基本命令

调试未运行的程序
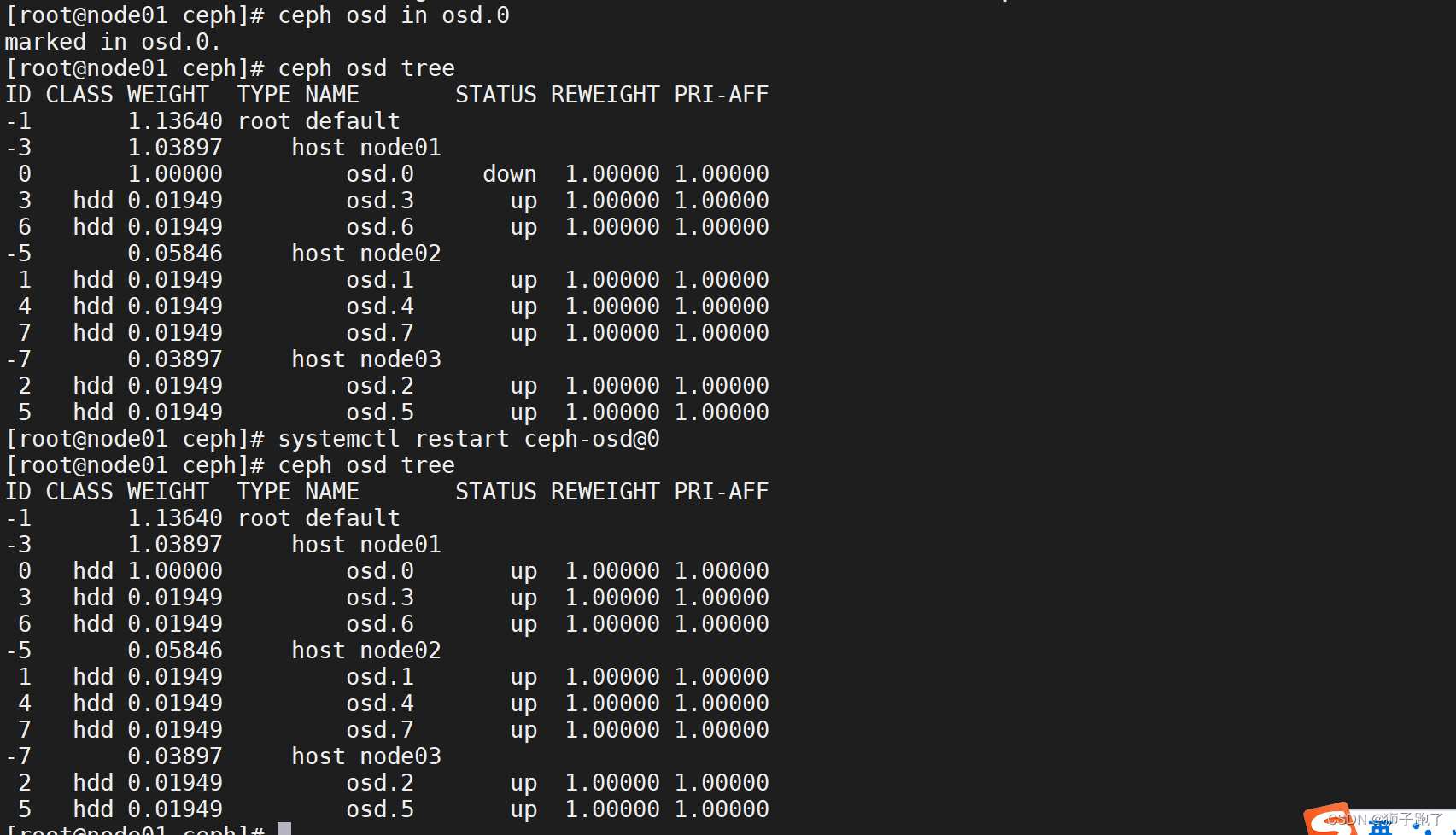
$ gdb helloworld Reading symbols from helloWorld...(no debugging symbols found)...done.
如果没有调试信息,会提示no debugging symbols found。
如果是下面的提示:
Reading symbols from helloWorld...done.
则可以进行调试。
- readelf查看段信息
例如:
$ readelf -S helloWorld|grep debug [28] .debug_aranges PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000106d [29] .debug_info PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000109d [30] .debug_abbrev PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000115b [31] .debug_line PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000011b9 [32] .debug_str PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000011fc
helloWorld为文件名,如果没有任何debug信息,则不能被调试。
- file查看strip状况
下面的情况也是不可调试的:
$ file helloWorld helloWorld: (省略前面内容) stripped
如果最后是stripped,则说明该文件的符号表信息和调试信息已被去除,不能使用gdb调试。但是not stripped的情况并不能说明能够被调试。
调试例如:
$ gdb helloWorld (gdb)
输入run命令,即可运行程序
调试启动带参程序
假设有以下程序,启动时需要带参数:
#include<stdio.h> int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if(1 >= argc) { printf("usage:hello name\n"); return 0; } printf("Hello World %s!\n",argv[1]); return 0 ; }
编译:
$ gcc -g -o hello hello.c
这种情况如何启动调试呢?需要设置参数:
$ gdb hello (gdb)run 编程珠玑 Starting program: /home/shouwang/workspaces/c/hello 编程珠玑 Hello World 编程珠玑! [Inferior 1 (process 20084) exited normally] (gdb)
只需要run的时候带上参数即可。
或者使用set args,然后在用run启动:
$ gdb hello (gdb) set args 编程珠玑 (gdb) run Starting program: /home/hyb/workspaces/c/hello 编程珠玑 Hello World 编程珠玑! [Inferior 1 (process 20201) exited normally] (gdb)
调试正在运行的程序
如果程序已经运行了怎么办呢?
首先使用ps命令找到进程id:
$ ps -ef|grep 进程名
或者:
$ pidof 进程名
attach方式
假设获取到进程id为20829,则可用下面的方式调试进程:
$ gdb (gdb) attach 20829
接下来就可以继续你的调试啦。
可能会有下面的错误提示:
Could not attach to process. If your uid matches the uid of the target process, check the setting of /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope, or try again as the root user. For more details, see /etc/sysctl.d/10-ptrace.conf ptrace: Operation not permitted.
解决方法,切换到root用户:
将/etc/sysctl.d/10-ptrace.conf中的
kernel.yama.ptrace_scope = 1
修改为
kernel.yama.ptrace_scope = 0
直接调试相关id进程
还可以是用这样的方式gdb program pid,例如:
gdb hello 20829
或者:
gdb hello --pid 20829
已运行程序没有调试信息
为了节省磁盘空间,已经运行的程序通常没有调试信息。但如果又不能停止当前程序重新启动调试,那怎么办呢?还有办法,那就是同样的代码,再编译出一个带调试信息的版本。然后使用和前面提到的方式操作。对于attach方式,在attach之前,使用file命令即可:
$ gdb (gdb) file hello Reading symbols from hello...done. (gdb)attach 20829
错误文件调试分析
调试core文件
当程序core dump时,可能会产生core文件,它能够很大程序帮助我们定位问题。但前提是系统没有限制core文件的产生。可以使用命令limit -c查看:
$ ulimit -c 0
如果结果是0,那么恭喜你,即便程序core dump了也不会有core文件留下。我们需要让core文件能够产生:
$ ulimit -c unlimied #表示不限制core文件大小 $ ulimit -c 10 #设置最大大小,单位为块,一块默认为512字节
上面两种方式可选其一。第一种无限制,第二种指定最大产生的大小。
调试core文件也很简单:
$ gdb 程序文件名 core文件名 bt 可以查看函数调用栈
调试多进程
- 调试父进程:set follow-fork-mode parent(默认)
- 调试子进程:set follow-fork-mode chiled
- 设置调试模式:set detach-on-fork [on|off],缺省是on,表示调试当前进程的时候,其它的进程继续运行,如果用off,调试当前进程的时候,其它的进程被gdb挂起。
- 查看调试的进程:info inferiors
- 切换当前调试的进程:inferior 进程 id
调试多线程
- 查看当前运行的进程:ps -aux | grep 进程名
- 查看当前运行的轻量级进程:ps -aL | grep 进程名
- 查看主线程与新线程的关系:pstree -p 主线程id
- 查看线程:info threads
- 切换线程:thread 线程id
- 只运行当前线程:set scheduler-locking on
- 运行全部的线程:set scheduler-locking off
- 指定某线程执行某gdb命令:thread apply 线程id cmd
- 全部的线程执行某gdb命令:thread apply all cmd