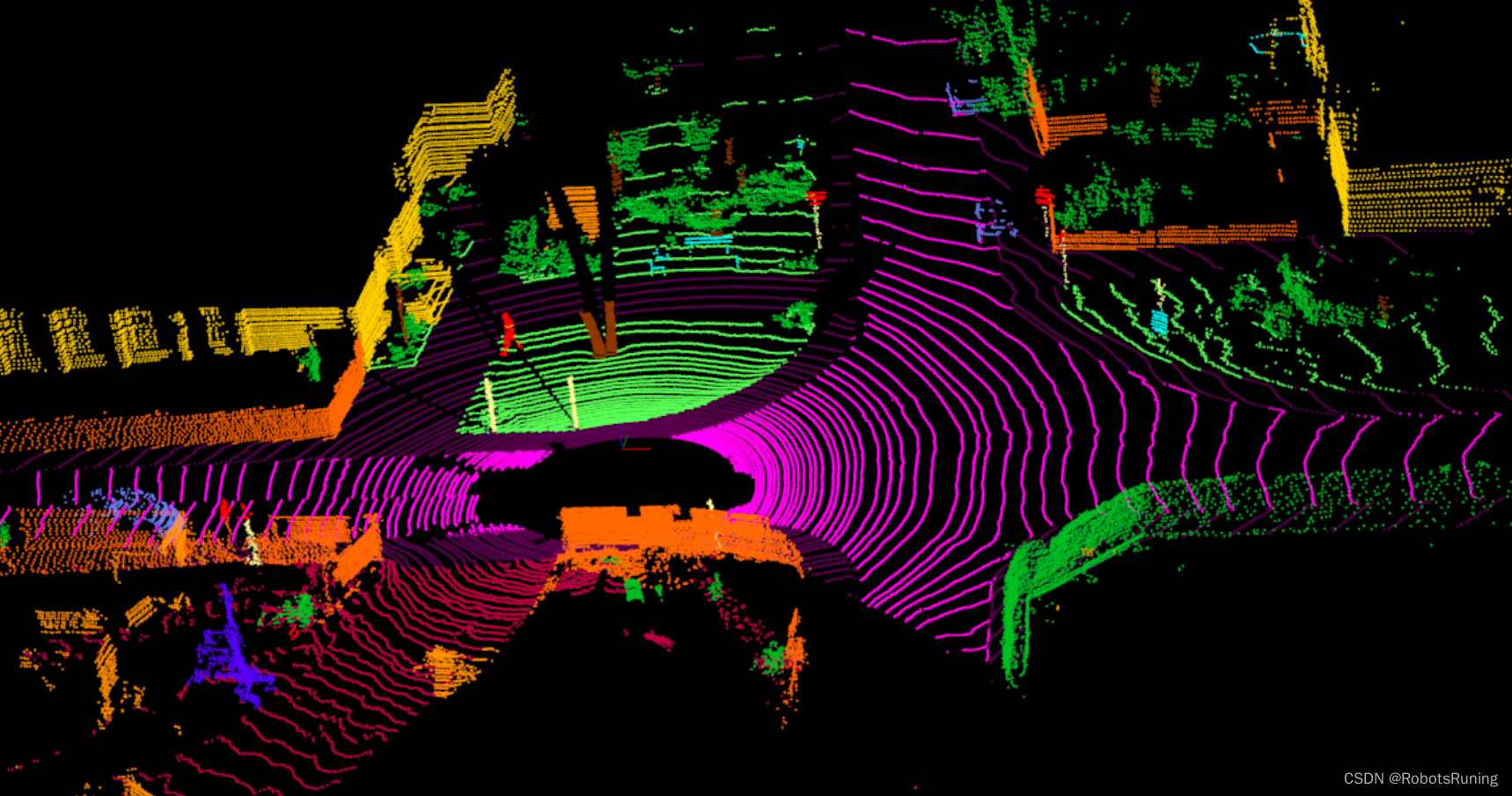
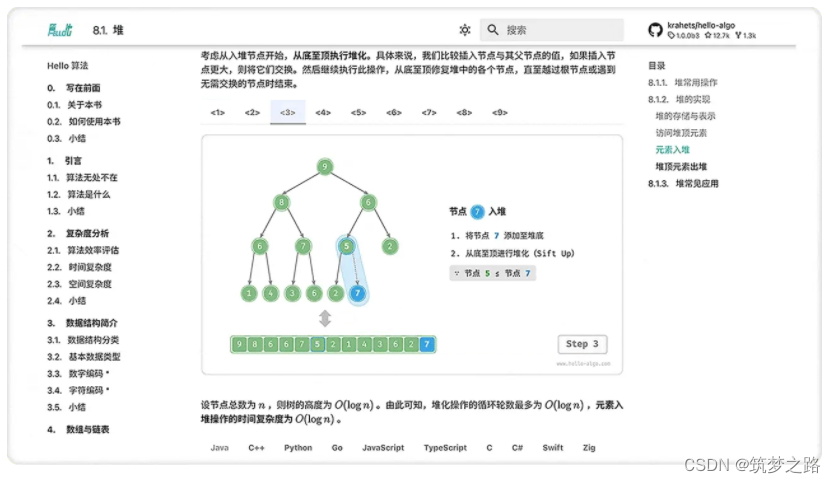
这段代码是一个C++程序,用于处理来自KITTI数据集的激光雷达(LiDAR)扫描数据。程序主要实现以下功能:
1. **读取和解析命令行参数**:使用Boost库中的`program_options`模块来定义和解析命令行参数。这包括扫描文件路径、模型路径以及是否启用详细模式(verbose)。
2. **处理KITTI数据集中的LiDAR扫描数据**:程序遍历指定KITTI数据集目录中的LiDAR扫描数据(`.bin`格式)。这些数据包含了LiDAR扫描的点云信息。
3. **LiDAR数据的语义分割**:使用`rangenet_lib`库创建一个网络模型来进行语义分割。这个库用于为LiDAR点云数据提供语义标签,例如将点分类为车辆、行人、道路等。
4. **读取和处理每个扫描文件**:对每个扫描文件,程序读取点云数据,并使用创建的网络模型进行推理(infer),得到每个点的语义标签。
5. **转换点云数据**:获取转换后的点云数据和颜色掩膜(color mask),这些颜色表示不同的语义类别。
6. **保存语义分割结果**:将每个点的坐标和对应的颜色标签保存到文本文件中。这些文件用于可视化或进一步分析处理。
7. **可视化(可选)**:如果启用了详细模式(verbose),则使用OpenCV的可视化工具(`cv::viz`)来显示语义分割后的点云。
总的来说,这个程序的主要作用是处理KITTI数据集中的LiDAR点云数据,通过使用语义分割网络对每个点进行分类,然后将分类结果保存并(可选地)进行可视化展示。这对于自动驾驶、机器人导航等领域的研究和应用是非常有用的。
1. infer中的内容
/* Copyright (c) 2019 lifeiya, Chongqing University.** This file is part of advanced rangenet_lib.**/// opencv stuff
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/viz.hpp>// c++ stuff
#include <chrono>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>// net stuff
#include <selector.hpp>
namespace cl = rangenet::segmentation;// boost
#include <boost/program_options.hpp>
namespace po = boost::program_options;
#include <boost/filesystem.hpp>
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;typedef std::tuple< u_char, u_char, u_char> color;int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) {// define optionsstd::string scan;std::string path;std::string backend = "tensorrt";// 如果verbose为true,则程序会输出更多的运行过程信息,如果为false,则只输出最基本的信息。bool verbose = false;std::ostringstream scanStream;std::string kitti_num = "10"; // Replace "01" with the actual value you wantstd::string base_path = "/home/fairlee/dataset/KITTI/sequences_kitti_00_21/" + kitti_num + "/velodyne/";std::string file_extension = ".bin";// Calculate the number of files in the directoryint N = std::distance(fs::directory_iterator(base_path), fs::directory_iterator{});for(int file_num = 1000; file_num < N; ++file_num) {// cout<<"正在处理-----"<<file_num<<"/"<< N <<"数据"<<endl;std::cout << std::left << "正在处理 " <<kitti_num<< " 数据集中的第: "<< file_num << " / " << N << " 帧数据" << std::endl;// Parse optionstry {po::options_description desc{"Options"};desc.add_options()("help,h", "Help screen")("scan,s", po::value<std::string>(&scan),"LiDAR scan to infer. No Default")("path,p", po::value<std::string>(),"Directory to get the inference model from. No default")("verbose,v", po::bool_switch(),"Verbose mode. Calculates profile (time to run)");po::variables_map vm;po::store(parse_command_line(argc, argv, desc), vm);po::notify(vm);std::cout << std::setfill('=') << std::setw(80) << "" << std::endl;if (vm.count("help")) {std::cout << desc << std::endl;return 0;}std::ostringstream scanStream;scanStream << base_path << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(6) << file_num << file_extension;scan = scanStream.str();// make defaults count, parameter check, and printpath = "/home/fairlee/darknet53/";if (vm.count("verbose")) {verbose = vm["verbose"].as<bool>();std::cout << "verbose: " << verbose << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "verbose: " << verbose << ". Using default!" << std::endl;}std::cout << std::setfill('=') << std::setw(80) << "" << std::endl;} catch (const po::error &ex) {std::cerr << ex.what() << std::endl;return 1;}// create a networkstd::unique_ptr<cl::Net> net = cl::make_net(path, backend);// set verbositynet->verbosity(verbose);// predict each imagestd::cout << std::setfill('=') << std::setw(80) << "" << std::endl;std::cout << "Predicting image: " << scan << std::endl;// Open a scanstd::ifstream in(scan.c_str(), std::ios::binary);if (!in.is_open()) {std::cerr << "Could not open the scan!" << std::endl;return 1;}in.seekg(0, std::ios::end);uint32_t num_points = in.tellg() / (4 * sizeof(float));in.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);std::vector<float> values(4 * num_points);in.read((char*)&values[0], 4 * num_points * sizeof(float));// predictstd::vector<std::vector<float>> semantic_scan = net->infer(values, num_points);// get point cloudstd::vector<cv::Vec3f> points = net->getPoints(values, num_points);// get color maskstd::vector<cv::Vec3b> color_mask = net->getLabels(semantic_scan, num_points);// Create output filenamestd::ostringstream outfileNameStream;outfileNameStream << "/home/fairlee/dataset/KITTI/sequences_kitti_00_21/" << kitti_num << "/RangeNet_point/" << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(6) << file_num << ".txt";std::string outfileName = outfileNameStream.str();// Create an ofstream objectstd::ofstream outfile(outfileName);if (!outfile) {std::cerr << "Unable to open output file: " << outfileName << std::endl;return 1;}// Iterate through each point and corresponding colorfor (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) {// Write the point coordinates and color to the fileoutfile << points[i][0] << " " << points[i][1] << " " << points[i][2];outfile << " " << static_cast<int>(color_mask[i][0]) << " " << static_cast<int>(color_mask[i][1]) << " " << static_cast<int>(color_mask[i][2]) << "\n";}// Close the fileoutfile.close();Create an ofstream object
//std::ofstream outfile("output.txt");Iterate through each point and corresponding color
//for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) {
// // Write the point coordinates and color to the file
// outfile << points[i][0] << " " << points[i][1] << " " << points[i][2];
// outfile << " " << static_cast<int>(color_mask[i][0]) << " " << static_cast<int>(color_mask[i][1]) << " " << static_cast<int>(color_mask[i][2]) << "\n";
//}Close the file
//outfile.close();// print the outputif (verbose) {cv::viz::Viz3d window("semantic scan");cv::viz::WCloud cloudWidget(points, color_mask);while (!window.wasStopped()) {window.showWidget("cloud", cloudWidget);window.spinOnce(30, true);}}std::cout << std::setfill('=') << std::setw(80) << "" << std::endl;std::cout << "Example finished! "<< std::endl;}return 0;
}
2. 编译通过后运行
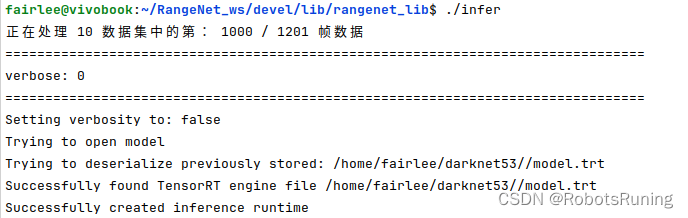
3. 运行结果(也可以保存为pcd)
4. 完整代码的github 连接
https://github.com/RobotsRuning/RangeNet_ws/tree/main