故障分析
Ping不通是指Ping报文在网络中传输,由于各种原因(如链路故障、ARP学习失败等)而接收不到所有Ping应答报文的现象。
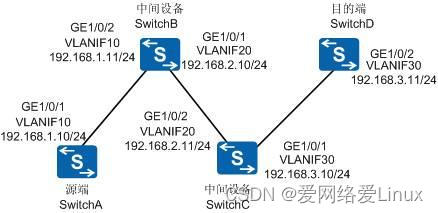
如图1-1所示,以一个Ping不通的尝试示例,介绍Ping不通故障的定位思路。
图1-1 Ping不通故障组网图
故障现象
SwitchA Ping不通SwitchD。
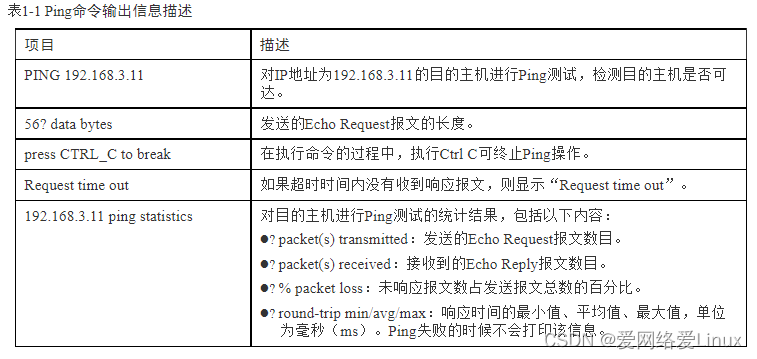
ping 192.168.3.11??
PING 192.168.3.11: 56? data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
??? Request time out
??? Request time out
??? Request time out
??? Request time out
??? Request time out
?
? --- 192.168.3.11 ping statistics ---
??? 5 packet(s) transmitted
??? 0 packet(s) received
??? 100.00% packet loss
故障定位:
如图1-1所示,Ping操作涉及三个角色:
l?? 源端:Ping报文发起端SwitchA
l?? 中间设备:SwitchB和SwitchC
l?? 目的端:Ping报文接收端SwitchD
当执行Ping命令不通时,首先在SwitchA上使用tracert命令确定源端到目的端之间的故障节点,进而缩小故障定位范围。
tracert 192.168.3.11
traceroute to 192.168.3.11 (192.168.3.11), max hops: 30, packet length: 40, press CTRL_C to break
1 * * *
2 * * *
3 * * *
4 * * *
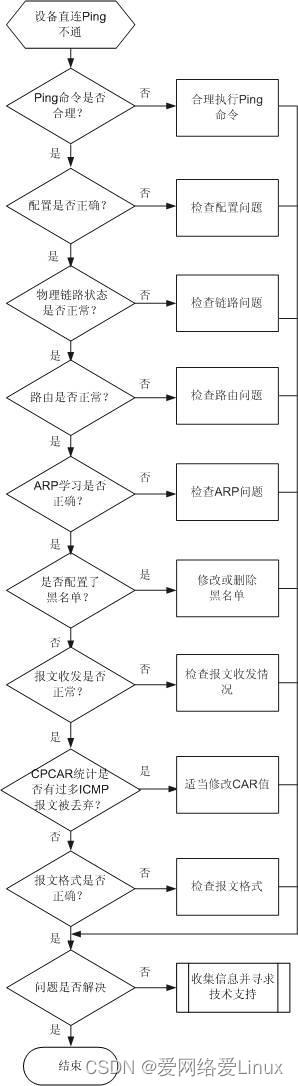
# 假设故障发生在SwitchA和SwitchB之间,即SwitchA Ping SwitchB的IP地址192.168.1.11不通,定位流程如下面的流程图所示(其他直连网段Ping不通的故障处理方法类似)
# 假设SwitchA Ping SwitchB的IP地址192.168.1.11能通,SwitchB Ping SwitchC的IP地址192.168.2.21能通,但是SwitchA Ping SwitchC的IP地址192.168.2.21不通,这种情况需要在SwitchA、SwitchB和SwicthC上做ICMP报文的流量统计,进而判断流量是在哪丢弃的。