React Scheduler
1 ) 概述
- react当中的异步调度,称为 React Scheduler
- 发布成单独的一个 npm 包就叫做 scheduler
- 这个包它做了什么?
- A. 首先它维护时间片
- B. 然后模拟
requestIdleCallback这个API- 因为现在浏览器的支持不是特别的多
- 所以在浏览当中只是去模拟了一个这个API,而不是直接使用这个API
- 因为需要考虑到浏览器兼容性
- 这个API的作用
- 调用这个API传入一个回调之后,这个API会等到浏览器把它的一些主要任务执行完了
- 当它有空闲的时间的时候,再回来调用这个回调
- 相对于
requestAnimationFrame来说,它的优先级会低很多 - 它是等浏览器器要做的事情做完了之后,再回来调这个回调
- 而
requestAnimationFrame是浏览器要渲染当前帧的时候,调用这个回调
- C. 调度列表和进行一个超时的判断
- 关于时间片
- 不管是在浏览器还是在App当中,要给用户很流畅的一个感觉的时候
- 至少要保证在一秒钟之内要渲染30帧以上
- 现在的一些高刷新率的浏览器,可能会要求在60帧以上,甚至还有更高的,比如,120帧
- 这个帧数就是我们1秒钟,页面要重新渲染刷新多少次
- 它并不是说我一秒钟之内刷新30次,满足就行了。
- 比如前面的半秒钟只刷新了一次,后面的半秒钟刷新了二十九次,这个也是不行的
- 这个给用户的感觉,就是前面这半秒钟会特别的卡就一动不动,然后后面又变得流畅
- 所以,它的要求还需要是平均的每33毫秒要刷新1帧,要保持这个频率
- 浏览器必须自己去渲染这些动画,要每1帧里面有固定的时间去渲染这个动画
- 在这里举个例子,比如说整个应用所有的js的操作,都是通过 react 来实现的
- 而浏览器有一个一直在更新的动画, 浏览器渲染这个动画如果要11毫秒
- 那么给每一帧的, 就是把一秒钟分成了30帧之后,每一帧是33毫秒
- 这个33毫秒里面的11毫秒是必须要留给浏览器去渲染这个动画的, 才能让这个动画看起来是流畅的
- 而在这个时候留给react去渲染它的应用更新的时候,每一帧里面就只有22毫秒
- 如果react它在这一帧里面的一个更新,它需要渲染的时间很长,比如说35毫秒
- 那这个时候,我们一帧的时间就全部给react渲染给占掉了
- 因为 js 引擎是单线程的, 如果react在一直在执行,浏览器它就没有机会去获得运行权
- 就没有机会去刷新它的一个动画, 这时候,不仅把一帧的时间占完了
- 这样还不够,还要去下一帧里面借用一点时间,那么这个时间用完之后
- 浏览器要去更新动画,如果这一帧里面我们就用掉了13毫秒,剩下的时间就只剩下20毫秒
- 那么这20毫秒,又可能要运行一部分react的更新,然后再去浏览器的一个渲染
- 这就会导致整个动画变得卡顿起来了
- 这就是 React Scheduler 它的一个目的, 为了保证react它去执行更新的这个时间
- 不超过在浏览器的每一帧里面特定的时间,它希望留给浏览器去刷新动画,或者是响应用户输入的反馈的时候
- 每一帧里面有足够的时间
2 )时间片源码
-
时间片源码在 packages/scheduler 这个包里面,是一个单独的模块,单独发布到 npm 上
-
在 ReactFiberScheduler.js 里面,哪个地方用到它呢?
- 在
requestWork函数里面,如果 expirationTime 异步的,就会调用scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTimefunction scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root: FiberRoot,expirationTime: ExpirationTime, ) {if (callbackExpirationTime !== NoWork) {// A callback is already scheduled. Check its expiration time (timeout).if (expirationTime > callbackExpirationTime) {// Existing callback has sufficient timeout. Exit.return;} else {if (callbackID !== null) {// Existing callback has insufficient timeout. Cancel and schedule a// new one.cancelDeferredCallback(callbackID);}}// The request callback timer is already running. Don't start a new one.} else {startRequestCallbackTimer();}callbackExpirationTime = expirationTime;const currentMs = now() - originalStartTimeMs;const expirationTimeMs = expirationTimeToMs(expirationTime);const timeout = expirationTimeMs - currentMs;callbackID = scheduleDeferredCallback(performAsyncWork, {timeout}); }- 全局变量
callbackExpirationTime对应的是 上一次调用 React Scheduler 去申请了一个callback - 这个callback 也会有一个 expirationTime, 因为是异步调度,所以会有一个 expirationTime 传进来
- 如果这个
callbackExpirationTime!==NoWork代表之前有一个callback在执行了 - 这边就会判断当前的 expirationTime 是否比之前回调中的那个要大
- 如果大,说明当前的这个的优先级要低,这个时候就直接return了不执行
- 因为它优先级更低,我们肯定要执行优先级更高的那个,调用
cancelDeferredCallback把之前的 cancel 掉 startRequestCallbackTimer这个函数跳过,不涉及主流程,涉及DEV Tool 相关- 接着更新一系列的变量
- 更新
callbackExpirationTime - 计算出
timeout
- 更新
- 最后调用
scheduleDeferredCallback这个方法来自于 ReactFiberHostConfig.js- 如果直接查找 这个文件,发现基本上没有什么内容, 是因为 React对于打包工具的配置,进行了文件名的映射
- 它实际映射的是 eact-reconciler/src/forks/ReactFiberHostConfig.dom.js
export * from 'react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMHostConfig'; - 发现里面就一行代码,找到对应的 ReactDOMHostConfig.js 文件,搜索
scheduleDeferredCallback方法export {unstable_scheduleCallback as scheduleDeferredCallback, } from 'scheduler';- 可追溯到 这个方法来自于 scheduler 包
- 这个方法涉及比较多,先跳过
callbackID = scheduleDeferredCallback(performAsyncWork, {timeout});
- 它最后返回 一个 callbackID, 这个id用于后期 cancel 的标识,
cancelDeferredCallback(callbackID);- 这里之前也说了,如果新的任务优先级更高,需要把老的取消,再调用新的callback
- 而里面的参数
performAsyncWork- 在
requestWork中,当 expirationTime === Sync 时,调用的也是performSyncWork这个是同步的 - 而如果是异步,则调用
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime函数,最终调用的是这里的performAsyncWork - 所以,这两个是对应的,同步和异步
- 在
- 全局变量
- 在
-
进入 scheduleDeferredCallback 函数的源码 packages/scheduler/src/Scheduler.js 找到
unstable_scheduleCallbackfunction unstable_scheduleCallback(callback, deprecated_options) {var startTime =currentEventStartTime !== -1 ? currentEventStartTime : getCurrentTime();var expirationTime;if (typeof deprecated_options === 'object' &&deprecated_options !== null &&typeof deprecated_options.timeout === 'number') {// FIXME: Remove this branch once we lift expiration times out of React.expirationTime = startTime + deprecated_options.timeout;} else {switch (currentPriorityLevel) {case ImmediatePriority:expirationTime = startTime + IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;break;case UserBlockingPriority:expirationTime = startTime + USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY;break;case IdlePriority:expirationTime = startTime + IDLE_PRIORITY;break;case NormalPriority:default:expirationTime = startTime + NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;}}var newNode = {callback,priorityLevel: currentPriorityLevel,expirationTime,next: null,previous: null,};// Insert the new callback into the list, ordered first by expiration, then// by insertion. So the new callback is inserted any other callback with// equal expiration.if (firstCallbackNode === null) {// This is the first callback in the list.firstCallbackNode = newNode.next = newNode.previous = newNode;ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();} else {var next = null;var node = firstCallbackNode;do {if (node.expirationTime > expirationTime) {// The new callback expires before this one.next = node;break;}node = node.next;} while (node !== firstCallbackNode);if (next === null) {// No callback with a later expiration was found, which means the new// callback has the latest expiration in the list.next = firstCallbackNode;} else if (next === firstCallbackNode) {// The new callback has the earliest expiration in the entire list.firstCallbackNode = newNode;ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();}var previous = next.previous;previous.next = next.previous = newNode;newNode.next = next;newNode.previous = previous;}return newNode; }- 首先看 参数
callback, deprecated_options- callback 是传进来的
performAsyncWork - deprecated_options 是即将被废弃的 optinos,这个即将被废弃
- callback 是传进来的
- 接着处理
var startTime = currentEventStartTime !== -1 ? currentEventStartTime : getCurrentTime();getCurrentTime是重新计算一个 xx.now()if (hasNativePerformanceNow) {var Performance = performance;getCurrentTime = function() {return Performance.now();}; } else {getCurrentTime = function() {return localDate.now();}; }- 这里,浏览器平台是这个
localDate.now();
- 下面有个判断
if (typeof deprecated_options === 'object' && deprecated_options !== null && typeof deprecated_options.timeout === 'number')- 接着判断 deprecated_options 这个参数,存在则计算出 expirationTime
// FIXME: Remove this branch once we lift expiration times out of React. expirationTime = startTime + deprecated_options.timeout;- 当把 expirationTime 相关的逻辑提取出来之后,这个 if判断就被删除了,后面只有 else 里面的东西了
- 所以说,这个
deprecated_options即将被废弃
- 接着判断 deprecated_options 这个参数,存在则计算出 expirationTime
- 如果走到 else 里面,进行switch case
currentPriorityLevel- 可以看下各个常量的值
var maxSigned31BitInt = 1073741823;// Times out immediately var IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = -1; // Eventually times out var USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY = 250; var NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 5000; // Never times out var IDLE_PRIORITY = maxSigned31BitInt; - 也就是说,将来很可能会把 expirationTime 相关逻辑移入 scheduler 包中
- 之前在 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberReconciler.js 中
- 不过,在目前的逻辑中 else 里面的东西,用不到
- 可以看下各个常量的值
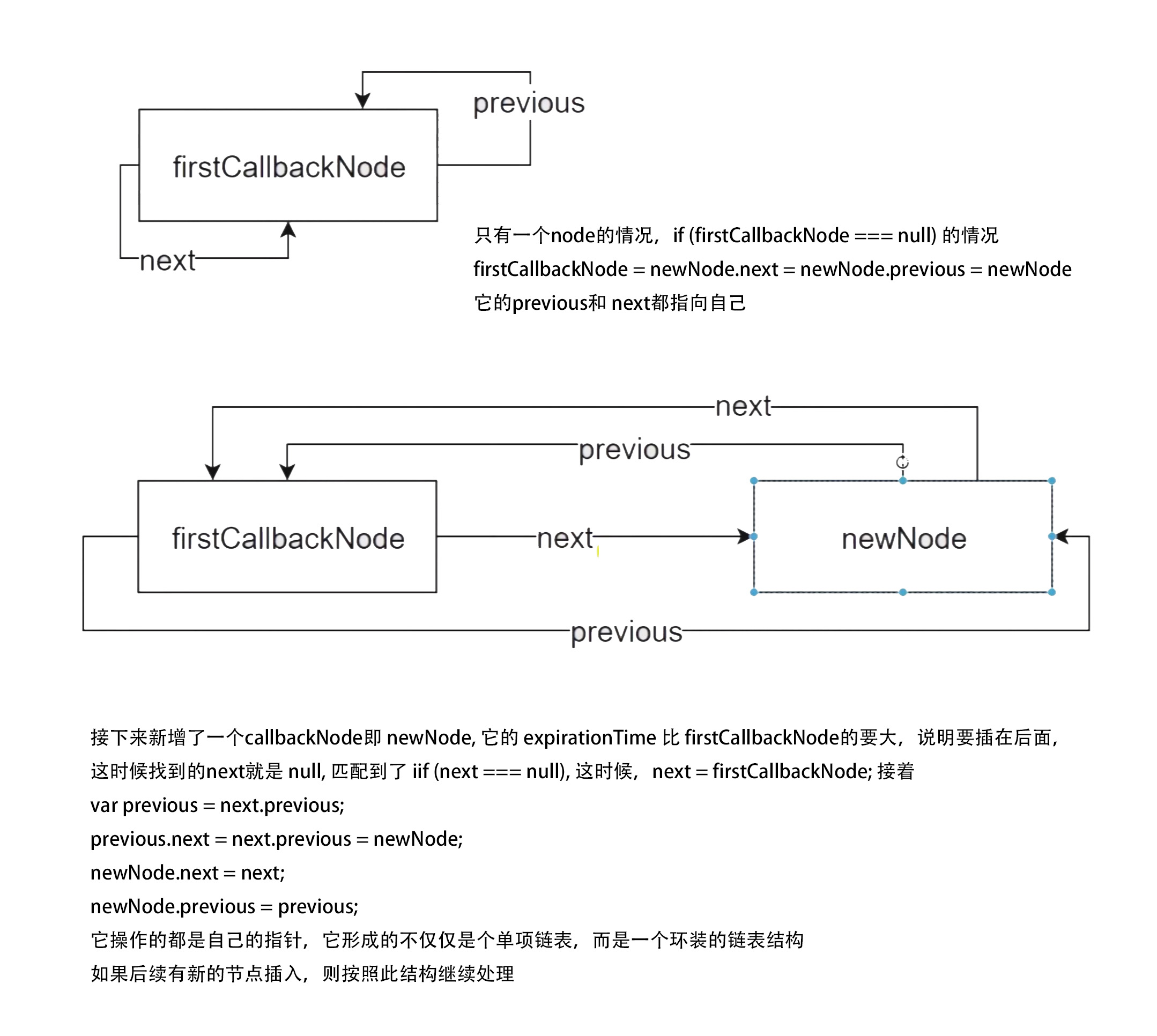
- 接下去,创建 newNode 的对象
var newNode = {callback,priorityLevel: currentPriorityLevel,expirationTime,next: null,previous: null, };- next 和 previous 是用来存储链表的数据结构的
- 接下来
if (firstCallbackNode === null)- firstCallbackNode 是 scheduler 中维护的一个单项列表的头部
- 如果匹配判断,说明传递进来的 callback 是第一个
- 进行赋值处理
firstCallbackNode = newNode.next = newNode.previous = newNode; - 并调用
ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();
- 进行赋值处理
- 不匹配的时候
- 有一个或多个callback, 则进行循环
- 在循环中判断,
node.expirationTime > expirationTime- 如果匹配,
next = node;并跳出循环 - 这是 scheduler 对于传进来的所有callback, 按照 expirationTime 的大小,也就是优先级的高低进行排序
- 它会把优先级更高的任务,排到最前面
- 如果匹配,
- 如果 next 是 null
- 这个节点要插在callbackList里面的最后一个
- 如果 next 是 firstCallbackNode,即第一个
- 因为当前节点要插在这个单项列表最前面,优先级最高
- 马上 firstCallbackNode 变化了,即更新了
firstCallbackNode = newNode; - 调用
ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();- 这个函数在上面两处调用了,但是没有在
if (next === null)中调用- 因为 这个条件下,firstCallbackNode 仍然处于第一位
- 后续要调用的话,第一个被调用的还是 firstCallbackNode
- 所以,顺序不会变,所以不需要重新调用
ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();
- 注意,调用上述方法会进入一个循环,循环的调用List里面的东西
- 当 firstCallbackNode 变化了,才会去调用,因为头部变了
- 这个函数在上面两处调用了,但是没有在
- 首先看 参数
-
下面为这个方法链表的处理示例
- 接着,进入
ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled这个方法让队列进入调度的过程function ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled() {if (isExecutingCallback) {// Don't schedule work yet; wait until the next time we yield.return;}// Schedule the host callback using the earliest expiration in the list.var expirationTime = firstCallbackNode.expirationTime;if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) {isHostCallbackScheduled = true;} else {// Cancel the existing host callback.cancelHostCallback();}requestHostCallback(flushWork, expirationTime); }isExecutingCallback变量表示已经调用callback, 直接 return- 代表着 已经有一个callbackNode 被调用了
- 也就是我们传入的
performAsyncWork正在被调用了 - 进入被调用的过程,自动进入一个循环的过程
- 就不需要再重新启动一次调度
- 获取变量
var expirationTime = firstCallbackNode.expirationTime; - 如果没有被调度,标识正在被调度
isHostCallbackScheduled = true; - 否则,取消之前的回调
cancelHostCallback(); - 最后
requestHostCallback, 进入这个方法,有很多种场景分别定义,但是找到我们需要的场景,搜索该方法名- 排除 mock, 非浏览器环境的判断
- 并进入直接到 else 中
// 这里跳过很多代码 // ... // 主要在这里 requestHostCallback = function(callback, absoluteTimeout) {scheduledHostCallback = callback;timeoutTime = absoluteTimeout;if (isFlushingHostCallback || absoluteTimeout < 0) {// Don't wait for the next frame. Continue working ASAP, in a new event.window.postMessage(messageKey, '*');} else if (!isAnimationFrameScheduled) {// If rAF didn't already schedule one, we need to schedule a frame.// TODO: If this rAF doesn't materialize because the browser throttles, we// might want to still have setTimeout trigger rIC as a backup to ensure// that we keep performing work.isAnimationFrameScheduled = true;requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick);} };cancelHostCallback = function() {scheduledHostCallback = null;isMessageEventScheduled = false;timeoutTime = -1; };
- 上述
requestHostCallback是我们需要关注的点cheduledHostCallback = callback;读取 callbacktimeoutTime = absoluteTimeout;是我们传进来的 expirationTime- 接着判断
if (isFlushingHostCallback || absoluteTimeout < 0)- 这两种情况,不需要等待下一帧去做这个事情
- 而是以最快的速度进入这个方法的调用
window.postMessage(messageKey, '*'); absoluteTimeout < 0说明已经超时了
- 不符合上述条件,按照正常的调度流程去走
- 判断
isAnimationFrameScheduled这个变量的状态 - 如果它没有设置为 true, 则还没有进入调度循环的过程
- 这时候就把它设置为 true, 并执行
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick); - 进入
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeoutvar requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout = function(callback) {// schedule rAF and also a setTimeoutrAFID = localRequestAnimationFrame(function(timestamp) {// cancel the setTimeoutlocalClearTimeout(rAFTimeoutID);callback(timestamp);});rAFTimeoutID = localSetTimeout(function() {// cancel the requestAnimationFramelocalCancelAnimationFrame(rAFID);callback(getCurrentTime()); // 这里 getCurrentTime 是一个模拟 timestamp 的参数}, ANIMATION_FRAME_TIMEOUT); };- 这里的
localRequestAnimationFrame相当于 window.requestAnimationFrame- 它内部做了两件事,清理 timeout, 执行callback
- 这个 callback 就是我们传进来的
animationTick这个方法 rAFTimeoutID是下面的 timeout 定时器- 这个定时器的作用是: 如果
localRequestAnimationFrame一直没有调用,超时了,这边设置的时间是 100ms - 超时后,取消
localRequestAnimationFrame的调用,并且直接调用callback(getCurrentTime()); - 也就是下一帧的时间必须在 100ms之内被调用
- 这个方法的作用就是,防止
localRequestAnimationFrame太长时间没有被调用 - 里面有相互取消的操作,这里面有一个竞争关系,谁先触发,谁先调用
- 这里的
- 同样,参数这里
animationTick也是个方法var animationTick = function(rafTime) {// 这里会匹配到if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) {// Eagerly schedule the next animation callback at the beginning of the// frame. If the scheduler queue is not empty at the end of the frame, it// will continue flushing inside that callback. If the queue *is* empty,// then it will exit immediately. Posting the callback at the start of the// frame ensures it's fired within the earliest possible frame. If we// waited until the end of the frame to post the callback, we risk the// browser skipping a frame and not firing the callback until the frame// after that.// 因为 firstCallbackNode 是一个队列,里面会有很多 callback// 当前 animationTick 只执行一个 callback// 如果后续还有,也会在下一帧中去执行// 不期望等待callback执行完成后,再去请求下一帧,可能会跳过很多的时间// 所以在这里立马执行requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick); // 立即进行调用,请求下一帧} else {// No pending work. Exit.// 如果下次进来,scheduledHostCallback 是没有的,则跳出isAnimationFrameScheduled = false;return;}// rafTime 是 animationTick 被调用的时间// frameDeadline 默认是 0// activeFrameTime 是 33,这个就是保持浏览器30帧的执行时间// 这里就是计算,这个方法到下一帧可以执行的时间var nextFrameTime = rafTime - frameDeadline + activeFrameTime;if (nextFrameTime < activeFrameTime &&previousFrameTime < activeFrameTime) {if (nextFrameTime < 8) {// Defensive coding. We don't support higher frame rates than 120hz.// If the calculated frame time gets lower than 8, it is probably a bug.nextFrameTime = 8;}// If one frame goes long, then the next one can be short to catch up.// If two frames are short in a row, then that's an indication that we// actually have a higher frame rate than what we're currently optimizing.// We adjust our heuristic dynamically accordingly. For example, if we're// running on 120hz display or 90hz VR display.// Take the max of the two in case one of them was an anomaly due to// missed frame deadlines.activeFrameTime =nextFrameTime < previousFrameTime ? previousFrameTime : nextFrameTime;} else {previousFrameTime = nextFrameTime;}frameDeadline = rafTime + activeFrameTime;if (!isMessageEventScheduled) {isMessageEventScheduled = true;window.postMessage(messageKey, '*');} };- 第一次计算的
nextFrameTime其实是没有用的,因为算出来的时间会比较大 - 第二次进来,这时候
frameDeadline就不是 0 了 - 而
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout又是连续调用的 - 因为我们进入这个方法就会立马调用这个方法
- 下个方法调用就是下一帧了,因为 requestAnimationFrame 是一帧一帧来调用的
- 下一帧时间进来,又重新计算出来了一个
nextFrameTime - 这个时候,rafTime 是小于 frameDeadline 的,因为 frameDeadline 加上了一个完整帧的时间 33
- 对于调用 requestAnimationFrame 的时候,是下一帧动画刚开始渲染的时候,肯定没有到 33 毫秒的时候
- 这时候
nextFrameTime是小于 33,说明机器的刷新频率高于30帧 if (nextFrameTime < activeFrameTime && previousFrameTime < activeFrameTime)- 这个判断的意义在于,如果连续两帧的调用都计算出来,发现小于 33 ms (目前的帧时间)
- 那么就把帧时间 activeFrameTime 变小,因为使用 frameDeadline 的时候,activeFrameTime
- 是非常重要的,
frameDeadline = rafTime + activeFrameTime; - 说明在接下去的 33ms之内都是可以运行react更新的代码
- 实际浏览器的刷新时间都要小于33ms, 比如 10ms, 这时候,占用33ms去渲染react应用
- 就会导致浏览器刷新动画的时间,非常不够,就导致动画变得比较卡顿
- 这个是考虑不同平台刷新频率的问题,不如 VR平台对刷新要求比较高
- 如果
nextFrameTime < 8这时候nextFrameTime = 8 - 这说明react目前不支持每帧小于8ms的场景
- 通过以上前后几次帧时间的判断,来判断平台的刷新频率来更新
activeFrameTime - 来减少 react 运行时间的目的
- 但是
frameDeadline = rafTime + activeFrameTime;这里计算出的 frameDeadline 要大于33的- 因为 activeFrameTime 是完整的一帧时间 33
- 而每帧留给 react 更新的时间要小于 33
- 一帧之内要处理 react的渲染 和 浏览器的更新,那么 react渲染一定要小于33
这里算出的 frameDeadline 是 当前时间 + 33
- 这是为什么呢?
- 这里用了js中任务队列的概念,像是 setTimeout, window.postMessage
- 都是把一个任务推到了一个队列里面, 然后再继续执行当前 js 的任务
- 对于浏览器来说,animationTick 是在 requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout 的callback中调用
- animationTick 方法执行完之后,立马进入浏览器动画刷新的流程
- 下面调用的 window.postMessage 要等到浏览器动画或用户反馈执行完了之后,才会执行 postMessage 的功能
- 这意味着需要等到浏览器刷新完成后,才会接收到 postMessage 的意图
- 这时候浏览器刷新动画的时间已经过了,相当于 rafTime + activeFrameTime 的时间已经流失掉一部分了(浏览器刷新需时)
- 剩下的时间给 react 执行更新的
- 这就是 react scheduler 中模拟 requestIdleCallback 的方法,通过 requestAnimationFrame 调用完 callback 之后
- 立马进入浏览器的动画更新的设定,在下面的判断中给任务队列插入一个任务
if (!isMessageEventScheduled)isMessageEventScheduled = true;window.postMessage(messageKey, '*');
- 在浏览器执行完之后,调用任务队列, 这个时间总共加起来是 33ms
- 当发送完 postMessage 到了哪里?可看到
window.addEventListener('message', idleTick, false) - 进入 idleTick
var idleTick = function(event) {// 先判断 keyif (event.source !== window || event.data !== messageKey) {return;}isMessageEventScheduled = false;// 赋值一份 callbackvar prevScheduledCallback = scheduledHostCallback;// 同样处理 timeoutvar prevTimeoutTime = timeoutTime;// 重置下面两个scheduledHostCallback = null;timeoutTime = -1;// 获取当前时间var currentTime = getCurrentTime();var didTimeout = false;// 这个条件如果 <= 0 说明浏览器动画或用户反馈超过 33ms, 意思是,把这一帧的时间已经用完了// 对于 react 来说,它已经没有时间执行它的更新了if (frameDeadline - currentTime <= 0) {// There's no time left in this idle period. Check if the callback has// a timeout and whether it's been exceeded.// 进入上述条件,它需要继续判断 timeout 是否已经过期,或者小于当前时间(说明任务也已经过期了)// 如果任务已经过期,这个任务就需要强行被更新// 可以在任务没有过期的时候,判断帧时间如果没有了,即: frameDeadline - currentTime <= 0// 先跳过,等下一帧来更新,但是在任务已经过期的时候,就需要强制执行了,于是就设置了下面的 didTimeout = true;if (prevTimeoutTime !== -1 && prevTimeoutTime <= currentTime) {// Exceeded the timeout. Invoke the callback even though there's no// time left.didTimeout = true;} else {// No timeout.// 没有过期,并且 isAnimationFrameScheduled === false 去调用 requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout 这个方法if (!isAnimationFrameScheduled) {// Schedule another animation callback so we retry later.// 恢复isAnimationFrameScheduled = true;requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick);}// Exit without invoking the callback.scheduledHostCallback = prevScheduledCallback;timeoutTime = prevTimeoutTime;return;}}// 接来下如果 存在 prevScheduledCallback 则设置 isFlushingHostCallback 并调用 prevScheduledCallbackif (prevScheduledCallback !== null) {isFlushingHostCallback = true;try {prevScheduledCallback(didTimeout);} finally {isFlushingHostCallback = false;}} };- 这里最后的
prevScheduledCallback向上溯源,找到ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled
function ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled() {if (isExecutingCallback) {// Don't schedule work yet; wait until the next time we yield.return;}// Schedule the host callback using the earliest expiration in the list.var expirationTime = firstCallbackNode.expirationTime;if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) {isHostCallbackScheduled = true;} else {// Cancel the existing host callback.cancelHostCallback();}requestHostCallback(flushWork, expirationTime); }- 可以看到这里
requestHostCallback(flushWork, expirationTime);传入了flushWork方法- 输出任务需要调用 flushWork 方法
- 现在来看下
flushWork方法, 这是 react scheduler 调度到 要执行 callback 的流程 - 在执行callback的时候,调用了 flushWork 这个方法
// didTimeout 参数是 firstCallbackNode 的 expirationTime 是否已超时 function flushWork(didTimeout) {// 真正调用 callback 设置为 true// 对于 ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled 方法来说,如果为 true, 则直接 return 了isExecutingCallback = true;deadlineObject.didTimeout = didTimeout; // deadlineObject 是上层设置的一个通用的对象try {if (didTimeout) {// Flush all the expired callbacks without yielding.while (firstCallbackNode !== null) {// Read the current time. Flush all the callbacks that expire at or// earlier than that time. Then read the current time again and repeat.// This optimizes for as few performance.now calls as possible.var currentTime = getCurrentTime();if (firstCallbackNode.expirationTime <= currentTime) {// 执行 callbackNode 的链表直到遇到第一个不过期的为止,把已过期的任务都强制输出do {flushFirstCallback();} while (firstCallbackNode !== null &&firstCallbackNode.expirationTime <= currentTime); // 这里 firstCallbackNode 是 next, firstCallbackNode.expirationTime <= currentTime 这表示下一个节点的任务还是过期的任务continue; // 这里continue 跳出后即 break 跳出 外层while循环}break;}} else {// 这里表示没有任务是过期的// Keep flushing callbacks until we run out of time in the frame.if (firstCallbackNode !== null) {do {flushFirstCallback();} while (firstCallbackNode !== null &&getFrameDeadline() - getCurrentTime() > 0); // getFrameDeadline() - getCurrentTime() > 0 表示 有空,闲暇 会执行 flushFirstCallback}}} finally {isExecutingCallback = false;// 最后,如果还有,再次进入调度if (firstCallbackNode !== null) {// There's still work remaining. Request another callback.ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();} else {isHostCallbackScheduled = false;}// Before exiting, flush all the immediate work that was scheduled.flushImmediateWork();} }- 关于这里的
deadlineObject
var deadlineObject = {timeRemaining,didTimeout: false, };- 而这里的
timeRemaining是一个方法
var timeRemaining; if (hasNativePerformanceNow) {timeRemaining = function() {// 这个判断不成立,跳过if (firstCallbackNode !== null &&firstCallbackNode.expirationTime < currentExpirationTime) {// A higher priority callback was scheduled. Yield so we can switch to// working on that.return 0;}// We assume that if we have a performance timer that the rAF callback// gets a performance timer value. Not sure if this is always true.// getFrameDeadline() 方法就是 frameDeadline = rafTime + activeFrameTime;// 也就是说,确定,这一帧的渲染时间,是否已经超过var remaining = getFrameDeadline() - performance.now();return remaining > 0 ? remaining : 0;}; } else {timeRemaining = function() {// Fallback to Date.now()if (firstCallbackNode !== null &&firstCallbackNode.expirationTime < currentExpirationTime) {return 0;}var remaining = getFrameDeadline() - Date.now();return remaining > 0 ? remaining : 0;}; }- 这里根据
hasNativePerformanceNow来进行一个区分,这两个基本差不多,选择其一 - 所以,timeRemaining 用于计算还剩多少时间,比如在 ReactFiberSchedler.js中的
shouldYield// When working on async work, the reconciler asks the renderer if it should // yield execution. For DOM, we implement this with requestIdleCallback. function shouldYield() {if (deadlineDidExpire) {return true;}if (deadline === null ||deadline.timeRemaining() > timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork) {// Disregard deadline.didTimeout. Only expired work should be flushed// during a timeout. This path is only hit for non-expired work.return false;}deadlineDidExpire = true;return true; }- 这里
deadline.timeRemaining() > timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork, 这里timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork是 1 - 用剩下时间是否 > 1 来判断是否已经过期了,如果 > 1 说明还有时间执行 react的更新,这里 return false
- 如果剩下时间 < 1 了,代表这一帧的渲染时间已经超时,设置全局变量
deadlineDidExpire = true;并且 return true - 这个 shouldYield 方法就是判断这个任务要跳出还是继续执行下去
- 这里
- 接着是一个 try finally 里面
if (didTimeout)这时候已经过期了,进入while循环while (firstCallbackNode !== null)- 里面 有个if 判断是肯定匹配的,
if (firstCallbackNode.expirationTime <= currentTime)- 执行 do while
- flushFirstCallback 是真正调用callback的方法
function flushFirstCallback() {var flushedNode = firstCallbackNode;// Remove the node from the list before calling the callback. That way the// list is in a consistent state even if the callback throws.var next = firstCallbackNode.next;// 说明链表里只有一个节点,直接设置 nullif (firstCallbackNode === next) {// This is the last callback in the list.firstCallbackNode = null;next = null;} else {// 如果不是,多个节点,则构建链表(环形链表) var lastCallbackNode = firstCallbackNode.previous;firstCallbackNode = lastCallbackNode.next = next; // firstCallbackNode 变成了 next 的节点 对应上面调用方法的 do while firstCallbackNode.exirationTime <= currentTime next.previous = lastCallbackNode;}// 把之前的指向清空,如果指针还留着,可能会导致问题flushedNode.next = flushedNode.previous = null;// Now it's safe to call the callback.var callback = flushedNode.callback;var expirationTime = flushedNode.expirationTime;var priorityLevel = flushedNode.priorityLevel;var previousPriorityLevel = currentPriorityLevel;var previousExpirationTime = currentExpirationTime;currentPriorityLevel = priorityLevel;currentExpirationTime = expirationTime;var continuationCallback;try {// 这里 callback 就是传进来的 performAsyncWorkcontinuationCallback = callback(deadlineObject); // 这里应该是 undefined} finally {currentPriorityLevel = previousPriorityLevel;currentExpirationTime = previousExpirationTime;}// A callback may return a continuation. The continuation should be scheduled// with the same priority and expiration as the just-finished callback.// 因为 performAsyncWork 这个 callback 没有返回值 所以这个目前来说不成立,也许后续会有用if (typeof continuationCallback === 'function') {var continuationNode: CallbackNode = {callback: continuationCallback,priorityLevel,expirationTime,next: null,previous: null,};// Insert the new callback into the list, sorted by its expiration. This is// almost the same as the code in `scheduleCallback`, except the callback// is inserted into the list *before* callbacks of equal expiration instead// of after.if (firstCallbackNode === null) {// This is the first callback in the list.firstCallbackNode = continuationNode.next = continuationNode.previous = continuationNode;} else {var nextAfterContinuation = null;var node = firstCallbackNode;do {if (node.expirationTime >= expirationTime) {// This callback expires at or after the continuation. We will insert// the continuation *before* this callback.nextAfterContinuation = node;break;}node = node.next;} while (node !== firstCallbackNode);if (nextAfterContinuation === null) {// No equal or lower priority callback was found, which means the new// callback is the lowest priority callback in the list.nextAfterContinuation = firstCallbackNode;} else if (nextAfterContinuation === firstCallbackNode) {// The new callback is the highest priority callback in the list.firstCallbackNode = continuationNode;ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();}var previous = nextAfterContinuation.previous;previous.next = nextAfterContinuation.previous = continuationNode;continuationNode.next = nextAfterContinuation;continuationNode.previous = previous;}} }
- 在finally 中执行了
ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled- 在这个方法中,有个判断是
isHostCallbackScheduled仅且仅有 在这个判断中,isHostCallbackScheduled 才会被设置为 true - 所以,在有
firstCallbackNode时,调用 ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled() 时,isHostCallbackScheduled 是 true 的 - 它为 true 时,在 ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled() 中,会执行 cancelHostCallback()
cancelHostCallback = function() {scheduledHostCallback = null;isMessageEventScheduled = false;timeoutTime = -1; }; - 也就是说把之前调度的变量都重置了,不能让老的callback再执行一遍,以此可能导致产生错误
- 在 finally 中的 else 环节 isHostCallbackScheduled 被设置成 false
- 在这个方法中,有个判断是
- 最后执行了
flushImmediateWork这个API 以后可能会用到function flushImmediateWork() {// 这里 ImmediatePriority 是一个固定的值 但是 firstCallbackNode.priorityLevel// 这里 firstCallbackNode.priorityLevel 是 固定的 3 这个if 不会被执行// 所以,这个api 暂未开放if (// Confirm we've exited the outer most event handlercurrentEventStartTime === -1 &&firstCallbackNode !== null &&firstCallbackNode.priorityLevel === ImmediatePriority) {isExecutingCallback = true;deadlineObject.didTimeout = true;try {do {flushFirstCallback();} while (// Keep flushing until there are no more immediate callbacksfirstCallbackNode !== null &&firstCallbackNode.priorityLevel === ImmediatePriority);} finally {isExecutingCallback = false;if (firstCallbackNode !== null) {// There's still work remaining. Request another callback.ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled();} else {isHostCallbackScheduled = false;}}} }
- 关于这里的
- 这里最后的
- 第一次计算的
- 判断
总结
- 以上是 react scheduler 模拟 requestIdleCallback 时间片的操作和调度
- 能够控制把更多的优先权交给浏览器,让它去做动画或用户输入反馈的更新
- 在有空闲的时间,回过头来执行 react 的异步更新操作
- 在这里面会有各种各样的计时来控制帧时间的判断
- 如果发现浏览器的刷新频率更高,则调低帧时间,以及判断任务是否有过期
- 如果过期了,需要强制输出
- 从这个React版本来看,react scheduler 只开放了一部分代码,还有一部分代码暂时没有用到