yolov8代码:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
yolov8的整体结构如下图(来自mmyolo):
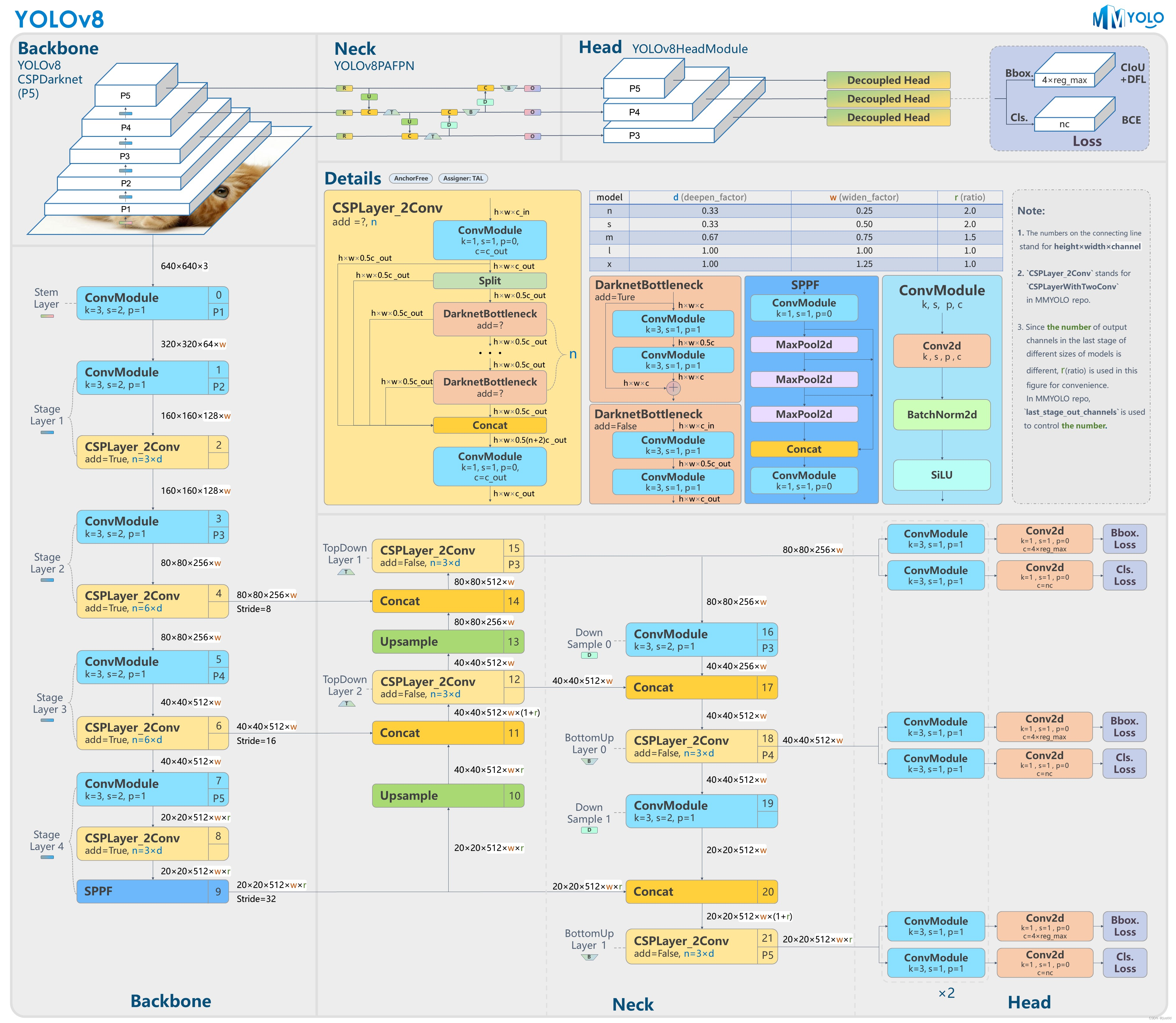
yolov8的配置文件:
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'# [depth, width, max_channels]n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPss: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPsm: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPsl: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPsx: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:# [from, repeats, module, args]- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9# YOLOv8.0n head
head:- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
可以看出,主要包含Conv,C2f,SPPF,Concat,Detect几个模块。
一、Conv
Conv模块包含卷积层、BN层和激活函数层。
代码如下:
class Conv(nn.Module):"""Standard convolution with args(ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups, dilation, activation)."""default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activationdef __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, d=1, act=True):"""Initialize Conv layer with given arguments including activation."""super().__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p, d), groups=g, dilation=d, bias=False)self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):"""Apply convolution, batch normalization and activation to input tensor."""return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))def forward_fuse(self, x):"""Perform transposed convolution of 2D data."""return self.act(self.conv(x))二、C2f
C2f就是模型结构图中的CSPLayer_2Conv,包含多个DarkNetBottleNeck。代码如下:
class C2f(nn.Module):"""Faster Implementation of CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions."""def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):"""Initialize CSP bottleneck layer with two convolutions with arguments ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups,expansion."""super().__init__()self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channelsself.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)self.m = nn.ModuleList(Bottleneck(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))def forward(self, x):"""Forward pass through C2f layer."""y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1))y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))def forward_split(self, x):"""Forward pass using split() instead of chunk()."""y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))class Bottleneck(nn.Module):"""Standard bottleneck."""def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5):"""Initializes a bottleneck module with given input/output channels, shortcut option, group, kernels, andexpansion."""super().__init__()c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channelsself.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g)self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2def forward(self, x):"""'forward()' applies the YOLO FPN to input data."""return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
三、SPPF
yolov8的SPPF实现是通过多次池化实现不同大小的池化窗口运算,代码如下:
class SPPF(nn.Module):"""Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher."""def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5):"""Initializes the SPPF layer with given input/output channels and kernel size.This module is equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))."""super().__init__()c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channelsself.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)def forward(self, x):"""Forward pass through Ghost Convolution block."""x = self.cv1(x)y1 = self.m(x)y2 = self.m(y1)return self.cv2(torch.cat((x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)), 1))四、Concat
和torch.cat功能几乎一致:
class Concat(nn.Module):"""Concatenate a list of tensors along dimension."""def __init__(self, dimension=1):"""Concatenates a list of tensors along a specified dimension."""super().__init__()self.d = dimensiondef forward(self, x):"""Forward pass for the YOLOv8 mask Proto module."""return torch.cat(x, self.d)五、Detect
yolov8的检测头:
class Detect(nn.Module):"""YOLOv8 Detect head for detection models."""dynamic = False # force grid reconstructionexport = False # export modeshape = Noneanchors = torch.empty(0) # initstrides = torch.empty(0) # initdef __init__(self, nc=80, ch=()):"""Initializes the YOLOv8 detection layer with specified number of classes and channels."""super().__init__()self.nc = nc # number of classesself.nl = len(ch) # number of detection layersself.reg_max = 16 # DFL channels (ch[0] // 16 to scale 4/8/12/16/20 for n/s/m/l/x)self.no = nc + self.reg_max * 4 # number of outputs per anchorself.stride = torch.zeros(self.nl) # strides computed during buildc2, c3 = max((16, ch[0] // 4, self.reg_max * 4)), max(ch[0], min(self.nc, 100)) # channelsself.cv2 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c2, 3), Conv(c2, c2, 3), nn.Conv2d(c2, 4 * self.reg_max, 1)) for x in ch)self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c3, 3), Conv(c3, c3, 3), nn.Conv2d(c3, self.nc, 1)) for x in ch)self.dfl = DFL(self.reg_max) if self.reg_max > 1 else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):"""Concatenates and returns predicted bounding boxes and class probabilities."""shape = x[0].shape # BCHWfor i in range(self.nl):x[i] = torch.cat((self.cv2[i](x[i]), self.cv3[i](x[i])), 1)if self.training:return xelif self.dynamic or self.shape != shape:self.anchors, self.strides = (x.transpose(0, 1) for x in make_anchors(x, self.stride, 0.5))self.shape = shapex_cat = torch.cat([xi.view(shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in x], 2)if self.export and self.format in ('saved_model', 'pb', 'tflite', 'edgetpu', 'tfjs'): # avoid TF FlexSplitV opsbox = x_cat[:, :self.reg_max * 4]cls = x_cat[:, self.reg_max * 4:]else:box, cls = x_cat.split((self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1)dbox = dist2bbox(self.dfl(box), self.anchors.unsqueeze(0), xywh=True, dim=1) * self.stridesif self.export and self.format in ('tflite', 'edgetpu'):# Normalize xywh with image size to mitigate quantization error of TFLite integer models as done in YOLOv5:# https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/0c8de3fca4a702f8ff5c435e67f378d1fce70243/models/tf.py#L307-L309# See this PR for details: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/pull/1695img_h = shape[2] * self.stride[0]img_w = shape[3] * self.stride[0]img_size = torch.tensor([img_w, img_h, img_w, img_h], device=dbox.device).reshape(1, 4, 1)dbox /= img_sizey = torch.cat((dbox, cls.sigmoid()), 1)return y if self.export else (y, x)def bias_init(self):"""Initialize Detect() biases, WARNING: requires stride availability."""m = self # self.model[-1] # Detect() module# cf = torch.bincount(torch.tensor(np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0]).long(), minlength=nc) + 1# ncf = math.log(0.6 / (m.nc - 0.999999)) if cf is None else torch.log(cf / cf.sum()) # nominal class frequencyfor a, b, s in zip(m.cv2, m.cv3, m.stride): # froma[-1].bias.data[:] = 1.0 # boxb[-1].bias.data[:m.nc] = math.log(5 / m.nc / (640 / s) ** 2) # cls (.01 objects, 80 classes, 640 img)