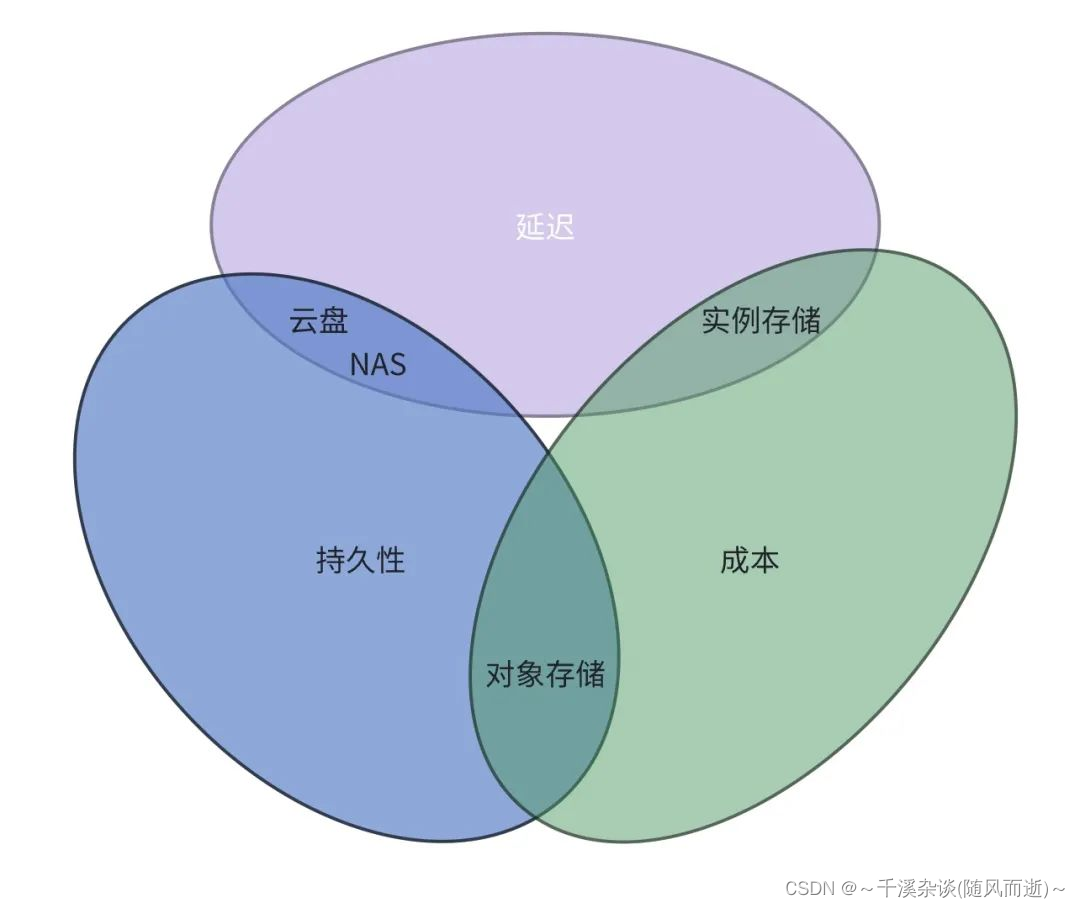
- 1 查看 Eigen库表示的矩阵 方法
1.1 列矩阵x在监视中,这样查看,数值右侧的圈圈 可用于更新数值 随程序

1.2 比较全的方法:来自于知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/625334009?utm_id=0
1.3 eigen的用法:https://www.xjx100.cn/news/602489.html?action=onClick
https://blog.csdn.net/wonengguwozai/article/details/125029383
#include <Eigen/Dense> // 基本函数只需要包含这个头文件
Matrix<double, Matrix<double, 3, 3> A; // 固定了行数和列数的矩阵和Matrix3d一致.
Matrix<double, 3, Dynamic> B; // 固定行数.
Matrix<double, Dynamic, Dynamic> C; // 基本和MatrixXd一致
Matrix<double, 3, 3, RowMajor> E; // 按行存储; 默认按列存储.
Matrix3f P, Q, R; // 3x3 float 矩阵.
Vector3f x, y, z; // 3x1 float 列向量.
RowVector3f a, b, c; // 1x3 float 行向量.
VectorXd v; // 动态长度double型列向量// Eigen // Matlab // comments
x.size() // length(x) // 向量长度
C.rows() // size(C,1) // 矩阵行数
C.cols() // size(C,2) // 矩阵列数
x(i) // x(i+1) // 下标0开始
C(i,j) // C(i+1,j+1) //Eigen 中矩阵的基本使用方法
A.resize(4, 4);// 如果越界触发运行时错误.
B.resize(4, 9);// 如果越界触发运行时错误.
A.resize(3, 3);// Ok; 没有越界.
B.resize(3, 9);// Ok; 没有越界.
A<< 1, 2, 3,// Initialize A. The elements can also be4, 5, 6,// matrices, which are stacked along cols7, 8, 9;// and then the rows are stacked.
B<< A, A, A;// B is three horizontally stacked A's. 三行A
A.fill(10);// Fill A with all 10's.//Eigen 特殊矩阵生成
// Eigen // Matlab
MatrixXd::Identity(rows,cols) // eye(rows,cols) 单位矩阵
C.setIdentity(rows,cols) // C = eye(rows,cols) 单位矩阵
MatrixXd::Zero(rows,cols) // zeros(rows,cols) 零矩阵
C.setZero(rows,cols) // C = ones(rows,cols) 零矩阵
MatrixXd::Ones(rows,cols) // ones(rows,cols)全一矩阵
C.setOnes(rows,cols) // C = ones(rows,cols)全一矩阵
MatrixXd::Random(rows,cols) // rand(rows,cols)*2-1 // 元素随机在-1->1
C.setRandom(rows,cols) // C = rand(rows,cols)*2-1 同上
VectorXd::LinSpaced(size,low,high)// linspace(low,high,size)'线性分布的数组
v.setLinSpaced(size,low,high)// v = linspace(low,high,size)'线性分布的数组// Eigen 矩阵分块
// Eigen // Matlab
x.head(n) // x(1:n) 用于数组提取前n个[vector]
x.head<n>() // x(1:n) 同理
x.tail(n) // x(end - n + 1: end)同理
x.tail<n>() // x(end - n + 1: end)同理
x.segment(i, n) // x(i+1 : i+n)同理
x.segment<n>(i) // x(i+1 : i+n)同理
P.block(i, j, rows, cols)// P(i+1 : i+rows, j+1 : j+cols)i,j开始,rows行cols列
P.block<rows, cols>(i, j)// P(i+1 : i+rows, j+1 : j+cols)i,j开始,rows行cols列
P.row(i) // P(i+1, :)i行
P.col(j) // P(:, j+1)j列
P.leftCols<cols>() // P(:, 1:cols)左边cols列
P.leftCols(cols) // P(:, 1:cols)左边cols列
P.middleCols<cols>(j) // P(:, j+1:j+cols)中间从j数cols列
P.middleCols(j, cols) // P(:, j+1:j+cols)中间从j数cols列
P.rightCols<cols>() // P(:, end-cols+1:end)右边cols列
P.rightCols(cols) // P(:, end-cols+1:end)右边cols列
P.topRows<rows>() // P(1:rows, :)同列
P.topRows(rows) // P(1:rows, :)同列
P.middleRows<rows>(i) // P(i+1:i+rows, :)同列
P.middleRows(i, rows) // P(i+1:i+rows, :)同列
P.bottomRows<rows>() // P(end-rows+1:end, :)同列
P.bottomRows(rows) // P(end-rows+1:end, :)同列
P.topLeftCorner(rows, cols) // P(1:rows, 1:cols)上左角rows行,cols列
P.topRightCorner(rows, cols) // P(1:rows, end-cols+1:end)上右角rows行,cols列
P.bottomLeftCorner(rows, cols) // P(end-rows+1:end, 1:cols)下左角rows行,cols列
P.bottomRightCorner(rows, cols)// P(end-rows+1:end, end-cols+1:end)下右角rows行,cols列
P.topLeftCorner<rows,cols>() // P(1:rows, 1:cols)同上
P.topRightCorner<rows,cols>() // P(1:rows, end-cols+1:end)同上
P.bottomLeftCorner<rows,cols>() // P(end-rows+1:end, 1:cols)同上
P.bottomRightCorner<rows,cols>()// P(end-rows+1:end, end-cols+1:end)同上// Eigen 矩阵元素交换
// Eigen // Matlab
R.row(i)= P.col(j); // R(i, :) = P(:, i)交换列为行
R.col(j1).swap(mat1.col(j2)); // R(:, [j1 j2]) = R(:, [j2, j1]) 交换列123//Eigen 矩阵转置
// Views, transpose, etc; all read-write except for .adjoint().
// Eigen // Matlab
R.adjoint()// R' 伴随矩阵
R.transpose()// R.' or conj(R')转置
R.diagonal()// diag(R)对角
x.asDiagonal()// diag(x)对角阵(没有重载<<)
R.transpose().colwise().reverse();// rot90(R)所有元素逆时针转了90度
R.conjugate()// conj(R)共轭矩阵//Eigen 矩阵乘积
// 与Matlab一致, 但是matlab不支持*=等形式的运算.
// Matrix-vector. Matrix-matrix. Matrix-scalar.
y= M*x; R= P*Q; R= P*s;
a= b*M; R= P- Q; R= s*P;
a*= M; R= P+ Q; R= P/s;R*= Q; R= s*P;R+= Q; R*= s;R-= Q; R/= s;12345678// Eigen 矩阵单个元素操作
// Vectorized operations on each element independently
// Eigen // Matlab
R= P.cwiseProduct(Q);// R = P .* Q 对应点相乘
R= P.array()* s.array();// R = P .* s 对应点相乘
R= P.cwiseQuotient(Q);// R = P ./ Q 对应点相除
R= P.array()/ Q.array();// R = P ./ Q对应点相除
R= P.array()+ s.array();// R = P + s对应点相加
R= P.array()- s.array();// R = P - s对应点相减
R.array()+= s;// R = R + s全加s
R.array()-= s;// R = R - s全减s
R.array()< Q.array();// R < Q 以下的都是针对矩阵的单个元素的操作
R.array()<= Q.array();// R <= Q矩阵元素比较,会在相应位置置0或1
R.cwiseInverse();// 1 ./ P
R.array().inverse();// 1 ./ P
R.array().sin()// sin(P)
R.array().cos()// cos(P)
R.array().pow(s)// P .^ s
R.array().square()// P .^ 2
R.array().cube()// P .^ 3
R.cwiseSqrt()// sqrt(P)
R.array().sqrt()// sqrt(P)
R.array().exp()// exp(P)
R.array().log()// log(P)
R.cwiseMax(P)// max(R, P) 对应取大
R.array().max(P.array())// max(R, P) 对应取大
R.cwiseMin(P)// min(R, P) 对应取小
R.array().min(P.array())// min(R, P) 对应取小
R.cwiseAbs()// abs(P) 绝对值
R.array().abs()// abs(P) 绝对值
R.cwiseAbs2()// abs(P.^2) 绝对值平方
R.array().abs2()// abs(P.^2) 绝对值平方
(R.array()< s).select(P,Q);// (R < s ? P : Q)这个也是单个元素的操作
R.cwiseSign();// 符号函数,矩阵大于0的置为1,小于0的变为-1,其余为0;// Eigen 矩阵化简
// Reductions.
int r, c;
// Eigen // Matlab
R.minCoeff()// min(R(:))最小值
R.maxCoeff()// max(R(:))最大值
s= R.minCoeff(&r,&c)// [s, i] = min(R(:)); [r, c] = ind2sub(size(R), i);
s= R.maxCoeff(&r,&c)// [s, i] = max(R(:)); [r, c] = ind2sub(size(R), i);
R.sum()// sum(R(:))求和
R.colwise().sum()// sum(R)列求和1×N
R.rowwise().sum()// sum(R, 2) or sum(R')'行求和N×1
R.prod()// prod(R(:))所有乘积
R.colwise().prod()// prod(R)列乘积
R.rowwise().prod()// prod(R, 2) or prod(R')'行乘积
R.trace()// trace(R)迹
R.all()// all(R(:))且运算
R.colwise().all()// all(R) 且运算
R.rowwise().all()// all(R, 2) 且运算
R.any()// any(R(:)) 或运算
R.colwise().any()// any(R) 或运算
R.rowwise().any()// any(R, 2) 或运算1234567891011121314151617181920// Eigen 矩阵点乘
// Dot products, norms, etc.
// Eigen // Matlab
x.norm()// norm(x). 模
x.squaredNorm()// dot(x, x) 平方和
x.dot(y)// dot(x, y)
x.cross(y)// cross(x, y) Requires #include <Eigen/Geometry>123456// Eigen 矩阵类型转换 Type conversion
// Eigen // Matlab
A.cast<double>();// double(A)
A.cast<float>();// single(A)
A.cast<int>();// int32(A) 向下取整
A.real();// real(A)
A.imag();// imag(A)
// if the original type equals destination type, no work is done12345678// Eigen 求解线性方程组 Ax= b
// Solve Ax = b. Result stored in x. Matlab: x = A \ b.
x= A.ldlt().solve(b));// #include <Eigen/Cholesky>LDLT分解法实际上是Cholesky分解法的改进
x= A.llt() .solve(b));// A sym. p.d. #include <Eigen/Cholesky>
x= A.lu() .solve(b));// Stable and fast. #include <Eigen/LU>
x= A.qr() .solve(b));// No pivoting. #include <Eigen/QR>
x= A.svd() .solve(b));// Stable, slowest. #include <Eigen/SVD>
// .ldlt() -> .matrixL() and .matrixD()
// .llt() -> .matrixL()
// .lu() -> .matrixL() and .matrixU()
// .qr() -> .matrixQ() and .matrixR()
// .svd() -> .matrixU(), .singularValues(), and .matrixV()1234567891011// Eigen 矩阵特征值
// Eigen // Matlab
A.eigenvalues();// eig(A);特征值
EigenSolver<Matrix3d> eig(A);// [vec val] = eig(A)
eig.eigenvalues();// diag(val)与前边的是一样的结果
eig.eigenvectors();// vec 特征值对应的特征向量在不确定是否会发生混淆时,采用.noalias() 来提升效率
xFixed.noalias() = x; //x和xFixed同时为eigen矩阵
在变量中查看 ttps://blog.csdn.net/liualiang/article/details/123832340