✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌟🌟 追风赶月莫停留 🌟🌟
🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀
🌟🌟 平芜尽处是春山🌟🌟
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
🍋栈和队列
- 🍑栈
- 🍍栈的含义
- 🍍栈的结构
- 🍍栈的实现
- 🍌栈的补充条件
- 🍌初始化栈
- 🍌入栈
- 🍌出栈
- 🍌获取栈顶元素
- 🍌获取栈中有效元素的个数
- 🍌检查栈是否为空
- 🍌销毁栈
- 🍍栈的整体代码的实现
- 🍑队列
- 🍍队列的含义
- 🍍队列的结构
- 🍍队列的实现
- 🍌队列的补充条件
- 🍌初始化队列
- 🍌队尾入队列
- 🍌队头出队列
- 🍌获取队列头部元素
- 🍌获取队列队尾元素
- 🍌获取队列中有效元素个数
- 🍌检测队列是否为空
- 🍌 销毁队列
- 🍍队列的整体代码的实现
🍑栈
🍍栈的含义
栈是一种特殊类型的线性表,它的特点是仅允许在其一端进行插入(压入)和删除(弹出)操作。这一端被称为栈顶,而相对的另一端则被称为栈底。栈通常遵循“后进先出”(LIFO)的原则,意味着新加入的元素总是位于栈顶,而要访问或移除的元素必须从前部移除。
🍍栈的结构
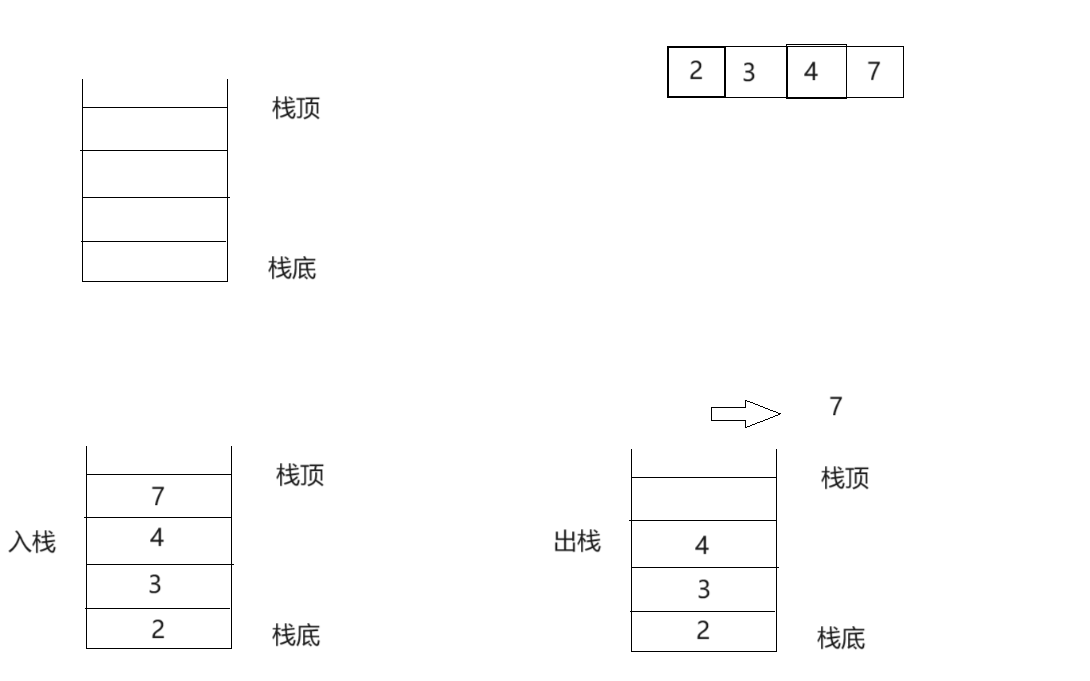
栈的结构就是如图片中的形容的类似,满足先进后出
🍍栈的实现
🍌栈的补充条件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int STDatetype;//方便后续数据不只是int,也可以方便的换其他类型typedef struct Stack//利用结构体来定义栈
{STDatetype* a;int top; int capacity;
}ST;
int main()
{ST st;STInia(&st);STPush(&st, 1);STPush(&st, 2);STPush(&st, 3);STPush(&st, 4);STPush(&st, 5);while (!STEmpty(&st)){printf("%d ", STTop(&st));STPop(&st);}printf("\n");STDestroy(&st);return 0;
}🍌初始化栈
void STInia(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;ps->a = NULL;
}
🍌入栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDatetype x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newcapacity = 0;if (ps->capacity == 0){newcapacity = 2;}else{newcapacity = newcapacity * 2;}STDatetype* tem = (STDatetype*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDatetype) * newcapacity);if (tem == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tem;ps->capacity = newcapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}
(1)之所以在这里不用malloc创建空间,是因为后面还要用realloc进行扩容,所以就直接用realloc进行空间的创建。
(2)在ps->top和ps->capacity相等时进行扩容,在这里进行了判断,有两种情况。第一种是ps->capacity等于0,那就得先创建空间。第二种是ps->capacity不为0,就直接扩容为原来2倍的空间
🍌出栈
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);//判断数据是否为空(ps->top)--;}
🍌获取栈顶元素
STDatetype STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);//判断是否为空return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
🍌获取栈中有效元素的个数
int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}
在栈中数据个数其实就是ps->top
🍌检查栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
如果为空就返回1,不为空就返回0
🍌销毁栈
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
🍍栈的整体代码的实现
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int STDatetype;typedef struct Stack
{STDatetype* a;int top; int capacity;
}ST;void STInia(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;ps->a = NULL;
}void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}void STPush(ST* ps, STDatetype x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newcapacity = 0;if (ps->capacity == 0){newcapacity = 2;}else{newcapacity = ps->capacity * 2;}STDatetype* tem = (STDatetype*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDatetype) * newcapacity);if (tem == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tem;ps->capacity = newcapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;(ps->top)++;
}void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);(ps->top)--;}int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}STDatetype STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}int main()
{ST st;STInia(&st);STPush(&st, 1);STPush(&st, 2);STPush(&st, 3);STPush(&st, 4);STPush(&st, 5);while (!STEmpty(&st)){printf("%d ", STTop(&st));STPop(&st);}printf("\n");STDestroy(&st);return 0;
}
🍑队列
🍍队列的含义
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。
🍍队列的结构
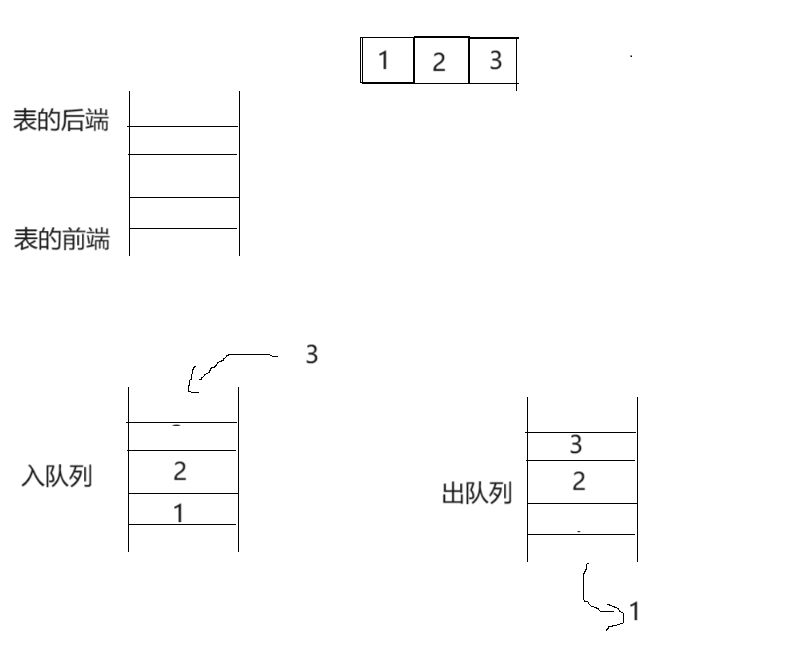
队列和栈有点类似,只不过栈是先进后出,而队列是先进先出
🍍队列的实现
🍌队列的补充条件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int QDatetype;
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDatetype date;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;
///
int main()
{Que qq;QueueInia(&qq);QueuePush(&qq, 1);QueuePush(&qq, 2);QueuePush(&qq, 3);QueuePush(&qq, 4);while (!QueueEmpty(&qq)){printf("%d ", QueueFront(&qq));QueuePop(&qq);}printf("\n");return 0;
}
在这个队列中,我是采用了单链表(单向不循环)的结构来实现队列,所以再这里要注意头可能是空指针的问题,在前面我介绍单链表的时候是利用二级指针解决这个问题,而在这里是采用了新的方法,也就是结构体指针,把头和尾重新用一个结构体来定义
🍌初始化队列
void QueueInia(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->head = NULL;ps->tail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}
🍌队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Que* ps, QDatetype x)
{assert(ps);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->date = x;if (ps->tail == NULL){ps->head = ps->tail = newnode;}else{ps->tail->next = newnode;ps->tail = newnode;}(ps->size)++;
}
🍌队头出队列
void QueuePop(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size > 0);if (ps->head->next == NULL){free(ps->head);ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* cur = ps->head->next;free(ps->head);ps->head = cur;}(ps->size)--;
}
🍌获取队列头部元素
QDatetype QueueFront(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));return ps->head->date;
}
🍌获取队列队尾元素
QDatetype QueueBake(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));return ps->tail->date;
}
🍌获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->size;
}
🍌检测队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->head == NULL;
}
🍌 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);QNode* cur = ps->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}
🍍队列的整体代码的实现
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int QDatetype;
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDatetype date;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;void QueueInia(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->head = NULL;ps->tail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->head == NULL;
}void QueuePush(Que* ps, QDatetype x)
{assert(ps);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->date = x;if (ps->tail == NULL){ps->head = ps->tail = newnode;}else{ps->tail->next = newnode;ps->tail = newnode;}(ps->size)++;
}void QueuePop(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size > 0);if (ps->head->next == NULL){free(ps->head);ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* cur = ps->head->next;free(ps->head);ps->head = cur;}(ps->size)--;
}QDatetype QueueFront(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));return ps->head->date;
}QDatetype QueueBake(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));return ps->tail->date;
}int QueueSize(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->size;
}void QueueDestroy(Que* ps)
{assert(ps);QNode* cur = ps->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}int main()
{Que qq;QueueInia(&qq);QueuePush(&qq, 1);QueuePush(&qq, 2);QueuePush(&qq, 3);QueuePush(&qq, 4);while (!QueueEmpty(&qq)){printf("%d ", QueueFront(&qq));QueuePop(&qq);}printf("\n");return 0;
}
队列和栈我就不详细介绍了,如果有需要可以看我写的这篇博客:单链表
本期的内容就结束了,文章有错误的地方欢迎大家指正!!!