}
};template <typename Coll>
void printItems(const std::string& msg, const Coll& coll) {std::cout << msg << std::endl;for (const auto& elem: coll) {std::cout << " " << elem->getName() << ": " << elem->getPrice() << std::endl;}
}int main() {using namespace std;typedef shared_ptr<Item> ItemPtr;set<ItemPtr> allItems;deque<ItemPtr> bestsellers;bestsellers = {ItemPtr(new Item("Kong Yize", 20.10)),ItemPtr(new Item("A Midsummer Night's Dream", 14.99)),ItemPtr(new Item("The Maltese Falcon", 9.88))};allItems = {ItemPtr(new Item("Water", 0.44)),ItemPtr(new Item("Pizza", 2.22))};allItems.insert(bestsellers.begin(), bestsellers.end());printItems("bestsellers: ", bestsellers);printItems("all: ", allItems);cout << endl;for_each(bestsellers.begin(), bestsellers.end(),[](shared_ptr<Item>& elem) {elem->setPrice(elem->getPrice() * 2);});bestsellers[1] = *(find_if(allItems.begin(), allItems.end(),[](shared_ptr<Item> elem) {return elem->getName() == "Pizza";}));bestsellers[0]->setPrice(44.88);printItems("bestsellers: ", bestsellers);printItems("all: ", allItems);return 0;
}面的set使用find的时候,会找出拥有相等value的元素,现在却比较的是内部的指针,
allItems.find(ItemPtr(new Item("Pizza", 2.22))) //can't be successful,所以这里必须使用find_if算法。
2、advance
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{list<int> coll;// insert elements from 1 to 9for (int i=1; i<=9; ++i) {coll.push_back(i);}list<int>::iterator pos = coll.begin();// print actual elementcout << *pos << endl;// step three elements forwardadvance (pos, 3);// print actual elementcout << *pos << endl;// step one element backwardadvance (pos, -1);// print actual elementcout << *pos << endl;
}
输出:
1
4
33、iter_swap()
交换迭代器的值,迭代器类型不必相同,所指的两个值必须可以相互赋值。
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include "print.hpp"
using namespace std;int main()
{list<int> coll;// insert elements from 1 to 9for (int i=1; i<=9; ++i) {coll.push_back(i);}PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);// swap first and second valueiter_swap (coll.begin(), next(coll.begin()));PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);// swap first and last valueiter_swap (coll.begin(), prev(coll.end()));PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 2#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{// create list with elements from 1 to 9vector<int> coll = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };// find position of element with value 5vector<int>::const_iterator pos;pos = find (coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),5);// print value to which iterator pos referscout << "pos: " << *pos << endl;// convert iterator to reverse iterator rposvector<int>::const_reverse_iterator rpos(pos);// print value to which reverse iterator rpos referscout << "rpos: " << *rpos << endl;
}
输出:
pos: 5
rpos: 4
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;void print (int elem)
{cout << elem << ' ';
}int main()
{// create deque with elements from 1 to 9deque<int> coll = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };// find position of element with value 2deque<int>::const_iterator pos1;pos1 = find (coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), // range2); // value// find position of element with value 7deque<int>::const_iterator pos2;pos2 = find (coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), // range7); // value// print all elements in range [pos1,pos2)for_each (pos1, pos2, // rangeprint); // operationcout << endl;// convert iterators to reverse iteratorsdeque<int>::const_reverse_iterator rpos1(pos1);deque<int>::const_reverse_iterator rpos2(pos2);// print all elements in range [pos1,pos2) in reverse orderfor_each (rpos2, rpos1, // rangeprint); // operationcout << endl;
}
输出:
2 3 4 5 6
6 5 4 3 24、使用base()将reverse迭代器转回正常
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{// create list with elements from 1 to 9list<int> coll = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };// find position of element with value 5list<int>::const_iterator pos;pos = find (coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), // range5); // value// print value of the elementcout << "pos: " << *pos << endl;// convert iterator to reverse iteratorlist<int>::const_reverse_iterator rpos(pos);// print value of the element to which the reverse iterator referscout << "rpos: " << *rpos << endl;// convert reverse iterator back to normal iteratorlist<int>::const_iterator rrpos;rrpos = rpos.base();// print value of the element to which the normal iterator referscout << "rrpos: " << *rrpos << endl;
}
输出:
pos: 5
rpos: 4
rrpos: 55、back_inserter
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include "print.hpp"using namespace std;int main() {vector<int> coll;back_insert_iterator<vector<int>> iter(coll);*iter = 1;*iter++;*iter = 2;iter++;*iter = 3;PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);// convenient wayback_inserter(coll) = 44;back_inserter(coll) = 55;PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);// use back inserter to append all elements again// - reserve enough memory to avoid reallocationcoll.reserve(2*coll.size());copy(coll.begin(), coll.end(), back_inserter(coll));PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3
1 2 3 44 55
1 2 3 44 55 1 2 3 44 556、front_inserter
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include "print.hpp"using namespace std;int main() {list<int> coll;front_insert_iterator<list<int>> iter(coll);*iter = 1;iter++;*iter = 2;iter++;*iter = 3;PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);front_inserter(coll) = 44;front_inserter(coll) = 55;PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);copy(coll.begin(), coll.end(), front_inserter(coll));PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);return 0;
}
输出:
3 2 1
55 44 3 2 1
1 2 3 44 55 55 44 3 2 17、inserter
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include "print.hpp"using namespace std;int main() {set<int> coll;insert_iterator<set<int>> iter(coll, coll.begin());*iter = 1;iter++;*iter = 2;iter++;*iter = 3;PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll,"set: ");inserter(coll, coll.end()) = 44;inserter(coll, coll.end()) = 55;PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "set: ");list<int> coll2;copy(coll.begin(), coll.end(), inserter(coll2, coll2.begin()));PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll2, "list: ");copy(coll.begin(), coll.end(), inserter(coll2, ++coll2.begin()));PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll2, "list: ");return 0;
}
输出:
set: 1 2 3
set: 1 2 3 44 55
list: 1 2 3 44 55
list: 1 1 2 3 44 55 2 3 44 558、ostream迭代器
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>using namespace std;int main() {ostream_iterator<int> intWriter(cout, "\n");*intWriter = 43;intWriter++;*intWriter = 77;intWriter++;*intWriter = -5;vector<int> coll = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};copy(coll.begin(), coll.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout));cout << endl;copy(coll.begin(), coll.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " < "));cout << endl;return 0;
}
输出:
43
77
-5
123456789
1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 6 < 7 < 8 < 9 <9、istream迭代器
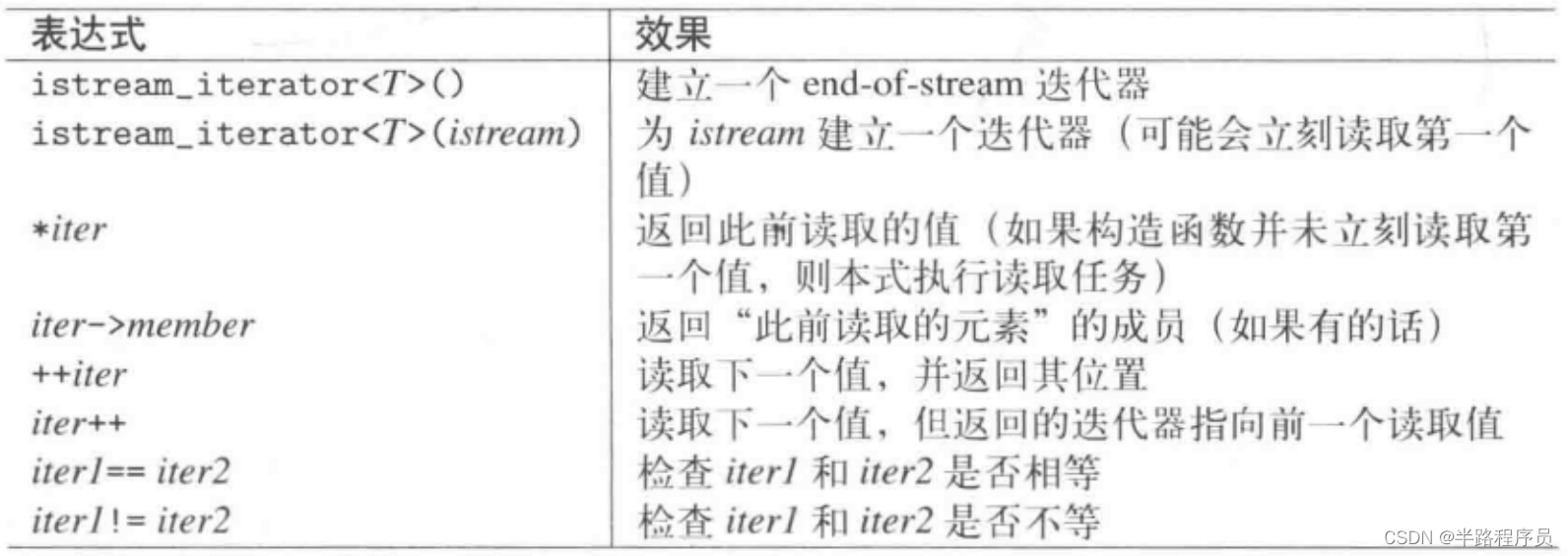
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int main() {istream_iterator<string> cinPos(cin);ostream_iterator<string> coutPos(cout, " ");while (cinPos != istream_iterator<string>()) {advance(cinPos, 2);if (cinPos != istream_iterator<string>()) {*coutPos++ = *cinPos++;}}cout << endl;return 0;
}
输入:
No one objects if you are doing
a good programming job for
someone whom you respect
输出:
objects are good for you
10、move迭代器
std::vector<string> v2(make_move_iterator(s.begin()),make_move_iterator(s.end()));