1. 为什么需要签名认证呢?
假设我们开放了一个接口,而我们的服务器只允许处理1000个请求,如果这个时候由用户疯狂发送几万个请求,可能会导致服务器宕机,影响其他用户的正常使用。这个情况下我们需要对接口进行限流,而如果我们接口的内容很重要,有一定的保密性 ,这个时候就不可以随便让用户调用,需要让用户去申请签名认证来调取接口,通过接口的认证之后才可以访问到资源。
2. 代码设计
我们以一个简单的接口为例,一步一步从接口的开发到签名认证系统的设计:
2.1. 接口开发
首先我们先简单的创建get和post请求的接口:
package com.stukk.model;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;/*** @Author: stukk* @Description: 用户类(仅供测试)* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 16:20**/
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {private String userName;
}package com.stukk.controller;import com.stukk.model.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;/*** @Author: stukk* @Description: 测试开发API的接口* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 16:20**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {@GetMapping("/")public String getNameByGet(String name){return "用户名是:"+name;}@PostMapping("/name")public String getNameByPost(@RequestParam String name){return "用户名是:"+name;}@PostMapping("/")public String getUserNameByPost(@RequestBody User user){return "用户名是:"+user.getUserName();}}
application.yml文件配置:
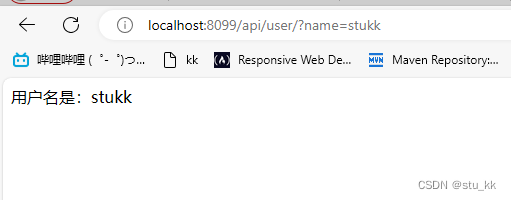
server:port: 8099servlet:context-path: /api启动springboot之后,我们在浏览器输入:localhost:8099/api/user/?name=stukk
2.2. 第三方接口的客户端开发
每次让用户使用http去调用显然不太好,我们需要封装方法给用户传参调用就行了。
package com.stukk.client;import cn.hutool.http.HttpRequest;
import cn.hutool.http.HttpResponse;
import cn.hutool.http.HttpUtil;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
import com.stukk.model.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;/*** @Author: stukk* @Description: 第三方接口客户端* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 16:33**/
public class ApiClient {public String getNameByGet(String name){
// Get请求Map<String,Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();paramMap.put("name",name);String result = HttpUtil.get("http://localhost:8099/api/user/", paramMap);System.out.println(result);return result;}public String getNameByPost( String name){
// Post请求Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();paramMap.put("name",name);String result = HttpUtil.post("http://localhost:8099/api/user/name", paramMap);System.out.println(result);return result;}public String getUserNameByPost(User user){
// Post请求String jsonStr = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(user);Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();HttpResponse httpResponse = HttpRequest.post("http://localhost:8099/api/user/").body(jsonStr).execute();System.out.println(httpResponse.getStatus());String result = httpResponse.body();System.out.println(result);return result;}public static void main(String[] args) {ApiClient apiClient = new ApiClient();apiClient.getNameByGet("stukk");apiClient.getNameByPost("吴坤坤");apiClient.getUserNameByPost(User.builder().userName("kkkkkk").build());}}
运行结果:
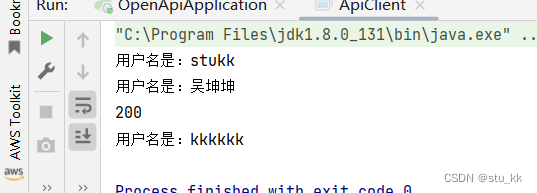
好了,我们已经实现了接口的开发和调用了,但是上述例子只是一个简单的例子,具体情况还需要根据项目需求去添加内容。
2.3.简单的校验
上述接口最大的问题就是,任何人、任何时间都可以来访问我的接口,这样子相当于接口在裸奔了,安全性是没有的,所以我们可以初步一些简单的校验功能:
加上公钥和私钥:
private String accessKey; //公钥private String secretKey; //私钥public ApiClient(String accessKey, String secretKey) {this.accessKey = accessKey;this.secretKey = secretKey;}

然后我们现在接口处加上很呆的判定:
@PostMapping("/")public String getUserNameByPost(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletRequest request){String accessKey = request.getHeader("accessKey");String secretKey = request.getHeader("secretKey");if(!accessKey.equals("stukk") || !secretKey.equals("kkkkkk")){throw new RuntimeException("无权限");}return "用户名是:"+user.getUserName();}
之后运行就无权限了:
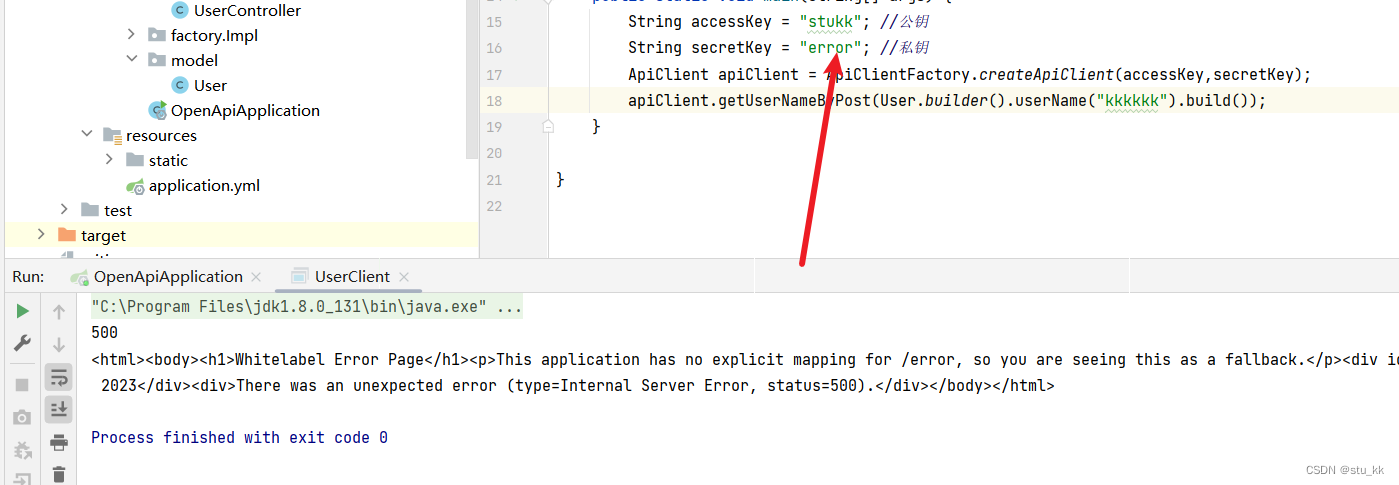
但是显然这种虽然能有效的防止别人随意调用,但是只要有人拦截了我们的请求,获取到请求头中的ak和sk,那么就能随意调用了,所以密码是不能以明文的形式传输的!不传递怎么确定是合规的访问呢?
2.4.标准的API签名认证
在标准的 API 签名认证中,我们需要传递一个签名(Sign)。通常我们不是直接将密钥传递给后台,而是根据密钥生成一个签名。我们可以使用MD5单向加密算法来加密密钥生成签名,单向意味着只可加密不可解密的,所以我们需要保存用户的密钥,在判定时,再加密一次对比加签名既可以判断是不是合规的请求了。
为了更加的安全,我们还可以
1. 在请求头加上随机数,后端只接受随机数一次,这样可以解决请求重放问题,更加的安全了
2. 每个请求在发送时携带一个时间戳,并且后端会验证该时间戳是否在指定的时间范围内,例如不超过10分钟或5分钟。这可以防止对方使用昨天的请求在今天进行重放。
详情见代码:
/*** @Author: stukk* @Description: 签名工具* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 17:47**/
public class SignUtil {public static String genSign(String body,String secretKey){
// 使用基于SHA256的MD5算法Digester md5 = new Digester(DigestAlgorithm.SHA256);String content = body + "." + secretKey;
// 加密得到签名return md5.digestHex(content);}
}/*** @Author: stukk* @Description: 第三方接口客户端* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 16:33**/
public class ApiClient {private String accessKey; //公钥private String secretKey; //私钥public ApiClient(String accessKey, String secretKey) {this.accessKey = accessKey;this.secretKey = secretKey;}public String getNameByGet(String name){
// Get请求Map<String,Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();paramMap.put("name",name);String result = HttpUtil.get("http://localhost:8099/api/user/", paramMap);System.out.println(result);return result;}public String getNameByPost( String name){
// Post请求Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();paramMap.put("name",name);String result = HttpUtil.post("http://localhost:8099/api/user/name", paramMap);System.out.println(result);return result;}public String getUserNameByPost(User user){
// Post请求String jsonStr = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(user);HttpResponse httpResponse = HttpRequest.post("http://localhost:8099/api/user/").addHeaders(getHeaders(jsonStr)).body(jsonStr).execute();System.out.println(httpResponse.getStatus());String result = httpResponse.body();System.out.println(result);return result;}private Map<String,String> getHeaders(String body){Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("accessKey",accessKey);
// 不能直接加上密钥map.put("secretKey",secretKey);
// 生成随机数,4个随机数字字符串map.put("nonce", RandomUtil.randomNumbers(4));
// 请求体map.put("body",body);
// 时间戳map.put("timestamp",String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000));
// 签名:map.put("sign", SignUtil.genSign(body,secretKey));return map;}
}package com.stukk.controller;import com.stukk.model.User;
import com.stukk.utils.SignUtil;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;/*** @Author: stukk* @Description: 测试开发API的接口* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 16:20**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {@GetMapping("/")public String getNameByGet(String name){return "用户名是:"+name;}@PostMapping("/name")public String getNameByPost(@RequestParam String name){return "用户名是:"+name;}@PostMapping("/")public String getUserNameByPost(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletRequest request){String accessKey = request.getHeader("accessKey");String nonce = request.getHeader("nonce");String timestamp = request.getHeader("timestamp");String sign = request.getHeader("sign");String body = request.getHeader("body");Set<String> nonces = new HashSet<>();
// 数据库查询验证这个accessKeyif(!accessKey.equals("stukk")){throw new RuntimeException("无权限");}
// 检验随机数,判断是不是出现过if(nonces.contains(nonce)){throw new RuntimeException("请重试");}nonces.add(nonce);long preTimestamp = Long.parseLong(timestamp);long nowTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis()/1000;if(nowTimestamp - preTimestamp > 36000){ //10小时?throw new RuntimeException("签名超时");}//根据accessKey从数据库查出secretkey,这里假设为kkkkkkString secretLKey = "kkkkkk";String correctSign = SignUtil.genSign(body, secretLKey);if(!correctSign.equals(sign)){throw new RuntimeException("签名错误");}return "用户名是:"+user.getUserName();}
}/*** @Author: stukk* @Description:* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 17:09**/
public class UserClient {public static void main(String[] args) {String accessKey = "stukk"; //公钥String secretKey = "kkkkkk"; //私钥ApiClient apiClient = new ApiClient(accessKey, secretKey);apiClient.getUserNameByPost(User.builder().userName("kkkkkk").build());}}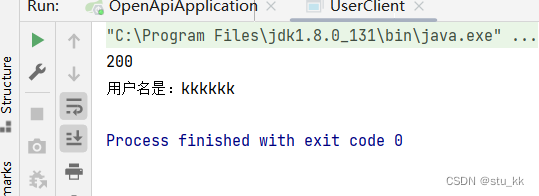
这样子我们就完成了标准的API签名认证了,接下来开发SDK:
3.开发SDK
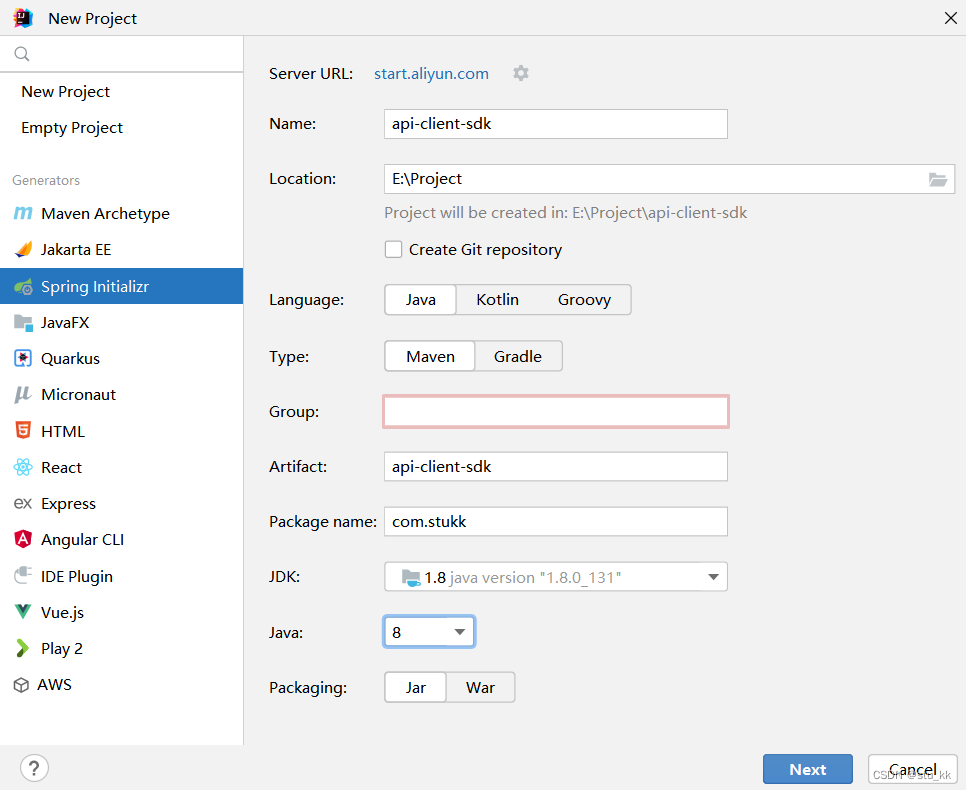
3.1.新建项目
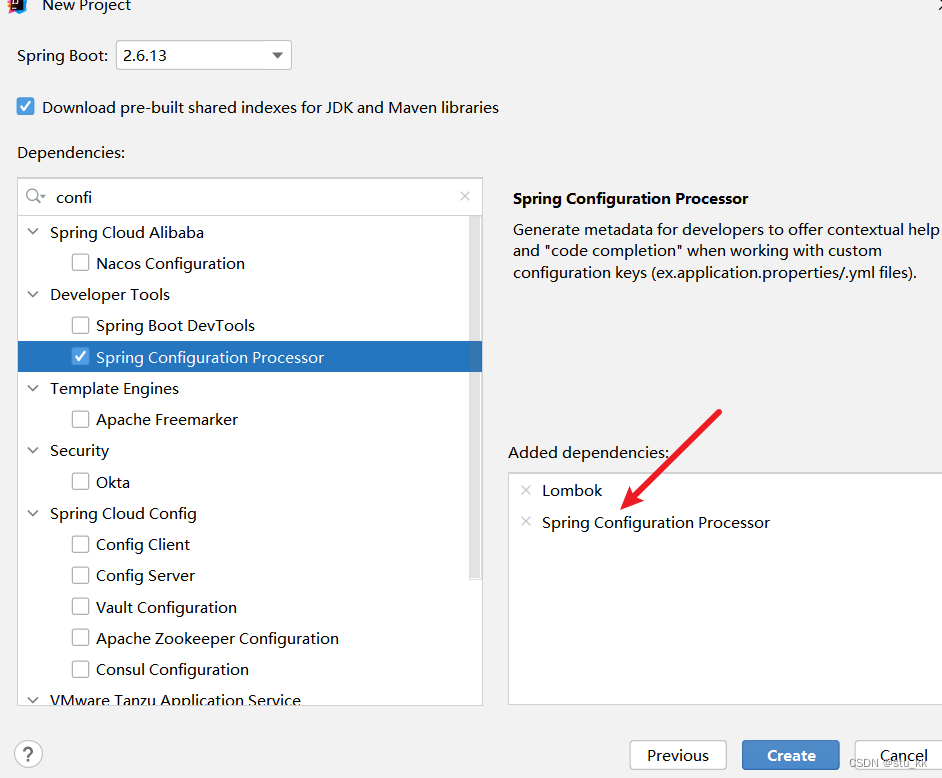
3.2.配置pom.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><parent><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><version>2.7.13</version><relativePath/></parent><groupId>com.stukk</groupId><artifactId>api-client-sdk</artifactId>
<!-- 版本号--><version>1.1.1</version><name>api-client-sdk</name><description>api-client-sdk</description><properties><java.version>1.8</java.version></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency></dependencies></project>

3.3.创建配置类
package com.stukk;import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** @Author: stukk* @Description: 创建配置类* @DateTime: 2023-12-20 19:04**/
//标记为配置类
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("stukk.api") //能够读取application.yml配置,载入属性
@Data //lombok注解
@ComponentScan //自动扫描组件
public class ApiClientConfig {private String accessKey;private String secretKey;
}
项目中的 client包、model包、utils包复制:

在resources目录下创建META-INF/spring.factories文件:
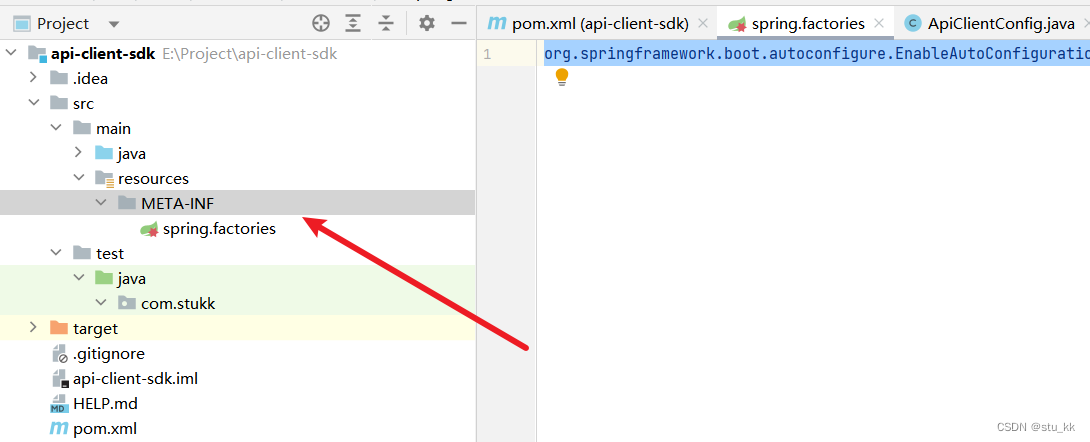
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.stukk.ApiClientConfig3.4.下载jar包

下载的地方就是我们maven配置的地方:

4.引入SDK
接下来回到原来的项目,删掉model、client、utils包,引入这个SDK依赖:

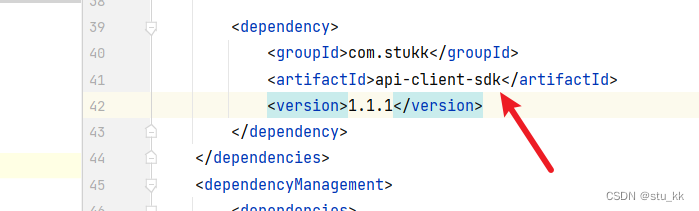
<dependency><groupId>com.stukk</groupId><artifactId>api-client-sdk</artifactId><version>1.1.1</version></dependency>我们会发现application.yml会提示我们生成这个accessKey和secretKey配置:
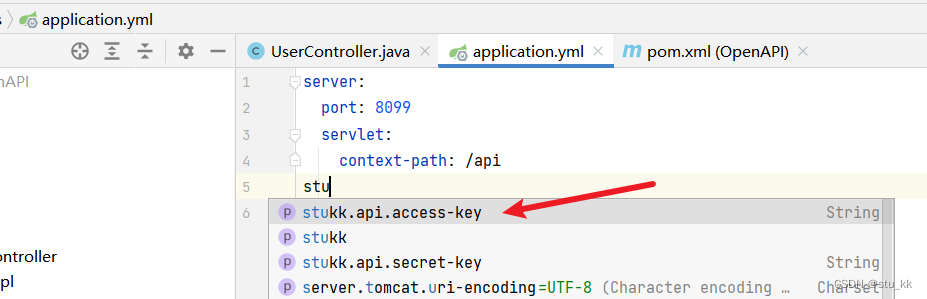
server:port: 8099servlet:context-path: /api
stukk:api:access-key: stukksecret-key: kkkkkk
3.5编写测试类测试:
package com.stukk;import com.stukk.client.ApiClient;
import com.stukk.model.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import javax.annotation.Resource;@SpringBootTest
class OpenApiApplicationTests {@Resourceprivate ApiClient apiClient;@Testvoid testSDK() {User user = new User(kk__SDK");String result = apiClient.getUserNameByPost(user);System.out.println(result);}}
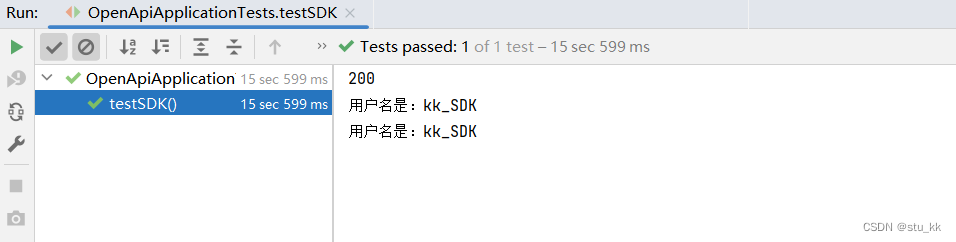
成功调用了。