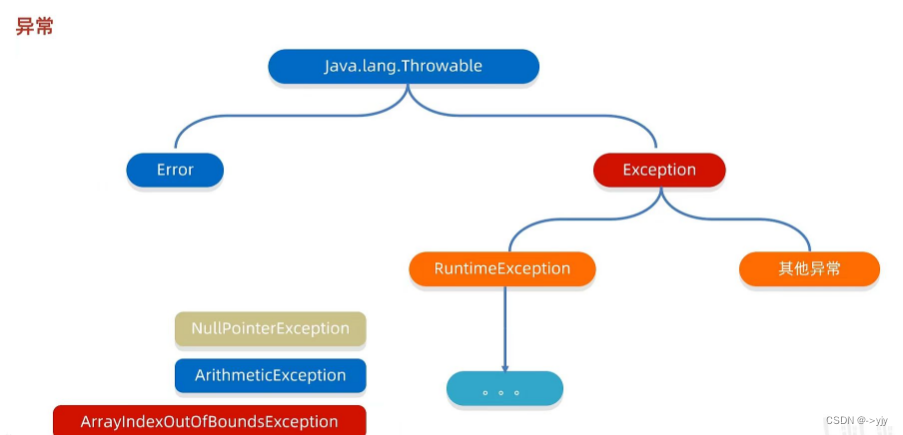
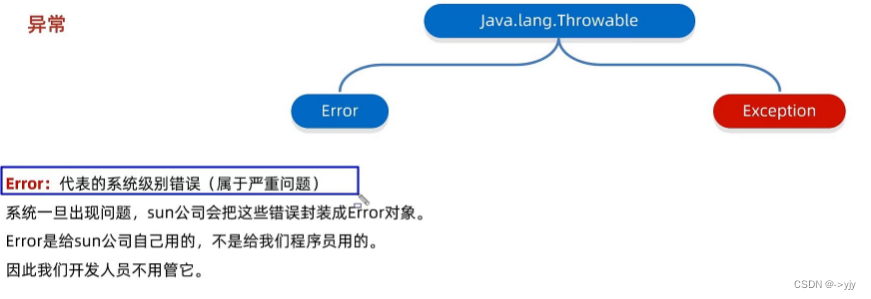
异常
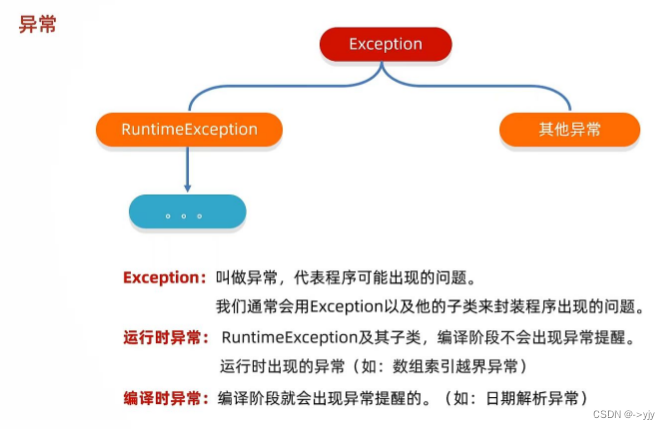
异常:异常就是代表程序出现的问题
误区:不是让我们以后不出现异常,而是程序出现了异常之后,该如何处理
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {//编译时异常(在编译阶段 必须手动出路 否则代码报错)String time ="2030年1月1日";SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");Date date = sdf.parse(time);System.out.println(date);/** 运行时异常(在编译阶段不需要处理 是代码运行时出现的异常)* int[] arr ={1,2,3,4,5};* * System.out.println(arr[10]);* * */}
}Java为什么要这样分?


为什么不把全部异常归到运行时异常呢?因为编译异常是为了 提醒 程序员检查本地信息



public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {Student[] arr =new Student[3];String name = arr[0].getName();System.out.println(name);}//NullPointerException
}
import java.text.ParseException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {//1.创建学生对象Student s1 =new Student();s1.setAge(23);//就知道50赋值失败//选择1:自己悄悄处理//选择2:打印在控制台上}
}改一下标准Javabean中的这个构造方法
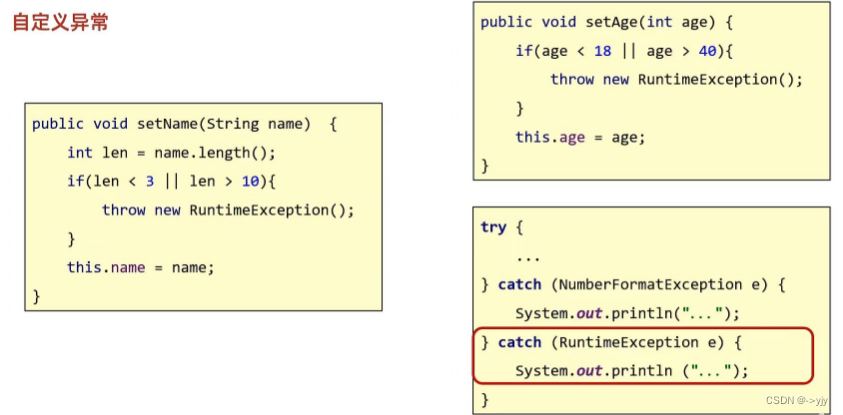
public int getAge() {if(age<18||age>40){throw new RuntimeException();}else{}return age;}


public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("1");System.out.println(2/0);//算数异常 程序停止 后面都不允许System.out.println("2");System.out.println("3");}
}

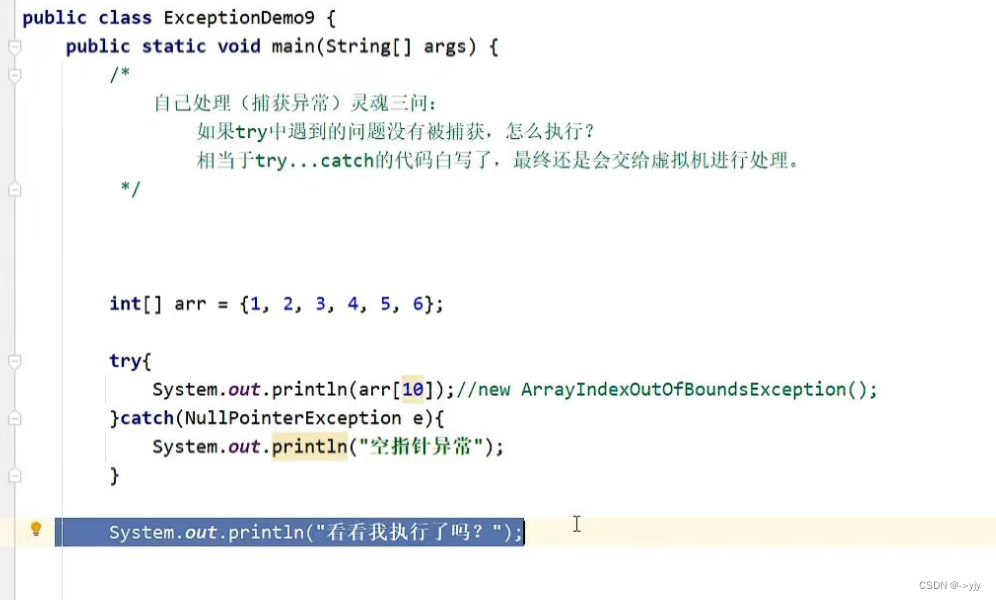
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5,6};try {//可能出现异常的代码System.out.println(arr[10]);}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){//如果出现了 这个异常 我该如何处理System.out.println("索引越界了");}System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");}
} 
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5,6};try {//可能出现异常的代码System.out.println(arr[0]);}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("索引越界了");}System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");}//如果try中没有问题://会把try里面的代码全部执行完毕 不会执行catch//里面的代码 注意:只有出现了异常才会执行catch里面的代码}
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5,6};try {//可能出现异常的代码System.out.println(arr[10]);System.out.println(2/0);String s =null;System.out.println(s.equals(s.equals("abc")));}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("索引越界了");}catch (ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("除数不能为0");}catch (NullPointerException e){System.out.println("空指针异常");}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("Exception");}System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");//JDK7//用|可以一起用//catch (ArithmeticException| NullPointerException e)//在JDK7之后 我们可以在catch中同时捕获多种异常,中间使用|进行隔开//表示如果出现了A异常或者B异常的话 才去同一种解决处理方案}//如果try中遇到多个问题怎么办?//会写多个catch与之对应//注意:如果我们捕获多个异常 这些异常中如果存在父子关系的话,那么父类一定要写在下面}

public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5,6};
//
// try {
// System.out.println(arr[10]);
// } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// //String message = e.getMessage();
// //System.out.println(message);//Index 10 out of bounds for length 6
//
// // String str = e.toString();
// //System.out.println(str);//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 10 out of bounds for length 6
//
//
// e.printStackTrace();//仅仅是将红色字体打印在控制台 不会结束虚拟机 下面的代码也打印出来了
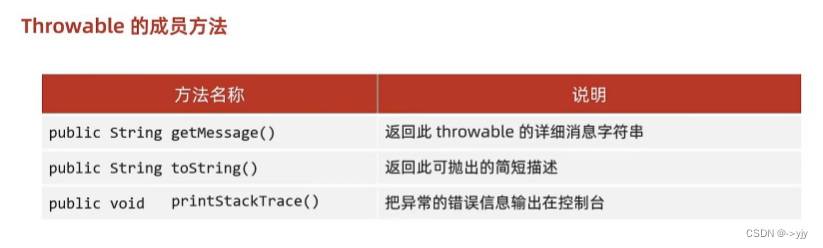
// //包含了getMessage 和toString// }//ctrl+alt+t//System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");//正常输出语句 黑色字体System.out.println(123);//错误的输出语句(而是用来打印错误信息的 红色字体System.err.println(123);//了解即可 多线程知识}
} 

public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//定义一个方法求数组的最大值int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5};int max = 0;try {max = getMax(arr);} catch (NullPointerException e) {System.out.println("空指针异常");e.printStackTrace();}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("索引越界异常");}System.out.println(max);}public static int getMax(int[] arr)/* throws NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException*/{if(arr==null){//手动创建一个异常对象 并把这个异常交给方法的调用者处理//此时方法就会结束,下面的代码不会再执行了throw new NullPointerException();}if(arr.length==0){//手动创建一个异常对象 并把这个异常交给方法的调用者处理//此时方法就会结束,下面的代码不会再执行了throw new NullPointerException();}System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");int max=arr[0];for(int i=1;i< arr.length;i++){if(arr[i]>max){max=arr[i];}}return max;}
}

public class GirlFriend {private String name;private int age;public GirlFriend() {}public GirlFriend(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}/*** 获取* @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 设置* @param name*/public void setName(String name) {int len = name.length();if(len<3||len>10){throw new RuntimeException();}this.name = name;}/*** 获取* @return age*/public int getAge() {return age;}/*** 设置* @param age*/public void setAge(int age) {if(age<18||age>40){throw new RuntimeException();}this.age = age;}public String toString() {return "GirlFriend{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";}
}
import java.util.Scanner;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//抛出和捕获://抛出:告诉调用者出错了//捕获:不让程序停止Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);GirlFriend gf =new GirlFriend();while (true) {try {System.out.println("请输入您心仪的女朋友的名字");String name = sc.nextLine();gf.setName(name);System.out.println("请输入您心仪女朋友的年龄");String ageStr = sc.nextLine();int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);gf.setAge(age);break;//所有数据都正确 就跳出} catch (NumberFormatException e) {System.out.println("年龄的格式有误,请输入数字");} catch (RuntimeException e) {System.out.println("姓名的长度或者年龄的范围有问题");}}System.out.println(gf);}
}

import java.util.Scanner;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//抛出和捕获://抛出:告诉调用者出错了//捕获:不让程序停止Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);GirlFriend gf = new GirlFriend();while (true) {try {System.out.println("请输入您心仪的女朋友的名字");String name = sc.nextLine();gf.setName(name);System.out.println("请输入您心仪女朋友的年龄");String ageStr = sc.nextLine();int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);gf.setAge(age);break;//所有数据都正确 就跳出} catch (NumberFormatException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NameFormatException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (AgeOutOfBoundsException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(gf);}
}public class GirlFriend {private String name;private int age;public GirlFriend() {}public GirlFriend(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}/*** 获取* @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 设置* @param name*/public void setName(String name) {int len = name.length();if(len<3||len>10){throw new NameFormatException(name+"格式有误,长度应该为:3-10");}this.name = name;}/*** 获取* @return age*/public int getAge() {return age;}/*** 设置* @param age*/public void setAge(int age) {if(age<18||age>40){throw new AgeOutOfBoundsException(age+"超出了范围");}this.age = age;}public String toString() {return "GirlFriend{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";}
}
public class NameFormatException extends RuntimeException{//技巧://NameFormat:当前异常的名字 表示姓名格式化问题//Exception:表示当前类是一个异常类//运行时:RuntimeException 核心:由于参数错误导致的问题//编译时:Exception 核心:提醒程序员检查本地信息public NameFormatException() {}public NameFormatException(String message) {super(message);}
}
public class AgeOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException{public AgeOutOfBoundsException() {}public AgeOutOfBoundsException(String message) {super(message);}
}
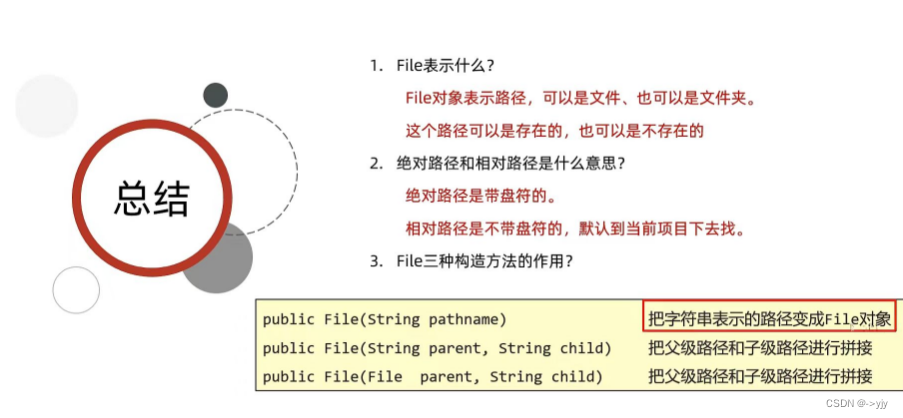
File



import java.io.File;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.根据字符串表示的路径,变成File对象String str ="C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\IdeaProjects\\basic-code\\day02-code\\src\\Day18\\1.jpg";File f1 = new File(str);System.out.println(f1);//C:\Users\Lenovo\IdeaProjects\basic-code\day02-code\src\Day18\1.jpg//2.父路径 - 父级路径//C:\Users\Lenovo\IdeaProjects\basic-code\day02-code\src\Day18//子级路径 -//1.jpgString parent = "C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\IdeaProjects\\basic-code\\day02-code\\src\\Day18";String child = "1.jpg";File f2 = new File(parent,child);System.out.println(f2);//C:\Users\Lenovo\IdeaProjects\basic-code\day02-code\src\Day18\1.jpg//操作系统 - 转义字符//window:\//Linux:/File parent2 = new File("C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\IdeaProjects\\basic-code\\day02-code\\src\\Day18");String child2 = "1.jpg";File f4 = new File(parent2,child2);System.out.println(f4);}
}


import java.io.File;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.对一个文件的路径进行判断File f1 = new File("C:\\arr\\1.txt");System.out.println(f1.isDirectory());//falseSystem.out.println(f1.isFile());//trueSystem.out.println(f1.exists());//true//2.对一个文件夹的路径进行判断File f2 = new File("C:\\arr\\2");System.out.println(f2.isDirectory());//trueSystem.out.println(f2.isFile());//falseSystem.out.println(f2.exists());//true//3.对一个不存在的路径进行判断File f3 = new File("C:\\arr\\3");System.out.println(f3.isDirectory());//falseSystem.out.println(f3.isFile());//falseSystem.out.println(f3.exists());//false}
}

import java.io.File;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// length 返回文件的大小(字节数量)//细节:这个方法只能获取文件的大小 单位是字节//如果单位我们要是M,G,可以不断的除以1024//这个方法无法获取文件夹的大小//如果我们要获取一个文件夹的大小,需要把这个文件夹里面的所有//文件都累加在一起File f1 =new File("C:\\arr\\1.txt");long len = f1.length();System.out.println(len);//0File f2 =new File("C:\\arr\\2");System.out.println(f2.length());//0System.out.println("-------------------------------------");File f3 =new File("basic-code\\1.txt");String path = f3.getAbsolutePath();System.out.println(path);//C:\Users\Lenovo\IdeaProjects\basic-code\basic-code\1.txtSystem.out.println("-------------------------------------");File f4 =new File("basic-code\\1.txt");String path2 = f4.getPath();System.out.println(path2);//basic-code\1.txtSystem.out.println("-------------------------------------");File f5 = new File("basic-code\\1.txt");String name1 = f5.getName();System.out.println(name1);//1.txt//1 :文件名 txt:后缀名,扩展名File f6 = new File("C:\\arr\\1.txt");long time = f6.lastModified();System.out.println(time);//1702364504068//如何把时间的毫秒值变成字符串表示的时间呢?}
}

注意: delete方法默认只能删除文件和空文件夹,delete方法直接删除不走回收站
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// //1.createNewFile 创建一个新的空的文件
// //如果当前路径表示的文件是不存在 的则成功
// //否则失败
// //如果父级路径不存在 方法会有异常
// //createNewFile方法创建的一定是文件
// //如果路径中不包含后缀名,则创建没有后缀的文件
// File f1 =new File("C:\\arr\\2.txt");
// boolean b = f1.createNewFile();
// System.out.println(b);//2.mkdir make Directory. 文件夹(目录)File f2=new File("C:\\arr\\3");boolean b = f2.mkdir();System.out.println(b);//windows路径唯一 如果路径已经存在 则创建失败//mkdirs:创建多级文件夹File f3=new File("C:\\arr\\4\\5");boolean c = f3.mkdirs();System.out.println(c);}
}import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// File f1 = new File("C:\\arr\\1.txt");
// boolean b = f1.delete();
// System.out.println(b);//不走回收站 直接没了File f1 = new File("C:\\arr\\4");boolean b = f1.delete();System.out.println(b);//falseFile f2 = new File("C:\\arr\\3");boolean c = f2.delete();System.out.println(c);//false//删除的是文件 则直接删除 不走回收站//如果删除的是空文件夹 则直接删除 不走回收站//如果删除的是有内容的文件夹 则删除失败}
}

import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建File对象File f = new File("C:\\arr");//2.listFiles方法//作用:获取arr文件夹里面的所有内容 把所有的内容放到数组中返回File[] files = f.listFiles();for (File file : files) {//file:依次表示文件或者文件夹System.out.println(file);}}
}

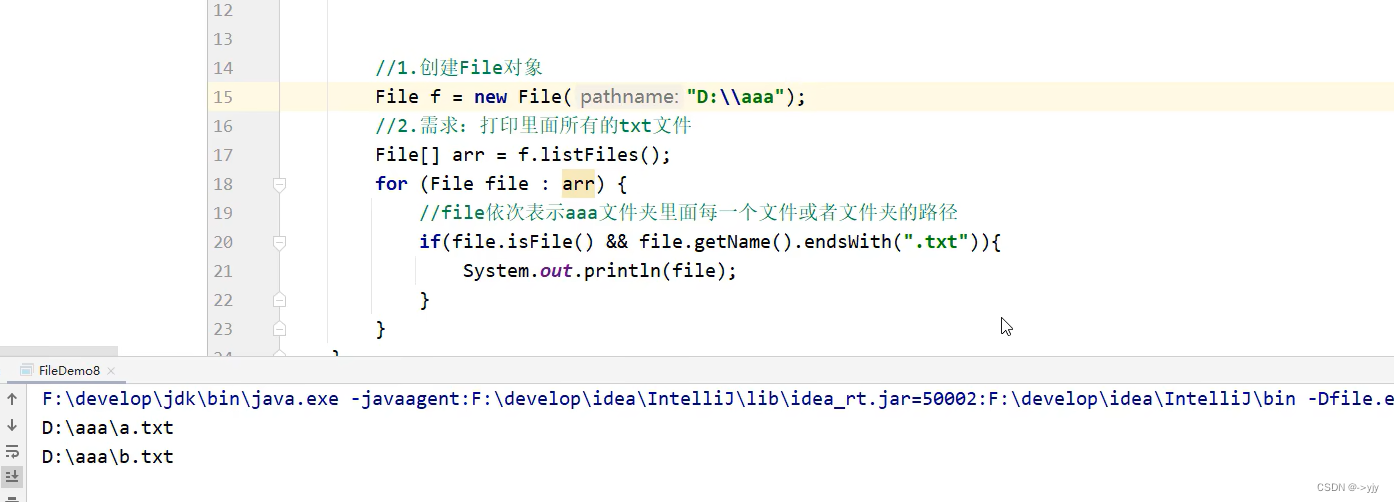

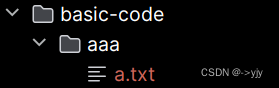
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//需求:在当前模块下的aaa文件夹中创建一个a.txt文件//1.创建a.txt的父级路径File file = new File("basic-code\\aaa");//2.创建父级路径//如果aaa是存在的 那么创建失败的//如果aaa是不存在的,那么此时创建成功file.mkdirs();//3.拼接父级路径和子级路径File src = new File(file,"a.txt");boolean b = src.createNewFile();if(b){System.out.println("创建成功");}else{System.out.println("创建失败");}}
}
//需求:定义一个方法找某一个文件夹中 是否有以avi结尾的电影 //(暂时不需要考虑子文件夹)

import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//需求:找到电脑中所有的所有avi结尾的电影.(考虑子文件夹)//套路://第一步:进入文件夹//2.遍历数组//3.判断//4.判断findAVI();}public static void findAVI(){//获取本地所有的盘符File[] arr = File.listRoots();for (File file : arr) {findAVI(file);}}public static void findAVI(File src){//进入文件夹srcFile[] files =src.listFiles();
// if(files == null){
// System.out.println(src);//C:\$Recycle.Bin\S-1-5-18
// }if(files!=null){for (File file : files) {//3.判断,如果是文件就可以执行题目的业务逻辑if(file.isFile()){String name = file.getName();if(name.endsWith(".avi")){System.out.println(file);}}else{//4.判断,如果是文件夹就可以递归//细节:再次调用本方法的时候,参数一定要是src的次一级路径findAVI(file);}}//2.遍历数组,依次得到src里面每一个文件或者文件夹}}
}
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//删除一个多级文件夹//如果我们要删除一个有内容的文件夹//1.先删除文件夹里面所有的内容//2.再删除自己File file = new File("D:\\aaa\\src");delete(file);}/** 作用:删除src文件夹* 参数:要删除的文件夹* * */public static void delete(File src){//1.先删除文件夹里面的内容//进入src文件夹File[] files = src.listFiles();//遍历for (File file : files) {//判断if(file.isFile()){file.delete();}else{//判断delete(file);}}//2.再删除自己src.delete();}
}
import java.io.File;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){/*需求:统计一个文件夹的总大小*/File file =new File("D:\\aaa\\src");}/** 作用:统计了一个文件夹的总大小* 参数:表示要统计的那个文件夹* 返回值:统计之后的结果* 文件夹的总大小:* 说白了,文件夹里面的所有文件的大小* */public static long getLen(File src){//1.定义变量进行累加long len =0;//2.进入src文件夹File[] files = src.listFiles();//3.遍历数组for (File file : files) {//4判断if(file.isFile()){//我们就把当前文件的大小累加到len当中len = len+file.length();}else{//判断 如果是文件夹就递归len += getLen(file);}}return len;}
}
import java.io.File;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){//需求:统计一个文件夹中每种文件的个数并打印(考虑子文件夹)File file =new File("D:\\aaa\\src");HashMap<String, Integer> hm = getCount(file);System.out.println(hm);}/*作用:统计一个文件夹中每种文件的个数* 形参:要统计的那个文件夹* 返回值:用来统计的map集合键:后缀名 值:次数* */public static HashMap<String,Integer> getCount(File src){//定义集合用来统计HashMap<String,Integer>hm=new HashMap<>();//进入src文件夹File[] files =src.listFiles();//遍历数组for (File file : files) {//判断如果是文件就统计if(file.isFile()){String name = file.getName();String[] arr = name.split("\\.");if(arr.length>=2){String endName=arr[arr.length-1];if(hm.containsKey(endName)){//存在int count = hm.get(endName);count++;hm.put(endName,count);}else{//不存在hm.put(endName,1);}}}else{//文件夹//sonMap里面是子文件中每一种文件的个数HashMap<String, Integer> sonMap = getCount(file);//遍历sonMap把里面的值累加到hm当中Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = sonMap.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {String key = entry.getKey();int value = entry.getValue();if(hm.containsKey(key)){//存在Integer count = hm.get(key);count = count+value;hm.put(key,count);}else{//不存在hm.put(key,value);}}}}return hm;}
}