在zygote进程对应的文件是app_main.cpp文件,在app_main.cpp文件的main()方法中先解析了init.rc中配置的参数并根据配置的参数设置zygote的状态。
在状态设置阶段主要做了:
- 设置进程名称为zygote
- 通过startSystemServer = true标示启动的是systemServer
- 调用runtime.start()方法
............if (zygote) {
336 runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
337 } else if (className) {
338 runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
339 } else {
340 fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
341 app_usage();
342 LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
343 }然后调用runtime.start()方法。runtime的类型是由AndroidRuntime派生类AppRunTime,start()方法定义在AndroidRunTime类中。在启动zygote进程是start()方法接受的第一参数是com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit,这个参数很重要。下面看一下AndroidRuntime——>start()方法的实现:
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
1137 {
1138 ALOGD(">>>>>> START %s uid %d <<<<<<\n",
1139 className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)", getuid());
1140
1141 static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
1142 // Whether this is the primary zygote, meaning the zygote which will fork system server.
1143 bool primary_zygote = false;
1144
1145 /*
1146 * 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
1147 * init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
1148 */
1149 for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
1150 if (options[i] == startSystemServer) {
1151 primary_zygote = true;
1152 /* track our progress through the boot sequence */
1153 const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
1154 LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
1155 }
1156 }
1157
1158 const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
1159 if (rootDir == NULL) {
1160 rootDir = "/system";
1161 if (!hasDir("/system")) {
1162 LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /system does not exist.");
1163 return;
1164 }
1165 setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
1166 }
1167
1168 const char* artRootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ART_ROOT");
1169 if (artRootDir == NULL) {
1170 LOG_FATAL("No ART directory specified with ANDROID_ART_ROOT environment variable.");
1171 return;
1172 }
1173
1174 const char* i18nRootDir = getenv("ANDROID_I18N_ROOT");
1175 if (i18nRootDir == NULL) {
1176 LOG_FATAL("No runtime directory specified with ANDROID_I18N_ROOT environment variable.");
1177 return;
1178 }
1179
1180 const char* tzdataRootDir = getenv("ANDROID_TZDATA_ROOT");
1181 if (tzdataRootDir == NULL) {
1182 LOG_FATAL("No tz data directory specified with ANDROID_TZDATA_ROOT environment variable.");
1183 return;
1184 }
1185
1186 //const char* kernelHack = getenv("LD_ASSUME_KERNEL");
1187 //ALOGD("Found LD_ASSUME_KERNEL='%s'\n", kernelHack);
1188
1189 /* start the virtual machine */
1190 JniInvocation jni_invocation;
1191 jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
1192 JNIEnv* env;
1193 if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote, primary_zygote) != 0) {
1194 return;
1195 }
1196 onVmCreated(env);
1197
1198 /*
1199 * Register android functions.
1200 */
1201 if (startReg(env) < 0) {
1202 ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
1203 return;
1204 }
1205
1206 /*
1207 * We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
1208 * At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
1209 * Create an array to hold them.
1210 */
1211 jclass stringClass;
1212 jobjectArray strArray;
1213 jstring classNameStr;
1214
1215 stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
1216 assert(stringClass != NULL);
1217 strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
1218 assert(strArray != NULL);
1219 classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
1220 assert(classNameStr != NULL);
1221 env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
1222
1223 for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
1224 jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
1225 assert(optionsStr != NULL);
1226 env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
1227 }
1228
1229 /*
1230 * Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
1231 * not return until the VM exits.
1232 */
1233 char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : "");
1234 jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
1235 if (startClass == NULL) {
1236 ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
1237 /* keep going */
1238 } else {
1239 jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
1240 "([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
1241 if (startMeth == NULL) {
1242 ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
1243 /* keep going */
1244 } else {
1245 env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
1246
1247 #if 0
1248 if (env->ExceptionCheck())
1249 threadExitUncaughtException(env);
1250 #endif
1251 }
1252 }
1253 free(slashClassName);
1254
1255 ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
1256 if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
1257 ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
1258 if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
1259 ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
1260 }AndroidRuntime主要做了三件事儿:
- 调用startVM()函数启动虚拟机
- 调用startReg()函数注册jni方法
- 通过调用的方法调用com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit类main()方法。
startVM()方法多了大量的命令参数拼接最后通过JNI_CreateJavaVM()方法创建虚拟机。
startReg()方法注册JNI方法,Android中java和Native层的交互需要通过JNI机制来完成,并且Android中大量使用JNI函数。
看下面截图方法:
 其中CallStaticVoidMethod 这个方法就是调用ZygoteInit这个类中的main方法,终于到java中了。
其中CallStaticVoidMethod 这个方法就是调用ZygoteInit这个类中的main方法,终于到java中了。
public static void main(String argv[]) {
833 ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
834
835 // Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
836 // an error.
837 ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
838
839 // Zygote goes into its own process group.
840 try {
841 Os.setpgid(0, 0);
842 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
843 throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
844 }
845
846 Runnable caller;
847 try {
848 // Store now for StatsLogging later.
849 final long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
850 final boolean isRuntimeRestarted = "1".equals(
851 SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"));
852
853 String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
854 TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
855 Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
856 bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
857 RuntimeInit.preForkInit();
858
859 boolean startSystemServer = false;
860 String zygoteSocketName = "zygote";
861 String abiList = null;
862 boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
863 for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
864 if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
865 startSystemServer = true;
866 } else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
867 enableLazyPreload = true;
868 } else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
869 abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
870 } else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
871 zygoteSocketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
872 } else {
873 throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
874 }
875 }
876
877 final boolean isPrimaryZygote = zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
878 if (!isRuntimeRestarted) {
879 if (isPrimaryZygote) {
880 FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
881 BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
882 startTime);
883 } else if (zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME)) {
884 FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
885 BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
886 startTime);
887 }
888 }
889
890 if (abiList == null) {
891 throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
892 }
893
894 // In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
895 // In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
896 if (!enableLazyPreload) {
897 bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
898 EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
899 SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
900 preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
901 EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
902 SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
903 bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
904 }
905
906 // Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
907 bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
908 gcAndFinalize();
909 bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
910
911 bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
912
913 Zygote.initNativeState(isPrimaryZygote);
914
915 ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
916
917 zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
918
919 if (startSystemServer) {
920 Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
921
922 // {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
923 // child (system_server) process.
924 if (r != null) {
925 r.run();
926 return;
927 }
928 }
929
930 Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
931
932 // The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
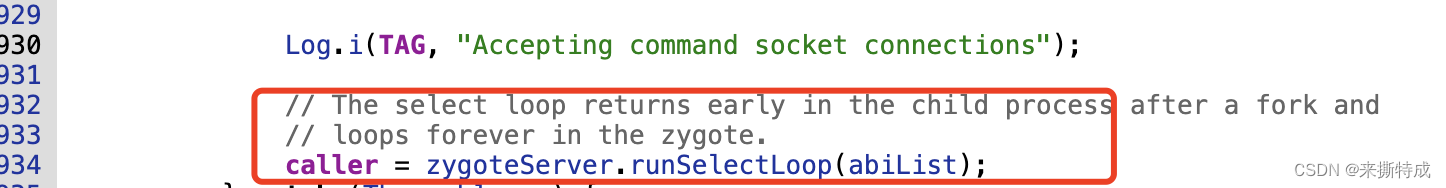
933 // loops forever in the zygote.
934 caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
935 } catch (Throwable ex) {
936 Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
937 throw ex;
938 } finally {
939 if (zygoteServer != null) {
940 zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
941 }
942 }
943
944 // We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
945 // command.
946 if (caller != null) {
947 caller.run();
948 }
949 }ZygoteInit的main()方法主要做了5件事儿:
通过registerZygoteSocket()函数创建了一个Zygote的socket接口用来和AMS进行通信。
调用preload()预加载类和资源
调用startSystemServer()方法启动systemServer
调用runSelectLoop()方法监听socket接口
通过捕获一个MethodAndArgsCaller异常并调用捕获的异常的run()方法。
1.预加载 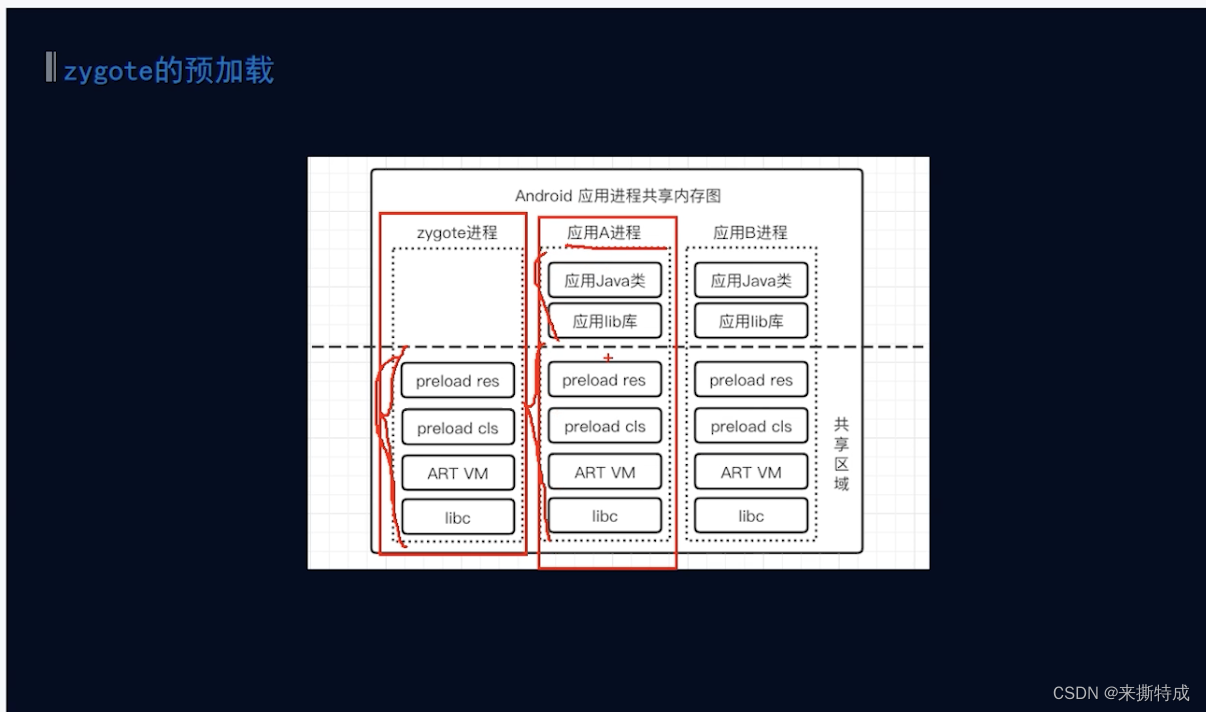
其中画红线的部分是拷贝到我们的应用进程中的。代码如下:
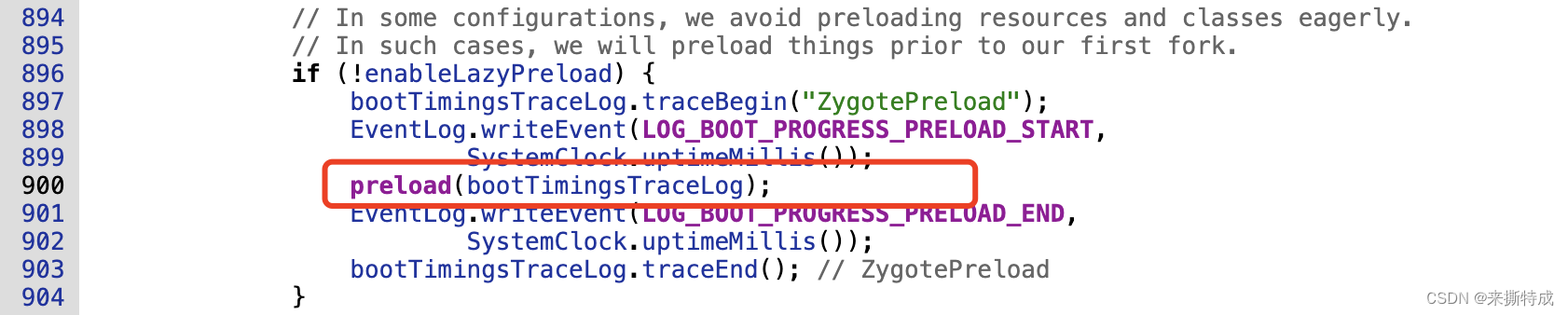
preload()方法主要预先加载了framework中通用的类和资源(core/res/res/values/arrays.xml)、openGL、本地共享库、webView的一些资源。
预先加载主要是为了在启动新应用程序时不用重复加载这些资源从而加快启动速度。
2.创建Zygote Socket 服务
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);这里没有用Binder机制,
(1).binder 没有初始化完成
(2)fork写时拷贝,容易死锁
zygote的socket接口主要是通过/dev/socket/zygote文件的文件操作符进行通信。
3. 然后创建 system_server进程
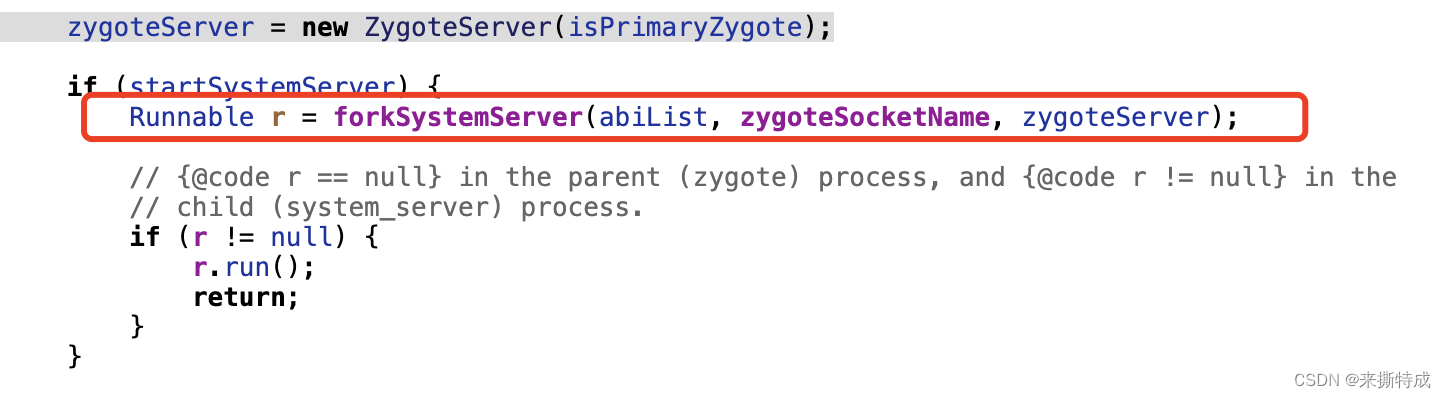
最终调用的事Zygote类里面的forkSystemServer方法

4. runSelectLoop,等待AMS发送消息,创建进程