JDBC介绍
JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。
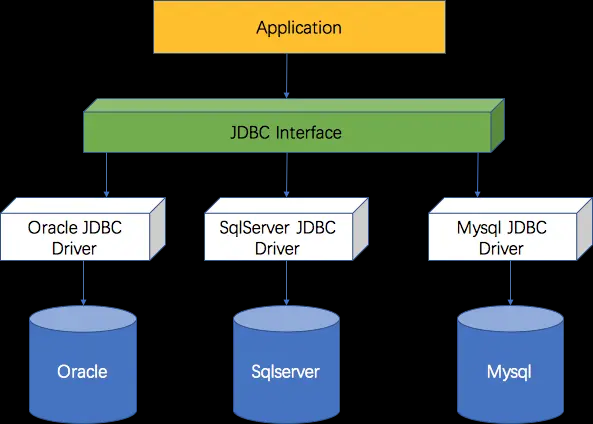
开发者不必为每家数据通信协议的不同而疲于奔命,只需要面向JDBC提供的接口编程,在运行时,由对应的驱动程序操作对应的DB。
java.sql 包中包含用于以下方面的 API:
-
通过
DriverManager实用程序建立与数据库的连接DriverManager类:建立与驱动程序的连接SQLPermission类:当代码在 Security Manager(比如 applet)中运行时提供权限,试图通过DriverManager设置一个记录流Driver接口:提供用来注册和连接基于 JDBC 技术(“JDBC 驱动程序”)的驱动程序的 API,通常仅由DriverManager类使用DriverPropertyInfo类:提供 JDBC 驱动程序的属性,不是供一般用户使用的
-
向数据库发送 SQL 语句
Statement:用于发送基本 SQL 语句PreparedStatement:用于发送准备好的语句或基本 SQL 语句(派生自Statement)CallableStatement:用于调用数据库存储过程(派生自PreparedStatement)Connection接口:提供创建语句以及管理连接及其属性的方法Savepoint:在事务中提供保存点
-
获取和更新查询的结果
ResultSet接口
-
SQL 类型到 Java 编程语言中的类和接口的标准映射关系
Array接口:SQLARRAY的映射关系Blob接口:SQLBLOB的映射关系Clob接口:SQLCLOB的映射关系Date类:SQLDATE的映射关系NClob接口:SQLNCLOB的映射关系Ref接口:SQLREF的映射关系RowId接口:SQLROWID的映射关系Struct接口:SQLSTRUCT的映射关系SQLXML接口:SQLXML的映射关系Time类:SQLTIME的映射关系Timestamp类:SQLTIMESTAMP的映射关系Types类:提供用于 SQL 类型的常量
-
自定义映射 SQL 用户定义类型 (UDT) 到 Java 编程语言中的类
SQLData接口:指定 UDT 到此类的一个实例的映射关系SQLInput接口:提供用来从流中读取 UDT 属性的方法SQLOutput接口:提供用来将 UDT 属性写回流中的方法
-
元数据
DatabaseMetaData接口:提供有关数据库的信息ResultSetMetaData接口:提供有关ResultSet对象的列的信息ParameterMetaData接口:提供有关PreparedStatement命令的参数的信息
-
异常
SQLException:由大多数方法在访问数据出问题时抛出,以及因为其他原因由其他一些方法抛出SQLWarning:为了指示一个警告而抛出DataTruncation:为了指示数据可能已经被截断而抛出BatchUpdateException:为了指示并不是批量更新中的所有命令都成功执行而抛出
JDBC 的操作步骤
在进行JDBC 操作的时候可以按照以下的步骤完成:
- 加载数据库驱动程序,加载的时候需要将驱动程序配置到
classpath之中 - 连接数据库,通过
Connection接口和DriverManager类完成 - 操作数据库,通过
Statement、PreparedStatement、ResultSet三个接口完成 - 关闭数据库,在实际开发中数据库资源非常有限,操作完之后必须关闭
在JDBC 的操作中,如果要想进行数据库的连接,则必须按照以上的几步完成
- 通过
Class.forName()加载数据库的驱动程序 - 通过
DriverManager类进行数据库的连接,连接的时候要输入数据库的连接地址、用户名、密码 - 通过
Connection接口接收连接 - 通过
Statement接口操作数据。
代码示例
1、引入驱动
<dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>8.0.15</version></dependency>2、加载驱动
3、建立与数据库的连接
4、创建Statement
Connection接口的createStatement()方法用于创建语句对象(Statement )。 Statement 对象负责对数据库执行查询。
5、执行SQL语句
6、关闭连接
public static void main(String[] args) {//连接对象Connection conn = null;//SQL statement 对象Statement stmt = null;try {//加载驱动Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//创建连接对象conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT","root", "root");//创建Statementstmt = conn.createStatement();System.out.println("连接成功,获取连接对象: " + conn);//执行SQL语句String sql = "update a set x = x +6 where id > 6";int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);System.out.println("返回结果count:" + count);} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//05、关闭连接对象if (stmt != null) {try {stmt.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}if (conn != null) {try {conn.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}1、驱动类
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver已被弃用。 新的驱动程序类是com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver。 驱动程序通过SPI自动注册,通常不需要手动加载驱动程序类。2、从
JDBC 4.0开始,显式注册驱动程序是可选的。 我们只需要将相应的驱动jar放在类路径中,然后JDBC驱动程序管理器就可以自动检测并加载驱动程序。3、因为新版本的数据库驱动需要指定UTC时区,将url地址后加上时区即可解决,
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT4、从Java 7开始,JDBC能够使用
try-with-resources语句来自动关闭Connection,ResultSet和Statement类型的资源。
Java接口定义
Jdbc的主要接口定义在包java.sql,javax.sql下.
主要接口
- DriverManager: 管理驱动程序,主要用于调用驱动从数据库获取连接。
- Connection: 代表了一个数据库连接。
- Statement: 持有Sql语句,执行并返回执行后的结果。
- ResulSet: Sql执行完毕,返回的记过持有
接口定义
DriverManager
DriverManager 是用于管理JDBC驱动程序的基础服务。DriverManger 可以注册、删除、加载的驱动程序,可以根据给定的url获取符合url协议的驱动Driver 并建立Conenction连接,进行数据库交互。当DriverManager被使用时,DriverManager类将尝试加载“ jdbc.drivers”系统属性中的驱动程序类。
JDBC 4.0驱动程序必须包含文件 META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver,该文件包含了实现java.sql.Driver的JDBC驱动程序的名称。例如,要加载my.sql.Driver类,META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver文件中将包含以下内容:my.sql.Driver。
使用DriverManager之后,应用程序不再需要使用 Class.forName() 显式加载JDBC驱动程序了。已经使用 Class.forName() 显式加载JDBC驱动的程序也不会受到影响,也无需刻意去修改。
当调用方法getConnection时,DriverManager将尝试从初始化时加载的驱动程序和当前应用程序显式加载的驱动程序中找到合适的驱动程序。
public interface Driver {/**尝试建立给定URL的数据库连接。 如果驱动程序意识到连接到给定URL的驱动程序类型错误,则应返回“ null”。 这是很常见的,因为当要求JDBC驱动程序管理器连接到给定的URL时,它将URL依次传递给每个已加载的驱动程序。注意:如果将属性指定为url的一部分,并且也在Properties对象中指定了属性,则该实现将由实现定义,以哪个值优先。 为了获得最大的可移植性,应用程序应仅指定一次属性。*/Connection connect(String url, java.util.Properties info)throws SQLException;/**
检索驱动程序是可以打开 给定URL的连接。 通常,如果驱动程序识别出 URL中指定的子协议,则将返回true;否则,将返回false。*/boolean acceptsURL(String url) throws SQLException;/**获取有关此驱动程序可能的属性的信息。getPropertyInfo方法旨在允许通用的GUI工具发现应该提示的属性,以便获得足够的信息以连接到数据库。 */DriverPropertyInfo[] getPropertyInfo(String url, java.util.Properties info)throws SQLException;/**获取驱动程序的主版本号。 最初应为1。*/int getMajorVersion();int getMinorVersion();/**报告此驱动程序是否是正版JDBC Compliant™驱动程序。 如果驱动程序通过了JDBC兼容性测试,则仅在此处报告true。 否则需要返回false。JDBC合规性要求对JDBC API的完全支持和对SQL 92 Entry Level的完全支持。 期望所有主要的商业数据库都可以使用符合JDBC的驱动程序。*/boolean jdbcCompliant();//------------------------- JDBC 4.1 -----------------------------------/**返回此驱动程序使用的所有Logger的父Logger。 这应该是距离根Logger最远的Logger,它仍然是该驱动程序使用的所有Logger的祖先。 配置此Logger将影响驱动程序生成的所有日志消息。 在最坏的情况下,它可能是根Logger。*/public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
}
Class.forName() 手动加载驱动
Class.forName()将对应的驱动类加载到内存中时,会执行驱动类中的static 静态代码快,创建一个驱动Driver的实例,注册到DriverManager中,供DriverManager使用。
//加载MySQL 数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
DriverManager 源码分析
DriverManager 加载驱动
DriverManager 作为 Driver 的管理器,在首次被使用时,会执行其定义的static静态代码块,在静态代码快中,有一个 loadInitialDrivers() 静态方法,会首先加载配置在jdbc.drivers 系统属性内的驱动Driver。
static {loadInitialDrivers();println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");}private static void loadInitialDrivers() {String drivers;//尝试从系统属性"jdbc.drivers"中获取驱动类try {drivers = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<String>() {public String run() {return System.getProperty("jdbc.drivers");}});} catch (Exception ex) {drivers = null;}//使用ServiceLoader 加载驱动程序AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {public Void run() {ServiceLoader<Driver> loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);Iterator<Driver> driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();// 加载这些驱动程序,以便可以实例化它们。try{while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {driversIterator.next();}} catch(Throwable t) {// Do nothing}return null;}});println("DriverManager.initialize: jdbc.drivers = " + drivers);//jdbc.drivers 中的驱动处理if (drivers == null || drivers.equals("")) {return;}String[] driversList = drivers.split(":");println("number of Drivers:" + driversList.length);for (String aDriver : driversList) {try {println("DriverManager.Initialize: loading " + aDriver);Class.forName(aDriver, true,ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());} catch (Exception ex) {println("DriverManager.Initialize: load failed: " + ex);}}}DriverManager 注册驱动
//同步注册
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver)throws SQLException {registerDriver(driver, null);}//CopyOnWriteArrayListprivate final static CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver,DriverAction da)throws SQLException {/* Register the driver if it has not already been added to our list */if(driver != null) {registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da));} else {// This is for compatibility with the original DriverManagerthrow new NullPointerException();}println("registerDriver: " + driver);}DriverManager 取消注册驱动
@CallerSensitivepublic static synchronized void deregisterDriver(Driver driver)throws SQLException {if (driver == null) {return;}SecurityManager sec = System.getSecurityManager();if (sec != null) {sec.checkPermission(DEREGISTER_DRIVER_PERMISSION);}println("DriverManager.deregisterDriver: " + driver);DriverInfo aDriver = new DriverInfo(driver, null);//包含if(registeredDrivers.contains(aDriver)) {if (isDriverAllowed(driver, Reflection.getCallerClass())) {DriverInfo di = registeredDrivers.get(registeredDrivers.indexOf(aDriver));// If a DriverAction was specified, Call it to notify the// driver that it has been deregisteredif(di.action() != null) {di.action().deregister();}//移除registeredDrivers.remove(aDriver);} else {// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then// throw a SecurityException.throw new SecurityException();}} else {println(" couldn't find driver to unload");}}
DriverManager 创建连接
通过遍历已加载的驱动程序,分别尝试连接指定的数据库,如果连接上则返回连接对象。
@CallerSensitivepublic static Connection getConnection(String url)throws SQLException {java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));}@CallerSensitivepublic static Connection getConnection(String url,java.util.Properties info) throws SQLException {return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));}@CallerSensitivepublic static Connection getConnection(String url,String user, String password) throws SQLException {java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();if (user != null) {info.put("user", user);}if (password != null) {info.put("password", password);}return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));}private static Connection getConnection(String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {/*当callerCl为空时,检查应用程序的类加载器,以便可以从此处加载rt.jar外部的JDBC驱动程序类。*/ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;synchronized(DriverManager.class) {// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.if (callerCL == null) {callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();}}if(url == null) {throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");}println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");SQLException reason = null;// 遍历每个驱动尝试连接指定的数据库地址for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then// skip it.if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {try {println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);if (con != null) {// Success!println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());return (con);}} catch (SQLException ex) {if (reason == null) {reason = ex;}}} else {println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());}}// if we got here nobody could connect.if (reason != null) {println("getConnection failed: " + reason);throw reason;}println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");}
DataSource接口提供了另一种连接数据源的方法。 使用DataSource对象是连接数据源的首选方法。
Wrapper
java.sql.Wrapper 是 JDBC 的接口,当相关实例实际上是代理类时,该接口提供检索委托实例的功能。
许多 JDBC 驱动程序实现使用包装器模式提供超越传统 JDBC API 的扩展功能,传统 JDBC API 是特定于数据源的。开发人员可能希望访问那些被包装(代理)为代表实际资源代理类实例的资源。
public interface Wrapper {<T> T unwrap(java.lang.Class<T> iface) throws java.sql.SQLException;boolean isWrapperFor(java.lang.Class<?> iface) throws java.sql.SQLException;
}
T unwrap(java.lang.Class iface)
返回一个实现给定接口的对象,以允许访问非标准方法或代理未公开的标准方法。
如果接收者实现了该接口,那么结果是接收者或接收者代理。如果接收者是包装器且包装对象实现了该接口,那么结果是包装对象或包装对象的代理。否则,返回对该包装对象或该结果的代理进行递归调用的结果。如果接收者不是包装器且未实现该接口,则抛出 sqlexception。
boolean isWrapperFor(java.lang.Class<?> iface)
如果此方法实现了接口参数,或者直接或间接地对该对象进行了包装,则返回true。 否则返回false。
如果实现了接口,那么返回true,否则如果这是一个包装器,那么返回在包装对象上递归调用isWrapperFor的结果。
如果不实现接口并且不是包装器,则返回false。
与 unwrap 相比,此方法应作为一种低成本操作来实现,以便调用者可以使用此方法来避免可能失败的昂贵的 unwrap 调用。 如果此方法返回true,则使用相同参数调用unwrap应该会成功。
java.sql.Wrapper 主要有以下子接口:
- DataSource:该工厂用于提供到此 DataSource 对象所表示的物理数据源的连接。
- Connection:与特定数据库的连接(会话)。
- DatabaseMetaData:关于数据库的整体综合信息。
- ParameterMetaData:可用于获取关于 PreparedStatement 对象中每个参数标记的类型和属性信息的对象。
- ResultSet:表示数据库结果集的数据表,通常通过执行查询数据库的语句生成。
- ResultSetMetaData:可用于获取关于 ResultSet 对象中列的类型和属性信息的对象。
- Statement:用于执行静态 SQL 语句并返回它所生成结果的对象。
- CallableStatement:用于执行 SQL 存储过程的接口。
- PreparedStatement:表示预编译的 SQL 语句的对象。
- RowSet:该接口添加了对 JavaBeansTM 组件模型的 JDBC API 支持。
- RowSetMetaData:该对象包含关于 RowSet 对象的列的信息。
Connection
Connection 是Java应用程序和特定数据库之间的会话。 用来执行SQL语句,并在连接的上下文中返回结果。
public interface Connection extends Wrapper, AutoCloseable {/**创建一个Statement对象,用于将SQL语句发送到数据库。 不带参数的SQL语句通常使用Statement对象执行。 如果多次执行同一条SQL语句,则使用PreparedStatement对象可能会更合适。
默认情况下,使用返回的Statement对象创建的结果集的类型为TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY,并发级别为CONCUR_READ_ONLY。 可以通过调用getHoldability()确定创建的结果集的可保存性。*/Statement createStatement() throws SQLException;/***/PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql)throws SQLException;CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException;String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException;void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException;boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException;void commit() throws SQLException;void rollback() throws SQLException;void close() throws SQLException;boolean isClosed() throws SQLException;DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException;void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException;boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException;void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException;String getCatalog() throws SQLException;/*** A constant indicating that transactions are not supported.*/int TRANSACTION_NONE = 0;int TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1;int TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED = 2;int TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4;int TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE = 8;void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException;int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException;SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException;void clearWarnings() throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 2.0-----------------------------Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency)throws SQLException;PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType,int resultSetConcurrency)throws SQLException;CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException;java.util.Map<String,Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException;void setTypeMap(java.util.Map<String,Class<?>> map) throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 3.0-----------------------------void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException;int getHoldability() throws SQLException;Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException;Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException;void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException;void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException;Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency,int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException;PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType,int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)throws SQLException;CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,int resultSetConcurrency,int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException;PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys)throws SQLException;PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int columnIndexes[])throws SQLException;PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String columnNames[])throws SQLException;Clob createClob() throws SQLException;Blob createBlob() throws SQLException;NClob createNClob() throws SQLException;SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException;boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException;void setClientInfo(String name, String value)throws SQLClientInfoException;void setClientInfo(Properties properties)throws SQLClientInfoException;String getClientInfo(String name)throws SQLException;Properties getClientInfo()throws SQLException;Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws
SQLException;Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes)
throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 4.1 -----------------------------void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException;String getSchema() throws SQLException;void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException;void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException;int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException;
}Statement及子接口
PreparedStatement 表示预编译的SQL语句的对象,SQL语句已预编译并存储在PreparedStatement对象中。 然后可以使用该对象多次有效地执行该语句。
String sql = "insert into users values(?,?,?)";
//可以通过setter来为每个参数赋值。pstmt.setBigDecimal(1, 153833.00)pstmt.setInt(2, 110592)
public interface Statement extends Wrapper, AutoCloseable {ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) throws SQLException;int executeUpdate(String sql) throws SQLException;void close() throws SQLException;//----------------------------------------------------------------------int getMaxFieldSize() throws SQLException;void setMaxFieldSize(int max) throws SQLException;int getMaxRows() throws SQLException;void setMaxRows(int max) throws SQLException;void setEscapeProcessing(boolean enable) throws SQLException;int getQueryTimeout() throws SQLException;void setQueryTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException;void cancel() throws SQLException;SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException;void clearWarnings() throws SQLException;void setCursorName(String name) throws SQLException;boolean execute(String sql) throws SQLException;ResultSet getResultSet() throws SQLException;int getUpdateCount() throws SQLException;boolean getMoreResults() throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 2.0-----------------------------void setFetchDirection(int direction) throws SQLException;int getFetchDirection() throws SQLException;void setFetchSize(int rows) throws SQLException;int getFetchSize() throws SQLException;int getResultSetConcurrency() throws SQLException;int getResultSetType() throws SQLException;/** 批次 加 sql */void addBatch( String sql ) throws SQLException;void clearBatch() throws SQLException;int[] executeBatch() throws SQLException;Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 3.0-----------------------------int CLOSE_CURRENT_RESULT = 1;int KEEP_CURRENT_RESULT = 2;int CLOSE_ALL_RESULTS = 3;int SUCCESS_NO_INFO = -2;int EXECUTE_FAILED = -3;int RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS = 1;int NO_GENERATED_KEYS = 2;boolean getMoreResults(int current) throws SQLException;ResultSet getGeneratedKeys() throws SQLException;int executeUpdate(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException;int executeUpdate(String sql, int columnIndexes[]) throws SQLException;int executeUpdate(String sql, String columnNames[]) throws SQLException;boolean execute(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException;boolean execute(String sql, int columnIndexes[]) throws SQLException;boolean execute(String sql, String columnNames[]) throws SQLException;int getResultSetHoldability() throws SQLException;boolean isClosed() throws SQLException;void setPoolable(boolean poolable)throws SQLException;boolean isPoolable()throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 4.1 -----------------------------public void closeOnCompletion() throws SQLException;public boolean isCloseOnCompletion() throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 4.2 -----------------------------default long getLargeUpdateCount() throws SQLException {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("getLargeUpdateCount not implemented");}default void setLargeMaxRows(long max) throws SQLException {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("setLargeMaxRows not implemented");}default long getLargeMaxRows() throws SQLException {return 0;}default long[] executeLargeBatch() throws SQLException {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("executeLargeBatch not implemented");}default long executeLargeUpdate(String sql) throws SQLException {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("executeLargeUpdate not implemented");}default long executeLargeUpdate(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys)throws SQLException {throw new SQLFeatureNotSupportedException("executeLargeUpdate not implemented");}default long executeLargeUpdate(String sql, int columnIndexes[]) throws SQLException {throw new SQLFeatureNotSupportedException("executeLargeUpdate not implemented");}default long executeLargeUpdate(String sql, String columnNames[])throws SQLException {throw new SQLFeatureNotSupportedException("executeLargeUpdate not implemented");}
}
public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement {ResultSet executeQuery() throws SQLException;int executeUpdate() throws SQLException;/** 下面是各种数据类型的设置 */void setNull(int parameterIndex, int sqlType) throws SQLException;void setXXXX(int parameterIndex, <Type> x) throws SQLException;void setAsciiStream(int parameterIndex, java.io.InputStream x, int length)throws SQLException;@Deprecatedvoid setUnicodeStream(int parameterIndex, java.io.InputStream x,int length) throws SQLException;void setBinaryStream(int parameterIndex, java.io.InputStream x,int length) throws SQLException;void clearParameters() throws SQLException;//----------------------------------------------------------------------// Advanced features:void setObject(int parameterIndex, Object x, int targetSqlType)throws SQLException;void setObject(int parameterIndex, Object x) throws SQLException;boolean execute() throws SQLException;//--------------------------JDBC 2.0-----------------------------/** 把当前参数 的设置 加到批次 */void addBatch() throws SQLException;void setYYY(int parameterIndex, YYY y) throws SQLException;//------------------------- JDBC 3.0 -----------------------------------void setURL(int parameterIndex, java.net.URL x) throws SQLException;ParameterMetaData getParameterMetaData() throws SQLException;//------------------------- JDBC 4.0 -----------------------------------/** 新增的数据类型*/void setRowId(int parameterIndex, RowId x) throws SQLException;void setNString(int parameterIndex, String value) throws SQLException;void setNCharacterStream(int parameterIndex, Reader value, long length) throws SQLException;//------------------------- JDBC 4.2 -----------------------------------default void setObject(int parameterIndex, Object x, SQLType targetSqlType,int scaleOrLength) throws SQLException {throw new SQLFeatureNotSupportedException("setObject not implemented");}default void setObject(int parameterIndex, Object x, SQLType targetSqlType)throws SQLException {throw new SQLFeatureNotSupportedException("setObject not implemented");}default long executeLargeUpdate() throws SQLException {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("executeLargeUpdate not implemented");}
}使用 Statement 对象进行批处理更新
Statement,PreparedStatement 和 CallableStatement 对象具有与其关联的命令列表。 该列表在创建时与 Statement 对象相关联,初始是空的。 您可以使用addBatch方法将SQL命令添加到此列表,并使用clearBatch方法将其清空。 完成将语句添加到列表后,请调用executeBatch方法将其全部发送到数据库以作为一个单元或批处理执行。
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {batchUpdate();}/*** 使用 Statement 对象进行批处理更新*/private static void batchUpdate() {//Step 1: 创建 Connection 对象try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT", "root", "root");// Step 2:使用 connection 创建 statement 对象Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {connection.setAutoCommit(false);statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO Users VALUES (1, 'XXX', 'xxx@qq.com', 'China', '1234');");statement.addBatch("INSERT INTO Users VALUES (2, 'YYY', 'yyy@qq.com', 'China', '1235');");//批处理int[] updateCounts = statement.executeBatch();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(updateCounts));connection.commit();} catch (BatchUpdateException batchUpdateException) {printBatchUpdateException(batchUpdateException);} catch (SQLException e) {printSQLException(e);}}进行参数化的批量更新
private static void parameterizedBatchUpdate() {String INSERT_USERS_SQL = "INSERT INTO users" + " (id, name, email, country, password) VALUES " +" (?, ?, ?, ?, ?);";try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT", "root", "root");PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(INSERT_USERS_SQL)) {connection.setAutoCommit(false);preparedStatement.setInt(1, 8);preparedStatement.setString(2, "XXX");preparedStatement.setString(3, "xxx@qq.com");preparedStatement.setString(4, "China");preparedStatement.setString(5, "1");preparedStatement.addBatch();preparedStatement.setInt(1, 9);preparedStatement.setString(2, "YYYY");preparedStatement.setString(3, "yyyy@qq.com");preparedStatement.setString(4, "China");preparedStatement.setString(5, "2");preparedStatement.addBatch();preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10);preparedStatement.setString(2, "ZZZZ");preparedStatement.setString(3, "zzzz@qq.com");preparedStatement.setString(4, "China");preparedStatement.setString(5, "3");preparedStatement.addBatch();preparedStatement.setInt(1, 11);preparedStatement.setString(2, "DDDD");preparedStatement.setString(3, "dddd.com");preparedStatement.setString(4, "China");preparedStatement.setString(5, "4");preparedStatement.addBatch();int[] updateCounts = preparedStatement.executeBatch();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(updateCounts));connection.commit();connection.setAutoCommit(true);} catch (BatchUpdateException batchUpdateException) {printBatchUpdateException(batchUpdateException);} catch (SQLException e) {printSQLException(e);}}ResultSet
ResultSet 接口提供了用于检索和处理已获得结果集的方法,并且ResultSet对象具有不同的功能和特性。 这些特性是type(类型), concurrency(并发性), cursor holdability(游标可保持性)。
ResultSet 对象维护一个游标,该游标指向其当前数据行。 next 方法将光标移动到下一行,当ResultSet对象中没有更多行时它返回false,因此可以在while循环中使用它来迭代结果集。
默认的 ResultSet 对象是不可更新的,并且只有仅向前移动的光标。 因此,您只能从第一行到最后一行迭代一次。
可以生成可滚动或可更新的ResultSet对象。 下面的代码片段(其中con是有效的Connection对象)说明了如何创建一个可滚动且对其他更新不敏感并且可更新的结果集。
Statement stmt = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT a, b FROM test");ResultSet 接口提供了用于从当前行检索列值的getter方法(getBoolean,getLong等)。 可以使用列的索引号或列的名称来检索值。 通常,使用列索,列索引编号从1开始编号。为了实现最大的可移植性,应按从左到右的顺序读取每一行中的结果集列,并且每一列只能读取一次。
对于getter方法,JDBC驱动程序尝试将基础数据转换为getter方法中指定的Java类型,并返回合适的Java值。 JDBC规范具有一个表,该表显示了ResultSet getter方法可以使用的从SQL类型到Java类型的映射。
用作getter方法的列名不区分大小写。 当使用列名调用getter方法并且多个列具有相同的名称时,将返回第一个匹配列的值。 对于在查询中未明确命名的列,最好使用列号。 如果使用了列名,则应注意确保它们的唯一,这可以通过SQL AS子句来确保。
在JDBC 2.0 API中,向该接口添加了一组更新程序方法。 有关getter方法的参数的注释也适用于updater方法的参数。
更新方法有两种使用方式:
1、更新当前行中的列值:在可滚动的ResultSet对象中,光标可以前后移动,移动到绝对位置或相对于当前行的位置
rs.absolute(6); // 移动光标到 rs 的第6行
rs.updateString("NAME", "xxx"); // 更新 NAME 列的值为 xxx
rs.updateRow(); // 更新当前数据源 rs 中的第6行操作2、将列值插入到插入行中:可更新的ResultSet对象具有与其关联的特殊行,该行用作构建要插入的行的暂存区。
rs.moveToInsertRow(); // 移动游标到插入行rs.updateString(1, "xxx"); // 更新插入行第一列的值为 xxxrs.updateInt(2,3); // 更新第二列的值为 3rs.updateBoolean(3, true); // 更新第三列的值为 truers.insertRow();rs.moveToCurrentRow();ResultSet 类型
ResultSet 对象的类型在两个方面确定其功能级别:游标的操作方式以及ResultSet对象如何反映对基础数据源进行的并发更改。
游标的操作方式:
-
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY
结果集无法滚动,它的光标只能从第一行之前移到最后一行之后。 结果集中包含的行取决于基础数据库如何生成的结果。 即,它包含在执行查询时或在检索行时满足查询条件的行。 -
TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE
结果集可以滚动, 它的光标可以相对于当前位置向前和向后移动,并且可以移动到绝对位置。 结果集在打开时对基础数据源所做的更改不敏感。 它包含在执行查询时或在检索行时满足查询条件的行。 -
TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE
结果可以滚动,它的光标可以相对于当前位置向前和向后移动,并且可以移动到绝对位置。 结果集反映在结果集保持打开状态时对基础数据源所做的更改。
ResultSet 并发性:
ResultSet 对象的并发性确定了支持什么级别的更新功能。
- CONCUR_READ_ONLY:无法使用ResultSet接口更新ResultSet对象。
- CONCUR_UPDATABLE:可以使用ResultSet接口更新ResultSet对象。
Cursor Holdability(游标可保持性)
调用方法Connection.commit可以关闭在当前事务期间创建的ResultSet对象。 但是,在某些情况下,这可能不是所需的行为。 ResultSet属性的可保留性使应用程序可以控制在调用提交时是否关闭ResultSet对象(光标)。
可以将以下ResultSet常量提供给Connection方法的createStatement,prepareStatement和prepareCall:
HOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT: ResultSet游标未关闭,它是可保持的,调用方法commit时,它们保持打开状态。 如果您的应用程序主要使用只读的ResultSet对象,则可保持游标可能是理想的选择。CLOSE_CURSORS_AT_COMMIT: 调用commit方法时,将关闭ResultSet对象(光标)。 调用此方法时关闭游标可以提高某些应用程序的性能。
ResultSetMetaData
ResultSetMetaData 对象用于收集ResultSet的所有信息,例如列的类型和属性,列数,列的名称,列的数据类型等。简单来说,它用于收集 ResultSet 的信息。
ResultSetMetaData 封装了描述 ResultSet 对象的数据,内部提供了大量的方法来获取 ResultSet 的信息
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT a, b, c FROM test");
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//获取有多少列
int numberOfColumns = rsmd.getColumnCount();
boolean b = rsmd.isSearchable(1);
常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
int getColumnCount() throws SQLException | 返回 ResultSet 对象列的数量 |
String getColumnName(int column) throws SQLException | 根据指定的索引获取列名 |
int getColumnType(int column) throws SQLException | 根据指定索引检索指定列的SQL类型 |
String getTableName(int column) throws SQLException | 根据列索引获取表名 |
String getSchemaName(int column) | 获取指定列的表的结构 |
int getScale(int column) throws SQLException | 获取指定列的小数点右边的位数。 对于不适用小数位数的数据类型,返回0。 |
int getPrecision(int column) throws SQLException | 获取指定列的指定列大小。 |
DatabaseMetaData
DatabaseMetaData 接口提供了获取数据库元数据的方法,例如数据库名称,数据库版本,驱动程序名称,表总数,视图总数等。
数据库实现
数据库的实现以mysql为例。
Driver实现
当Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") 被执行时,com.mysql.jdbc.Driver类就会被加载,同时也在静态代码块中完成了向DriverManager的注册
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {public Driver() throws SQLException {}static {try {DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());} catch (SQLException var1) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");}}
}
具体实现在类NonRegisteringDriver中。
public class NonRegisteringDriver implements Driver {//System.getProperty("os.name");public static String getOSName() {return Constants.OS_NAME;}//System.getProperty("os.arch");public static String getPlatform() {return Constants.OS_ARCH;}static int getMajorVersionInternal() {return StringUtils.safeIntParse("8");}static int getMinorVersionInternal() {return StringUtils.safeIntParse("0");}public NonRegisteringDriver() throws SQLException {}public boolean acceptsURL(String url) throws SQLException {try {//helper类return ConnectionUrl.acceptsUrl(url);} catch (CJException var3) {throw SQLExceptionsMapping.translateException(var3);}}public Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {try {try {if (!ConnectionUrl.acceptsUrl(url)) {return null;} else {ConnectionUrl conStr = ConnectionUrl.getConnectionUrlInstance(url, info);switch (conStr.getType()) {//单实例case SINGLE_CONNECTION:return ConnectionImpl.getInstance(conStr.getMainHost());case LOADBALANCE_CONNECTION:return LoadBalancedConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance((LoadbalanceConnectionUrl)conStr);case FAILOVER_CONNECTION:return FailoverConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance(conStr);//复制case REPLICATION_CONNECTION:return ReplicationConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance((ReplicationConnectionUrl)conStr);default:return null;}}} catch (UnsupportedConnectionStringException var5) {return null;} catch (CJException var6) {throw (UnableToConnectException)ExceptionFactory.createException(UnableToConnectException.class, Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.17", new Object[]{var6.toString()}), var6);}} catch (CJException var7) {throw SQLExceptionsMapping.translateException(var7);}}public int getMajorVersion() {return getMajorVersionInternal();}public int getMinorVersion() {return getMinorVersionInternal();}public DriverPropertyInfo[] getPropertyInfo(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {try {String host = "";String port = "";String database = "";String user = "";String password = "";if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(url)) {//解析urlConnectionUrl connStr = ConnectionUrl.getConnectionUrlInstance(url, info);if (connStr.getType() == Type.SINGLE_CONNECTION) {HostInfo hostInfo = connStr.getMainHost();info = hostInfo.exposeAsProperties();}}if (info != null) {host = info.getProperty(PropertyKey.HOST.getKeyName());port = info.getProperty(PropertyKey.PORT.getKeyName());database = info.getProperty(PropertyKey.DBNAME.getKeyName());user = info.getProperty(PropertyKey.USER.getKeyName());password = info.getProperty(PropertyKey.PASSWORD.getKeyName());}DriverPropertyInfo hostProp = new DriverPropertyInfo(PropertyKey.HOST.getKeyName(), host);hostProp.required = true;hostProp.description = Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.3");DriverPropertyInfo portProp = new DriverPropertyInfo(PropertyKey.PORT.getKeyName(), port);portProp.required = false;portProp.description = Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.7");DriverPropertyInfo dbProp = new DriverPropertyInfo(PropertyKey.DBNAME.getKeyName(), database);dbProp.required = false;dbProp.description = Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.10");DriverPropertyInfo userProp = new DriverPropertyInfo(PropertyKey.USER.getKeyName(), user);userProp.required = true;userProp.description = Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.13");DriverPropertyInfo passwordProp = new DriverPropertyInfo(PropertyKey.PASSWORD.getKeyName(), password);passwordProp.required = true;passwordProp.description = Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.16");//5个关键属性。DriverPropertyInfo[] dpi = (new JdbcPropertySetImpl()).exposeAsDriverPropertyInfo(info, 5);dpi[0] = hostProp;dpi[1] = portProp;dpi[2] = dbProp;dpi[3] = userProp;dpi[4] = passwordProp;return dpi;} catch (CJException var15) {throw SQLExceptionsMapping.translateException(var15);}}public boolean jdbcCompliant() {return false;}public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {throw new SQLFeatureNotSupportedException();}static {try {Class.forName(AbandonedConnectionCleanupThread.class.getName());} catch (ClassNotFoundException var1) {}}
}ConnectionUrl
附录
参考
java.sql包API
PreparedStatement 性能
数据库解析SQL字符串并为其创建查询计划需要花费时间。 查询计划则是对数据库如何以最有效的方式执行查询的分析。
如果为每个查询或对数据库的更新提交新的完整SQL语句,则数据库必须解析SQL,并为查询创建查询计划。 通过重用现有的 PreparedStatement,您可以将SQL解析和查询计划复用于后续查询。 通过减少每次执行的解析和查询计划开销,这可以加快查询的执行速度。
PreparedStatement 的复用有以下两个方面:
- JDBC驱动程序重用 PreparedStatement。
- 数据库重用 PreparedStatement。
首先,JDBC驱动程序可以在内部缓存PreparedStatement对象,从而可以重用PreparedStatement对象。 这样可以节省少许PreparedStatement创建时间。
其次,缓存的解析和查询计划可能会使用相同的数据库跨Java应用程序(例如集群中的应用程序服务器)重用。