自定义频率类
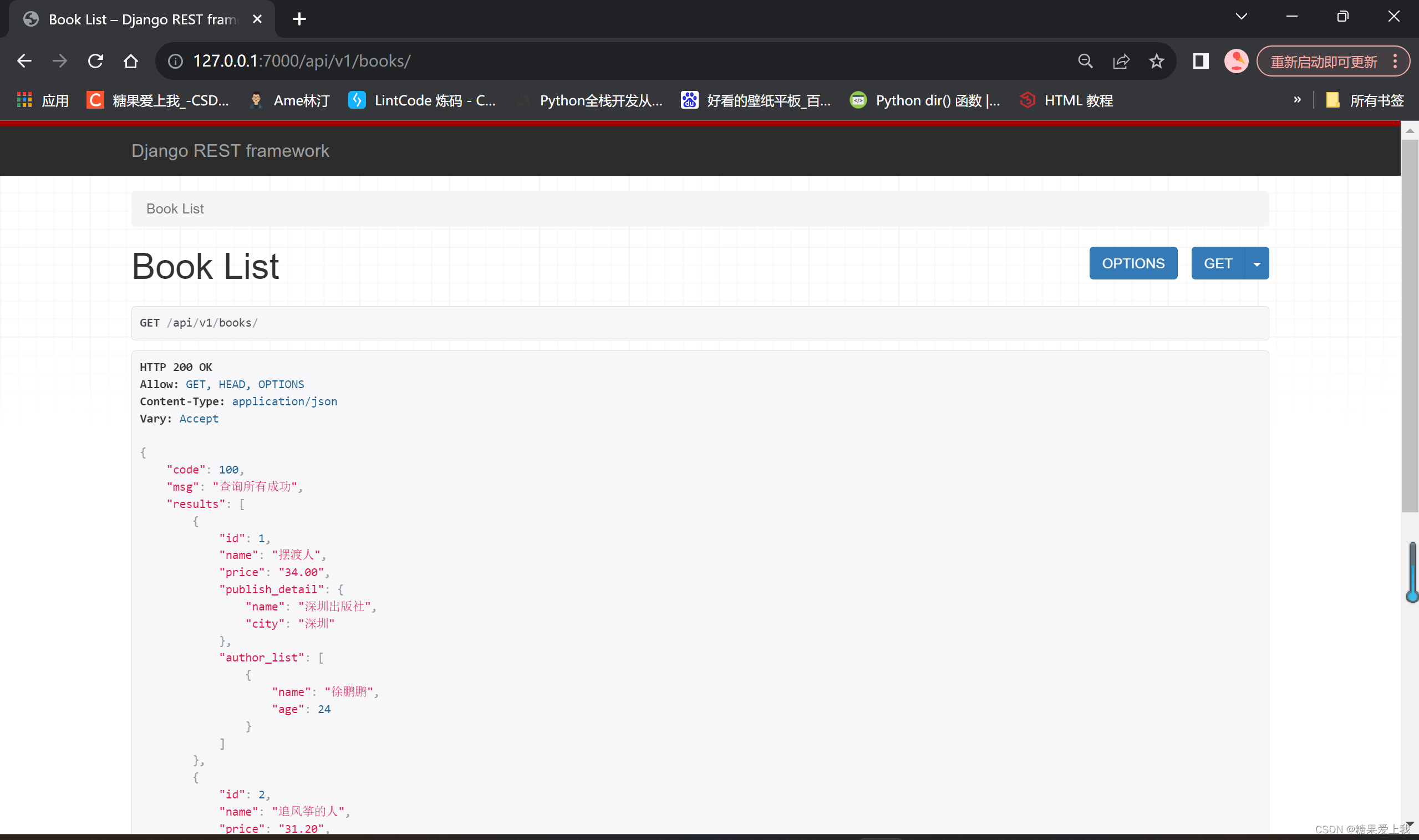
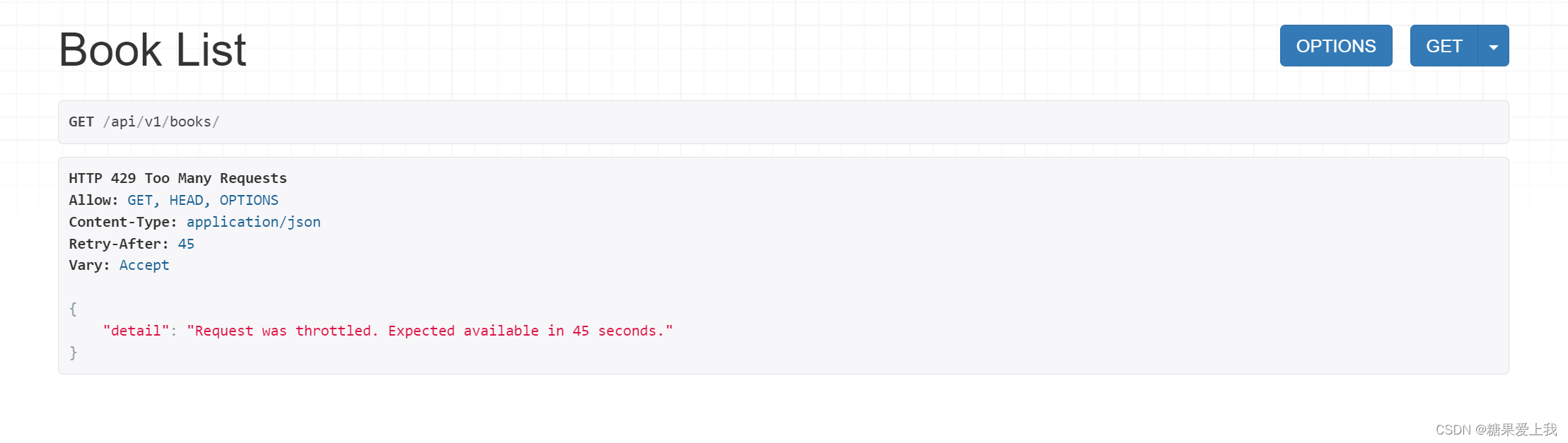
# throttling 频率限制 # 简单方案 from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle class CommonThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):rate = '3/m'def get_cache_key(self, request, view):ip = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')return ip# 复杂方案---》通用方案---》后期任何框架都可以使用这个逻辑 from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle import time class MyThrottling(BaseThrottle):VISIT_RECORD = {} # {192.168.1.11:[时间2,时间1],192.168.1.99:[时间3,时间2,时间1]}def __init__(self):self.history = Nonedef allow_request(self, request, view):ip = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR') # 取出访问者ipctime = time.time()if ip not in self.VISIT_RECORD:self.VISIT_RECORD[ip] = [ctime, ]return Trueself.history = self.VISIT_RECORD.get(ip) # 访问时间列表while self.history and ctime - self.history[-1] > 3600:self.history.pop()if len(self.history) < 5:self.history.insert(0, ctime)return Trueelse:return Falsedef wait(self):ctime = time.time()return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])# exceptions 异常处理自己写个函数,处理drf异常和自己的异常 from rest_framework.views import exception_handler from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework.exceptions import Throttleddef common_exception_handler(exc, context):res = exception_handler(exc, context) # 处理drf异常处理if res:if isinstance(exc, Throttled):return Response({'code': 20016, 'msg': '使用过于频繁,稍后再试:%s' % res.data.get('detail')})else:detail = res.data.get('detail') or res.data or "drf异常,请联系系统管理员"return Response({'code': 999, 'msg': detail})# return reselse: # 如果没值,说明是自己的异常# exc 错误对象,判断具体是什么错误 :数据错误, 除以0,。。。。print(type(exc))if isinstance(exc, ZeroDivisionError):return Response({'code': 20001, 'msg': '不能除以0'})if isinstance(exc, IndexError):return Response({'code': 20002, 'msg': '超长了'})else:return Response({'code': 888, 'msg': '操作失败,请稍后再试:%s' % str(exc)})# common 更改显示格式 from rest_framework.mixins import ListModelMixin from rest_framework.response import Responseclass CommonListModelMixin(ListModelMixin):def list(self, request, *args, **kwargs):res = super().list(request, *args, **kwargs)return Response({'code': 100, 'msg': '查询所有成功', 'results': res.data})# serializer.py 序列化类 from rest_framework import serializers from .models import Book class BookSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):class Meta:model = Bookfields = ['id', 'name', 'price', 'publish', 'authors', 'publish_detail', 'author_list']extra_kwargs = {'publish': {'write_only': True},'authors': {'write_only': True},'publish_detail': {'read_only': True},'author_list': {'read_only': True},}# views.py 视图层 # 查询所有图书 from .models import Book from .serializer import BookSerializer from .common import CommonListModelMixin as ListModelMixin from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSetfrom .throttling import MyThrottling class BookView(GenericViewSet, ListModelMixin):queryset = Book.objects.all()serializer_class = BookSerializer# throttle_classes = [CommonThrottling]throttle_classes = [MyThrottling]# urls 路由 from . import views from rest_framework.routers import SimpleRouter, DefaultRouterrouter = SimpleRouter() router.register('books', views.BookView, 'books') urlpatterns = [ ] urlpatterns += router.urls# 总路由 from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path,includeurlpatterns = [path('admin/', admin.site.urls),path('api/v1/', include('app01.urls')), ]
频率源码执行流程
# 1 APIView--->dispatch--->self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)--->self.check_throttles(request) # 2 APIView的check_throttlesdef check_throttles(self, request):throttle_durations = []# self.get_throttles() 是视图类中配置的一个个频率类的对象列表for throttle in self.get_throttles():# throttle.allow_request 返回false ,说明到频率了if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):# 到了频率,走了它# throttle.wait() 返回还剩多长时间能访问throttle_durations.append(throttle.wait())# 被频率限制住了,它就有值if throttle_durations:durations = [duration for duration in throttle_durationsif duration is not None]#duration=[35,54]# duration=[]duration = max(durations, default=None)# duration=56# duration=Noneself.throttled(request, duration)# 3 self.throttled(request, duration) ---》APIViewdef throttled(self, request, wait):# wait=56或Noneraise exceptions.Throttled(wait)# 4 Throttled类实例化得到对象,传了数字进去 from rest_framework.exceptions import Throttled 内部 拼接错误信息--》但是是英文的,如果要换成中文 # 5 超过了频率,就不返回False了,直接抛异常raise Throttled(None, '超过了限制,还剩:%s 时间' % self.wait())
SimpleRateThrottle 执行流程
# 1 咱们写的 CommonThrottling没有写allow_request class CommonThrottling(SimpleRateThrottle):rate = '3/m'def get_cache_key(self, request, view):return request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')# 2 一定是 SimpleRateThrottle 写了,完成了频率校验 # 3 SimpleRateThrottle--》allow_request---》跟咱们的逻辑一样def allow_request(self, request, view):if self.rate is None: # 自己写了 '3/m'return True# 返回了 ip地址,self.key 就是访问者的ip地址self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)if self.key is None:return True# self.history 当前ip,访问的时间列表,self.key是ip# self.cache 缓存,去缓中,根据ip,取出访问者时间列表,如果没有就是 []self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])# 当前时间self.now = self.timer() # timer = time.time# self.now 当前时间,# self.duration 就是60while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:self.history.pop()# self.num_requests 是3if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:return self.throttle_failure()return self.throttle_success()# 4 self.duration 就是60 self.num_requests 是3 # 3 60 self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate) #5 self.parse_rate(self.rate)def parse_rate(self, rate):if rate is None: # '3/minute'return (None, None)# 3 period=mmmmmnum, period = rate.split('/')# 3num_requests = int(num)duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]# duration 是60,# num_requests 是3return (num_requests, duration)
drf回顾之入门规范
# 前后端开发模式:混合开发(不分离),前后端分离
# API接口
# 接口测试:postman
测试:接口测试: jmeter是java开发的软件
# restful规范:10条规范
drf 帮助我们快速实现符合restful规范的接口
# APIView执行流程:重写了as_view,重写了dispatch
1、去除了csrf认证
2、包装了新的request
3、三大认证 --根据请求方式,执行视图类的方法(认证组件、权限组件、频率组件)
4、处理了全局异常
# Request 类的对象
1、多了data
2、重写了 __getattr__ 对象.属性触发
去旧的request中找:通过反射 getattr(self._request,'path')
3、以后用起来跟之前一样
4、query_params
drf回顾之序列化组件
# 序列化:
1、写一个类,继承(序列化类)
2、写字段,需要跟表中有对应关系(手动对应:Serializer 自动对应:ModelSerializer)
3、视图类中使用:# 多条Queryset对象:使用orm查询出来的 # django执行原生sql-->使用序列化类完成序列化 ser=BookSerializer(instnce=qs,many=True) ser.data+Response# 反序列化:
1、写一个类,继承(序列化类)
2、写字段,需要跟表中有对应关系(手动: Serializer 自动:ModelSerializer)
3、视图类中使用修改ser=BookSerializer(instance=对象,data=request.data)
新增ser=BookSerializer(data=request.data)
ser.is_valid()
ser.save()--->触发序列化类的:update,create# 序列化和反序列化用在一起:
read_only 和 write_only
extra_kwargs={ }# 校验:三层
Serializer-重写 update和create
ModelSerializer-重写字段-class Meta: model 、fields 、extra_kwargsclass BookSerializer(serializers.Serializer): # 手动name = serializers.CharField() # 公共的price = serializers.CharField() # 公共的publish = serializers.IntegerField(write_only=True) # 只用来做反序列化authors = serializers.ListField(write_only=True) # 只用来做反序列化publish_detail = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True) # 只用来做序列化author_list = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True) # 只用来做序列化def get_publish_detail(self, obj):return {'name': obj.publish.name, 'city': obj.publish.city}def get_author_list(self, obj):l = []for author in obj.authors.all():l.append({'name': author.name, 'age': author.age})return ldef create(self, validated_data):# {name,price,publish:1,authors:[1,2]}authors = validated_data.pop('authors')book = Book.objects.create(name=validated_data.get('name'), price=validated_data.get('price'),publish_id=validated_data.get('publish'))book.authors.add(*authors)return bookdef update(self, instance, validated_data):# {name,price,publish:1,authors:[1,2]}authors = validated_data.pop('authors')validated_data['publish_id'] = validated_data.pop('publish')for key in validated_data:setattr(instance, key, validated_data[key])instance.save()# 先清空在放入# instance.authors.clear()# instance.authors.add(*authors)# 直接存instance.authors.set(authors)return instancefrom rest_framework import serializers from .models import Book class BookSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):class Meta:model = Bookfields = ['id', 'name', 'price', 'publish', 'authors', 'publish_detail', 'author_list']extra_kwargs = {'publish': {'write_only': True},'authors': {'write_only': True},'publish_detail': {'read_only': True},'author_list': {'read_only': True},}# source定制:表中字段,表中方法,跨表
#1 修改字段,映射字段:
publish_name表中不存在
publish_name = serializers.CharField(source='name')#2 修改字段,映射方法:
sb_name是表模型中一个方法
name = serializers.CharField(source='sb_name')#3 修改字段,跨表查询
book表中可以链表查询
publish=models.ForeignKey(to='Publish.name')# 定制返回格式:序列化
表模型中写方法
序列化类中:SerializerMethod--》get_字段名)# models.py from django.db import models class Book(models.Model):name = models.CharField(max_length=32)price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2)publish = models.ForeignKey(to='Publish', on_delete=models.CASCADE)authors = models.ManyToManyField(to='Author')def __str__(self):return self.name# def book_name(self):# return self.name+'sb'# def publish_detail(self):# return {'name': self.publish.name, 'city': self.publish.city}## def author_list(self):# l = []# for author in self.authors.all():# l.append({'name': author.name, 'age': author.age})# serializer.py class BookSerializer(serializers.Serializer):name = serializers.CharField()price = serializers.CharField()#方案一:在表模型中写方法,在序列化类中做映射# publish_detail = serializers.DictField() # publish_detail 会映射表模型中 publish_detail方法,方法返回值是 字典,用DictField接收# author_list = serializers.ListField()#方案二:在序列化类中写 SerializerMethodField# 只要写了这个字段类SerializerMethodField,必须配合一个方法:get_字段名,这个方法返回什么,前端这个字段就显示什么publish_detail = serializers.SerializerMethodField()def get_publish_detail(self, obj):return {'name': obj.publish.name, 'city': obj.publish.city}author_list = serializers.SerializerMethodField()def get_author_list(self, obj):l = []for author in obj.authors.all():l.append({'name': author.name, 'age': author.age})return l
# BookReadSerializer
BookWriteSerializer
LoginSerializerget_serializer_class()--影响:list retrieve update create 自己写的
get_queryset()--影响:list retrieve update create delete
get_object--影响:list,retrieve,update,delete,不会影响到create
class BookView(ModelViewSet):query_set=xxserializer_class=BookReadSerializerdef get_serializer_class(self): # 重写 get_serializer_class 方法if self.action=='list' or self.action=='retrieve':# if self.request.method=='get':# get_serializer() 获取使用哪个序列化类return BookReadSerializerelif self.action=='login':return LoginSerializerelse:return BookWriteSerializer def get_queryset(self):pass# 返回所有数据,但会影响 list,retrieve,update,delete ,自己写的@action(methods=['POST'],detail=False)def login(self,requset):self.get_serializer() #让它拿到 LoginSerializerself.get_object()self.get_queryset
drf回顾之请求和响应
# 请求:
Request源码
能够解析的编码格式:默认三种:json,urlencoded,form-data1、视图类上配置
2、settings.py 配置文件中配置
from rest_framework.parsers import JSONParser, FormParser, MultiPartParser # JSONParser:json # FormParser:urlencoded # MultiPartParser:form-data class TestView(APIView):# parser_classes = [JSONParser]parser_classes = [JSONParser,FormParser]def post(self, request):print(request.data)return Response('ok')setting.py # 所有drf的配置,都要写在REST_FRAMEWORK 字典中REST_FRAMEWORK = {'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': [# 'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser',# 'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser','rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser',],}views.py class TestView(APIView):parser_classes = [JSONParser,FormParser]# 响应:
*Response源码
*实例化时可传入的参数:data=None----响应体 status=None---http响应状态码 import status 状态码 headers=None---响应头 content_type=None---响应编码格式list方法: res=super().list(request) # res 就是Response 类的对象 res.status res.data res.headers res.data [{},{},{}] {code:100,msg:成功,results:res.data} # 响应编码格式
drf回顾之视图组件
# APIView:
1、继承了View
2、重写了 as_view
3、重写了 dipatch---相当于给之前的视图类的方法加了装饰器
4、写跟请求方式同名的方法:get,post,delete,put,get
# GenericAPIView:
*继承了APIView*类属性: queryset =Book.object.all().filter(is_delete=False) # self.get_queryset拿到要序列化的数据 lookup_field = 'pk' # 分组,转换器出来的参数 filter_backends # 过滤和排序 pagination_class # 分页*方法: get_serializer_class # 通过重写控制视图类的方法使用哪个序列化类 serializer_class # 获取序列化类,list,retrieve(get_object间接),put,create get_queryset # 要序列化的总数据或单条查询的数据源 get_object # 获取单条,通过get_queryset拿到的 filter_queryset # 过滤使用,必须配合list使用,视图类中重写它可以完成过滤,就不用配置过滤类了 get_paginated_response # 获取分页后的返回数据,必须配合listdef get_paginated_response(self, data):assert self.paginator is not Nonereturn Response({'code': 100,'msg': 'asdfasfasfdasf','next': self.paginator.get_next_link(),'pre': self.paginator.get_previous_link(),'result': data})# 5个视图扩展类--必须搭配GenericAPIView
ListModelMixin # 过滤,排序,分页 def list(self, request, *args, **kwargs):queryset = self.filter_queryset(self.get_queryset())page = self.paginate_queryset(queryset) # 处理了分页if page is not None: # 如果没有分页,正常返回serializer = self.get_serializer(page, many=True)return self.get_paginated_response(serializer.data)serializer = self.get_serializer(queryset, many=True)return Response(data=serializer.data)RetrieveModelMixin def retrieve(self, request, *args, **kwargs):instance = self.get_object() # 序列化单挑数据--》重写serializer = self.get_serializer(instance) # 重写--》使用哪个序列化类return Response(serializer.data) CreateModelMixin def create(self, request, *args, **kwargs):serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data) # 重写serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)self.perform_create(serializer) #做了真正的保存serializer.save(),重写return Response(serializer.data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED) def perform_create(self, serializer): #可以重写serializer.save()DestroyModelMixin def destroy(self, request, *args, **kwargs):instance = self.get_object() # 通过重写它,决定删除谁self.perform_destroy(instance) # 重写-软删除,不在数据库删除,is_delete# 设置为True,以后要序列化的时候,不查出来了return Response(status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT) def perform_destroy(self, instance):instance.delete()UpdateModelMixin def update(self, request, *args, **kwargs):instance = self.get_object()serializer = self.get_serializer(instance, data=request.data)serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)self.perform_update(serializer)return Response(serializer.data) def perform_update(self, serializer):serializer.save()# views.py from rest_framework.mixins import CreateModelMixin, ListModelMixin, RetrieveModelMixin, UpdateModelMixin, \DestroyModelMixinclass BookView(GenericAPIView, CreateModelMixin, ListModelMixin):queryset = Book.objects.all()serializer_class = BookSerializerdef get(self, request):return super().list(request)def post(self, request):# 做保存,加了这一句---》目的是:子类可以重写,增强扩展性# self.perform_create(serializer)return super().create(request)class BookDetailView(GenericAPIView, RetrieveModelMixin, DestroyModelMixin, UpdateModelMixin):queryset = Book.objects.all()serializer_class = BookSerializerdef put(self, request, *args, **kwargs):return super().update(request, *args, **kwargs)def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):return super().retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs)def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):return super().destroy(request, *args, **kwargs)# 9 个视图子类--重写 get_serializer_class,get_queryset,get_object
ListAPIView:GenericAPIView+ListModelMixin # 重写:list,get RetrieveAPIView # 重写retrieve,get CreateAPIView # 重写create,perform_create UpdateAPIView DestroyAPIView ListCreateAPIView RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView, RetrieveDestroyAPIView, RetrieveUpdateAPIView# views.py from rest_framework.generics import CreateAPIView, ListAPIView from rest_framework.generics import RetrieveAPIView, DestroyAPIView, UpdateAPIView from rest_framework.generics import ListCreateAPIView from rest_framework.generics import RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView, RetrieveDestroyAPIView, RetrieveUpdateAPIView # from rest_framework.generics import DestroyUpdateAPIView # 一般不存在,所以就没有# 实现新增,查所有和查询一条 class BookView(ListCreateAPIView):# 配置两个类属性queryset = Book.objects.all()serializer_class = BookSerializerclass BookDetailView(RetrieveAPIView):queryset = Book.objects.all()serializer_class = BookSerializer# 视图集
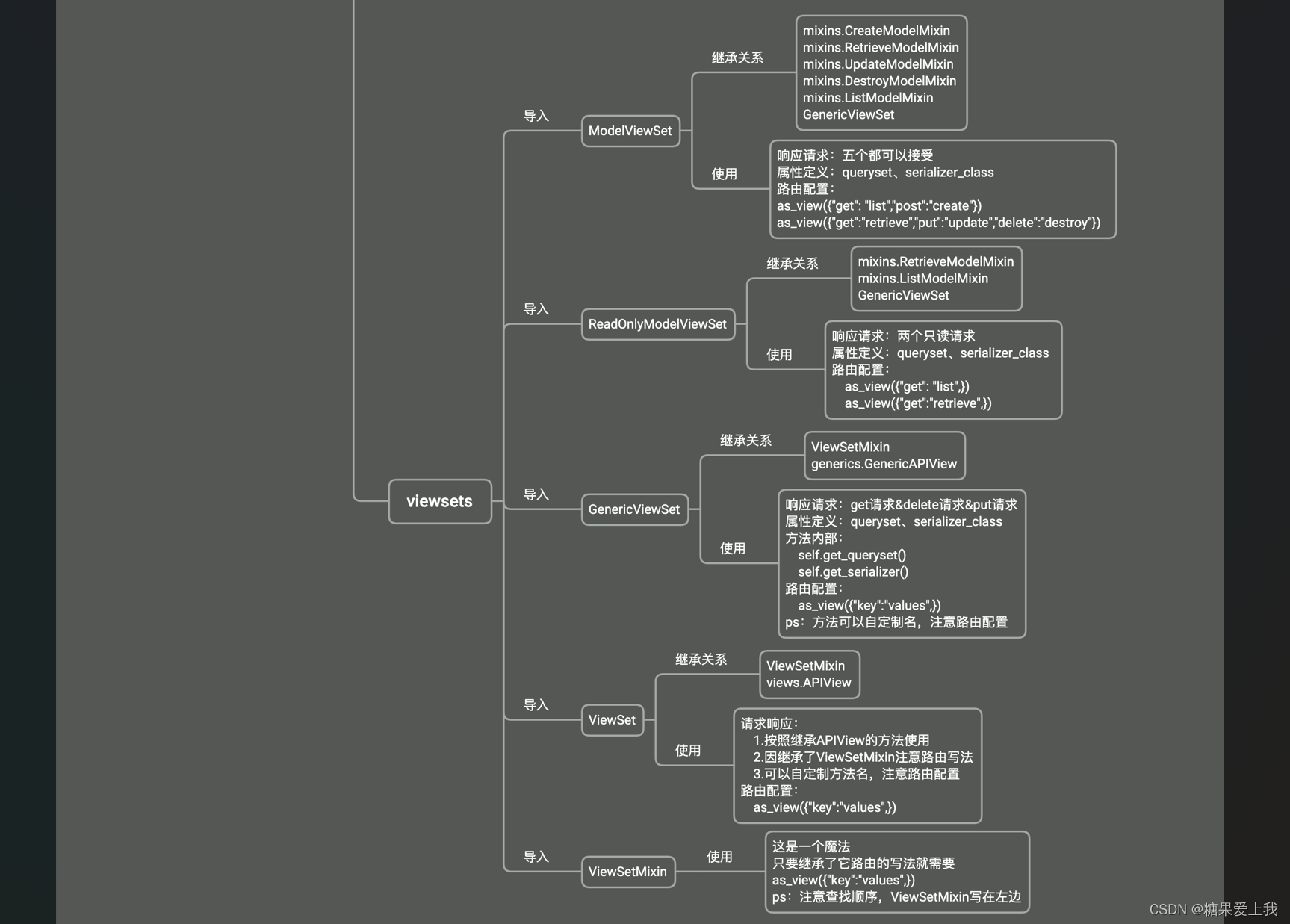
以后写视图类: 一般不会5个都写
比如只想写 查询所有和删除一条--继承--》GenericViewSet,ListModelMixinViewSetMixin # 路由写法变了---》多个视图类可以放到一起---》一个视图类中可以放多个方法 GenericViewSet ViewSet ModelViewSet # 有get,post这些方法吗?没有,只有list,create。。这些 # 重写:get_serializer_class,get_queryset,perform_destroy # 重写list,分页返回格式 ReadOnlyModelViewSet:只有 list,retrieve
drf回顾之路由组件
# 视图类没有继承了ViewSetMixin,路由写法跟之前一样
path('books/', views.BookView.as_view())# 映射写法:ViewSetMixin
SimperRouter和DefaultRouter 实例化
from rest_framework.routers import SimpleRouter,DefaultRouter router = SimpleRouter() # router = DefaultRouter() router.register('books', views.BookView, 'books') urlpatterns = [# path('', include(router.urls)), ] urlpatterns += router.urls# 视图类中自己的方法,再做映射--action装饰器
action装饰器:methods,detail
@action(methods=['POST'],detail=False,) def login(self,request):return Response('login')
drf回顾之三大认证
# 认证类的使用
# 权限类:
登录成功后,有没有权限---》request.user拿到登录用户,判断权限
# 频率类:
ip,用户id
用户访问记录:存在缓存中,默认在内存# auth.py 认证类 from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed from .models import UserTokenclass LoginAuth(BaseAuthentication):def authenticate(self, request):token = request.query_params.get('token') or request.META.get('HTTP_TOKEN')user_token = UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()if user_token:user = user_token.userreturn user, user_tokenelse:raise AuthenticationFailed("您没有登录")# permission.py 权限类 from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission class CommonPermission(BasePermission):def has_permission(self, request, view):try:user_type = request.user.user_typeif user_type == 2: # 只有超级管理员能访问,其他人都不能访问return Trueelse:self.message = '您是:%s,您没有权限操作这个' % request.user.get_user_type_display()return Falseexcept Exception as e: if 'login' in request.path: # 未登录用户也没有权限return Trueelse:self.message = '您没有登录,您没有权限操作这个'return False# throttling.py 频率类 from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottleclass CommonThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):rate = '3/m' def get_cache_key(self, request, view):ip = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')return ip# setting.py REST_FRAMEWORK = {# 全局配置登录认证'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ['app01.auth.LoginAuth'], # 认证组件'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': ['app01.permission.CommonPermission'], # 权限组件'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': ['app01.throttling.CommonThrottle'], # 频率组件 }# views.py 登录入口 1、拿到验证码 class UserView(ViewSet):authentication_classes = []permission_classes = []throttle_classes = []@action(methods=['POST'], detail=False)def login(self, request):username = request.data.get('username')password = request.data.get('password')user = User.objects.filter(name=username, password=password).first()if user:token = str(uuid.uuid4())UserToken.objects.update_or_create(defaults={'token': token}, user_id=user.pk)return Response({'code': '100', 'msg': '登录成功', 'token': token})else:return Response({'code': '101', 'msg': '用户名或密码错误'})class BookView(ViewSetMixin, ListCreateAPIView):authentication_classes = [LoginAuth] # 验证是否登录queryset = Book.objects.all()serializer_class = BookSerializer class BookDetailView(GenericViewSet, DestroyModelMixin, RetrieveModelMixin, UpdateModelMixin):queryset = Book.objects.all()serializer_class = BookSerializer
drf回顾之排序过滤和分页
-排序:内置排序 list接口,继承GenericAPIView+list
-filter_backends 配置 排序类
-ordering=id,-price
-过滤:
-内置
-第三方
-自定义:写个类,继承:BaseFilterBackend,重写filter_queryset在内部完成过滤,返回过滤后的qs对象
-过滤,排序可以连用,多个过滤也可以连用- list接口+GenericAPIView 配置分页类
- 三种分页方式
-都有自己的类属性
-继承APIView实现分页
from rest_framework.viewsets import ViewSet
from rest_framework.mixins import ListModelMixin,RetrieveModelMixin
from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
from . import pagination
class BookView(ViewSet):
def list(self, request):
book_list = Book.objects.all()
# 调用咱们写的分页类对象的paginate_queryset方法返回了 分页后的qs对象
# pagenation = pagination.CommonPageNumberPagination()
# pagenation = pagination.CommonLimitOffsetPagination()
pagenation = pagination.CommonCursorPagination()
page = pagenation.paginate_queryset(book_list, request, self)
ser = BookSerializer(instance=page, many=True)
# return pagenation.get_paginated_response(ser.data)
# CommonPageNumberPagination 返回格式
# return Response({'code': 100,
# 'msg': '查询成功',
# 'count': pagenation.page.paginator.count,
# 'next': pagenation.get_next_link(),
# 'pre': pagenation.get_previous_link(),
# 'result': ser.data})
# CommonLimitOffsetPagination
# return Response({
# 'code': 100,
# 'msg': '查询成功',
# 'count': pagenation.count,
# 'next': pagenation.get_next_link(),
# 'pre': pagenation.get_previous_link(),
# 'result': ser.data})# CommonCursorPagination
return Response({
'code': 100,
'msg': '查询成功',
'next': pagenation.get_next_link(),
'pre': pagenation.get_previous_link(),
'result': ser.data})
drf回顾之全局异常
-全局异常:
-写个函数,完成处理,配置到配置文件---》以后只要出了异常,都会走咱么的函数