Fastjson是一个Java语言编写的高性能的JSON处理器,由阿里巴巴公司开发。
无依赖,不需要例外额外的jar,能够直接跑在JDK上。
FastJson在复杂类型的Bean转换Json上会出现一些问题,可能会出现引用的类型,导致Json转换出错,需要制定引用。
FastJson采用独创的算法,将parse的速度提升到极致,超过所有json库。
一、导入依赖:
在maven项目的pom文件中直接配置fastjson依赖,fastjson最新版本都会发布到maven中央仓库,你可以直接依赖。
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>x.x.x</version>
</dependency>其中x.x.x是版本号,根据需要使用特定版本,建议使用最新版本。
二、Fastjson 主要的API
主要的3个类,JSON、JSONArray、JSONObject。JSONObject和JSONArray继承JSON。
JSONObject代表json对象,JSONArray代表json对象数组,JSON代表JSONObject和JSONArray的转化。
对于JSON、JSONArray、JSONObject我的理解:
JSON提供了基本的转换方法,例如
JSON.toJSONString:将java对象转换为json字符串
JSON.parseObject:json字符串转换为指定java对象或转换为列表或者转换为JSONObject对象
JSON.parseArray:json字符串转换为JSONArray。而JSONObject对象继承了JSON,且实现了Map类。所以JSONObject是进一步封装类,这个类的主要作用就是,将Json字符串转换为JSONObject对象之后,实际上就相当于将Json字符串转换成了Map类型的key-value的格式,所以提供了很多丰富的api,可以让我们像操作Map对象那样,去操作JSONObject。例如去获得json字符串中某个属性,或某个节点下的属性。
JSONArray对象也继承了JSON,但是实现了List类,所以JOSNArray也是经过进一步的封装,这个类的主要作用就是,将Json字符串转换为JSONArray之后,实际上就相当于转换成了List类型的,提供了很多像操作List那样的api,例如判断该列表是否为空,或者获取某个索引下的属性。
所以我们使用fastObject时,如果只需要简单的转换,我们直接使用JSON类中的转换方法即可,但是如果需要更加细致的操作,例如直接获取json字符串中某个属性或者某个节点下的属性,可以进一步转换为JSONObject或者JSONArray来操作会更方便。
常用操作方法:
序列化
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(obj);
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(obj,true);//格式化输出
反序列化:
VO vo = JSON.parseObject("…", VO.class);
泛型反序列化:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference; List list = JSON.parseObject("…", new TypeReference<List>() {});
//对象转换为Json字符串Student student = new Student("姓名", null, LocalDateTime.now());String s = JSON.toJSONString(student);System.out.println("对象转json:"+s);//列表转json字符串List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();students.add(new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now()));students.add(new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now()));students.add(new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now()));String s1 = JSON.toJSONString(students);System.out.println("List转json:"+s1);//Map类型转字符串Map<Integer,Student> map = new HashMap<>();map.put(1,new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now()));map.put(2,new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now()));map.put(3,new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now()));String s2 = JSON.toJSONString(map);System.out.println("Map转json:"+s2);//Map类型中有List 转字符串Map<Integer,List<Student>> map1 = new HashMap<>();map1.put(1,students);map1.put(2,students);map1.put(3,students);String s3 = JSON.toJSONString(map1);System.out.println("Map中含有List转json:"+s3);//json转换为对象Student student1 = JSON.parseObject("{\"age\":\"性别\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T11:01:32.870\"}", Student.class);System.out.println("json转换为对象:"+student1);//json转换为List//使用parseObjectList<Student> studentList = JSON.parseObject("[{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T14:00:30.592\"},{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T14:00:30.592\"},{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T14:00:30.592\"}]", new TypeReference<List<Student>>() {});System.out.println("json转换为List:"+studentList);//使用parseArrayList<Student> studentList1 = JSON.parseArray("[{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T14:00:30.592\"},{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T14:00:30.592\"},{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T14:00:30.592\"}]", Student.class);System.out.println("json转换为List:"+studentList1);//json转Map//使用parseObjectMap<Integer, Student> map2 = JSON.parseObject("{1:{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T15:10:57.807\"},2:{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T15:10:57.807\"},3:{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T15:10:57.807\"}}", new TypeReference<Map<Integer, Student>>() {});System.out.println("json转Map:"+map2);对象转json:{"name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.474"}
List转json:[{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.925"},{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.925"},{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.925"}]
Map转json:{1:{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.927"},2:{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.927"},3:{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.927"}}
Map中含有List转json:{1:[{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.925"},{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.925"},{"age":"年龄","name":"姓名","time":"2023-12-22T15:28:18.925"}],2:[{"$ref":"$[1][0]"},{"$ref":"$[1][1]"},{"$ref":"$[1][2]"}],3:[{"$ref":"$[1][0]"},{"$ref":"$[1][1]"},{"$ref":"$[1][2]"}]}
json转换为对象:Student(name=姓名, age=性别, time=2023-12-22T11:01:32.870)
json转换为List:[Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T14:00:30.592), Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T14:00:30.592), Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T14:00:30.592)]
json转换为List:[Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T14:00:30.592), Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T14:00:30.592), Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T14:00:30.592)]
json转Map:{1=Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T15:10:57.807), 2=Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T15:10:57.807), 3=Student(name=姓名, age=年龄, time=2023-12-22T15:10:57.807)}
三、Fastjson方法总结:
Json相关方法:
1、parse():将json转换成object,也可以强转成指定类型与toJSON()方法类似
2、parseObject():将json字符串转成指定对象类型或者JSONObject
3、parseArray:将json字符串转成指定类型列表或者JSONArray4、toJSON():将json字符串转换为Object类型,与parse()方法类似:使用指定日期格式将 Java 对象序列化为 JSON 字符串,注意它可以是任意对象类型,也就是说将任意类型的参数传进去,会自动检测是否包含日期类Date或者LocalDateTime,然后进行自动转换。
5、toJavaObject():将JSONObject转换为指定对象类型,注意在使用JSON这个方法时,第一个参数是JSONObject类型的,而不是字符串类型。
6、toJSONBytes():将json字符出啊转换为字节数组
7、toJSONStringWithDateFormat()8、isValid():检查 JSON 字符串是否合法。(已弃用)
String str = "{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T15:51:01.993\"}";String arrayStr = "[{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T15:51:01.993\"},{\"age\":\"年龄\",\"name\":\"姓名\",\"time\":\"2023-12-22T15:51:01.993\"}]";//parse将对象转换为StringObject parse = JSON.parse(arrayStr);//parseObject转换为java对象,如果不指定对象类型,就转换为JSONObject类型,如果指定 就转换为指定类型JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(str);Student student = JSON.parseObject(str, Student.class);//parseArray转换为列表,如果不指定列表类型,就转换为List类型,如果指定 就转换为指定类型列表JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(arrayStr);List<Student> students = JSON.parseArray(arrayStr, Student.class);//toJSON,转换为Object,也可以强制转换为某种类型Object o = JSON.toJSON(student1);JSONObject o1 = (JSONObject)JSON.toJSON(student1);//toJavaObject,将JSONObject转换为指定的java对象JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSON.parseObject(str);Student student4 = JSON.toJavaObject(jsonObject1, Student.class);//toJSONBytes,将java对象转换为字节数组byte[] bytes = JSON.toJSONBytes(student1);//oJSONStringWithDateFormat()//转换为JSONObject类型JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();jsonObject.put("name", "David");jsonObject.put("birthDate", LocalDateTime.now());String jsonString = JSON.toJSONStringWithDateFormat(jsonObject, "yyyy-MM-dd");System.out.println(jsonString);//转换StudentString jsonString = JSON.toJSONStringWithDateFormat(new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now()), "yyyy-MM-dd");System.out.println(jsonString);JSONObject相关方法:
JSONObject转换成字符串:
1. toJSONString():将 Java 对象序列化为 JSON 字符串。(与JSON中的方法类似,JSON中的方法是将JSONObject对象序列化为字符串,这个是直接序列化为字符串)。
JSONObject删除、判断相关方法:
2. size():获取 JSON 对象或数组的元素数量。
3. remove():从 JSON 对象中删除指定的键。
4. clear():清空 JSON 对象中的所有键值对。
5. isEmpty():检查 JSON 对象是否为空。
6. containsKey():检查 JSON 对象是否包含指定的键。
7. containsValue(Object value): 检查 JSON 对象是否包含指定的值
Student student = new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now(),true);JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject)JSON.toJSON(student);System.out.println("jsonObject:"+jsonObject);System.out.println("toJavaString:"+jsonObject.toJSONString());System.out.println("size:"+jsonObject.size());System.out.println("isEmpty:"+jsonObject.isEmpty());System.out.println("containsKey:"+jsonObject.containsKey("age"));System.out.println("containsValue:"+jsonObject.containsKey("姓名"));jsonObject.remove("age");System.out.println("remove:"+jsonObject.toJSONString());jsonObject.clear();System.out.println("clear:"+jsonObject.toJSONString());
从JSONObject中获取key列表、value列表、key-value列表:
8. keySet():获取 JSON 对象的键集合。
9. values():获取 JSON 对象的值集合。
10. entrySet(): 获取 JSON 对象的键值对集合
Student student = new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now(),true);JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject)JSON.toJSON(student);System.out.println("jsonObject:"+jsonObject);System.out.println("keySet:"+jsonObject.keySet());System.out.println("values:"+jsonObject.values());System.out.println("entrySet:"+jsonObject.entrySet());
JSONObject中添加key-value:
11. put(String key, Object value): 向 JSON 对象添加键值对
12. putAll(Map<? extends String, ? extends V> map): 向 JSON 对象中添加键值对
13. putAll(JSONObject m) : 将另一个 JSON 对象中的键值对添加到当前 JSON 对象
14. putIfAbsent(String key, Object value): 如果不存在键,则向 JSON 对象添加键值对
Student student = new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now(),true);JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject)JSON.toJSON(student);System.out.println("jsonObject:"+jsonObject);System.out.println("put:"+jsonObject.put("new1","新添加1"));JSONObject jsonObject1 = new JSONObject();jsonObject1.put("new2","新添加2");jsonObject.putAll(jsonObject1);System.out.println("putAll(Map):"+jsonObject);Map map = new HashMap();map.put("new3","新添加3");jsonObject.putAll(map);System.out.println("putAll(Map):"+jsonObject);jsonObject.putIfAbsent("new1","新添加1");System.out.println("putIfAbsent:"+jsonObject);
JSONObject中获取相关方法::获取 JSON 对象中的子对象。
16.getJSONObject()
17. getJSONArray():获取 JSON 对象中的子数组。
18. get(Object key) : 获取 JSON 对象中的属性值
19. getInteger(String key): 获取 JSON 对象中的整数属性值
20. getLong(String key) : 获取 JSON 对象中的长整数属性值
21. getShort(String key) : 获取 JSON 对象中的短整数属性值
22. getByte(String key) : 获取 JSON 对象中的字节属性值
23. getFloat(String key): 获取 JSON 对象中的浮点数属性值
24. getDouble(String key) : 获取 JSON 对象中的双精度浮点数属性值
25. getBoolean(String key): 获取 JSON 对象中的布尔属性值
26. getBigDecimal(String key): 获取 JSON 对象中的 BigDecimal 属性值
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();jsonObject.put("one",new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now(),true));List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();students.add(new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now(),true));students.add(new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now(),true));jsonObject.put("two",students);jsonObject.put("three","string类型");jsonObject.put("four",true);System.out.println("getObject:"+jsonObject.getObject("one",Student.class));System.out.println("getJSONObject:"+jsonObject.getJSONObject("one"));System.out.println("getJSONArray:"+jsonObject.getJSONArray("two"));System.out.println("getString:"+jsonObject.getString("three"));System.out.println("getBoolean:"+jsonObject.getBoolean("four"));
Java对象、JSONObject、json字符串相互转化:
//java对象转JSONObjectStudent student = new Student("姓名","年龄",LocalDateTime.now(),true);JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject)JSON.toJSON(student);//java对象转json字符串String s = JSON.toJSONString(student);//JSONObject转java对象Student student1 = jsonObject.toJavaObject(Student.class);//JSONObject转JSONStringString s1 = jsonObject.toJSONString();//json字符串转java对象JSON.parseObject("{\"name\":\"姓名\",\"aboolean\":true,\"time\":\"2023-12-25T14:02:47.860\",\"age\":\"年龄\"}", Student.class);//json字符串转JSONObjectJSONObject jsonObject1 = JSON.parseObject("{\"name\":\"姓名\",\"aboolean\":true,\"time\":\"2023-12-25T14:02:47.860\",\"age\":\"年龄\"}");
JSONArray相关方法:
JSONArray就像是一个可以添加任意类型的列表,并不是只能存储json字符串。
1.toJavaList():将jsonArray转换为对应列表。
List<Student> students = jsonArray.toJavaList(Student.class);2.add():可以添加任意类型,相当于在列表中新增加一个元素
3.addAll():添加所有元素,可以是List类型,也可以是JSONArray.
4.contains():是否含有某个元素。
5.clear():清除列表。
6.clone():复制一个新列表。
7.size():列表元素总数
8..get():获取对应下标的元素
9.fluentAdd():流式添加,使用了这个之后,可以继续操作。
two.fluentAdd("aaa").add("bbb");
10.remove():删除对应索引的数据。
11.获取对应类型:
getBoolean()、getJSONObject()、getJSONArray()、 getString();等等,对应类型都有。
12.isEmpty():是否为空。
13.也可以使用stream()流对其操作。
其他略,基本跟List操作类似。
Fastjson过滤器用法:
SimplePropertyPreFilter 用法:
可以指定某些属性参与序列化、某些属性不参与序列化。
Student student = new Student("姓名", "年龄", LocalDateTime.now());SimplePropertyPreFilter filter = new SimplePropertyPreFilter();//排除某些属性不序列化filter.getExcludes().add("name");System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student,filter));SimplePropertyPreFilter filter1 = new SimplePropertyPreFilter();//只序列化指定的属性filter1.getIncludes().add("name");System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student,filter1));PropertyFilter用法:
SimplePropertyPreFilter 实现了 PropertyPreFilter ,也就是说我们可以自己实现过滤的逻辑例如:
Student student = new Student("姓名", "年龄", LocalDateTime.now());//重新过滤逻辑,只序列化 name 属性值PropertyFilter propertyFilter = new PropertyFilter() {@Overridepublic boolean apply(Object object, String name, Object value) {if(name.equals("name")){return true;}return false;}};String json = JSON.toJSONString(student,propertyFilter);System.out.println(json);
类过滤器:
fastjson提供类级别的SerializeFilter支持,也就是说,可以设置过滤器只对某些类序列化的时候生效。
例如只对Student类中的属性名转换成大写:
Student student = new Student("姓名", "年龄", LocalDateTime.now());NameFilter nameFilter = new NameFilter() {@Overridepublic String process(Object object, String name, Object value) {return name.toUpperCase();}};// 对A类添加过滤器SerializeConfig.getGlobalInstance().addFilter(Student.class, nameFilter);String s = JSON.toJSONString(student);System.out.println(s);
或者指定Student类只序列化name属性:
Student student = new Student("姓名", "年龄", LocalDateTime.now());//重新过滤逻辑,只序列化 name 属性值PropertyFilter propertyFilter = new PropertyFilter() {@Overridepublic boolean apply(Object object, String name, Object value) {if(name.equals("name")){return true;}return false;}};// 对A类添加过滤器SerializeConfig.getGlobalInstance().addFilter(Student.class, propertyFilter);String s = JSON.toJSONString(student);System.out.println(s);

ValueFilter:
对value进行修改
Student student = new Student("姓名", "年龄", LocalDateTime.now());//修改属性值为 字段名—属性值ValueFilter valueFilter = (object, name, value) -> name + "-" + value;SerializeConfig.getGlobalInstance().addFilter(Student.class, valueFilter);String s = JSON.toJSONString(student);System.out.println(s);SerializeFilter:
以上的过滤器都实现了SerializeFilter:
SerializeFilter · alibaba/fastjson Wiki · GitHub
四、fastjson中常用注解:
@JSONField
使用fastjson进行需要对字段进行一些特殊处理,比如时间格式,前后端名字不一致,字段为null是否依然序列化等问题。那么fastjson的@JSONField就能很好的解决这些问题。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER })
public @interface JSONField {int ordinal() default 0; //是根据fieldName的字母序进行序列的,你可以通过ordinal指定字段的顺序String name() default ""; //序列化和反序列化时候的别名String format() default ""; //用于字符串格式的日期转换boolean serialize() default true; // 是否参与序列化boolean deserialize() default true; //是否参与反序列化SerializerFeature[] serialzeFeatures() default {}; //序列化选项 SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero 如空Number填充0Feature[] parseFeatures() default {}; //反序列化选项String label() default ""; //标签,boolean jsonDirect() default false; //当你有⼀个字段是json字符串的数据,你希望直接输出,⽽不是经过转义之后再输出。Class<?> serializeUsing() default Void.class; // 属性的序列化类,可定制。可有现存的,比如本来是Long,序列化的时候转为String:serializeUsing= ToStringSerializer.classClass<?> deserializeUsing() default Void.class; // 属性的反序列化类,可定制。String[] alternateNames() default {}; //参与反序列化时候的别名boolean unwrapped() default false; // 对象映射到父对象上。不进行子对象映射。简单而言,就是属性为对象的时候,属性对象里面的属性直接输出当做父对象的属性输出String defaultValue() default ""; //设置默认值
}1、 几个基本属性:
ordinal :指定字段的顺序
name :序列化和反序列化时候的别名
serialize: 是否参与序列化
deserialize:是否参与反序列化
format:用于字符串格式的日期转换
defaultValue:设置默认值
示例:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student {@JSONField(name = "NAME",ordinal = 1,serialize = true)private String name;@JSONField(name = "AGE",ordinal = 2,serialize = true,defaultValue = "默认的姓名")private String age;@JSONField(name = "JOB",ordinal = 3,serialize = false)private String job;@JSONField(name = "SEX",ordinal = 4,serialize = true)private String sex;@JSONField(name = "TIME",ordinal = 5,serialize = true ,format = "yyyy-MM-dd")private LocalDateTime time;
} Student student = new Student("姓名", null, "工作", "性别", LocalDateTime.now());System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student,true)); 正常输出:
加上上面注解之后:

2、serialzeFeatures、parseFeatures: 序列化、反序列化时候的一些可选的特征
序列化的时候比如fastjson默认是不会将为null的属性输出的,若是我们也想输出,可以加入@JSONField(serialzeFeatures = SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue) 数值型为null的话,就输出0,可以使用@JSONField(serialzeFeatures = SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero)
反序列化的时候,比如parser是否将允许使用非双引号属性名字。@JSONField(parseFeatures = Feature.AllowSingleQuotes)
示例:
Student student = new Student("姓名", null, "工作", "性别", LocalDateTime.now());System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student,true)); 正常输出:
没有打印age的值,如果加上注解:
//输出null,使用单引号@JSONField(serialzeFeatures = {SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,SerializerFeature.UseSingleQuotes } )private String age;输出了age的值,而且是单引号。
具体名称还包括:
PrettyFormat
3、label:可以给属性设置标签,这样可以批量处理某一类的属性,比如不序列化某一类属性。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student {@JSONField(label = "a")private String name;@JSONField(label = "a")private String age;@JSONField(label = "a")private String job;@JSONField(label = "b")private String sex;@JSONField(label = "b")private LocalDateTime time;
}
Student student = new Student("姓名", null, "工作", "性别", LocalDateTime.now());System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student, Labels.includes("a"), SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat));System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student, Labels.includes("b"), SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat));System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student, Labels.includes("a","b"), SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat)); 
4、 jsonDirect:不经过转义直接输出:
@JSONField(jsonDirect = true)private String name; Student student = new Student("{}", "年龄", "工作", "性别", LocalDateTime.now());System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student, SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat)); 正常输出:
加上注解之后:
5、serializeUsing和deserializeUsing:
可定制的序列化和反序列化的类,但是也有原生的。
比如原生:比如字段本来是Long,序列化的时候转为String。
比如自定义:我对某个字段加上我想要的处理结果“Chinese are Japanese fathers”
@JSONField(serializeUsing = DemoController.MySerializer.class)private String name;@JSONField(serializeUsing = ToStringSerializer.class)private Integer age;@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
@Slf4j
public class DemoController {public static void main(String[] args) {Student student = new Student("{}", 22, "工作", "性别", LocalDateTime.now());System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student, SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat));}public static class MySerializer implements ObjectSerializer {@Overridepublic void write(JSONSerializer serializer, Object object, Object fieldName, Type fieldType, int features) throws IOException {String text = "Chinese are Japanese fathers" + (String) object;serializer.write(text);}}
}加上之后输出: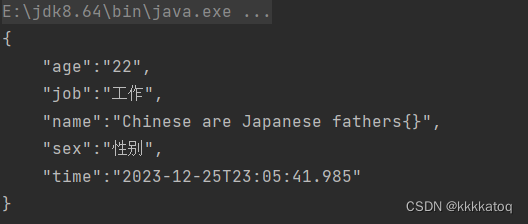
6、alternateNames:反序列化时候的别名
public class JSONController {public static void main(String[] args) {String str ="{\"Name\":\"汉族\",\"num\":2323}";System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(JSON.parseObject(str, Nation.class)));//{"name":"汉族","num":2323}}}@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
class Nation {@JSONField(alternateNames = {"name", "Name"})private String name;private String dress;private Integer num;private Date celebrateHoliday;
}7、unwrapped
对象映射到父对象上。不进行子对象映射。简单而言,就是属性为对象的时候,属性对象里面的属性直接输出当做父对象的属性输出,意思就是说有一个属性为对象时,直接将这个对象中的属性并入到父类属性中,也就是外层对象中。
示例:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student {private String name;private Integer age;@JSONField(unwrapped = true)private Job job;}@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic static class Job{private String jobName;private LocalDateTime jobNum;} Job job = new Job("工作名称", LocalDateTime.now());Student student = new Student("{}", 22, job);System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(student, SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat));正常输出:
加上注解后:
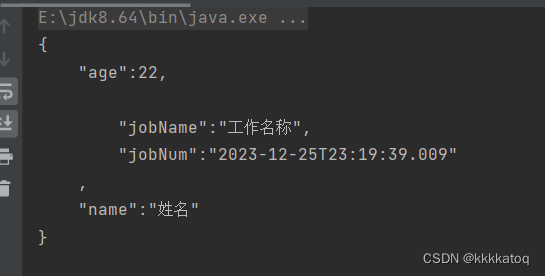
@JSONType
该注解作用于类上 , 对该类的字段进行序列化和反序列化时的特性功能定制。
- 注解属性 : includes 要被序列化的字段.
- 注解属性 : ignores 不要被序列化的字段.
- 注解属性 : orders 序列化后的顺序.
- 注解属性 : serialzeFeatures 序列化时的特性定义
等等,主要用的就是上面的属性,还有其他属性跟JSONField中用法类似,主要就是JSONType是作用在类上的。其他的可以自行搜索。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@JSONType(orders = {"name","age","time","strings"},ignores = {"age"},includes = {"name"},serialzeFeatures = {SerializerFeature.BeanToArray,SerializerFeature.BrowserCompatible})
public class Student {private String name;private String age;private LocalDateTime time;private List<String> strings;
}@JSONCreator
作用就是,指定对象反序列化时的构造函数或者工厂方法。其作用可自己查,感觉用处不大。
@JSONPOJOBuilder
指定反序列化时创建java对象使用的build方法,具体作用可查