概述:是机器学习中的一种思想,通过多个模型的组合形成一个精度更高的模型,参与组合的模型称为弱学习器
1、Bagging 思想
有放回的抽样(booststrap抽样)产生不同的训练集,从而训练不同的学习器;
通过平权投票、多数表决的方式决定预测结果;
弱学习器可以并行训练
代表算法:随机森林
概述:是基于 Bagging 思想实现的一种集成学习算法,采用决策树模型作为每一个弱学习器
构建过程:1. 随机选数据,2. 随机选特征,3. 训练弱学习器,4. 重复1~3训练n个弱学习器,
5. 平权投票
API
# 导包
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierparam = { ' n_estimators ':[40,50,60,70],' max_depth ':[2,4,6,8,10],' random_state ':[ 9 ] }from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
param = { ' n_estimators ':[40,50,60,70],' max_depth ':[2,4,6,8,10],' random_state ':[ 9 ] }
n_estimators:决策树数量,default = 10
max_features = ' auto ' :最大特征数量,= sqrt ( n_features )
log2( n_features ),None = n_features
bootstrap:是否采用有放回抽样,默认为 True
min_impurity_split:节点划分最小不纯度,一般不改,默认为 1e-7
泰坦尼克号案例
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCVdef dm01_随机森林():
# 1 获取数据集
titan = pd.read_csv(“./data/titanic/train.csv”)# 2 确定特征值和目标值
x = titan[[“Pclass”, “Age”, “Sex”]].copy()
y = titan[“Survived”]# 3-1 处理数据-处理缺失值
x[‘Age’].fillna(value=titan[“Age”].mean(), inplace=True)
print(x.head())# 3-2 one-hot编码
x = pd.get_dummies(x)# 4 数据集划分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=22, test_size=0.2# 5-1 使用决策树进行模型训练和评估
dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier()
dtc.fit(x_train, y_train)
dtc_y_pred = dtc.predict(x_test)
accuracy = dtc.score(x_test, y_test)
print('单一决策树accuracy-->\n', accuracy)# 5-2 随机森林进行模型训练和评估
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=6, random_state=9)
rfc.fit(x_train, y_train)
rfc_y_pred = rfc.predict(x_test)
accuracy = rfc.score(x_test, y_test)
print('随机森林进accuracy-->\n', accuracy)# 5-3 随机森林 交叉验证网格搜索 进行模型训练和评估
estimator = RandomForestClassifier()
param = {"n_estimators": [40, 50, 60, 70], "max_depth": [2, 4, 6, 8, 10], "random_state":[9]}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(estimator, param_grid=param, cv=2)
grid_search.fit(x_train, y_train)
accuracy = grid_search.score(x_test, y_test)
print("随机森林网格搜索accuracy:", accuracy)
print(grid_search.best_estimator_)2、Boosting 思想
每一个训练器重点关注前一个训练器不足的地方进行训练;
通过加权投票的方式,得出预测结果;
串行的训练方式
代表算法:Adaboost、GBDT、XGBoost、LightGBM
1. Adaboost 算法
概述:自适应提升算法(Adaptive Boosting)通过逐步提高那些被前一步分类错误的样本的权重来
训练一个强分类器
算法推导:
1 初始化数据权重,来训练第1个弱学习器。找最小的错误率计算模型权重,再更新模数据权重
2 根据新权重的样本集 训练第 2 个学习器,重复上述的计算、更新
3 迭代训练在前一个学习器的基础上,根据新的样本权重训练当前学习器,直到训练出 m 个弱学习器
4 m 个弱学习器集成预测公式

α 为模型的权重,输出结果大于 0 则归为正类,小于 0 则归为负类
5 模型权重计算公式
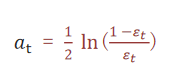
a_t 为模型权重
ε_t 表示第 t 个弱学习器的错误率
6 样本权重计算公式
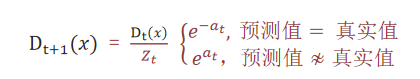
Z_t 为归一化值(所有样本权重总和)
D_t(x)为样本权重
a_t 为模型权重
API
# 导包
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder# 训练模型
y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(y)# 导入Adaboost分类包
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifiermyada = AdaBoostClassifier ( base_estimator = mytree, n_estimators = 500, learning_rate = 0.1, random_state = 0 )from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
类别转换:y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(y)
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
myada = AdaBoostClassifier ( base_estimator = mytree,n_estimators = 500,learning_rate = 0.1,random_state = 0 )
葡萄酒数据案例
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier # 集成学习# 1 读数据到内存 df_wine
df_wine = pd.read_csv('./wine0501.csv')
df_wine.info()# 2 特征处理
# 2-2 Adaboost一般做二分类 去掉一类(1,2,3)
df_wine = df_wine[df_wine['Class label']!=1]# 2-3 准备特征值和目标值 Alcohol酒精含量 Hue颜色
x = df_wine[['Alcohol','Hue']].values
y = df_wine['Class label']# 2-4 类别转化 y (2,3)=>(0,1)
y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(y)# 2-5 划分数据
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,random_state=22,test_size=0.2)
print(X_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape)# 3 实例化单决策树 实例化 Adaboost,由 500颗树组成
mytree = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy',max_depth=1,random_state=0)
myada = AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator=mytree,n_estimators=500,learning_rate=0.1,random_state=0)# 4 单决策树训练和评估
mytree.fit(X_train,y_train)
myscore = mytree.score(X_test,y_test)
myscore# 5 AdaBoost训练和评估
myada.fit(X_train,y_train)
myscore = myada.score(X_test,y_test)
myscore2. GBDT 梯度提升树
Gradient Boosting Decision Tree
提升树:通过 拟合残差 的思想来进行提升,残差:真实值 - 预测值
梯度提升树:不再拟合残差,而是利用梯度下降的近似方法,利用损失函数的负梯度作为提升树算法中的残差近似值
构建流程:1 初始化弱学习器(目标值的均值作为预测值)
2 迭代构建学习器,每一个学习器拟合上一个学习器的负梯度;
3 直到达到指定的学习器个数
4 当输入未知样本时,将所有弱学习器的输出结果组合起来作为强学习器的输出
API
# 导包
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifierfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report导包:from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
3. XGBoost 极端梯度提升树
eXtreme Gradient Boosting
构建思想
1 构建模型的方法是最小化训练数据的损失函数,训练的模型复杂度较高,易过拟合
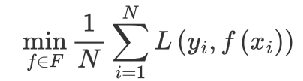
tips:使用二阶泰勒展开式去近似目标函数
2 在损失函数中加入正则化项,提高对未知的测试数据的泛化性能
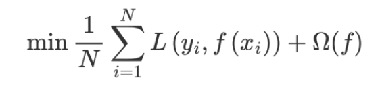
tips:正则化项由树的叶子节点的个数以及L2正则化项组成
3 从样本角度转为按照叶子节点输出角度,优化损失函数,目标函数最终为:
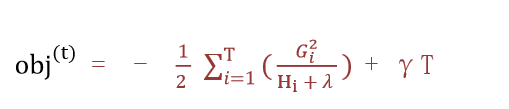
Gi:每个样本的一阶导
Hi:每个样本的二阶导
ft(xi):样本的预测值
T:叶子结点的数目
打分函数:确定某个节点是否能够继续分裂,以及某个特征的最佳分割点
目标函数:

模型复杂度:
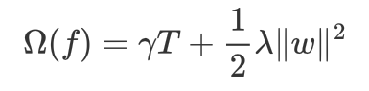
||w||2:由叶子结点值组成向量的模
API
# 导包
import xgboost as xgb# 模型训练
estimator = xgb.XGBClassifier(n_estimators=100, objective='multi:softmax', eval_metric='merror', eta=0.1, use_label_encoder=False, random_state=22)导包:import xgboost as xgb
模型训练:estimator = xgb.XGBClassifier(n_estimators=100, objective='multi:softmax',eval_metric='merror', eta=0.1, use_label_encoder=False, random_state=22)
交叉验证--分层抽取
# 导包
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFoldspliter = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True)导包:from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
spliter = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5,shuffle=True)
分类权重
# 导包
from sklearn.utils import class_weightclasses_weights = class_weight.compute_sample_weight(class_weight = ‘balanced’, y = y_train)导包:from sklearn.utils import class_weight
classes_weights = class_weight.compute_sample_weight(class_weight = ‘balanced’, y = y_train)
xgb案例:红酒品质分类
from sklearn.utils import class_weightdef dm01_训练模型():
# 1 加载数据集
train_data = pd.read_csv(‘./data/红酒品质分类-train.csv’)
test_data = pd.read_csv(‘./data/红酒品质分类-test.csv’)# 2 准备数据 训练集测试集
x_train = train_data.iloc[:, :-1]
y_train = train_data.iloc[:, -1]
x_test = test_data.iloc[:, :-1]
y_test = test_data.iloc[:, -1]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape)# 2-2 样本不均衡问题处理
classes_weights = class_weight.compute_sample_weight(class_weight=‘balanced’, y=y_train)# 3 xgb模型训练
estimator = xgb.XGBClassifier(n_estimators=100,objective=‘multi:softmax’,eval_metric=‘merror’, eta=0.1, use_label_encoder=False, random_state=22)# 训练的时候,指定样本的权重
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train, sample_weight=classes_weights)# 4 xgb模型评估
y_pred = estimator.predict(x_test)
print(classification_report(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred)) from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCVdef dm02_交叉验证网格搜索():
# 1 加载数据集
train_data = pd.read_csv('./data/红酒品质分类-train.csv')
test_data = pd.read_csv('./data/红酒品质分类-test.csv')# 2 准备数据 训练集测试集
x_train = train_data.iloc[:, :-1]
y_train = train_data.iloc[:, -1]
x_test = test_data.iloc[:, :-1]
y_test = test_data.iloc[:, -1]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape)# 3 交叉验证时,采用分层抽取
spliter = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True)# 4 模型训练
# 4-1定义超参数
param_grid = {‘max_depth’: np.arange(3, 5, 1),‘n_estimators’: np.arange(50, 150, 50),‘eta’: np.arange(0.1, 1, 0.3)}# 4-2 实例化xgb
estimator = xgb.XGBClassifier(n_estimators=100,objective=‘multi:softmax’,eval_metric=‘merror’,eta=0.1,use_label_encoder=False,random_state=22)# 4-2 实例化cv工具
estimator = GridSearchCV(estimator=estimator, param_grid=param_grid, cv=spliter)# 4-3 训练模型
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)# 5 模型评估
y_pred = estimator.predict(x_test)
print(classification_report(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred))
print(‘estimator.best_estimator_-->’,estimator.best_estimator_)
print(‘estimator.best_params_-->’, estimator.best_params_)3、Bagging与Boosting的对比
| bagging | boosting | |
| 数据采样 | 对数据进行有放回的采样训练 | 全部样本,根据前一轮学习结果调整数据的重要性 |
| 投票方式 | 所有学习器平权投票 | 对学习器进行加权投票 |
| 学习顺序 | 并行的,每个学习器没有依赖关系 | 串行,学习有先后顺序 |